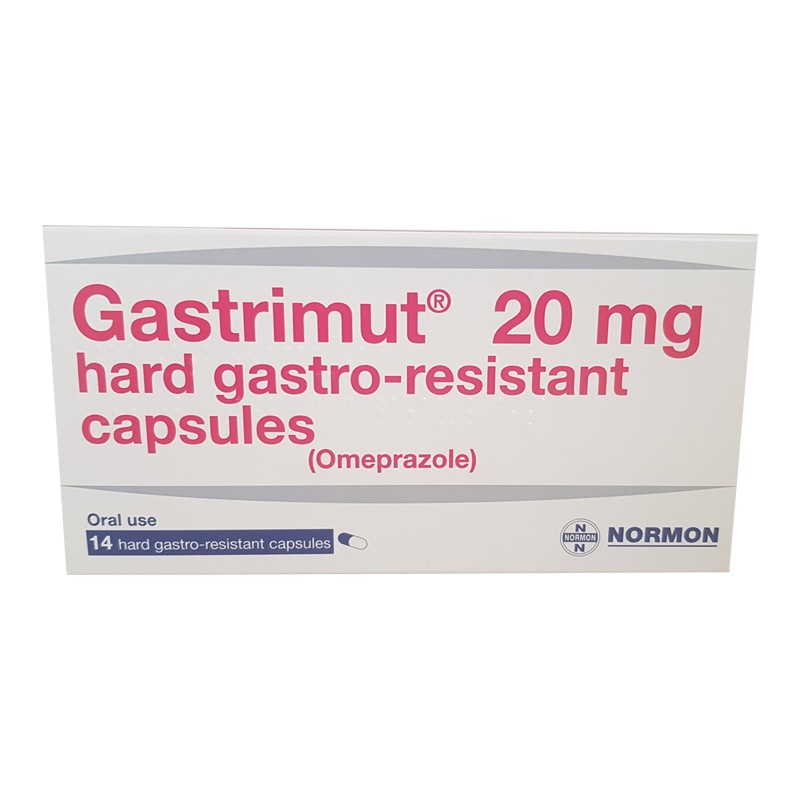
GASTRIMUT 20 mg CAPSULES

How to use GASTRIMUT 20 mg CAPSULES
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Gastrimut 20mg hard gastro-resistant capsules
Omeprazole
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you, do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Contents of the pack:
- What Gastrimut is and what it is used for
- Before you take Gastrimut
- How to take Gastrimut
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Gastrimut
- Further information
1. What Gastrimut is and what it is used for
Gastrimut contains the active substance omeprazole. It belongs to a group of medicines called “proton pump inhibitors”. These medicines work by reducing the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
Gastrimut is used to treat the following conditions:
In adults:
- “Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease” (GORD). In this condition, acid from the stomach passes into the gullet (the tube that connects the throat to the stomach), causing pain, inflammation and heartburn.
- Ulcers in the upper part of the intestine (duodenal ulcer) or stomach (gastric ulcer).
- Ulcers caused by a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. If you have this condition, your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection and allow the ulcer to heal.
- Ulcers caused by medicines called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Gastrimut may also be used to prevent ulcers if you are taking NSAIDs.
- Too much acid in the stomach caused by a tumour in the pancreas (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome).
In children:
Children over 1 year of age and = 10 kg
- “Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease” (GORD). In this condition, acid from the stomach passes into the gullet (the tube that connects the throat to the stomach), causing pain, inflammation and heartburn. In children, the symptoms of the disease can include reflux of stomach contents into the mouth (regurgitation), vomiting and insufficient weight gain.
Children over 4 years of age and adolescents
- Ulcers caused by a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. If your child has this condition, your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection and allow the ulcer to heal.
2. Before you take Gastrimut
Do not take Gastrimut
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to omeprazole or any of the other ingredients of Gastrimut if you are allergic to medicines that contain proton pump inhibitors (e.g. pantoprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, esomeprazole).
- if you are taking a medicine that contains nelfinavir (used to treat HIV infection).
If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Gastrimut.
Take special care with Gastrimut
Gastrimut may hide the symptoms of other diseases. Therefore, if you experience any of the following before starting or during treatment with Gastrimut, consult your doctor immediately:
- You lose a lot of weight without reason and have trouble swallowing.
