
Amiodaron Accord

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Amiodaron Accord

How to use Amiodaron Accord
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Amiodarone Accord, 30 mg/ml, concentrate for solution for injection/infusion
Amiodarone hydrochloride
You should read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Amiodarone Accord and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Amiodarone Accord
- 3. How to use Amiodarone Accord
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Amiodarone Accord
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Amiodarone Accord and what is it used for
Amiodarone Accord contains the active substance amiodarone hydrochloride, which belongs to a group of medicines called antiarrhythmic medicines. Its action is to control irregular heartbeats (called arrhythmia).
Amiodarone Accord is used to treat adult patients with:
- severe, symptomatic ventricular tachyarrhythmias;
- symptomatic arrhythmias requiring treatment, with rapid heart rate of supraventricular origin (supraventricular tachyarrhythmias), such as:
- atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia,
- supraventricular tachycardia in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, when the heart beats extremely fast, or
- paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (fast or irregular heartbeat).
This indication applies to patients who do not respond to treatment with other antiarrhythmic medicines or for whom other antiarrhythmic medicines are not indicated.
Amiodarone Accord is used when rapid action of the medicine is necessary or when oral administration is not possible. This medicine will be administered by a doctor, and the patient's condition will be monitored in a hospital or under the supervision of a specialist.
2. Important information before using Amiodarone Accord
When not to use Amiodarone Accord:
- if the patient is allergic to amiodarone hydrochloride, iodine, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has heart problems that can cause a slow heart rate (such as sinoatrial block or sinus bradycardia);
- if the patient has various forms of conduction disorders (atrioventricular block of a high degree, bifascicular or trifascicular block, or sick sinus syndrome) and the patient does not have a pacemaker;
if the patient has heart failure or weakening of the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy);
- if the patient has thyroid problems or has had thyroid problems in the past;
- if the patient has severe respiratory failure, circulatory collapse, or severe hypotension (very low blood pressure);
- if the patient has a pre-existing prolongation of the QT interval (a specific change in the ECG);
- if the patient has low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia);
- if the patient has had angioedema (a certain type of skin and mucous membrane swelling) in the past;
- if the patient is taking MAO inhibitors (certain antidepressants) at the same time;
- if the patient is taking other medicines that can cause a specific type of rapid heartbeat (torsades de pointes type);
- if the patient is pregnant, suspects she may be pregnant, or is breastfeeding (unless the doctor considers the treatment absolutely necessary).
All of the above contraindications do not apply if amiodarone is used in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (if the patient has had a cardiac arrest and stopped breathing due to ventricular fibrillation resistant to defibrillation).
Amiodarone Accord should not be given to premature infants, newborns, or children under 3 years of age.
Do not use this medicine if any of the above apply to you; you should talk to your doctor or nurse.
Warnings and precautions
Amiodarone Accord can only be administered in an intensive care unit and under constant monitoring (ECG recording and blood pressure monitoring).
Before starting treatment with Amiodarone Accord, you should discuss it with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if:
- you have mild to moderate low blood pressure,
- you have a weak heart or heart failure,
- you have thyroid problems,
- you have liver problems,
- you are receiving high-dose oxygen therapy or have other lung problems, including asthma,
- you are going to have surgery under general anesthesia,
- you are elderly,
- you are taking a medicine called sofosbuvir, used to treat hepatitis C virus infection.
In the case of arrhythmias (ventricular arrhythmias), the start of amiodarone administration requires very careful monitoring of heart function and can only be performed when cardiac monitoring equipment is available.
During long-term treatment (e.g., after switching to oral treatment), cardiac checks should be performed at regular intervals.
During amiodarone treatment, a slow heart rate (bradycardia) may occur. A decreased heart rate may be more pronounced in patients over 65 years of age. Treatment should be discontinued in case of severe bradycardia or heart block.
There have been cases of new arrhythmias or worsening of arrhythmias being treated. They usually occur as a result of a combination with other medicines or electrolyte disturbances (such as changes in potassium levels in the blood). In such cases, it is necessary to consider stopping treatment with this medicine.
Particular caution is required in case of hypotension, severe respiratory failure, severe heart failure, or uncontrolled cardiomyopathy.
