TRANGOREX 150 mg / 3 ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use TRANGOREX 150 mg / 3 ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Trangorex 150 mg / 3 ml injectable solution
amiodarone hydrochloride
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Trangorex is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Trangorex
- How to use Trangorex
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Trangorex
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Trangorex is and what it is used for
Trangorex belongs to a group of medicines known as antiarrhythmic agents (used to control fast or irregular heart rhythm).
Trangorex is used to treat serious heart rhythm disorders when the patient does not respond to other antiarrhythmics or when alternative medications are not tolerated. It is administered in cases of:
- Tachyarrhythmias associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
- Prevention of the recurrence of atrial fibrillation and flutter.
- All types of paroxysmal tachyarrhythmias, including: supraventricular, nodal, and ventricular tachycardias, ventricular fibrillation.
The intravenous route will be used when a rapid response is necessary. It should be used in units with adequate means for cardiac monitoring and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
2. What you need to know before you use Trangorex
Do not use Trangorex
- If you are allergic to iodine, amiodarone, or any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have a low heart rate (sinus bradycardia) or suffer from other heart rhythm or conduction disorders (sinoatrial block, sinus node disease, severe atrioventricular conduction disorders), unless a pacemaker is implanted.
- If you have sick sinus syndrome and do not have a pacemaker. If you are experiencing cardiovascular collapse or severe arterial hypotension.
- If you have any thyroid-related disease.
- If you are pregnant, except in special circumstances or during breastfeeding (see "Pregnancy and breastfeeding").
- In combination with medications that may cause "torsades de pointes" (serious heart rhythm problems): see "Using Trangorex with other medicines".
If you have hypotension (low blood pressure), severe respiratory failure, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, or cardiac arrest, this medicine should not be administered by intravenous injection.
All the contraindications mentioned above do not apply when the doctor uses amiodarone for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (in a situation where the patient has suffered a cardiopulmonary arrest) in the treatment of ventricular fibrillation resistant to defibrillation.
Warnings and precautions
Amiodarone by intravenous injection should only be used in a specialized hospital setting and under constant control (electrocardiogram, blood pressure).
Intravenous administration (direct) should be limited to emergency situations when other therapeutic alternatives fail.
The decrease in heart rate may be more pronounced in patients over 65 years of age.
There are cases where new arrhythmias may occur or the treated arrhythmias may worsen. This usually happens when associated with other medications or with electrolyte disturbances (such as alterations in calcium levels in the blood). In these cases, the withdrawal of treatment with this medicine should be assessed.
Special caution should be taken in cases of hypotension, severe respiratory failure, severe heart failure, or decompensated cardiomyopathy.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Trangorex if you are currently taking a medicine that contains sofosbuvir for the treatment of hepatitis C, as it may cause a potentially fatal decrease in heart rate. Your doctor may consider alternative treatments. If treatment with amiodarone and sofosbuvir is needed, you may need additional cardiac monitoring.
Consult your doctor immediately if you are taking a medicine that contains sofosbuvir for the treatment of hepatitis C and during treatment you experience:
- slow or irregular heartbeats or heart rhythm problems;
- shortness of breath or worsening of existing shortness of breath;
- chest pain;
- dizziness;
- palpitations;
- fainting or feeling like you are about to faint.
During treatment, your doctor may indicate that tests be performed: chest X-ray (to rule out respiratory complications), determination of transaminases through blood tests (before starting treatment and regularly while treatment lasts, to check that your liver is functioning correctly), and blood potassium levels.
Consult your doctor if you experience vision changes: blurred vision, decreased vision, colored halos, feeling of fog. If any of these problems appear, a complete eye exam should be performed.
Anesthesia: before surgery, the anesthesiologist should be informed that you are being administered amiodarone.
During treatment, skin changes (severe blistering reactions) such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis may appear, which can be very serious or even fatal (see section 4). If symptoms or signs of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis (progressive skin rash often with blisters or mucosal lesions) appear, treatment with amiodarone should be interrupted immediately.
The safety and efficacy of amiodarone in children have not been established, so the administration of amiodarone in children is not recommended.
Recently, cases of liver toxicity have been reported after intravenous administration, which could be due to the solvent (polysorbate 80) rather than the medicine itself.
Before starting treatment with amiodarone, if blood potassium levels are low, they should be corrected.
If you are on a waiting list for a heart transplant, your doctor may change your treatment. This is because taking amiodarone before a heart transplant has been shown to increase the risk of a life-threatening complication (primary graft dysfunction) in which the transplanted heart fails to function correctly within the first 24 hours after surgery.