- You have stomach pain or indigestion.
- You start vomiting food or vomiting blood.
- Your stools are black (blood-stained).
- If you have severe or persistent diarrhoea, as omeprazole has been associated with a slight increase in infectious diarrhoea.
- You have severe liver problems.
- if you have ever had a skin reaction after treatment with a medicine similar to Gastrimut to reduce stomach acid.
If you get a rash, especially in areas of the skin exposed to the sun, consult your doctor as soon as possible, as it may be necessary to interrupt treatment with Gastrimut. Remember to mention any other symptoms you may notice, such as joint pain.
If you take Gastrimut for a long period (more than 1 year), your doctor will probably perform regular check-ups. You should inform your doctor of any new or unusual symptoms or circumstances whenever you visit your doctor.
Using other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription. Gastrimut may affect the action of some medicines and some medicines may affect Gastrimut.
Do not take Gastrimut if you are taking a medicine that contains nelfinavir(used to treat HIV infection).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Ketoconazole, itraconazole or voriconazole (used to treat fungal infections)
- Digoxin (used to treat heart problems)
- Diazepam (used to treat anxiety, relax muscles or in epilepsy)
- Phenytoin (used in epilepsy). If you are taking phenytoin, your doctor will need to monitor you when you start or stop treatment with Gastrimut.
- Medicines used to prevent blood clots, such as warfarin or other vitamin K antagonists. Your doctor will need to monitor you when you start or stop treatment with Gastrimut.
- Rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis)
- Atazanavir (used to treat HIV infection)
- Tacrolimus (in cases of organ transplantation)
- St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) (used to treat mild depression)
- Cilostazol (used to treat intermittent claudication)
- Saquinavir (used to treat HIV infection)
- Clopidogrel (used to prevent blood clots (thrombi))
If your doctor has also prescribed the antibiotics amoxicillin and clarithromycin for you to treat ulcers caused by Helicobacter pyloriinfection, it is very important that you inform your doctor of any other medicines you are taking.
Warnings and precautions
Before taking this medicine, tell your doctor if:
- A specific blood test (Chromogranin A) is scheduled.
When taking omeprazole, kidney inflammation may occur. The signs and symptoms may include decreased urine output or blood in the urine and/or hypersensitivity reactions such as fever, rash and joint stiffness. You should inform your doctor of these signs.
Taking Gastrimut with food and drinks
You can take your capsules with food or on an empty stomach.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Before taking Gastrimut, tell your doctor if you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant. Your doctor will decide if you can take Gastrimut during this time.
Your doctor will decide if you can take Gastrimut if you are breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Gastrimut is unlikely to affect your ability to drive or use tools or machines. However, side effects such as dizziness and visual disturbances (see section 4) may occur. If this happens, do not drive or use machines.
Gastrimut containslactose, sucrose, glucose and sodium.
This medicine contains lactose, sucrose and glucose. If your doctor has told you that you have an intolerance to some sugars, consult your doctor before taking this medicine.
This medicine contains less than 23 mg of sodium (1mmol) per capsule; this is, essentially “sodium-free”
3. How to take Gastrimut
Always take Gastrimut exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Your doctor will tell you how many capsules to take and for how long. This will depend on your condition and age.
The usual doses are as follows.
Adults:
Treatment of symptoms of GORD, such as heartburn and acid regurgitation:
- If your doctor confirms that you have mild damage to the oesophagus, the normal dose is 20 mg once a day for 4-8 weeks. Your doctor may prescribe a dose of 40 mg for another 8 weeks if the oesophagus has not yet healed.
- The normal dose once the oesophagus has healed is 10 mg once a day.
- If you do not have damage to the oesophagus, the normal dose is 10 mg once a day.
Treatment of duodenal ulcers:
- The normal dose is 20 mg once a day for 2 weeks. Your doctor may prescribe the same dose for another 2 weeks if the ulcer has not yet healed.
- If the ulcer does not heal completely, the dose may be increased to 40 mg once a day for 4 weeks.
Treatment of gastric ulcers:
- The normal dose is 20 mg once a day for 4 weeks. Your doctor may prescribe the same dose for another 4 weeks if the ulcer has not yet healed.
- If the ulcer does not heal completely, the dose may be increased to 40 mg once a day for 8 weeks.
