

Beriplex P/n 1000

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Beriplex P/n 1000

How to use Beriplex P/n 1000
Patient Information Leaflet
Beriplex P/N 1000
Powder and solvent for solution for injection
Human prothrombin complex
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again
- Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any further questions
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others
- This medicine may harm others, even if their symptoms are the same as yours
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What Beriplex P/N 1000 is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before using Beriplex P/N 1000
- 3. How to use Beriplex P/N 1000
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Beriplex P/N 1000
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Beriplex P/N 1000 is and what it is used for
What Beriplex P/N 1000 is
Beriplex P/N 1000 is available as a powder with a solvent provided. It is a white or slightly colored powder or a brittle, solid mass. The reconstituted solution is for intravenous injection.
Beriplex P/N 1000 is made from human plasma (the liquid part of the blood) and contains human clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X. Concentrates containing these clotting factors are called prothrombin complex products. Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X play an important role in the blood clotting process (coagulation). A deficiency of any of these clotting factors can cause the blood to clot more slowly than it should, increasing the risk of bleeding. Replacing clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X with Beriplex P/N 1000 will restore the blood clotting mechanism.
What Beriplex P/N 1000 is used for
Beriplex P/N 1000 is used to prevent and treat bleeding caused by acquired or congenital deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X, when a specific clotting factor product is not available.
2. Important information before using Beriplex P/N 1000
The following section contains information that you and your doctor should read before using Beriplex P/N 1000.
When not to use Beriplex P/N 1000:
if you are allergic to the active substances or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Tell your doctor if you are allergic to any medicines or foods.
if you have an increased risk of forming blood clots (patients at risk of disseminated intravascular coagulation)
if you have had an allergic reaction to heparin, which caused a decrease in platelet count (heparin-induced thrombocytopenia type II, HIT type II).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have such a condition.
Warnings and precautions
Discuss the use of Beriplex with your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment.
- In the case of acquired deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. This may be caused by taking medicines that block the action of vitamin K. Beriplex P/N 1000 should only be used when rapid correction of prothrombin complex factor levels is necessary, e.g., in the case of major bleeding or emergency surgery.
- In the case of congenital deficiency of any of the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, a specific clotting factor product should be used whenever possible.
- In the event of an allergic or anaphylactic reaction (a severe allergic reaction causing serious breathing difficulties or dizziness):
Beriplex P/N 1000 administration should be stopped immediately (e.g., discontinue injection).
- If there is an increased risk of blood clot formation in blood vessels (thrombosis), particularly in the following cases:
- in patients after a heart attack (with diagnosed coronary artery disease or myocardial infarction)
- in patients with liver disease
- in patients immediately before and after surgery
- in newborns
- in patients with an increased risk of forming blood clots (patients at risk of thromboembolic disease or disseminated intravascular coagulation, or with a deficiency of clotting inhibitors)
- If there is an increased risk of bleeding disorders due to increased consumption of platelets or clotting factors. Treatment with Beriplex P/N 1000 may be started after the underlying condition has been treated.
- Heparin-induced reduction in platelet count (heparin-induced thrombocytopenia type II, HIT type II). Heparin, a protein that dissolves blood clots, is a component of Beriplex. A significant decrease in platelet count may be associated with:
- formation of blood clots in the veins of the lower limbs,
- increased tendency to form blood clots,
- in some cases, a skin rash at the injection site,
- bruising, and
- the appearance of black stools. In such cases, the action of heparin may be impaired (heparin tolerance). If these symptoms occur, the administration of the medicine should be stopped immediately and a doctor should be consulted. In the future, do not take medicines containing heparin.
- A special form of kidney inflammation has been reported in patients with hemophilia B and inhibitors of factor IX who have a history of allergic reactions.
Your doctor should weigh the benefits of Beriplex P/N 1000 therapy against the risk of these complications.