Using Trangorex with other medicines
This medicine may alter the response to other medicines; therefore, you should inform your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicine, even those purchased without a prescription. Your doctor will decide which medication to abandon or if the dose should be modified.
1- Medicines that may induce torsades de pointes(serious heart rhythm problems) or prolongation of the QT interval:
- Medicines that induce torsades de pointes
Concomitant treatment with medicines that may induce torsades de pointesis contraindicated:
- Medicines used to control irregular heart rhythm, such as antiarrhythmic medicines of Class Ia (quinidine, hydroquinidine, disopyramide), sotalol, bepridil.
- Non-antiarrhythmic medicines such as vincamine (used to increase oxygen in the brain), some neuroleptics (medicines that have a sedative effect and reduce anxiety, such as chlorpromazine, levomepromazine, thioridazine, trifluoperazine, haloperidol, amisulpride, sulpiride, tiapride, pimozide), cisapride (used to treat esophageal reflux), intravenous erythromycin (antibiotic), pentamidine (when this antibiotic is administered parenterally), as there is a higher risk of potentially fatal torsades de pointes.
- Medicines that prolong the QT interval
The administration of amiodarone with medicines that prolong the QT interval should be based on a careful evaluation of the risks and benefits for each patient, as the risk of torsades de pointesmay increase. QT interval prolongation should be monitored.
The use of a type of antibiotic (fluoroquinolones) should also be avoided during treatment with amiodarone.
2 - Medicines that reduce heart rate or produce automaticity or conduction disorders:
Treatment with the following medicines is not recommended:
- With other antiarrhythmics (to control irregular heart rhythm) or medicines that may cause arrhythmia (heart rhythm alteration, such as phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, terfenadine).
- Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers that decrease heart rate (verapamil, diltiazem).
- Sofosbuvir, used to treat hepatitis C.
3- Agents that may induce hypokalemia:
Concomitant treatment with the following medicines is not recommended:
- Stimulant laxatives that may induce a decrease in blood potassium levels and thus increase the risk of torsades de pointes.
Special caution should be taken when amiodarone is combined with the following medicines:
- Diuretics that decrease blood potassium levels alone or in combination, corticosteroids, tetracosactide (used to diagnose adrenal problems and to treat ulcerative colitis), intravenous amphotericin B (antibiotic).
- Oral anticoagulants: (acenocoumarol, warfarin, dabigatran) as they increase the risk of bleeding.
- Digitalis (used to treat heart failure), phenytoin (antiepileptic), flecainide (to treat heart rhythm problems), fentanyl (to treat pain), lidocaine (to treat pain), sildenafil (to treat erectile dysfunction), midazolam (muscle relaxant and antiepileptic), triazolam (to treat anxiety), dihydroergotamine (to treat migraines), ergotamine (to treat migraines), colchicine (to treat gout), as they may increase the concentration of these medicines in the blood.
- Cyclosporin, tacrolimus, and sirolimus (used to help prevent transplant rejection), as they may increase the effect of these medicines.
- Statins such as simvastatin, atorvastatin, and lovastatin (medicines used to lower high blood fat levels, mainly cholesterol and triglycerides), as they increase the risk of muscle toxicity (e.g., rhabdomyolysis, a disease characterized by muscle tissue breakdown).
General anesthesia
Potentially serious complications have been observed after combination with general anesthetics.
Amiodarone contains iodine and may interfere with the uptake of labeled iodine. However, thyroid function tests (free T3, free T4, and TSH) remain interpretable.
It is recommended to avoid consuming grapefruit juice during treatment with amiodarone, as amiodarone levels may increase.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
In case of pregnancy, Trangorex should not be administered, unless the benefits outweigh the risks, as it affects the fetus's thyroid gland. Inform your doctor if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant.
In case of breastfeeding, Trangorex should not be administered, as it passes into breast milk in significant amounts.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Trangorex contains benzyl alcohol
This medicine contains 60 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 3 ml ampoule, equivalent to 20 mg/ml.
Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions.
Benzyl alcohol has been linked to the risk of serious side effects, including respiratory problems ("gasping syndrome") in small children.
This medicine should not be used in newborns (up to 4 weeks of age) unless your doctor has recommended it.
This medicine should not be used for more than one week in children under 3 years of age unless your doctor or pharmacist has indicated it.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. This is because large amounts of benzyl alcohol can accumulate in your body and cause side effects (metabolic acidosis).
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have liver or kidney disease. This is because large amounts of benzyl alcohol can accumulate in your body and cause side effects (metabolic acidosis).
3. How to use Trangorex
Treatment will only be started under the supervision of a specialist doctor. In case of doubt, consult your doctor again.
