

Cordarone

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Cordarone

How to use Cordarone
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Cordarone
50 mg/ml, solution for injection
Amiodarone hydrochloride
{logo sanofi}
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Package Leaflet
- 1. What Cordarone is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before using Cordarone
- 3. How to use Cordarone
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Cordarone
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Cordarone is and what it is used for
Cordarone is a solution for injection containing the active substance amiodarone hydrochloride. Amiodarone is a powerful anti-arrhythmic medicine used to treat irregular heartbeats.
Amiodarone is given intravenously in situations where rapid action is needed or when oral administration is not possible.
It is used to treat life-threatening heart rhythm disorders:
- arrhythmias in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
- atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias: supraventricular tachycardias and nodal tachycardias, when other medicines cannot be used
- ventricular arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation), when other anti-arrhythmic medicines are ineffective.
2. Important information before using Cordarone
When not to use Cordarone:
- in patients with heart disease: sinus bradycardia, sinoatrial block and sick sinus syndrome, except in patients with a pacemaker (risk of inhibition of sinus node activity);
- in patients with atrioventricular block of second or third degree, except in patients with a pacemaker;
- in patients with bifascicular or trifascicular block, except in patients with a pacemaker or a temporary pacing system;
- concomitantly with medicines that may cause life-threatening arrhythmias (type torsade de pointes);
- in case of circulatory collapse, severe hypotension;
- in case of severe respiratory failure;
- in patients with congestive cardiomyopathy or heart failure.
The above contraindications do not apply if amiodarone is used in the intensive care unit for cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest due to ventricular fibrillation when defibrillation is not effective.
Warnings and precautions
Cordarone should be administered intravenously only in an intensive care unit,
where the patient's clinical condition is constantly monitored (ECG recording, blood pressure measurements).
Cordarone may cause changes in the ECG - this does not necessarily mean that the medicine is toxic.
- Cordarone may cause arrhythmias or worsen existing arrhythmias, especially as a result of interactions with certain medicines (see "Cordarone and other medicines" and section 4) and/or in case of electrolyte disturbances (decreased potassium and/or magnesium levels in the blood). Do not allow potassium levels to become too low (hypokalemia) and supplement the deficiency.
- It is not recommended to use Cordarone concomitantly with the following medicines: beta-adrenergic blockers, calcium channel blockers that slow heart rate (verapamil, diltiazem), laxatives that can cause hypokalemia (see "Cordarone and other medicines").
- Before starting Cordarone, discuss with your doctor or pharmacist if you are currently taking a medicine containing sofosbuvir, used to treat hepatitis C virus, as it may cause life-threatening slowing of the heart rate. Your doctor may consider alternative treatment methods. If treatment with amiodarone and sofosbuvir is necessary, additional heart monitoring may be required.
- You must immediately inform your doctorif you are taking a medicine containing sofosbuvir, used to treat hepatitis C virus, and if during treatment you experience:
- slow or irregular heartbeat or arrhythmias,
- shortness of breath or worsening of existing shortness of breath,
- chest pain,
- dizziness,
- palpitations,
- feeling of impending faint or fainting.
- Cordarone may cause pulmonary interstitial inflammation. It is characterized by shortness of breath and cough without expectoration. If interstitial pneumonia is suspected in a patient, the doctor will perform a chest X-ray and consider further treatment with Cordarone, as interstitial pneumonia usually resolves if therapy with the medicine is quickly discontinued. The doctor may also consider treatment with corticosteroids.
- Very rarely, severe respiratory complications have been observed, sometimes leading to death, usually in the post-operative period (see "Cordarone and other medicines" and section 4).
- Before surgery, the anesthesiologist must be informed that the patient has been given Cordarone.
- During Cordarone treatment and within 24 hours of its administration, acute or chronic liver dysfunction may occur, leading to death. Therefore, from the start of therapy, the doctor will regularly order liver function tests (determination of aminotransferase activity in the blood). If liver dysfunction occurs, the doctor will consider reducing the dose of the medicine or discontinuing treatment.
- Discontinue Cordarone treatment immediatelyif severe skin reactions occur (e.g., progressive rash with blisters or changes in mucous membranes, fever and joint pain, severe rapidly progressing disease characterized by bursting giant blisters, extensive skin erosion, shedding of large skin flakes, and fever - see also section 4). These symptoms can be life-threatening.