Viral safety
When medicines are obtained from human blood or plasma, various methods are used to prevent the transmission of infectious agents to the patient. These include:
- proper selection of blood and plasma donors to exclude the possibility of transmitting infectious agents,
- testing of individual donors and plasma pools for the presence of viruses and other infections,
- inclusion of steps in the manufacturing process to inactivate or remove viruses.
Despite these precautions, when using medicines obtained from human blood or plasma, it is not possible to completely exclude the risk of transmitting infectious diseases due to the possibility of transmitting infectious agents. This also applies to unknown pathogens and other types of infections.
The methods used are considered effective against such enveloped viruses as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV, the virus that causes AIDS), hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus (viral hepatitis), and non-enveloped hepatitis A virus (viral hepatitis) and parvovirus B19.
Your doctor may recommend appropriate vaccination against hepatitis A and B if you regularly receive medicines obtained from human plasma.
It is strongly recommended that each administration of Beriplex P/N 1000 be recorded in the patient's medical record, including the name and batch number of the medicine, to document the batches used.
Other medicines and Beriplex P/N 1000
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
- Beriplex P/N 1000 may inhibit the action of vitamin K antagonists. Interactions with other medicines are not known.
- Beriplex P/N 1000 should not be mixed with other medicines, except for those listed in section 6.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
- If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or think you may be pregnant, or if you are planning to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
- In pregnant or breastfeeding women, Beriplex P/N 1000 should only be used when justified.
- There are no available data on the effect on fertility.
Driving and using machines
There are no appropriate studies documenting the effect of using the medicine on driving and using machines.
Beriplex P/N 1000 contains sodium
Beriplex P/N 1000 contains up to 343 mg of sodium (approximately 15 mmol) per 100 ml. This amount should be taken into account in patients on a controlled sodium diet.
3. How to use Beriplex P/N 1000
Treatment should be started under the supervision of a doctor experienced in the treatment of this type of disorder.
Dosage
The recommended dose of clotting factors and the duration of treatment depend on several factors, such as body weight, disease severity and progression, bleeding location and intensity, and the need to prevent bleeding during surgery or diagnostic procedures (see "Information intended for healthcare professionals only").
In case of any doubts about the use of the medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Overdose
During treatment, your doctor should regularly monitor your blood clotting parameters.
Administration of high doses of prothrombin complex concentrate has been associated with myocardial infarction, development of disseminated intravascular coagulation, and blood clot formation in blood vessels in patients at high risk of these disorders.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been commonlyobserved (in less than 1 in 10 patients):
- Risk of increased blood clot formation (see section 2)
- Headache
- Increased body temperature
The following side effects have been uncommonlyobserved (in less than 1 in 100 patients):
- Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions (see section 2)
The frequency of the following side effects is unknown(cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Severe bleeding due to excessive clotting
- Anaphylactic reactions, including shock (see section 2)
- Formation of circulating antibodies that inhibit one or more clotting factors
Children and adolescents
There are no data available on the use of Beriplex in children and adolescents.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocides of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocides, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, phone: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Beriplex P/N 1000
- Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use Beriplex P/N 1000 after the expiry date stated on the label and carton.
- Do not store above 25°C.
- Do not freeze.
- Store the vial in the outer carton to protect from light.
- Beriplex P/N 1000 does not contain preservatives, the reconstituted product should be used immediately.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Beriplex P/N 1000 contains
Beriplex P/N 1000 nominally contains the following amounts of human clotting factors per vial:
| Component name | Content after reconstitution (IU/ml) | Content in one vial of Beriplex P/N 1000 (IU) |
| Active substances | ||
| Human clotting factor II |
|
|
| Human clotting factor VII |
|
|
| Human clotting factor IX |
|
|
| Human clotting factor X |
|
|
| Other active substances | ||
| Protein C |
|
|
| Protein S |
|
|
The total protein content after reconstitution is 6 - 14 mg/ml in the solution.
The specific activity of factor IX is 2.5 IU per mg of total protein.
The activity of all clotting factors as well as proteins C and S (antigens) was tested according to current international WHO standards.
Dosage and administration Dosage
The following are only general dosage guidelines.