If the patient is currently taking a medicine containing sofosbuvir used to treat hepatitis C virus infection, they should discuss this with their doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Amiodarone Accord, as it may lead to life-threatening slow heart rate. The doctor may consider alternative treatment methods. If treatment with amiodarone and sofosbuvir is necessary, additional heart monitoring may be required.
The patient should immediately inform their doctor if they are taking a medicine containing sofosbuvir for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection and during treatment, they experience:
- slow or irregular heartbeat or arrhythmias;
- shortness of breath or worsening of existing shortness of breath;
- chest pain;
- dizziness;
- palpitations;
- near-fainting or fainting.
During amiodarone treatment, there is a risk of severe lung inflammation. Therefore, if possible, a chest X-ray and lung function test should be performed before starting treatment.
Recently, cases of toxic liver damage have been reported after intravenous administration, which may be caused by the solvent (polysorbate 80) rather than the medicine itself.
Both during oral and intravenous administration, liver function disorders (in the case of intravenous administration, already within the first 24 hours) may occur. Therefore, the dosage of amiodarone should be reduced or treatment discontinued if the increase in aminotransferase activity (related to liver function) exceeds three times the reference value.
During treatment, the doctor may decide to perform tests: chest X-ray (to rule out respiratory complications) and blood tests to determine aminotransferase activity (before starting treatment and regularly during treatment to check if the liver is functioning properly) and potassium levels in the blood.
The patient should tell their doctor if they experience vision disturbances: blurred vision, decreased vision, seeing colored halos, feeling of blurred vision. In case of any of these problems, the patient should have a complete eye examination.
General anesthesia
Caution is recommended in patients undergoing general anesthesia or receiving high-dose oxygen therapy.
Potentially severe complications have been observed with general anesthesia. Before surgery, the anesthesiologist should be informed that the patient is being treated with amiodarone.
During treatment, skin disorders (severe blistering reactions) such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis may occur, which can be very serious or even life-threatening (see section 4). If subjective or objective symptoms of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis appear (progressive skin rash, often with blisters or ulcers on mucous membranes), amiodarone treatment should be discontinued immediately.
If the potassium level is low, it should be corrected before starting amiodarone treatment.
Amiodarone contains iodine and may interfere with the uptake of radioactive iodine. However, this does not affect the interpretation of thyroid function test results (free T4, free T3, and TSH).
ThyroidDue to the risk of thyroid dysfunction during amiodarone treatment, thyroid function tests should be performed before starting treatment.
These tests should be repeated regularly during treatment and for about a year after treatment is stopped, and patients should be monitored for symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
The following symptoms may indicate thyroid dysfunction:
Hypothyroidism:
Weight gain, sensitivity to cold, fatigue, extreme slow heart rate (bradycardia) exceeding the expected effects of Amiodarone Accord.
Hyperthyroidism:
Weight loss, fast heart rate (tachycardia), muscle tremors, nervousness, increased sweating, and heat intolerance, recurrence of arrhythmias or angina pectoris, heart failure.
Neuromuscular diseases
Amiodarone may cause peripheral nerve or muscle damage (peripheral neuropathies and/or myopathies). These symptoms usually resolve after a few months of stopping treatment.
However, in single cases, they may not be completely reversible.
Protect your skin from the sun
You should avoid direct sunlight during treatment with this medicine and for several months after stopping it. This also applies to UV radiation and sunbeds.
This is because the skin will be more sensitive to the sun, and not taking the following precautions may cause burning, stinging, or severe blisters:
- you should make sure to use a cream with a high sun protection factor,
- you should always wear a hat and clothing that covers your arms and legs.
Primary graft dysfunction (PGD) after heart transplantation
If the patient is on the waiting list for a heart transplant and is taking amiodarone, they have an increased risk of life-threatening complications (primary graft dysfunction), so the doctor may change the treatment before the transplant. In case of this complication, the transplanted heart stops working properly shortly after the heart transplant surgery, and in severe cases, it may be irreversible.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of amiodarone in children have not been established, so amiodarone is not recommended for these patients.
Amiodarone Accord and other medicines
This medicine may affect the action of other medicines; therefore, you should inform your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, including those available without a prescription. The doctor will decide which medicines should be discontinued or if the dosage should be changed.
Due to the long half-life of amiodarone, interactions with other medicines may also occur several months after stopping amiodarone treatment.
Medicines that can cause serious heart rhythm disorders of the torsades de pointes type.