- In case of blurred vision or worsening vision, a complete ophthalmological examination, including a fundus examination, should be performed immediately. If damage and/or inflammation of the optic nerve is found, Cordarone should be discontinued due to the risk of vision loss.
- To avoid unwanted effects at the injection site, Cordarone should be administered through central venous access.
- If the patient is on the waiting list for a heart transplant, the treating doctor may change the treatment before the transplant. This is because taking amiodarone before a heart transplant increases the risk of a life-threatening complication (primary graft dysfunction), in which the transplanted heart stops working properly within the first 24 hours after surgery.
Cordarone and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking, or have recently taken, and about medicines you plan to take.
Do not use Cordarone concomitantly with medicines that may cause life-threatening arrhythmias (type torsade de pointes). These medicines include:
- medicines used to treat arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats): quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide, sotalol, bretylium, bepridil,
- intravenously administered erythromycin (antibiotic), cotrimoxazole (anti-infective) or the antiprotozoal medicine pentamidine,
- antipsychotic medicines, such as: chlorpromazine, thioridazine, fluphenazine, pimozide, haloperidol, amisulpride, sertindol,
- certain medicines used in other psychiatric disorders: lithium preparations and tricyclic antidepressants, e.g., doxepin, amitriptyline,
- certain antihistamines used to treat allergies: terfenadine, astemizole, mizolastine,
- medicines used to treat malaria: quinine, chloroquine, mefloquine, halofantrine,
- a medicine used to treat cerebral circulation disorders, dizziness, tinnitus, memory and learning disorders, especially in the elderly - vincamine,
- neuroleptics,
- a medicine used to treat delayed gastric emptying - cisapride.
It is not recommended to use Cordarone concomitantly with:
- fluoroquinolones - anti-infective medicines: ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin,
- beta-adrenergic blockers - used in heart diseases, e.g., propranolol,
- calcium channel blockers that slow heart rate - used in angina pectoris (heart disease) or hypertension (high blood pressure): verapamil, diltiazem,
- antiviral medicines used to treat hepatitis C virus, e.g., sofosbuvir, daclatasvir, simeprevir or ledipasvir, due to the risk of slowing down the heart rate (bradycardia),
- certain laxatives (used to treat constipation) that can cause low potassium levels in the blood: bisacodyl, senna,
- cholesterol-lowering medicines - statins, e.g., simvastatin, atorvastatin, lovastatin. Caution should be exercised when using the following medicines concomitantly with Cordarone:
- diuretics, e.g., furosemide,
- systemic corticosteroids, e.g., hydrocortisone, prednisolone,
- tetracosactide - a medicine used to test certain hormonal disorders,
- the antifungal medicine amphotericin B administered intravenously,
- agents used in general anesthesia or high oxygen concentrations administered during surgical procedures (see "Warnings and precautions" in section 2 and section 4). Before surgery, the anesthesiologist should be informed about the use of Cordarone,
- phenytoin - used to treat epileptic seizures: close monitoring of the patient is necessary and the dose of phenytoin should be reduced immediately if symptoms of overdose occur and phenytoin levels in the blood should be measured,
- digoxin - used to treat heart diseases: the doctor will order measurements of digoxin levels in the blood and perform an ECG and change the dose of digoxin; the patient should be monitored for signs of digoxin toxicity,
- anticoagulant medicines - warfarin, dabigatran: regular blood coagulation tests will be necessary to adjust the oral doses of anticoagulant medicines, both during and after treatment with Cordarone; it may be necessary to adjust the dose of dabigatran,
- medicines used to prevent transplant rejection - cyclosporine, tacrolimus and sirolimus,
- flecainide - used to treat arrhythmias: treatment will be carried out under close medical supervision; the doctor will change the dose of flecainide,
- fentanyl - a strong pain reliever,
- lidocaine - a local anesthetic,
- sildenafil - used to treat impotence,
- midazolam - used to treat anxiety and to sedate before surgical procedures,
- triazolam - used to treat insomnia,
- dihydroergotamine and ergotamine - medicines used to treat migraines,
- colchicine - used to treat acute gout attacks.
Cordarone with food and drink
It is recommended to avoid consuming grapefruit juice during treatment with Cordarone.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a child, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
Due to the effect of Cordarone on the fetal thyroid, the use of the medicine during pregnancy is contraindicated. Consult your doctor before using the medicine.