The dose and frequency of administration should be calculated individually for each patient. The intervals between doses should be adjusted according to the half-life of the individual clotting factors of the prothrombin complex. The individual dose is determined based on regular measurement of the activity of individual clotting factors in the blood or based on laboratory tests that generally determine the activity of the prothrombin complex (INR, Quick test) and by continuously monitoring the patient's clinical condition.
In the case of major surgical interventions, careful monitoring of substitution therapy is necessary (tests for individual clotting factors as well as general tests for prothrombin complex clotting factors).
- Bleeding and perioperative bleeding prophylaxis during treatment with vitamin K antagonists::
The dose of the medicine depends on the INR value measured before starting treatment and the INR value that the patient is to achieve. The INR value before treatment should be measured as close as possible to the time of administration of the medicine to allow calculation of the appropriate dose of the medicine. The following table indicates the doses (ml/kg body weight of reconstituted product and IU of factor IX/kg body weight) to achieve normalization of the INR (i.e., INR ≤ 1.3) at different initial INR values.
| Initial INR value | 2.0 – 3.9 | 4.0 – 6.0 | >6.0 |
| Approximate dose in ml/kg body weight | 1 | 1.4 | 2 |
| Approximate dose in IU (factor IX) per kilogram body weight | 25 | 35 | 50 |
Dosing is based on body weight, provided it does not exceed 100 kg. In patients with a body weight above 100 kg, the maximum single dose (IU of factor IX) should not exceed 2500 IU for an INR of 2.0-3.9, 3500 IU for an INR of 4.0-6.0, and 5000 IU for an INR > 6.0.
Normalization of hemostasis disorders caused by vitamin K antagonists is usually achieved within about 30 minutes after injection. Concurrent administration of vitamin K should be considered in patients receiving Beriplex for urgent reversal of vitamin K antagonist activity, as the effect of vitamin K is usually achieved within 4-6 hours.
Repeated dosing of Beriplex in patients requiring urgent reversal of vitamin K antagonist activity is not supported by clinical studies and is therefore not recommended.
These recommendations are based on clinical studies in a limited number of individuals.
It is necessary to monitor the INR value during treatment, as the efficacy and duration of action may vary between patients.
- Bleeding and perioperative bleeding prophylaxis in patients with congenital deficiency of any vitamin K-dependent clotting factor, when specific clotting factor product is not available
The calculation of the required dose of prothrombin complex concentrate is based on clinical studies:
- 1 IU of factor IX per kg body weight increases the activity of factor IX in the blood by 1.3% (0.013 IU/ml) relative to normal,
- 1 IU of factor VII per kg body weight increases the activity of factor VII in the blood by 1.7% relative to normal (0.017 IU/ml),
- 1 IU of factor II per kg body weight increases the activity of factor II in the blood by 1.9% relative to normal (0.019 IU/ml),
- 1 IU of factor X per kg body weight increases the activity of factor X in the blood by 1.9% relative to normal (0.019 IU/ml).
The dose of each clotting factor is expressed in international units (IU), in accordance with the applicable WHO standard for each clotting factor. The activity of a clotting factor in the blood is expressed as a percentage (relative to normal human blood) or in international units (in accordance with the international standard for the specific clotting factor in the blood).
One international unit (IU) of clotting factor activity is equal to the activity of that factor contained in 1 ml of normal human blood.
For example, the calculation of the required dose of factor X is based on the empirical finding that 1 IU of factor X per kg body weight increases the activity of factor X in the blood by 0.019 IU/ml.
The required dose is calculated using the following formula:
Required dose (IU) = body weight (kg) x desired increase in factor X activity (IU/ml) x 53,
where 53 (ml/kg) is the inverse of the estimated recovery value.
Note that these calculations are based on data from patients receiving vitamin K antagonists. Calculations based on data from healthy individuals would provide a lower required dose.
If the individual recovery value is known, it should be used for calculations.
Data on the product are available based on clinical studies conducted in healthy volunteers (N=15), in the reversal of vitamin K antagonist activity in the treatment of acute major bleeding or perioperative bleeding prophylaxis. (N=98, N=43)
Administration
General instructions
- The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent. After filtration and withdrawal of the reconstituted solution (see below), before administration, check that it does not contain any visible particles or discoloration. Do not use cloudy solutions or those containing sediment or particles.
- Reconstitution and withdrawal from the vial should be performed under aseptic conditions.
Reconstitution
Bring the solvent to room temperature.
Make sure the caps of the vials with the powder and solvent are removed, wipe the rubber stoppers with an aseptic fluid and let them dry before opening the Mix2Vial package.
1 |
|
2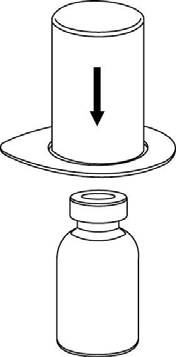 |
|
3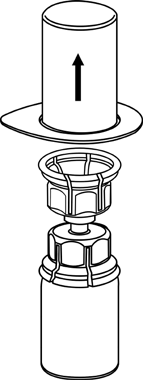 |
|
4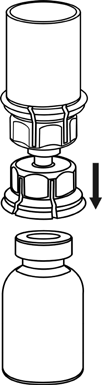 |
|
5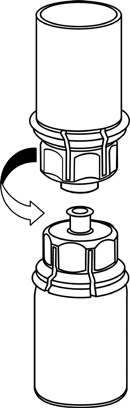 |
|
6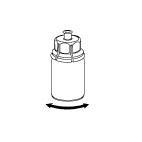 |
|
7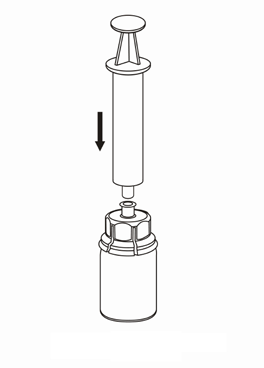 |
|
Withdrawal and administration
8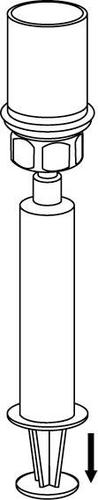 |
|
9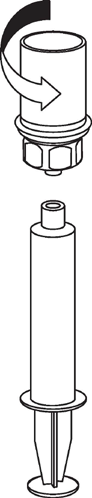 |
|
Be careful not to let blood enter the syringe filled with the product. This can cause a reaction of the clotting factors in the product and the formation of fibrin clots, which can be administered to the patient.
If it is necessary to administer more than one vial of Beriplex, it is possible to combine several vials for administration as a single infusion using a commercially available administration set.
The reconstituted solution of Beriplex should not be diluted.
The reconstituted solution should be administered intravenously (no faster than 8 ml/min*).
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Special warnings and precautions for use.
There are no available clinical data on the use of Beriplex P/N 1000 in the case of perinatal bleeding due to vitamin K deficiency in newborns.
_________________________________________________
*In clinical studies of Beriplex, patients weighing less than 70 kg had recommended dosing with a maximum infusion rate of 0.12 ml/kg/min (less than 8 ml/min).
Notes on platelet count monitoring:
Platelet count should be closely monitored.
Interactions with other medicines and other types of interactions
In the case of performing coagulation tests sensitive to the presence of heparin, in patients receiving high doses of prothrombin complex concentrate, the heparin dose contained in the product should be taken into account in the test results.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterCSL Behring GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Beriplex P/n 1000Dosage form: Powder, 250 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IX, II, VII and X in combinationPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 500 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IX, II, VII and X in combinationPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 500 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IX, II, VII and X in combinationPrescription required
Alternatives to Beriplex P/n 1000 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Beriplex P/n 1000 in Spain
Alternative to Beriplex P/n 1000 in Ukraine
Online doctors for Beriplex P/n 1000
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Beriplex P/n 1000 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