Treatment in combination with the following medicines that cause torsades de pointes-type arrhythmias is contraindicated:
- medicines used to control irregular heart rhythm, such as quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide, sotalol, and bretylium;
- medicines other than antiarrhythmic medicines, such as vincamine (used to increase oxygen supply to the brain);
- medicines used for infections (such as erythromycin given by intravenous injection, cotrimoxazole, moxifloxacin, or pentamidine);
- certain antipsychotic medicines (medicines with a calming and anxiety-reducing effect), such as chlorpromazine, levomepromazine, thioridazine, fluphenazine, sulpiride, tiapride, pimozide, haloperidol, amisulpride, and sertindol;
- medicines for other mental disorders (such as antidepressants, e.g., doxepin, maprotiline, amitriptyline);
- medicines used for hay fever, rash, or other allergies called antihistamines, e.g., terfenadine, astemizole, mizolastine;
- medicines against malaria, such as quinine, mefloquine, chloroquine, halofantrine;
- MAO inhibitors (certain antidepressants).
Administration of amiodarone with medicines that prolong the QT interval (prolonging the heart rate) should be based on a careful assessment of the risk and benefit for each patient, as the risk of serious heart rhythm disorders of the torsades de pointes type may be increased. QT interval prolongation (ECG examination) should be monitored.
Fluoroquinolones: during amiodarone treatment, you should also avoid taking a certain type of antibiotic (fluoroquinolones).
Medicines that slow the heart rate or cause conduction or automatism disorders:
it is not recommended to treat in combination with beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers that slow the heart rate (diltiazem and verapamil).
It is also not recommended to treat in combination with the following medicines:
- Medicines that can cause low potassium levels:
- irritant laxatives, which can cause a decrease in potassium levels in the blood, thereby increasing the risk of torsades de pointes-type arrhythmias. Other types of laxatives should be used.
- particular caution is required when amiodarone is used in combination with diuretics that singly or in combination reduce potassium levels in the blood, systemic corticosteroids, tetracosactide (used in the diagnosis of adrenal problems and treatment of ulcerative colitis), and amphotericin B given by intravenous injection (antibiotic).
Particular caution is required when combining amiodarone with the following medicines. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage of other medicines by the doctor:
- oral anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin or phenprocoumon); amiodarone may enhance the effect of these medicines, increasing the risk of bleeding,
- digitalis glycosides, such as digoxin (used to treat heart failure),
- dabigatran (used to prevent blood clots),
- phenytoin (used in epilepsy),
- flecainide (used to treat arrhythmias),
- medicines metabolized by a specific enzyme system (cytochrome P450 3A4)
- cyclosporine (a medicine that prevents transplant rejection)
- fentanyl (a strong pain reliever)
- certain cholesterol-lowering medicines (certain statins, e.g., simvastatin, atorvastatin, lovastatin)
- other such medicines, e.g., tacrolimus and sirolimus (preventing transplant rejection), lidocaine (a local anesthetic), sildenafil (used to treat erectile dysfunction), midazolam and triazolam (sleeping pills), macrolide antibiotics (clarithromycin), ergotamine, dihydroergotamine (used in migraine), and colchicine (in the treatment of gout). Potentially severe complications have been observed after general anesthesia.
It is not recommended to use amiodarone and a sofosbuvir regimen at the same time, as it may lead to severe symptomatic bradycardia (life-threatening slow heart rate). If concurrent administration cannot be avoided, heart monitoring is recommended.
Amiodarone Accord with food, drink, and alcohol
While taking this medicine, you should not drink grapefruit juice, as it may increase the level of amiodarone in the blood.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
- The doctor will prescribe Amiodarone Accord only in exceptional cases when the expected benefits of treatment outweigh the potential risk during pregnancy. Amiodarone can be used during pregnancy only in life-threatening situations.
- The patient should not become pregnant for at least six months after stopping treatment to avoid exposing the child to amiodarone during early pregnancy.
- The patient should not receive amiodarone while breastfeeding. If the patient is receiving amiodarone while breastfeeding, breastfeeding should be discontinued, as amiodarone passes into breast milk in significant amounts and may reach effective concentrations in infants.
- After long-term treatment, testicular disorders may occur.
Driving and using machines
Amiodarone hydrochloride may affect your ability to drive and use machines. Treatment with this medicine requires regular medical check-ups. This medicine, even when used as intended, may alter reaction time to such an extent that it may impair your ability to actively participate in traffic, operate machinery, or work safely. This may occur especially when starting treatment, increasing the dose, changing the medicine, or in combination with alcohol.
Amiodarone Accord contains benzyl alcohol
This medicine contains 200 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 10 ml ampoule, which corresponds to 20 mg/ml. Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions. Patients with liver or kidney function disorders and pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor or pharmacist, as large amounts of benzyl alcohol may accumulate in the body and cause side effects (called "metabolic acidosis"). Benzyl alcohol is associated with the risk of severe side effects, including breathing problems (called "gasping syndrome") in small children.
3. How to use Amiodarone Accord
The medicine must be dilutedbefore administration.
Treatment will be started only under the supervision of a specialist doctor. In case of doubts, you should consult your doctor again.
Direct intravenous injection as a bolus is generally not recommended due to the risk of severe hypotension, cardiogenic shock; therefore, if possible, intravenous infusion is preferred. Direct intravenous injection should be limited to emergency situations.
Doctors or healthcare professionals must familiarize themselves with the "information for healthcare professionals" at the end of this leaflet.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of amiodarone in children have not been established, so amiodarone is not recommended for children.
Due to the content of benzyl alcohol, this medicine is not intended for use in premature infants, newborns, infants, and children under 3 years of age.
Elderly patients
As with all patients, it is important to use the minimum effective dose.
Amiodarone may slow the heart rate, which may be more pronounced in elderly patients. The doctor will carefully calculate the dose of amiodarone the patient should receive and will closely monitor the pulse and thyroid function.
Using a higher dose of Amiodarone Accord than recommended
The doctor will carefully calculate the dose of Amiodarone Accord the patient should receive. Therefore, it is unlikely that the doctor, nurse, or pharmacist will administer too much of this medicine to the patient. However, if the patient thinks they have received too much or too little Amiodarone Accord, they should tell their doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.
The following symptoms may occur: dizziness, fainting, vomiting, fatigue, or confusion.
Abnormal slow or fast heart rate. An overdose of amiodarone may damage the heart and liver.
Missing a dose of Amiodarone Accord
The doctor or nurse will receive instructions for administering this medicine. It is unlikely that the patient will miss a dose of the medicine. However, if the patient suspects that a dose of the medicine has been missed, they should inform their doctor or nurse.
Stopping treatment with Amiodarone Accord
It is essential to use Amiodarone Accord until the doctor decides to stop it.
If treatment with this medicine is stopped, irregular heartbeats may return. This may be dangerous.
If you have any further questions about using this medicine, you should ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following extremely rare side effect may be life-threatening in certain circumstances. Therefore, you should immediately inform your doctor if it occurs suddenly or with unexpected intensity:
Severe acute allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis): in this case, treatment with Amiodarone Accord should be discontinued immediately, and appropriate emergency treatment should be applied.
Side effects due to amiodarone use occur frequently, especially affecting the heart, lungs, and liver. Sometimes these symptoms are dose-dependent and resolve after dose reduction.
Other side effects
Observed side effects are presented according to their frequency of occurrence: very common (may occur in more than 1 in 10 people); common (may occur in up to 1 in 10 people); uncommon (may occur in up to 1 in 100 people); rare (may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 people); very rare (may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 people); frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
- Very rare:decreased platelet count (thrombocytopenia), anemia due to increased red blood cell destruction or blood formation disorders.
- Frequency not known:may occur with a higher than usual number of infections. This may be due to a decrease in the number of white blood cells (neutropenia). A significant decrease in the number of white blood cells, which increases the likelihood of infections (agranulocytosis).
Cardiac disorders
- Common:moderately slow heart rate (bradycardia), which changes depending on the dose administered.
- Uncommon:conduction disorders (sinoatrial block: heart block with conduction disturbance from the sinoatrial node to the atrium; atrioventricular block: disturbed conduction between the atria and ventricles). In single cases, cardiac arrest (asystole) has been observed (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions"). The onset or worsening of arrhythmias (changes in heart rhythm), which sometimes leads to cardiac arrest.
- Very rare:significantly slowed heart rate (bradycardia) or cessation of sinoatrial node activity, mainly in patients with sinoatrial dysfunction and/or over 65 years of age.
- Frequency not known:torsades de pointes-type arrhythmias (a specific type of arrhythmia); single cases of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter have been reported.
Endocrine disorders
- Common:the thyroid gland produces more thyroid hormone than the body needs (hyperthyroidism) or insufficient amounts of thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism). Severe hyperthyroidism (in single cases, fatal) has been reported.
- Very rare:malaise, confusion, nausea (feeling of needing to vomit), loss of appetite, irritability. This may be a condition known as "syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)".
Eye disorders
- Very common:microdeposits on the front surface of the cornea, which are usually limited to the area below the pupil and may cause vision disturbances (blurred vision, seeing colored halos around light sources). These usually resolve within 6-12 months after stopping the medicine.
- Very rare:optic neuritis, which can lead to blindness (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions").
Gastrointestinal disorders
- Very common:nausea, vomiting, taste disturbances at the start of treatment (during the loading dose), which resolve after dose reduction.
- Uncommon:abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, loss of appetite.
- Frequency not known:sudden pancreatitis (acute pancreatitis).
General disorders and administration site conditions
- Common:pain at the injection site may occur, red spots (erythema), swelling of the skin due to fluid accumulation, discoloration (necrosis), fluid leakage (exudation), fluid accumulation (infiltration), inflammation, hardening, phlebitis (vein inflammation), tissue inflammation, infection, changes in pigmentation.
- Uncommon:fatigue
Hepatobiliary disorders
- Very common:isolated and often moderate increase in aminotransferase activity (related to liver function) at the start of treatment. It may return to normal after dose reduction or even on its own.
- Common:acute liver function disorders with high aminotransferase activity in serum and/or jaundice (yellowing of the skin), including liver failure, which can be life-threatening.
- Very rare:chronic liver disease (in single cases, fatal), liver cirrhosis.
Immune system disorders
- Very rare:severe allergic reaction, which can be life-threatening (anaphylactic shock).
- Frequency not known:edema may also occur due to fluid accumulation under the skin and mucous membranes (Quincke's edema).
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
- Common:muscle weakness.
- Frequency not known:back pain.
Renal and urinary disorders
- Rare:transient renal function disorders.
Nervous system disorders
- Common:muscle tremors (extrapyramidal tremor), nightmares, sleep disturbances.
- Uncommon:peripheral nerve or muscle damage (peripheral sensory neuropathies and/or myopathies), usually reversible after stopping the medicine (see "Warnings and precautions"), dizziness, coordination problems, sensory disturbances (paresthesia).
- Very rare:mild increase in intracranial pressure, cerebellar ataxia, headache.
Psychiatric disorders
- Common:decreased sexual desire.
- Frequency not known:confusion (delirium), seeing, hearing, or feeling things that are not there (hallucinations).
Reproductive system and breast disorders
- Very rare:epididymitis, erectile dysfunction.
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders
- Common:due to the toxic effect of amiodarone on the lungs, pulmonary inflammation (atypical pulmonary inflammation as an expression of hypersensitivity reaction [pulmonary inflammation with hypersensitivity], alveolar or interstitial inflammation), fibrosis (scarring), pleuritis (pleural inflammation), or bronchiolitis (inflammatory disease of the bronchioles) (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions"). Single cases have been reported, which ended in death. Non-productive cough and shortness of breath are often the first signs of this pulmonary toxicity. Additionally, weight loss, fever, and weakness may occur.
- Very rare:usually observed shortly after surgery, severe respiratory complications (adult respiratory distress syndrome), sometimes fatal (possible interaction with high oxygen concentrations). Bronchospasm and/or shortness of breath (apnea) in cases of severe respiratory failure, mainly in patients with asthma. These usually resolve after stopping treatment.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
- Very common:increased sensitivity to light (phototoxicity) with an increased tendency to sunburn, which can lead to skin redness and rash.
- Common:itchy red rash (exanthema). Long-term treatment with amiodarone (after switching to oral therapy) may cause skin discoloration with a blue-violet to grayish color (pseudo-cyanosis), especially in areas exposed to sunlight. The discoloration will slowly resolve within 1-4 years after stopping the medicine.
- Very rare:sweating, skin redness after radiation therapy, inflammation of fat cells under the skin (erythema nodosum), rashes, inflammatory redness and peeling of the skin (exfoliative dermatitis), transient hair loss.