Preventionof recurrence of stomach and duodenal ulcers:
- The normal dose is 10 mg or 20 mg once a day. Your doctor may increase the dose to 40 mg once a day.
Treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers caused by NSAIDs:
- The normal dose is 20 mg once a day for 4-8 weeks.
Prevention of stomach and duodenal ulcersduring NSAID therapy:
- The normal dose is 20 mg once a day.
Treatment of ulcers caused byHelicobacter pyloriinfectionand prevention of recurrence:
- The normal dose is 20 mg of Gastrimut twice a day for one week.
- Your doctor will also tell you to take two antibiotics, amoxicillin and clarithromycin.
Treatment of excess acid in the stomach caused by a tumour in the pancreas (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome):
- The usual dose is 60 mg per day.
- Your doctor will adjust the dose according to your needs and decide how long you need to take the medicine.
Children:
Treatment of symptoms of GORD, such as heartburn and acid regurgitation:
- Children over 1 year of age who weigh more than 10 kg can take omeprazole. The dose for children is based on body weight and your doctor will decide the correct dose.
Treatment of ulcers caused byHelicobacter pyloriinfectionand prevention of recurrence:
- Children over 4 years of age can take omeprazole. The dose for children is based on body weight and your doctor will decide the correct dose.
- Your doctor will also prescribe two antibiotics, amoxicillin and clarithromycin, for your child.
How to take this medicine
- It is recommended to take the capsules in the morning.
- You can take your capsules with food or on an empty stomach.
- Swallow the capsules whole with half a glass of water. Do not chew or crush the capsules, as they contain coated granules that prevent the medicine from being broken down by the acid in the stomach. It is important not to damage the granules.
What to do if you or your child have trouble swallowing the capsules
- If you or your child have trouble swallowing the capsules:
- Open the capsules and swallow the contents directly with half a glass of water or pour the contents into a glass of still water, acidic fruit juice (e.g. apple, orange or pineapple) or apple sauce.
- Always shake the mixture well before drinking it (the mixture will not be clear). Then drink the mixture immediately or within 30 minutes.
- To make sure you have taken all the medicine, fill the glass with water, rinse it well and drink the water. The solid parts contain the medicine; do not chew or crush them.
If you take more Gastrimut than you should
If you have taken more Gastrimut than prescribed by your doctor, talk to your doctor or pharmacist immediately. You can also call the Toxicology Information Service, telephone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount taken.
If you forget to take Gastrimut
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, Gastrimut can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
If you notice any of the following rare but serious adverse effects, stop taking Gastrimut and consult your doctor immediately:
- Sudden whistling when breathing (sudden wheezing), swelling of the lips, tongue, and throat or body, skin rash, fainting, or difficulty swallowing (severe allergic reaction).
- Redness of the skin with blistering or peeling. Intense blisters and bleeding may also appear on the lips, eyes, mouth, nose, and genitals. This could be "Stevens-Johnson syndrome" or "toxic epidermal necrolysis".
- Yellowing of the skin, dark urine, and fatigue, which can be symptoms of liver problems.
Adverse effects can occur with certain frequencies, which are defined as follows:
Very frequent: | affect more than 1 patient in 10 |
Frequent: | affect 1 to 10 patients in 100 |
Infrequent: | affect 1 to 10 patients in 1,000 |
Rare: | affect 1 to 10 patients in 10,000 |
Very rare: | affect less than 1 patient in 10,000 |
Unknown frequency: | cannot be estimated from available data |
Other adverse effects are:
Frequent Adverse Effects
- Headache.
- Effects on the stomach or intestine: diarrhea, stomach pain, constipation, and gas (flatulence).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Benign polyps in the stomach.
Infrequent Adverse Effects
- Swelling of the feet and ankles.
- Sleep disorders (insomnia).
- Dizziness, tingling sensation, drowsiness.
- Feeling that everything is spinning (vertigo).
- Alterations in blood tests that check liver function.
- Skin rash, hives, and itching.
- Feeling of general discomfort and lack of energy.
Rare Adverse Effects
- Blood problems, such as decreased white blood cells or platelets. This can cause weakness or bruising and increase the likelihood of infections.
- Allergic reactions, sometimes very intense, including swelling of the lips, tongue, and throat, fever, and wheezing.