Breastfeeding
The use of Cordarone during breastfeeding is contraindicated. Consult your doctor before using the medicine.
Fertility
There is no data on the effect of amiodarone on human fertility.
Driving and using machines
Based on the safety data of amiodarone, the medicine does not affect the ability to drive and use machines.
Cordarone contains benzyl alcohol
Cordarone contains 60 mg of benzyl alcohol per ampoule (corresponding to 20 mg/ml) as a preservative.
Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions.
Administration of benzyl alcohol to small children is associated with a risk of serious adverse effects, including respiratory distress (so-called "gasping syndrome").
This medicine should not be given to newborns (up to 4 weeks of age) without a doctor's recommendation.
This medicine should not be given to small children (under 3 years of age) for more than a week without a doctor's or pharmacist's recommendation.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a doctor or pharmacist before using the medicine, as a large amount of benzyl alcohol may accumulate in their body and cause adverse effects (so-called metabolic acidosis).
Patients with liver or kidney disease should consult a doctor or pharmacist before using the medicine, as a large amount of benzyl alcohol may accumulate in their body and cause adverse effects (so-called metabolic acidosis).
3. How to use Cordarone
The medicine is administered by a doctor or nurse according to the doctor's prescription. In case of doubts, consult your doctor.
The medicine should be administered intravenously, constantly monitoring the patient's condition (ECG recording, blood pressure measurements).
Cordarone is diluted before administration to the patient.
The doctor will choose the appropriate dose for each patient, depending on their weight and disease.
Usually, the following dosing is used:
Adults:
Intravenous infusion
Loading dose: 5 mg/kg body weight, administered in 250 ml of 5% glucose solution in an infusion lasting from 20 minutes to 2 hours. The infusion can be repeated 2 to 3 times a day. The infusion rate should be determined based on the effect of the medicine.
Maintenance dose:10-20 mg/kg body weight/day (usually 600 to 800 mg/24 hours to a dose of 1200 mg/24 hours) in an infusion of 250 ml of 5% glucose solution for several days.
Once the desired therapeutic effect is achieved, the doctor will prescribe concomitant oral administration of amiodarone in the usual loading dose (3 x 200 mg per day). The intravenous dose will be gradually reduced.
In emergency situations:150-300 mg of amiodarone is administered in 10-20 ml of 5% glucose solution in a slow injection lasting at least 3 minutes.
A subsequent injection can be repeated no earlier than 15 minutes later, even if only the solution from one ampoule (150 mg) was administered in the first injection, due to the risk of circulatory collapse. If further doses of amiodarone are necessary, they should be administered in an intravenous infusion.
Use in elderly patients
There are no specific data on dosing in elderly patients.
However, in elderly patients, special precautions should be taken due to the possibility of severe bradycardia or conduction disorders.
Use in children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of amiodarone in children have not been established. The available data are described in sections 5.1 and 5.2 of the Summary of Product Characteristics.
Due to the presence of benzyl alcohol, caution should be exercised when administering amiodarone intravenously to newborns, infants, and children under 3 years of age (see section 4.4).
Overdose of Cordarone
Since the medicine will be administered to the patient during their hospital stay, it is unlikely that too much or too little medicine will be used, but if the patient has any doubts, they should inform their doctor or nurse.
Missing a dose of Cordarone
The medicine is used in a hospital setting.
Stopping treatment with Cordarone
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Cordarone can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
You should stop using Cordarone and seek medical advice immediately if you experience:
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- angioedema - a severe allergic reaction causing swelling in the face, difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- life-threatening skin reactions characterized by rash, blisters, peeling of the skin and pain [toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), bullous dermatitis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)].
- irregular heartbeat, which may be a sign of life-threatening arrhythmia type torsade de pointes(see "Warnings and precautions" and "Cordarone and other medicines" in section 2);
- blurred vision or worsening vision; these may be symptoms of optic nerve damage, which can lead to vision loss (see "Warnings and precautions" in section 2);
- seeing, hearing or feeling things that are not there (hallucinations);
- you may experience more infections than usual. This may be due to a decrease in the number of white blood cells (neutropenia);
- a significant decrease in the number of white blood cells, which increases the risk of infections (agranulocytosis). Very rare (occurs in less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
- anaphylactic shock (a set of clinical symptoms when the body's autoregulatory mechanisms are unable to ensure proper blood flow to vital organs and tissues, caused by a severe allergic reaction) characterized by confusion, weakness, fainting
- dizziness, fatigue and shortness of breath; these may be symptoms of significant slowing of the heart rate, sinus node arrest, especially in patients with sinus node dysfunction and/or elderly patients, occurrence of new arrhythmias or worsening of existing arrhythmias, sometimes with cardiac arrest;
- yellowing of the eyes and skin (jaundice), abdominal pain, loss of appetite, fatigue, fever, high aminotransferase activity in blood tests; these are symptoms of life-threatening acute liver dysfunction or liver failure;
- shortness of breath and cough without expectoration; these may be symptoms of life-threatening pulmonary interstitial inflammation or pulmonary fibrosis (see "Warnings and precautions" in section 2) or bronchospasm and/or respiratory failure in case of severe respiratory failure, especially in patients with asthma;
- headache worsening in the morning or after exertion, nausea, seizures, fainting, vision disturbances or disorientation, which may be symptoms of cerebral dysfunction due to increased intracranial pressure (pseudotumor cerebri).
Other side effects of Cordarone may occur with the following frequency:
Common (occurs in 1 to 10 out of 100 patients):
- slow heart rate, usually moderate;
- reactions at the injection site, such as: pain, redness, swelling, necrosis, hemorrhage, infiltration, inflammation, induration, thrombophlebitis, phlebitis, inflammation of the connective tissue, infection, skin discoloration;
- decreased blood pressure, usually moderate and transient, characterized by dizziness, disorientation and fainting. Cases of severe hypotension or circulatory collapse have been reported following overdose or too rapid administration of the medicine;
- itching red rash (exanthema);
- decreased libido. Very rare (occurs in less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
- malaise, feeling of disorientation or weakness, nausea (vomiting), loss of appetite, irritability. This may indicate a condition called "syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)";
- nausea;
- increased aminotransferase activity in blood tests, which is usually moderately elevated (1.5 to 3 times above the upper limit of normal), occurring at the beginning of treatment. These abnormalities may return to normal after reducing the dose of the medicine or on their own;
- headache;
- sweating;
- sudden flushing of the face.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- back pain;
- hives;
- hyperthyroidism characterized by agitation, weight loss, increased sweating;
- sudden pancreatitis or acute pancreatitis;
- decreased libido;
- confusion (including delirium), hallucinations;
- life-threatening complication after heart transplantation (primary graft dysfunction), in which the transplanted heart stops working properly (see "Warnings and precautions" in section 2).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products,
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder or its representative in Poland.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Cordarone
Store the medicine at a temperature below 25°C.
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use the medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton after "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Cordarone contains
- The active substance of the medicine is amiodarone hydrochloride. One ampoule contains 150 mg of amiodarone hydrochloride
- The other ingredients are: benzyl alcohol, polysorbate 80, water for injections.
What Cordarone looks like and contents of the pack
The pack contains 6 ampoules of 3 ml each.
Marketing authorization holder:
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
82, Avenue Raspail
94250 Gentilly
France
Manufacturer:
Sanofi-Winthrop Industrie
1, rue de la Vierge
33440 Ambares
France
Delpharm Dijon
6 boulevard de l`Europe
21800 Quetigny
France
Sanofi S.r.l.
Via Valcanello, 4
03012 Anagni (FR)
Italy
To obtain more detailed information, please contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder in Poland:
Sanofi Sp. z o.o.
Marcina Kasprzaka Street 6
01-211 Warsaw
tel.: +48 22 280 00 00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only: To obtain full information about the medicine, please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC).
Dosage and administration
Cordarone, solution for injection should only be used in intensive care units with cardiac monitoring, defibrillation and cardiac pacing capabilities. The medicine should be administered intravenously.
In the case of continuous or repeated infusion, amiodarone should be administered through central venous access to avoid unwanted reactions at the injection site (see section 4.8).
Due to the risk of severe hypotension and circulatory collapse, intravenous amiodarone can only be administered in emergency situations when other medicines are ineffective, exclusively in an intensive care unit, with continuous electrocardiographic monitoring.
The dose used is approximately 5 mg/kg body weight. Except for the case of cardiopulmonary resuscitation of patients with ventricular fibrillation resistant to defibrillation, intravenous injection of the dose of amiodarone should last at least 3 minutes.
Cordarone, solution for injection is incompatible with physiological sodium chloride solution and can only be used with 5% glucose solution. A solution of amiodarone with a concentration less than 300 mg (2 ampoules) in 500 ml of 5% glucose solution is not stable and should not be used.
Intravenous infusion
Loading dose: usually, the loading dose is 5 mg/kg body weight, administered in 250 ml of 5% glucose solution in an infusion lasting from 20 minutes to 2 hours. The infusion can be repeated 2 to 3 times a day. The infusion rate should be determined based on the effect of the medicine.
The therapeutic effect occurs within the first few minutes and then gradually decreases, so to prolong it, the medicine should be continued to be administered in an infusion.
Maintenance dose: 10-20 mg/kg body weight/day (usually 600 to 800 mg/24 hours to a dose of 1200 mg/24 hours) in an infusion of 250 ml of 5% glucose solution for several days. In each case, the minimum effective dose should be administered.
Transition from intravenous to oral administration: once the desired therapeutic effect is achieved, concomitant oral administration of amiodarone should be started in the usual loading dose (3 x 200 mg per day). The intravenous dose should be gradually reduced.
Dosing in emergency situations:150-300 mg of amiodarone is administered in 10-20 ml of 5% glucose solution in a slow injection lasting at least 3 minutes.
A subsequent injection can be repeated no earlier than 15 minutes later, even if only the solution from one ampoule (150 mg) was administered in the first injection, due to the risk of circulatory collapse. If further doses of amiodarone are necessary, they should be administered in an intravenous infusion.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
In the specific case of cardiopulmonary resuscitation of a patient with ventricular fibrillation resistant to defibrillation, the first dose of 300 mg (or 5 mg/kg) of amiodarone is administered in a bolus injection, diluting the appropriate volume of Cordarone solution in 20 ml of 5% glucose solution. In case of persistent ventricular fibrillation, a further intravenous dose of amiodarone may be considered, at a dose of 150 mg (or 2.5 mg/kg).
Do not mix other medicines with amiodarone in the same syringe.
Do not inject other medicines into the same venous access.
Use in elderly patients
There are no specific data on dosing in elderly patients.
However, in elderly patients, special precautions should be taken due to the possibility of severe bradycardia or conduction disorders.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of amiodarone in children have not been established. The available data are described in sections 5.1 and 5.2 of the Summary of Product Characteristics.
Due to the presence of benzyl alcohol, caution should be exercised when administering amiodarone intravenously to newborns, infants, and children under 3 years of age (see section 4.4).
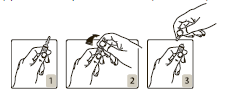
Opening the ampoule:
The ampoule should be held in such a way that the colored dot is facing the person holding it (Fig. 1). The top part of the ampoule should be placed between the thumb and index finger (the thumb should be placed on the colored dot), and then the ampoule should be pressed from behind (Figs. 2 and
- 3).
Incompatibilities
The use of medical devices made of plastic containing DEHP (di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate) in the presence of amiodarone solution for injection may lead to the release of DEHP. To minimize patient exposure to DEHP, it is recommended to perform the final dilution of amiodarone before infusion and administer the medicine using DEHP-free sets.
Cordarone solution for injection is also incompatible with physiological sodium chloride solution and can only be used with 5% glucose solution. A solution of amiodarone with a concentration less than 300 mg (2 ampoules) in 500 ml of 5% glucose solution is not stable and should not be used.
Special warnings and precautions for use
Amiodarone may be administered intravenously only in an intensive care unit, where the patient's clinical condition is constantly monitored (ECG recording, blood pressure measurements).
Whenever possible, amiodarone should be administered intravenously through central venous access to avoid unwanted reactions at the injection site (see section 4.8).
Attention should be paid to any symptoms of hypotension, severe respiratory failure, uncontrolled or severe heart failure.
Detailed information on intravenous injections
Due to the risk of hemodynamic disorders (severe hypotension, circulatory collapse), intravenous injection is not routinely recommended. In situations where possible, intravenous infusion is preferred. Amiodarone may be administered by intravenous injectiononly in emergency situations when other medications are ineffective, exclusively in the intensive care unit, where the patient is continuously monitored (ECG recording, blood pressure values). The dose is approximately 5 mg/kg body weight. Amiodarone should be administered by intravenous injection lasting at least 3 minutes, except in cases of cardiopulmonary resuscitation associated with ventricular fibrillation when defibrillation is not effective. The next injection can be repeated no earlier than 15 minutes later, even if only a solution from one ampoule (150 mg) was administered in the first injection, due to the risk of irreversible circulatory collapse. If it is necessary to administer subsequent doses of amiodarone, they should be administered in the form of intravenous infusion. Other medications should not be mixed with amiodarone in the same syringe. Other medications should not be injected into the same venous access. Cardiac disorders (see section 4.8 of the SmPC) The pharmacological action of amiodarone causes changes in the ECG: prolongation of the QT interval (related to the prolongation of the repolarization period) with possible formation of a U wave. However, these changes do not indicate amiodarone poisoning. There have been reports of the occurrence of a new type of cardiac rhythm disorder or worsening of treated cardiac rhythm disorders, sometimes leading to death. It is important, but difficult to distinguish, whether this is due to the lack of efficacy of the medication, which has a proarrhythmic effect, or is related to the exacerbation of cardiac rhythm disorders. Proarrhythmic effects of amiodarone have been reported less frequently than with other antiarrhythmic medications. The proarrhythmic effect of amiodarone occurs especially as a result of interactions with medications that prolong the QT interval and (or) in the case of electrolyte disorders (see sections 4.5 and 4.8). Regardless of the prolongation of the QT interval, amiodarone has a low activity of inducing cardiac rhythm disorders of the torsade de pointestype. Severe bradycardia and heart block During the use of regimens containing sofosbuvir concomitantly with amiodarone, life-threatening cases of bradycardia and heart block have been observed. Bradycardia usually occurred within a few hours to days, but cases have also been observed where this time was longer, most often up to 2 weeks after the start of HCV treatment. Patients receiving a regimen containing sofosbuvir should be given amiodarone only when the use of other alternative antiarrhythmic medications is contraindicated or not tolerated. If concomitant use of amiodarone is necessary, it is recommended to monitor the patient's heart function in a hospital setting for the first 48 hours after the start of concomitant administration; and then the heart rate should be monitored in an outpatient setting or by the patient themselves, daily for at least the first 2 weeks of treatment. Due to the long half-life of amiodarone, it is also recommended to monitor heart function in the manner described above in patients who have discontinued amiodarone use within the last few months and are about to start a regimen containing sofosbuvir. All patients receiving amiodarone in combination with a regimen containing sofosbuvir should be informed of the risk of bradycardia and heart block and the need for immediate medical attention in case of their occurrence. Respiratory disorders (see section 4.8 of the SmPC) The occurrence of dyspnea and non-productive cough may be related to toxic effects on the lungs, such as the occurrence of interstitial pneumonia. Very rare cases of interstitial pneumonia have been reported after the use of amiodarone in intravenous form. In case of suspected diagnosis in a patient who has developed exertional dyspnea as the only symptom, as well as associated with worsening of the patient's general condition (fatigue, weight loss, fever), a radiological examination of the chest should be performed. In such a case, the justification for further treatment with amiodarone should be re-evaluated, as interstitial pneumonia is usually reversible after early discontinuation of amiodarone (clinical symptoms usually resolve within 3 to 4 weeks, with subsequent gradual improvement of radiological examination results and lung function tests, over a period of several months). The introduction of treatment with corticosteroids should also be considered. Several very rare cases of severe respiratory complications, sometimes leading to death, have been reported, usually occurring immediately after surgical procedures (acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults). This may be related to the interaction of high concentrations of oxygen (see sections 4.5 and 4.8). Hepatic disorders (see section 4.8 of the SmPC) Regular, close monitoring of liver function (determination of aminotransferase activity) is recommended during treatment with amiodarone, starting from the moment of treatment initiation. The dose of amiodarone should be reduced or treatment discontinued in case of a three-fold increase in aminotransferase activity above the upper limit of normal, which may indicate the occurrence of acute, severe liver disorders (including severe liver cell failure or liver failure, sometimes leading to death) or chronic liver disorders. These disorders may occur during the use of both oral and intravenous forms of the product, and within 24 hours after intravenous administration of amiodarone. Clinical and biological signs of chronic liver disorders may be mild (possible liver enlargement, increased aminotransferase activity 1.5 to 5 times above the upper limit of normal). These abnormalities usually resolve after discontinuation of amiodarone treatment. However, cases with a fatal outcome have been reported. Severe skin reactions Treatment with amiodarone should be discontinued immediately if skin reactions occur that may indicate the occurrence of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (progressive rash with blisters or changes in mucous membranes, fever, and joint pain) or toxic epidermal necrolysis (severe, rapidly progressing disease characterized by bursting giant subepidermal blisters, extensive skin erosion, peeling of large skin flakes, and fever), blistering dermatitis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). These symptoms can be life-threatening and even lead to death. Eye disorders (see section 4.8) In case of blurred vision or worsening vision, a complete ophthalmological examination, including a fundus examination with an ophthalmoscope, should be performed immediately. The finding of optic neuropathy and (or) optic neuritis requires discontinuation of amiodarone treatment due to the possibility of progression to vision loss. Interactions with other medications (see section 4.5 of the SmPC) Concomitant use of amiodarone with the following medications is not recommended: beta-adrenergic blockers, calcium channel blockers that slow the heart rate (verapamil, diltiazem), irritating laxatives that may cause hypokalemia, antiviral medications used to treat hepatitis C, such as sofosbuvir, daclatasvir, simeprevir, or ledipasvir, due to the risk of severe bradycardia. Concomitant administration of amiodarone with regimens containing sofosbuvir may lead to serious, symptomatic bradycardia. If concomitant use of amiodarone with regimens containing sofosbuvir cannot be avoided, it is recommended to monitor the patient's heart function (see section 4.4). Anesthesia Before surgery, the anesthesiologist should be informed about the patient's use of amiodarone. Children and adolescents The safety and efficacy of amiodarone have not been established in children. Available data are described in sections 5.1 and 5.2. The Cordarone product in the form of a solution for injection contains benzyl alcohol at a concentration of 20 mg/ml (see section 6.1). Benzyl alcohol can cause toxic and allergic reactions in newborns, infants, and children up to 3 years of age. After intravenous administration of solutions containing this preservative, there have been reports of the occurrence of "gasping syndrome" with a fatal outcome in newborns (children before the end of the first month of life). Symptoms include sudden onset of "gasping syndrome", hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiocirculatory collapse. More special warnings regarding the long-term use of amiodarone are available in the Summary of Product Characteristics of Cordarone, tablets, 200 mg.
Overdose
There are no available data on overdose of amiodarone administered intravenously. There are few reports of overdose of amiodarone administered orally. Sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block, ventricular tachycardia, cardiac rhythm disorders of the torsade de pointestype, circulatory failure, as well as decreased blood pressure and liver damage may occur. Both amiodarone and its metabolites are not removed during dialysis. Overdose of the medication requires professional medical assistance; treatment is symptomatic.
- 4.4 SmPC). Anesthesia: Before surgery, the anesthesiologist should be informed about the patient's use of amiodarone.
Children and adolescents The safety and efficacy of amiodarone have not been established in children. Available data are described in sections 5.1 and 5.2. The Cordarone product in the form of a solution for injection contains benzyl alcohol at a concentration of 20 mg/ml (see section 6.1). Benzyl alcohol can cause toxic and allergic reactions in newborns, infants, and children up to 3 years of age. After intravenous administration of solutions containing this preservative, there have been reports of the occurrence of "gasping syndrome" with a fatal outcome in newborns (children before the end of the first month of life). Symptoms include sudden onset of "gasping syndrome", hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiocirculatory collapse. More special warnings regarding the long-term use of amiodarone are available in the Summary of Product Characteristics of Cordarone, tablets, 200 mg.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterDelpharm Dijon Sanofi S.r.l. Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to CordaroneDosage form: Concentrate, 30 mg/mlActive substance: amiodaronePrescription not requiredDosage form: Concentrate, 50 mg/mlActive substance: amiodaroneManufacturer: hameln rds s.r.o. HBM Pharma s.r.o.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 50 mg/mlActive substance: amiodaroneManufacturer: Krka, d.d., Novo mestoPrescription not required
Alternatives to Cordarone in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Cordarone in Ukraine
Alternative to Cordarone in Spain
Online doctors for Cordarone
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Cordarone – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










