
Fanhdi

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fanhdi

How to use Fanhdi
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR
THE USER
FANHDI
250 IU FVIII + 300 IU VWF
Powder and solvent for solution for injection and infusion
Human coagulation factor VIII and human von Willebrand factor complex
It is very important to read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so you can read it again later if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you personally. Do not give it to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the package leaflet:
- 1. What is FANHDI and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using FANHDI
- 3. How to use FANHDI
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store FANHDI
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. WHAT IS FANHDI AND WHAT IS IT USED FOR
FANHDI comes in the form of a powder and solvent for solution for injection and infusion in vials containing nominally 250 IU of human coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) and 300 IU of human von Willebrand factor (VWF). After reconstitution with the appropriate amount of solvent (water for injection), the product contains 25 IU/ml FVIII and 30 IU/ml VWF. Therapeutic category: antihemorrhagic agents, combination of factor VIII and von Willebrand factor. FANHDI is used to prevent and control bleeding in patients with hemophilia A (congenital factor VIII deficiency). FANHDI is also indicated for the prevention and control of bleeding (including surgical bleeding) in patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD) when desmopressin (DDAVP) treatment is ineffective or contraindicated.
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
The product may be used to treat acquired factor VIII deficiency.
2. IMPORTANT INFORMATION BEFORE USING FANHDI
When not to use FANHDI
- If the patient is hypersensitive (allergic) to the factor VIII and von Willebrand factor complex or to any of the other components of the medicine (listed in section 6).
You should consult your doctor if you need advice or additional information.
Warnings and precautions
- In rare cases, anaphylactic reactions (severe allergic reactions) may occur. Allergy to FANHDI may manifest as a rash, generalized urticaria, feeling of pressure in the chest, dizziness, even when standing. If these symptoms occur, the administration of the medicine should be stopped and the doctor should be informed.
- To determine the dose of FANHDI that will achieve and maintain the appropriate level of factor VIII, the doctor may order a series of tests.
- If bleeding does not stop despite the administration of FANHDI, the doctor should be informed. This may be due to the production of a factor VIII inhibitor, which requires confirmation by testing. Factor VIII inhibitors are antibodies that block the action of administered factor VIII, resulting in a decrease in the effectiveness of factor VIII in stopping bleeding.
- If a factor VIII inhibitor has previously been formed and then the treatment is changed to another product containing factor VIII, there is a higher risk of recurrence of this complication.
- During the treatment of von Willebrand disease with known clinical or laboratory risk factors, there is a risk of thrombotic complications. Therefore, it is necessary to perform appropriate tests to detect early signs of these complications and to use currently recommended treatments for thrombotic complications.
- In von Willebrand disease, particularly type 3, neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) to von Willebrand factor may be formed. Von Willebrand factor inhibitors are antibodies in the blood that can block the administered factor. In cases where the expected levels of von Willebrand factor activity in plasma are not achieved or bleeding is not controlled despite the use of appropriate doses, tests should be performed to detect the presence of a von Willebrand factor inhibitor. In patients with a high level of inhibitor, treatment with von Willebrand factor may be ineffective.
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
If it is necessary to use a central venous catheter for the administration of FANHDI, the doctor should be aware of the possibility of local infection, bacteremia (blood infection by bacteria), and thrombosis in the vein at the site of the inserted catheter.
- If the patient has previously formed a factor VIII inhibitor and then the treatment is changed to another product containing factor VIII, there is a higher risk of recurrence of this complication.
In the manufacturing process of products derived from human blood or plasma, the following measures are taken to ensure protection against the transmission of infectious agents:
- careful selection of donors to exclude carriers of infectious agents,
- testing of each donation and plasma pool for the presence of viruses,
- use of virus inactivation/removal procedures in the manufacturing process.
Despite this, it is not possible to completely exclude the transmission of infectious agents during the use of medicinal products obtained from human blood or plasma. This also applies to unknown or newly emerging viruses and other pathogens. The methods used are considered effective against enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and non-enveloped hepatitis A virus. The effectiveness of these methods against non-enveloped viruses such as parvovirus B19 may be limited. Parvovirus B19 infection can be particularly dangerous for pregnant women (fetal infection) and for people with impaired immunity or certain types of anemia (e.g., sickle cell anemia or hemolytic anemia). For patients receiving regular repeated doses of plasma-derived products containing factor VIII, the treating doctor may recommend vaccination against hepatitis A and B. It is strongly recommended that when administering FANHDI to a patient, the patient's name and batch number of the product be recorded, so that the patient can be linked to the batch of the medicine. See also section 4.
Children and adolescents
The warnings and precautions mentioned apply to both adults and children.
FANHDI and other medicines
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
You should tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take. Interactions between the human factor VIII and von Willebrand factor complex and other medicines are not known.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Since hemophilia A is rare in women, there is a lack of data on the use of the FVIII/VWF complex during pregnancy and breastfeeding. You should consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
FANHDI does not affect the ability to drive and use machines.
3. HOW TO USE FANHDI
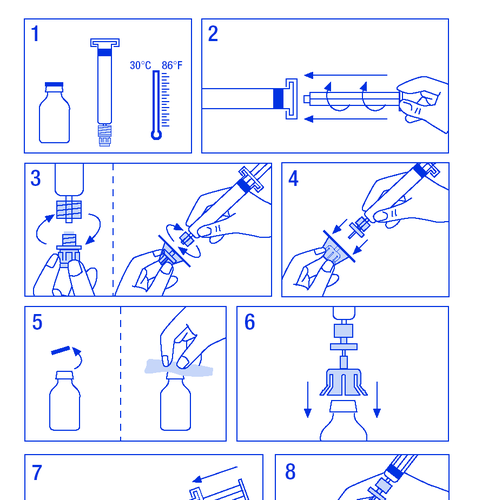
The medicine must be administered intravenously. The rate of administration should not exceed 10 ml/min. You should follow the instructions of your doctor or healthcare professional from a hemophilia treatment center. If you have any doubts, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist. The size of the dose of FANHDI depends on many factors, such as body weight, clinical condition, and type and severity of bleeding. To achieve the appropriate level of factor VIII and von Willebrand factor in the blood, the doctor will determine the dose of FANHDI and the frequency of administration. The doctor will determine the duration of treatment with FANHDI. Do not store the leftovers for later use, even if they are stored in the refrigerator. Preparation of the solution: You should ensure that the actions are performed in conditions that prevent contamination.
- 1. Warm the vials to a temperature not exceeding 30°C (Figure 1).
- 2. Attach the plunger to the syringe with the solvent (Figure 2).
- 3. Remove the filter from the packaging. Remove the plastic cap from the end of the syringe and attach the filter (Figure 3).
- 4. Remove the connector from the vial and connect the syringe with the filter (Figure 4).
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
- 5. Remove the plastic cap from the vial and expose the rubber stopper, disinfect it with a disinfectant (Figure 5).
- 6. Pierce the stopper in the vial with the needle of the connector (Figure 6).
- 7. Inject the entire solvent into the vial (Figure 7).
- 8. Gently swirl the vial until the powder is dissolved (Figure 8). As with other intravenous products, do not use if the product is not dissolved or particles are visible.
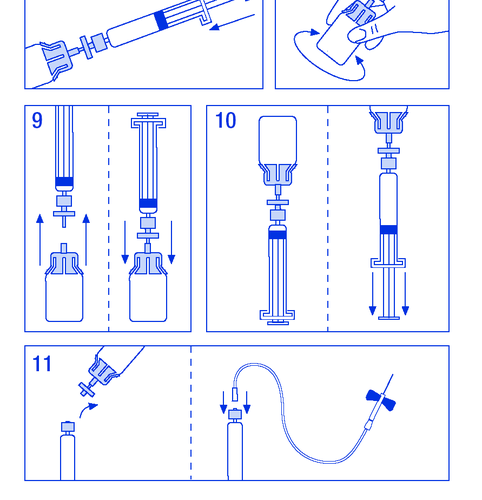
- 9. Disconnect the syringe with the filter from the vial for a moment to allow air to enter (Figure 9).
- 10. Invert the vial and aspirate the solution into the syringe (Figure 10).
- 11. Prepare the injection site, disconnect the syringe, and inject the product through a connected butterfly needle or other sterile needle. Administer slowly intravenously at a rate of 3 ml/min and never exceed 10 ml/min to avoid vascular reactions (Figure 11).
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
Do not reuse the administration set. Any unused product and other waste should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Use of a higher dose of FANHDI than recommended
No cases of overdose of the human factor VIII and von Willebrand factor complex have been reported. After significant overdose, thrombotic complications may occur. Regardless of this, any case of exceeding the recommended dose of FANHDI should be consulted with a pharmacist or doctor immediately.
Missing a dose of FANHDI
- If a dose is missed, the next dose should be administered immediately and treatment should be continued regularly according to the doctor's instructions.
- A double dose should not be used to make up for a missed dose.
4. POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Allergic reactions or hypersensitivity (vasovagal reaction, burning or stinging at the injection site, chills, flushing, generalized urticaria, headache, rash, hypotension, lethargy, nausea, anxiety, tachycardia, feeling of pressure in the chest, sweating, vomiting) have been observed rarely and only in some cases led to the development of severe anaphylaxis (including shock). In rare cases, an increase in body temperature has been observed. In the case of an anaphylactic or allergic reaction, the administration of the medicine should be stopped and the doctor should be informed immediately. It is not possible to completely exclude the possibility of allergic reactions after the administration of this medicine. Patients with hemophilia A may develop neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) against factor VIII. In the case of the development of such inhibitors, insufficient clinical response to treatment is observed. In very rare cases, patients with von Willebrand disease, particularly type 3, may develop neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) against von Willebrand factor. If such inhibitors occur, insufficient clinical response to treatment is observed.
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
Inhibitors may increase the risk of allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock). In the case of allergic reactions, tests for the presence of inhibitors should be performed. In such cases, it is recommended to contact a specialized hemostasis treatment center. During the use of factor VIII-containing products in patients with von Willebrand disease with known clinical or laboratory risk factors, there is a risk of thrombotic complications. Maintaining high levels of FVIII during treatment with factor VIII-containing products increases the risk of thrombotic complications. During several clinical trials conducted with the participation of 164 patients, a total of 7000 FANHDI infusions were administered. The results obtained from both studies indicate good tolerance of the medicine and a low frequency of adverse reactions. Only two cases of adverse reactions related to the administered medicinal product were observed. In these cases, an increase in body temperature was reported. Table of adverse reactions The following table lists the system organ classes and preferred terms (MedDRA classification). The frequency of adverse reactions is defined as follows:
- very common (≥ 1/10)
- common (≥ 1/100 to <1>
- uncommon (≥ 1/1000 to <1>
- rare (≥ 1/10,000 to <1>
- very rare (<1>
- not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data).
In each frequency category, adverse reactions are listed in order of severity, from the most severe to the least severe.
| System organ class | Adverse reactions | Frequency |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Increased body temperature. | Rare |
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
Children and adolescents
The frequency, type, and severity of adverse reactions expected in children do not differ from those observed in adults.
Reporting suspected adverse reactions
After the authorization of the medicinal product, it is important to report any suspected adverse reactions. This allows for continuous monitoring of the benefit/risk ratio of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the national reporting system:
Department for the Monitoring of Adverse Reactions of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 222 49 21 301, Fax: +48 222 49 21 309, e-mail: [email protected]. Reporting adverse reactions helps to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
Information on measures to prevent the transmission of infectious agents
See section 2.
- 5.HOW TO STORE FANHDI
The medicine should be stored out of the sight and reach of children. Do not store above 30°C. Do not freeze. Do not use the medicine after the expiry date. The solution should be clear and slightly opalescent. Do not use solutions that contain particles or precipitates. Do not use if the product contains particles or has changed color after reconstitution. After reconstitution, the chemical and physical stability of the product is maintained for 12 hours at 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If the product is not used after reconstitution, it can be stored for no more than 24 hours at 2°C – 8°C, but only if the user is responsible for preparing the solution in accordance with aseptic principles. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use the medicine after the expiry date stated on the label.
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
- 6.CONTENTS OF THE PACK AND OTHER INFORMATION
What FANHDI contains
The active substance is human coagulation factor VIII and von Willebrand factor complex. Each vial of powder contains 250 IU of human coagulation factor VIII and 300 IU of von Willebrand factor. After reconstitution with 10 ml of water for injection, the product contains 25 IU/ml FVIII and 30 IU/ml VWF. The other ingredients are human albumin, histidine, and arginine. Each syringe contains 10 ml of water for injection.
What FANHDI looks like and contents of the pack
Vial with white or light yellow powder and syringe with water for injection. Each pack of FANHDI contains a vial of 250 IU of human coagulation factor VIII and 300 IU of von Willebrand factor (powder for injection and infusion) and 1 syringe of 10 ml water for injection (solvent). Administration set and infusion set included in the pack. Available packs: FANHDI 500 IU FVIII + 600 IU VWF, FANHDI 1000 IU FVIII + 1200 IU VWF. Not all packs may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Instituto Grifols, S.A., Can Guasc, 2 - Parets del Vallès, 08150 Barcelona, Spain. For more information, please contact your local representative of the marketing authorization holder: Grifols Polska Sp. z o.o., Ul. Grzybowska 87, 00-844 Warszawa, Tel: +48 22 378 85 61
Date of last revision of the package leaflet:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Dosage
Factor VIII deficiency. The dosage and duration of substitution therapy depend on the severity of factor VIII deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. The administered dose of factor VIII is expressed in international units (IU) in accordance with the current WHO standards for factor VIII products. Factor VIII activity in plasma can be expressed as a percentage of normal activity or in IU/ml. One international unit (IU) of factor VIII activity is equivalent to the amount of factor VIII in 1 ml of normal human plasma.
Calculation of the required dose
The required dose is calculated based on the empirical observation that the administration of 1 IU of factor VIII per kg of body weight increases the activity of factor VIII in plasma by 1.7% to 2.5% of normal activity. The dose is calculated using the following formula:
Required dose (IU) = body weight (kg) x desired increase in factor VIII activity (%) x 0.5
The dose and frequency of administration should always be adjusted individually for each patient, depending on the patient's response to treatment. In the treatment of bleeding, depending on the cause and location of bleeding, the aim is to maintain the appropriate level of factor VIII activity (as a percentage of normal or IU/ml) for the recommended duration of treatment. When determining the dose based on the type of bleeding or surgical procedure, the following table can be used:
| Severity of bleeding/surgical procedure | Required factor VIII level (%) (IU/ml) | Dosing frequency (hours)/treatment duration (days) |
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
| Bleeding | Mild bleeding into joints, muscles, or oral bleeding. | 20 – 40 | Repeat every 12-24 hours for at least 1 day, until pain and disability are resolved. |
| Moderate bleeding into joints, muscles, or bleeding. | 30 – 60 | Repeat infusions every 12-24 hours for 3-4 days or longer, until pain and disability are resolved. | |
| Severe bleeding | 60 - 100 | Repeat infusions every 8-24 hours until the risk of bleeding is resolved. | |
| Surgical procedures | Minor, including tooth extraction | 30 – 60 | Every 24 hours, for at least 1 day, until wound healing. |
| Major | 80 – 100 (pre- and post-operative period) | Repeat infusions every 8-24 hours until adequate wound healing is achieved, then continue treatment for another 7 days, maintaining factor VIII activity at 30% to 60% (IU/ml). |
Prophylactic treatment. In long-term prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with severe hemophilia A, a dose of 20-40 IU/kg body weight is usually used at intervals of 2 to 3 days. In some cases, especially in young patients, it may be necessary to shorten the intervals between injections or increase the dose. During treatment, to determine the dose and frequency of infusions, it is recommended to monitor the levels of factor VIII in plasma. Especially in cases of major surgical procedures, close monitoring of substitution therapy is necessary using coagulation tests (factor VIII activity in plasma). Patients may respond individually to factor VIII treatment, which is reflected in different in vivo recovery levels and half-lives in individual patients.
- 1.3.1. SPC, labelling and package leaflet
Von Willebrand disease. In general, it is assumed that the administration of 1 IU of VWF:RCo per kg of body weight increases the VWF:RCo level by 2% in the circulation. The goal of treatment is to achieve a VWF:RCo level > 0.6 IU/ml (60%) and FVIII:C > 0.4 IU/ml (40%) in plasma. In most cases, to achieve hemostasis, a dose of 40-80 IU/kg body weight of von Willebrand factor and 20-40 IU/kg body weight of FVIII:C is recommended. Patients with type 3 von Willebrand disease, who may require higher doses to maintain adequate levels of factor, may need an initial dose of 80 IU/kg body weight of von Willebrand factor. The appropriate dose should be administered every 12-24 hours. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the patient's clinical condition, the location and extent of bleeding, and the levels of both VWF:RCo and FVIII:C. During the use of factor VIII-containing products, the treating doctor should consider the possibility of excessive increase in FVIII:C levels. To avoid excessive increase in FVIII:C levels, after 24-48 hours of treatment, it is recommended to consider reducing the dose or prolonging the interval between doses or using products containing VWF with lower factor VIII content.
- After 24-48 hours of treatment, consider reducing the dose or prolonging the interval between doses or using products containing VWF with lower factor VIII content.
Children and adolescents. In the above-mentioned indications, only limited data from clinical trials are available in children under 6 years of age, and therefore, there are no recommendations for the use of the medicinal product in this age group. In children, as in adults, the dose is adjusted based on clinical efficacy, taking into account body weight.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterInstituto Grifols, S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FanhdiDosage form: Powder, 50 IU/ml; 500 IU + 60 IU/ml; 600 IUActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 100 IU/ml; 1000 IU + 120 IU/ml; 1200 IUActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 1000 IU + 2400 IU/15 mlActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Fanhdi in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fanhdi in Ukraine
Alternative to Fanhdi in Spain
Online doctors for Fanhdi
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fanhdi – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