- Low sodium levels in the blood. This can cause weakness, vomiting, and cramps.
- Agitation, confusion, or depression.
- Taste disorders.
- Visual problems, such as blurred vision.
- Sudden feeling of difficult breathing (bronchospasm).
- Dry mouth.
- Inflammation of the inside of the mouth.
- Infection called "candidiasis" that can affect the intestine and is caused by a fungus.
- Liver problems, such as jaundice, which can cause yellowing of the skin, dark urine, and fatigue.
- Hair loss (alopecia).
- Skin rash with exposure to sunlight.
- Joint pain (arthralgias) or muscle pain (myalgias).
- Severe kidney problems (interstitial nephritis).
- Increased sweating.
Very Rare Adverse Effects
- Blood count alterations, such as agranulocytosis (lack of white blood cells).
- Aggression.
- Seeing, feeling, or hearing things that do not exist (hallucinations).
- Severe liver problems that cause liver failure and brain inflammation.
- Sudden appearance of an intense rash, blistering, or peeling of the skin. This can be accompanied by high fever and joint pain (erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
- Muscle weakness.
- Increased breast size in males.
In very rare cases, Gastrimut can affect the white blood cells in the blood and cause immunodeficiency. If you have an infection with symptoms such as fever with a very deteriorated general condition or fever with symptoms of local infection, such as neck, throat, or mouth pain, or difficulty urinating, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible to perform a blood test and rule out a lack of white blood cells (agranulocytosis). It is essential that you provide information about the medication you are taking at that time.
Adverse Effects of Unknown Frequency
If you are taking Gastrimut 20 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules for more than three months, it is possible that magnesium levels in the blood may decrease. Low magnesium levels can cause fatigue, muscle contractions, disorientation, convulsions, dizziness, and increased heart rate. If you have any of these symptoms, go to the doctor immediately. Low magnesium levels can also produce a decrease in potassium and calcium levels in the blood. Your doctor may decide to perform periodic blood tests to monitor magnesium levels.
Skin rash, possibly with joint pain.
If you are taking proton pump inhibitors like Gastrimut 20 mg hard gastro-resistant capsules, especially for a period of more than one year, you may have a slightly increased risk of hip, wrist, and spine fractures. Inform your doctor if you have osteoporosis or if you are taking corticosteroids (which can increase the risk of osteoporosis).
Do not worry about this list of possible adverse effects. You may not experience any of them. If you consider that any of the adverse effects you are suffering from is serious or if you notice any adverse effect not mentioned in this prospectus, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
5. Conservation of Gastrimut
- Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
- Do not use Gastrimut after the expiration date that appears on the packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Store below 30°C
Keep the blister pack in the original packaging to protect it from moisture.
- Medicines should not be thrown down the drain or into the trash. Deposit the packaging and unused medicines in the SIGRE point of the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and unused medicines. This will help protect the environment.
6. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Composition of Gastrimut
- The active ingredient is omeprazole. Gastrimut capsules contain 20 mg of omeprazole.
The other components (excipients) are: sucrose; cornstarch; hypromellose phthalate, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hypromellose), lactose, glucose, hydroxypropylcellulose, lauryl sulfate, diethyl phthalate, and sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate.
The gelatin capsule is composed of: gelatin, erythrosine (E-127), carmine indigo (E-132), and titanium dioxide (E-171).
Appearance of the Product and Packaging Content
The Gastrimut 20 mg capsules are formed by a body and a cap of white and red color.
Package sizes: blisters of 14, 28, 56, and 500 capsules.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
LABORATORIOS NORMON, S.A.
Ronda de Valdecarrizo, 6 – 28760 Tres Cantos – Madrid (SPAIN)
This prospectus was revised in: March 2023
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price1.28 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to GASTRIMUT 20 mg CAPSULESDosage form: CAPSULE, 20 mgActive substance: omeprazoleManufacturer: Arafarma Group S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 40 mgActive substance: omeprazoleManufacturer: Arafarma Group S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 20 mgActive substance: omeprazoleManufacturer: Especialidades Farmaceuticas Centrum S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for GASTRIMUT 20 mg CAPSULES
Discuss questions about GASTRIMUT 20 mg CAPSULES, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions