
NORMOBUCAL 200 MG/ML ORAL SPRAY SOLUTION

How to use NORMOBUCAL 200 MG/ML ORAL SPRAY SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Leaflet: Information for the Patient
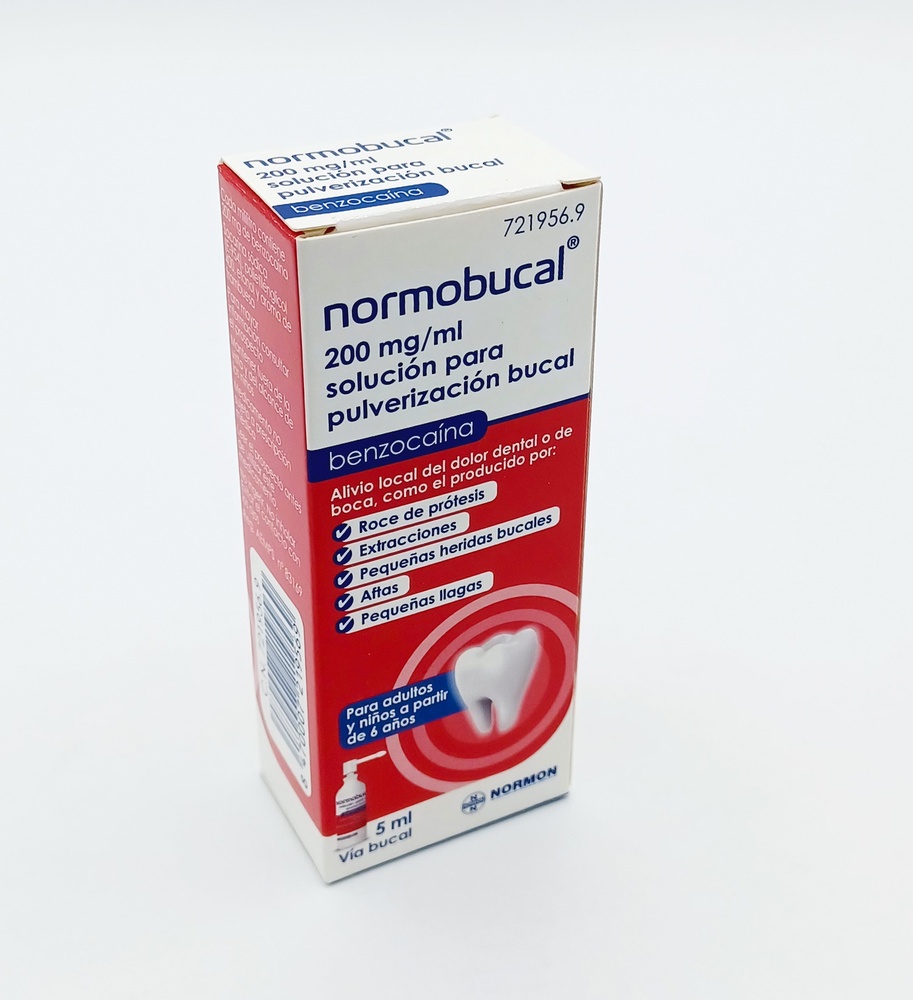
Normobucal 200 mg/ml Solution for Buccal Spraying
Benzocaine
Read the entire leaflet carefully before starting to use this medication, as it contains important information for you.
Follow the administration instructions of the medication contained in this leaflet or as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist exactly.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you need advice or more information, consult your pharmacist.
- If you experience side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
- You should consult a doctor if it worsens or does not improve after 2 days.
Contents of the Leaflet
- What Normobucal is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before starting to use Normobucal
- How to use Normobucal
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Normobucal
- Package contents and additional information
1. What Normobucal is and what it is used for
It is a topical anesthetic that acts by suppressing pain when applied externally to the area of the mouth to be treated.
It is indicated for the local relief of dental or mouth pain, such as that produced by the rubbing of prostheses, extractions, small oral wounds, canker sores, and small ulcers in adults and children from 6 years old.
You should consult a doctor if it worsens or does not improve after 2 days of treatment.
2. What you need to know before starting to use Normobucal
Do not use Normobucal
If you are allergic to benzocaine, other local anesthetics derived from p-aminobenzoic acid, or any of the components of this medication (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Normobucal.
- If you do not tolerate other local anesthetics like p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), parabens, or paraphenylenediamine (a component of hair dye).
- If you have any severe or extensive injury in the mouth.
- Do not take doses higher than recommended in section 3 (How to take Normobucal).
- If you have asthma, bronchitis, or emphysema.
- Stop taking the medication and consult your doctor immediately if you notice: headache, dizziness, shallow breathing, nausea, fatigue, or tachycardia.
- Elderly or debilitated patients should consult their doctor before taking this medication, as they are more sensitive to its possible adverse reactions.
- Do not ingest, do not inhale.
- Avoid contact and/or spraying in the eyes.
- Do not eat or drink while the numbness of the mouth persists, due to the risk of biting the tongue or the buccal mucosa and choking.
- In people over 65 years old and in debilitated patients, the risk of developing methemoglobinemia is increased.
- Small children (especially those under 2 years old) also have a higher risk of developing methemoglobinemia.
If the symptoms worsen or persist after 2 days of treatment, consult your doctor.
Children
The use of this medication is not indicated in children under 6 years old, as its efficacy and safety have not been established in this age group.
Use of Normobucal with other medications
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or may need to take any other medication.
This medication may interact with:
- Sulfonamides (medication to treat infections): should not be used at the same time as benzocaine, as it may decrease the antibacterial effect of sulfonamides.
- Medications containing hyaluronidase: should not be used at the same time as benzocaine, as it may increase the adverse effects of benzocaine.
- Medications containing cholinesterase, used to treat diseases such as Alzheimer's, myasthenia gravis, or glaucoma, as the metabolism of benzocaine may be inhibited when used at the same time.
- Other local anesthetics. There may be cross-sensitivity reaction, including anaphylaxis (unusual or exaggerated allergic reaction), between benzocaine and other local anesthetics of the ester type, sulfonamides, thiadiazoles, para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), aminobenzoic acid, aminosalicylic acid, and mepivacaine.
- In people sensitive to benzocaine, hair dyes of the paraphenylenediamine type may cause severe contact dermatitis.
- Pancreatic puncture test (diagnostic test): Benzocaine should not be used 72 hours before the pancreatic puncture test with bentiromide, as there is a possibility of interference with the test result.
Use of Normobucal with food and beverages
Do not use this medication before meals or before drinking (see warnings and precautions section).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
Benzocaine should not be used during pregnancy.
It is unknown whether benzocaine is excreted in breast milk, so breastfeeding women should not use this medication.
Use in people over 65 years old
People over 65 years old and debilitated patients may be more sensitive to the adverse effects of benzocaine, so they should consult their doctor.
Driving and using machines
Normobucal does not affect driving or using machines.
Normobucal contains ethanol
This medication contains 47% ethanol (alcohol), which corresponds to 38.8 mg per spray.
3. How to use Normobucal
Follow the administration instructions of the medication contained in this leaflet or as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist exactly. In case of doubt, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
This medication is for administration in the mouth. Do not ingest.
Each spray is equivalent to approximately 20 mg of benzocaine.
The recommended dose is:
Adults, adolescents, and children from 6 years old
Apply one spray to the area to be anesthetized, or soak a cotton swab and apply it to the area for a few minutes. Apply a maximum of 3 or 4 times a day.
In children (from 6 to less than 12 years old), the administration of this medication should only be done under adult supervision. The dose is the same as in the previous case.
Debilitated and elderly patients
The dose should be reduced, as elderly and debilitated patients may be more sensitive to the systemic toxicity of benzocaine. Apply to the area to be anesthetized up to 2 or 3 times a day.
Open the bottle and place the applicator nozzle on the valve. Press the sprayer for half a second, directing the applicator nozzle towards the area to be anesthetized, or soak a cotton swab with several sprays and apply it to the area for several minutes. Wash your hands after each application.
Do not apply this medication more than 3 or 4 times a day.
If it worsens or if the pain persists after 2 days of treatment, consult your doctor.
If you use more Normobucal than you should
There are no known cases of overdose.
The signs of overdose may be: bluish discoloration of the skin, slurred speech, numbness, staggering gait, blurred or double vision, dizziness, excitement, or convulsions, ringing in the ears, increased sweating. It may also decrease blood pressure.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor immediately or go to a medical center or call the Toxicology Information Service (phone 91 562 04 20), indicating the medication and the amount ingested.
If you have any other doubts about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone experiences them.
During the period of use of benzocaine, the following side effects have occurred, whose frequency could not be established with precision:
Hives, edema, anaphylactoid reaction (contact dermatitis). Cross-reactions with other local anesthetics of the ester type. Photosensitivity, bad taste in the mouth, dehydration of the mucous membranes, and difficulty swallowing.
Burning sensation in the mouth
Methemoglobinemia, whose symptoms are: headache, dizziness, shallow breathing, nausea, fatigue, or tachycardia. Methemoglobinemia is mainly due to prolonged use and also in cases of overdose. The risk of developing methemoglobinemia is increased in people with asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema, as well as in people over 65 years old and small children (especially under 2 years old), and in people with congenital defects, including glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, hemoglobin M disease, ADH-methemoglobin reductase deficiency, and pyruvate kinase deficiency.
Prolonged contact of benzocaine with the mucous membranes can cause dehydration of the epithelium and hardening of the mucous membranes.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any type of side effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible side effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medications: www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Normobucal
This medication does not require special storage conditions.
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date shown on the box after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medications should not be thrown away through the drains or in the trash. Deposit the containers and medications you no longer need in the SIGRE point of the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the containers and medications you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and additional information
Composition of Normobucal
- The active ingredient is benzocaine, each milliliter contains 200 mg of benzocaine.
- The other components (excipients) are: sodium saccharin (E-954), polyethylene glycol 400, 96º ethanol, and raspberry flavor.
Appearance of the product and package contents
Normobucal is a clear, colorless, or light yellow solution.
It is presented in aluminum bottles with 5 ml or 60 ml of solution for buccal spraying, the package contains the bottle with cap, an applicator nozzle with sprayer, and a leaflet.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
LABORATORIOS NORMON, S.A.
Ronda de Valdecarrizo, 6 – 28760 Tres Cantos – Madrid (Spain)
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:May 2018
Detailed and updated information on this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to NORMOBUCAL 200 MG/ML ORAL SPRAY SOLUTIONDosage form: TOPICAL ORAL PRODUCT, 5% benzocaineActive substance: benzocaineManufacturer: Laboratorios Vinas S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: GEL/PASTE/ORAL LIQUID, 100 mlActive substance: benzocaineManufacturer: Laboratorios Clarben S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: TOPICAL ORAL PRODUCT, 20% benzocaineActive substance: benzocaineManufacturer: Laboratorios Clarben S.A.Prescription not required
Online doctors for NORMOBUCAL 200 MG/ML ORAL SPRAY SOLUTION
Discuss questions about NORMOBUCAL 200 MG/ML ORAL SPRAY SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