Intravenous direct administration in bolus is generally discouraged due to hemodynamic risks (severe hypotension, cardiovascular collapse); therefore, whenever possible, intravenous perfusion is preferred. Intravenous direct administration should be limited to emergency situations.
Do not add any other product to the same syringe. Do not administer other preparations in the same line. If treatment needs to be prolonged, start a continuous infusion.
Doctors or healthcare professionals should consult the "INFORMATION FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS" section at the end of this leaflet.
In patients over 65 years of age, it is recommended to start with the lowest dose, taking into account the patient's cardiac, renal, and hepatic function, as well as any other disease or medication being taken.
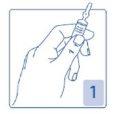
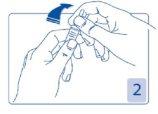
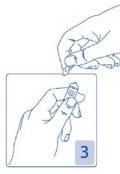
Opening the ampoule
|
|
|
Hold the ampoule firmly, with the colored point facing you (Figure 1).
Hold the head of the ampoule between your thumb and index finger (your thumb over the colored point); then press backwards (Figures 2 and 3).
Use in children and adolescents
Medicines administered intravenously that contain benzyl alcohol should be used with caution in children under 3 years of age (see also "Trangorex contains benzyl alcohol").
Data on safety and efficacy in children are limited. Your doctor will decide the appropriate dose.
Follow these instructions unless your doctor has given you different instructions.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have doubts.
If you use more Trangorex than you should
If you have received more medicine than you should, you will receive symptomatic treatment. Neither amiodarone nor its metabolites are eliminated through dialysis.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount taken.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
The adverse effects observed according to their frequency of presentation, very frequent (may affect more than 1 in 10 people); frequent (may affect up to 1 in 10 people); infrequent (may affect up to 1 in 100 people); rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people); very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people); frequency not known (cannot be estimated from available data), have been:
Of the blood and lymphatic system:
- Frequency not known: You may have more infections than usual. This may be due to a decrease in the number of white blood cells (neutropenia). Severe decrease in the number of white blood cells that makes infections more likely (agranulocytosis).
Cardiac:
- Frequent: Weak heart rhythm (bradycardia) of moderate severity, which varies depending on the administered dose.
- Very rare: Weak heart rhythm (bradycardia) of marked severity. In some cases, mainly in patients with sinus dysfunction and/or over 65 years, it requires the suppression of treatment. Onset or worsening of arrhythmia (change in heart rhythm), sometimes followed by cardiac arrest. These effects occur less frequently than with most other anti-arrhythmics and are usually observed with certain drug associations or electrolyte disorders. Alterations in the conduction of the heart's nervous impulse.
- Frequency not known: Torsades de pointes.
Endocrine:
- Very rare: Feeling of discomfort, confusion, or weakness, nausea (vomiting), loss of appetite, irritability. These could be inactive symptoms of a disease called "Syndrome of Inadequate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH)".
- Frequency not known: Hyperthyroidism (when the thyroid glands produce more thyroid hormone than the body needs).
Ocular:
- Very rare: Inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis) that can progress to blindness (see section 2, "Warnings and Precautions").
Gastrointestinal:
- Very rare: Nausea.
- Frequency not known: Sudden inflammation of the pancreas (acute pancreatitis).
General and at the administration site:
- Frequent: At the injection site, pain, red spots (erythema), swelling of the skin due to fluid accumulation (edema), blackening (necrosis), fluid leakage (extravasation), fluid accumulation (infiltration), inflammation, hardening (induration), vein inflammation (phlebitis, thrombophlebitis), cellulitis, infection, changes in pigmentation. This can be avoided with the placement of a central catheter.
Hepatobiliary:
- Very rare: Isolated and often moderate increase in transaminases (related to liver function) at the start of treatment. This may remit by reducing the dose or even spontaneously. Acute liver alterations with an increase in blood transaminases and/or yellowing of the skin (jaundice), which can be life-threatening.
The appearance of adverse reactions with amiodarone is frequent, particularly at the cardiac, pulmonary, and hepatic levels. On occasion, these manifestations are related to the dose and reverse after a dose reduction.
Immune system:
- Very rare: Severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening (anaphylactic shock).
- Frequency not known: Fluid accumulation under the skin (Quincke's edema) may also occur.
Muscular and skeletal:
- Frequency not known: Back pain.
Nervous system:
- Very rare: Increase in cranial pressure of a benign type, headache.
Psychiatric:
- Frequent: Decreased sexual desire.
- Frequency not known: State of confusion (delirium). Seeing, hearing, or feeling things that do not exist (hallucinations).