- Frequency not known:hives, skin irritation, and itching. Life-threatening skin reactions characterized by rash, blisters, peeling, and pain (toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) / Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), blistering exanthema, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Vascular disorders
- Common:low blood pressure (hypotension), usually moderate and transient. In case of overdose or too rapid injection, severe hypotension or shock may occur.
- Rare:vasculitis.
- Very rare:heat strokes.
Injury, poisoning, and procedural complications
- Frequency not known:life-threatening complication after heart transplantation (primary graft dysfunction), in which the transplanted heart stops working properly (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions").
Investigations
- Very rare:increased creatinine levels in the blood.
Other possible side effects
Rarely, allergic reactions to benzyl alcohol may occur.
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocides
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Amiodarone Accord
Medicines should be kept out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoule after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Do not store above 25°C. Store the ampoule in the outer packaging to protect from light.
After dilution, the chemical and physical stability of the solution has been demonstrated for 3 hours, 48 hours, and 15 minutes at concentrations of 1.2 mg/ml, 2.4 mg/ml, and 15 mg/ml at 20-25°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, the responsibility for the storage conditions and expiration date before use lies with the user.
Do not use this medicine if the container is damaged or if particles/crystals are visible.
For single use only. Any unused medicine should be disposed of.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Amiodarone Accord contains
- The active substance is amiodarone hydrochloride. Each ml of solution contains 30 mg of amiodarone hydrochloride. Each 10 ml ampoule contains 300 mg of amiodarone hydrochloride.
- The other ingredients are benzyl alcohol, polysorbate 80, and water for injections.
What Amiodarone Accord looks like and contents of the pack
Amiodarone Accord is a clear, colorless to light yellow solution in a colorless ampoule.
Amiodarone Accord is available in a pack containing 1 ampoule.
Marketing authorization holder
Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o.
Taśmowa Street 7
02-677 Warsaw
phone: +48 22 577 28 00
Manufacturer/Importer
Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o.
Lutomierska Street 50
95-200 Pabianice
Pharmadox Healthcare Limited
KW20A Kordin Industrial Park
Paola, PLA 3000
Malta
Laboratori Fundació Dau
C/, 12-14 Pol. Ind.
Zona Franca
08040 Barcelona
Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
| Member State | Medicinal product name |
| Austria | Amiodarone Accord 30 mg/ml Konzentrat zur Herstellung einer Injektions-/Infusionslösung |
| Czech Republic | Amiodarone Accord |
| Denmark | Amiodarone Accord |
| Finland | Amiodarone Accord |
| Spain | Amiodarona Accord 30 mg/ml concentrado para solución inyectable y para perfusión |
| Ireland | Amiodarone hydrochloride 30 mg/ml concentrate for solution for injection/infusion |
| Germany | Amiodaron Accord 30 mg/ml Konzentrat zur Herstellung einer Injektions-/Infusionslösung |
| Norway | Amiodarone Accord |
| Poland | Amiodaron Accord |
| Portugal | Amiodarona Accord |
| Romania | Amiodaronă Accord 30 mg/ml concentrat pentru soluție injectabilă / perfuzabilă |
| Sweden | Amiodarone Accord |
| Italy | Amiodarone Accord |
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Information intended for healthcare professionals only
Dosage
In the case of an attack or initial treatment, it is possible to administer the medicine by intravenous injection or infusion. Generally, intravenous injection is not recommended. If possible, intravenous infusion is recommended.
Intravenous infusion
Initial dose or in case of an attack
Usually, the recommended dose is 5 mg/kg body weight, administered by intravenous infusion, lasting from 20 minutes to 2 hours. The medicine should be administered in the form of a diluted solution in 250 ml of 5% dextrose solution.
The therapeutic effect appears within the first few minutes and then gradually weakens, so to prolong it, the medicine should be continued to be administered by maintenance infusion.
Maintenance dose
Up to 1200 mg (10-20 mg/kg body weight) in infusion in 250-500 ml of 5% dextrose solution per day; the infusion rate should be adjusted based on the clinical response.
Changing from intravenous to oral administration
Immediately after achieving the desired response, oral treatment should be started in parallel, usually administering the commonly used loading dose. Amiodarone Accord should be discontinued gradually.
Intravenous Injection (see "Special Warnings and Precautions for Use" in the SmPC)
In emergency situations, the drug can be administered, at the doctor's discretion, by slow intravenous injection in a dose of 150-300 mg (5 mg/kg body weight) in 10-20 ml of 5% dextrose, lasting at least 3 minutes. This should not be repeated for at least 15 minutes, even if the maximum dose was not administered during the first injection. Patients receiving amiodarone in this way should be closely monitored, e.g., in the intensive care unit.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the treatment of refractory ventricular fibrillation
The initial intravenous dose is 300 mg (or 5 mg/kg body weight) diluted in 20 ml of 5% dextrose, administered by rapid injection. If ventricular fibrillation does not stop, an additional dose of 150 mg intravenously (or 2.5 mg/kg body weight) may be considered.
Other drugs should not be mixed with amiodarone in the same syringe.
Other drugs should not be injected into the same venous access.
If treatment needs to be prolonged, it should be done in the form of intravenous infusion.
In the event of poisoning and/or severe symptoms, immediate treatment is necessary.
Neither amiodarone hydrochloride nor its metabolites can be removed by dialysis.
Method of Administration
Before intravenous administration, amiodarone must be dilutedaccording to the instructions given in section 4.2 of the Summary of Product Characteristics.
In the case of slow intravenous injections(only in emergency situations), amiodarone must befurther dilutedwith 10 or 20 ml of 5% dextrose, depending on the dose administered and the indication. For example: in the case of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, dilute the contents of one syringe (300 mg/10 ml) further with 20 ml of 5% dextrose (for further information, see sections 4.2 and 4.4 of the SmPC).
For single use only.
Only 5% dextrose solution should be used for infusion.
To avoid phlebitis, a central venous catheter should be inserted during continuous infusion.
Amiodarone Accord is administered only to initiate treatment, for no longer than one week.
Amiodarone is incompatible with saline solution.
Amiodarone may lead to the release of the softening agent DEHP (di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate) into the solution when using medical equipment containing DEHP.
To minimize exposure to DEHP, amiodarone should be administered in an infusion solution using DEHP-free sets.
The medicinal product should not be mixed with other medicinal products, except those mentioned in the package leaflet.
Instructions for Preparation and Administration of the Medicinal Product
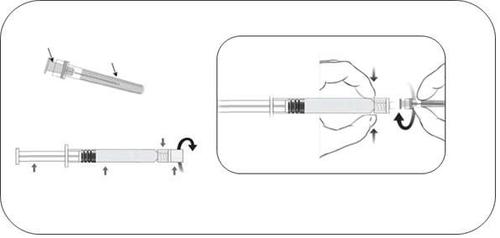
- The glass ampoule-syringe should be removed from the packaging and checked for damage.
- Solutions intended for parenteral administration should be inspected for particulate matter or discoloration before administration.
- The glass cap of the ampoule-syringe should be unscrewed by turning it counterclockwise (as shown in Figure 1).
- The needle should be attached to the ampoule-syringe by gently connecting the needle hub to the Luer Lock adapter and turning it a quarter turn to the right, until the needle is locked (as shown in Figure 2).
- The needle shield should be carefully removed by pulling it straight off.
- Dilute (see section 4.2 of the SmPC) with 5% dextrose solution according to the instructions for intravenous administration.
Before administration in intravenous infusion, Amiodarone Accord must be dilutedaccording to the instructions in 5% dextrose solution. One ampoule-syringe of Amiodarone Accord should be diluted according to the recommendations in 500 ml of 5% dextrose solution to obtain a concentration of 0.6 mg/ml of amiodarone hydrochloride.
Due to the stability of the solution, concentrations below 0.6 mg/ml should not be used, and other medicinal products should not be added to the infusion fluid.
Disposal
For single use only.
Any unused medicinal product or waste materials should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAccord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Laboratori Fundació Dau Pharmadox Healthcare Ltd.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Amiodaron AccordDosage form: Concentrate, 50 mg/mlActive substance: amiodaroneManufacturer: hameln rds s.r.o. HBM Pharma s.r.o.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 50 mg/mlActive substance: amiodaroneManufacturer: Krka, d.d., Novo mestoPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 50 mg/mlActive substance: amiodaronePrescription not required
Alternatives to Amiodaron Accord in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Amiodaron Accord in Ukraine
Alternative to Amiodaron Accord in Spain
Online doctors for Amiodaron Accord
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Amiodaron Accord – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