Respiratory:
- Very rare: Pneumonia or fibrosis (lung disease in which fibrous tissue forms), sometimes fatal (see section 2, "Warnings and Precautions"), severe respiratory complications. Contraction of the bronchial muscles (bronchospasm) and/or lack of breathing (apnea) in case of severe respiratory failure, mainly in asthmatic patients. These are generally reversible after treatment is finished.
Of the skin and subcutaneous tissue:
- Frequent: Itchy red rash (eczema).
- Very rare: Sweating.
- Frequency not known: Urticaria, characterized by the appearance of hives, irritation, and itching of the skin. Life-threatening skin reactions characterized by skin rash, blisters, peeling, and pain (Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)), Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), bullous dermatitis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Vascular:
- Frequent: Decrease in blood pressure, generally moderate and transient. In case of overdose or too rapid injection, severe hypotension or collapse may occur.
- Very rare: Hot flashes.
Traumatic injuries, poisonings, and complications of therapeutic procedures:
- Frequency not known: Life-threatening complication after heart transplant (primary graft dysfunction) in which the transplanted heart stops functioning correctly (see section 2, "Warnings and Precautions").
If you consider that any of the adverse effects you suffer from is serious or if you notice any other adverse effect not mentioned in this prospectus, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Adverse Effect Reporting:
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Conservation of Trangorex
Do not store at a temperature above 25 ºC.
Keep in the original packaging to protect it from light.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the packaging and on the ampoules after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be thrown away through the sewers or in the trash. Deposit the packaging and medicines that you no longer need in the SIGRE Point of the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines that you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Trangorex
- The active ingredient is amiodarone hydrochloride.
- The other components are: benzyl alcohol, polysorbate 80, and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
The injectable solution is a pale yellow liquid. It is presented in colorless glass ampoules. Each ampoule contains 3 ml of injectable solution.
Standard packaging: contains 6 ampoules.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
sanofi-aventis, S.A.
C/ Roselló i Porcel, 21
08016 Barcelona
Spain
Manufacturer:
Delpharm Dijon
6, boulevard de l’Europe
21800 Quétigny (France)
Or
Sanofi S.r.l.
Via Valcanello, 4
03012 Anagni (FR)
Italy
Date of the Last Revision of this Prospectus: January 2022
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS): http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
INFORMATION FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
This information is intended only for doctors or healthcare professionals.
See the "Warnings and Precautions" section.
Posology and Administration
Attack or Initial Treatment, two alternatives are possible:
Intravenous Infusion
- Initial or Attack Dose: The usual dose is 5 mg/kg of weight administered in 250 ml of 5% dextrose exclusively, administered over a period of 20 minutes to 2 hours. The infusion can be repeated 2 to 3 times in 24 hours. The infusion rate should be adjusted according to the clinical response.
- The action manifests from the first minutes and gradually decreases, so a maintenance infusion should be established.
- Maintenance Dose: 10 to 20 mg/kg of weight/24 hours (generally 600 to 800 mg/24 hours, limit 1,200 mg/24 hours) in 250 ml of 5% dextrose for several days. Take over the oral administration from the first day of infusion.
Intravenous Injection(see "Warnings and Precautions" section).
The dose is 5 mg/kg of weight. The duration of the injection should never be less than 3 minutes. Do not mix with other preparations in the same syringe.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the treatment of ventricular fibrillation resistant to defibrillation: The initial IV dose is 300 mg (or 5 mg/kg of weight) diluted in 20 ml of 5% dextrose and injected rapidly. A second IV dose of 150 mg (or 2.5 mg/kg of weight) should be considered if ventricular fibrillation persists.
Except in cardiopulmonary resuscitation, amiodarone should be injected over a time never less than 3 minutes and a second intravenous injection should not be administered before 15 minutes have passed after the first injection, even if only one ampoule has been administered (risk of irreversible collapse).
The use of medical equipment or products containing DEHP (di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate) type plastic material in the presence of amiodarone may cause the dilution of said material. In order to minimize patient exposure to DEHP, the final dilution of amiodarone for infusion should preferably be administered with materials that do not contain DEHP.
Do not add any other product to the same syringe. Do not administer other preparations in the same line. If treatment needs to be prolonged, start a continuous infusion.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to TRANGOREX 150 mg / 3 ml INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: TABLET, 200 mgActive substance: amiodaroneManufacturer: Aurovitas Spain, S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 200 mgActive substance: amiodaroneManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 400 mgActive substance: dronedaroneManufacturer: Aristo Pharma GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for TRANGOREX 150 mg / 3 ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about TRANGOREX 150 mg / 3 ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions