
EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g CREAM

How to use EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g CREAM
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g cream
lidocaine/prilocaine
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only, and you should not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is EMLA and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use EMLA
- How to use EMLA
- Possible side effects
- Storing EMLA
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is EMLA and what is it used for
EMLA contains two active substances called lidocaine and prilocaine. They belong to a group of medicines called local anaesthetics.
EMLA works by numbing the surface of the skin for a short time. It is applied to the skin before certain medical procedures. It helps to stop the pain on the skin; however, you may still feel sensations such as pressure and touch.
Adults, adolescents and children
It can be used to numb the skin before:
- Needle procedures (e.g. if you are going to have an injection or a blood test).
- Minor skin surgeries.
Adults and adolescents
It can also be used:
- To numb the genitals before:
- Having an injection.
- Medical procedures such as removal of warts.
The use of EMLA on the genitals should be supervised by a doctor or nurse.
Adults
It can also be used to numb the skin before:
- Cleaning or removing damaged skin from leg ulcers.
2. What you need to know before you use EMLA
Do not use EMLA
- if you are allergic to lidocaine or prilocaine, or other similar local anaesthetics or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use EMLA
- if you or your child have a rare inherited blood disease called “glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency”.
- if you or your child have a condition where the levels of a pigment in the blood are altered, called “methaemoglobinaemia”.
- do not use EMLA on areas with broken skin, cuts, abrasions or open wounds, except for leg ulcers. If any of these problems occur, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using the cream.
- if you or your child have a skin condition with itching called “atopic dermatitis”, a shorter application time may be sufficient. Application times of more than 30 minutes may increase the risk of local skin reactions (see also section 4 “Possible side effects”).
- if you are taking medicines for heart rhythm problems (antiarrhythmic medicines of class III, such as amiodarone). In this case, your doctor will monitor your heart function.
Due to the potentially greater absorption into the skin that has just been shaved, it is important to follow the recommended dose, skin area and application time.
Avoid getting EMLA in your eyes, as it may cause irritation and chemical burns to the eyes. If it accidentally gets into your eye, rinse it well with warm water or saline solution (sodium chloride solution). Be careful not to put anything in the eye until feeling returns.
Children should be carefully watched when using EMLA on any part of their body to avoid getting EMLA into their eyes.
EMLA should not be applied on a broken eardrum.
When using EMLA before being vaccinated with live vaccines (e.g. tuberculosis vaccine), revisit your doctor or nurse after the required follow-up period for the vaccination result.
Children and adolescents
In infants and newborns less than 3 months old, “methaemoglobinaemia”, a temporary and clinically unimportant increase in the levels of a pigment in the blood, is often seen up to 12 hours after application of EMLA.
Clinical studies could not confirm the efficacy of EMLA when blood is taken from the heel of newborns or to provide adequate pain relief during circumcision.
EMLA should not be applied to the genital mucosa (e.g. in the vagina) of children (under 12 years) because there are not enough data on the absorption of the active substances.
EMLA should not be used in children under 12 months of age who are also being treated with other medicines that affect the levels of the blood pigment “methaemoglobin” (e.g. sulphonamides, see also section 2 “Using EMLA with other medicines”).
EMLA should not be used in premature newborns.
Using EMLA with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription and herbal medicines. This is because EMLA may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect the way EMLA works.
In particular, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you or your child have recently taken or are taking any of the following medicines:
- Medicines used to treat infections called “sulphonamides” and nitrofurantoin.
- Medicines used to treat epilepsy, called phenytoin and phenobarbital.
- Other local anaesthetics.
- Medicines for heart rhythm problems, such as amiodarone.
- Cimetidine or beta-blockers, which may increase the levels of lidocaine in the blood. This interaction is not clinically significant in short-term treatment with EMLA at the recommended doses.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Occasional use of EMLA during pregnancy is unlikely to have any adverse effects on the foetus.
The active substances of EMLA (lidocaine and prilocaine) are excreted in breast milk. However, the amount is so small that it is generally not a risk for the child.
Animal studies have shown that there are no changes in male or female fertility.
Driving and using machines
EMLA has no effect on the ability to drive and use machines, or the effect is negligible, when used at the recommended doses.
EMLA contains macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate
This medicine may cause skin reactions because it contains macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate.
3. How to use EMLA
Follow exactly the instructions for administration of this medicine given by your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. If you are unsure, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse again.
Using EMLA
- The place where you apply the cream, the amount you use and how long you leave it on will depend on what it is used for.
- Your doctor, pharmacist or nurse will apply the cream or show you how to do it yourself.
- When using EMLA on the genitals, a doctor or nurse should supervise its use.
Do not use EMLA on the following areas:
- Cuts, abrasions or open wounds, except for leg ulcers.
- Areas with broken skin or eczema.
- On or near the eyes.
- Inside the nose, ear or mouth.
- On the anus.
- On the genitals of children.
People who frequently apply or remove the cream should take care to avoid contact to prevent the development of hypersensitivity.
The protective membrane of the tube is broken by pressing the cap against it.
Using on the skin before small procedures (such as needle procedures or minor skin procedures):
- Apply a thick layer of cream to the skin. Your doctor, pharmacist or nurse will tell you where to apply it.
- Cover the cream with a dressing [plastic film]. This is removed just before the procedure starts. If you apply the cream yourself, make sure your doctor, pharmacist or nurse provides you with the dressings.
- The usual dose for adults and adolescents over 12 years is 2 g (grams).
- In adults and adolescents over 12 years, apply the cream at least 60 minutes before the procedure (unless the cream is to be used on the genitals). However, do not apply it more than 5 hours before.
- In children, the amount of EMLA used and the application time depends on their age. Your doctor, nurse or pharmacist will tell you how much to use and when to apply it.
When applying the cream yourself, it is very important to follow the following instructions:
- Squeeze the tube to apply the required amount of cream to the skin where the procedure will be performed (e.g. where the needle will be inserted). A 3.5 cm line of cream from the 30 g tube is equivalent to 1 g of cream. Do not spread the cream.
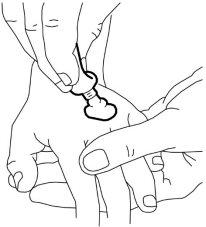
- Peel off the paper from the “central cut” of the non-adhesive side of the dressing (leaving a paper frame).
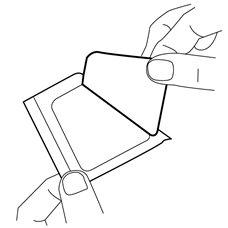
- Remove the cover from the adhesive side of the dressing.
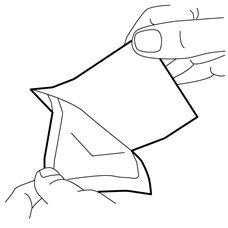
- Place the dressing carefully over the cream. Do not spread the cream under the dressing.
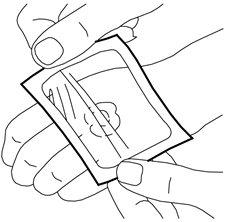
- Remove the paper backing. Smooth the edges of the dressing carefully. Then leave it on for at least 60 minutes if the skin is undamaged. The cream should not be left on for more than 60 minutes in children under 3 months or more than 30 minutes in children with atopic dermatitis. If the cream is used on the genitals or on ulcers, shorter application times can be used as described below.
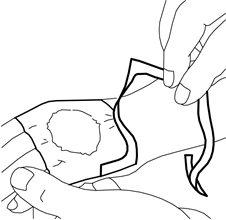
- Your doctor or nurse will remove the dressing and remove the cream just before carrying out the medical procedure (e.g. just before inserting the needle).
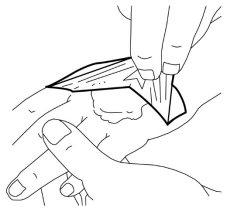
Using on large areas of freshly shaved skin before outpatient procedures (such as hair removal techniques):
The usual dose is 1 g of cream per 10 cm² (10 square centimetres) of skin area, applied under a dressing for 1 to 5 hours. EMLA should not be used on a shaved skin area larger than 600 cm² (600 square centimetres, e.g. 30 cm by 20 cm). The maximum dose is 60 g.
Using on the skin before hospital procedures (such as skin grafts) that require deeper skin anaesthesia:
- EMLA can be used in this way in adults and adolescents over 12 years.
- The usual dose is 1.5 g to 2 g of cream per 10 cm² (10 square centimetres) of skin area.
- The cream is applied under an occlusive dressing for 2 to 5 hours.
Using on the skin to remove wart-like lesions called “molluscum”
- EMLA can be used in children and adolescents with a skin condition called “atopic dermatitis”.
- The usual dose depends on the child’s age and is used for 30 to 60 minutes (30 minutes if the patient has atopic dermatitis). Your doctor, nurse or pharmacist will tell you how much cream to apply.
Using on the skin of the genitals before injecting local anaesthetics
- EMLA can only be used in this way in adults and adolescents over 12 years.
- The usual dose is 1 g of cream (1 g to 2 g on the female genital skin) per 10 cm² (10 square centimetres) of skin area.
- The cream is applied under an occlusive dressing. This is left on for 15 minutes on male genital skin and for 60 minutes on female genital skin.
Using on the genitals before minor skin surgery (removal of warts)
- EMLA can only be used in this way in adults and adolescents over 12 years.
- The usual dose is 5 g to 10 g of cream for 10 minutes. No occlusive dressing is used. The medical procedure should be started immediately.
Using on leg ulcers before cleaning or removing damaged skin
- The usual dose is 1 g to 2 g per 10 cm² (10 square centimetres) of skin area, up to a maximum of 10 g.
- The cream is applied under an occlusive dressing, e.g. a transparent plastic film. This is left on for 30 to 60 minutes before cleaning the ulcer. Remove the cream with a cotton swab and start cleaning without delay.
- EMLA can be used before cleaning leg ulcers up to 15 times over a period of 1-2 months.
- The EMLA tube is for single use when used on leg ulcers: the tube with any remaining contents should be discarded each time after treating a patient.
If you use more EMLA than you should
If you use more EMLA than your doctor, pharmacist or nurse has told you, contact them immediately, even if you do not have any symptoms.
The following are symptoms if you use too much EMLA. These symptoms are unlikely to occur if the recommendations for use of EMLA are followed.
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded.
- Numbness or tingling around the mouth and tongue.
- Altered taste.
- Blurred vision.
- Ringing in the ears.
- There is also a risk of “acute methaemoglobinaemia” (a problem with the levels of a pigment in the blood). This risk is higher when taking certain medicines at the same time. If this happens, the skin turns a bluish-grey colour due to lack of oxygen.
In severe cases of overdose, symptoms can include fits, low blood pressure, slow breathing, stopping breathing and changes in heart rhythm. These effects can be life-threatening.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, contact the Toxicology Information Service. Telephone 91 562 04 20.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Contact your doctor or pharmacist if any of the following adverse effects cause you discomfort or do not seem to disappear. Inform your doctor of anything else that makes you feel unwell while using EMLA.
A mild reaction (pallor or redness of the skin, slight swelling, initial burning or itching) may appear in the area where EMLA is applied. These are normal reactions to the cream and anesthetics and will disappear shortly without the need for any action.
If you experience any unpleasant or unusual effect while using EMLA, stop using it and consult your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible.
Frequent(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Local transient skin reactions (pallor, redness, swelling) in the application area during treatment on the skin, genital mucosa, or leg ulcers.
- A mild initial sensation of burning, itching, or heat in the application area during treatment on the genital mucosa or leg ulcers.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- A mild initial sensation of burning, itching, or heat in the treated area during treatment on the skin.
- Numbness (tingling) in the application area during treatment on the genital mucosa.
- Skin irritation in the application area during treatment of leg ulcers.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Allergic reactions that, in rare cases, can lead to anaphylactic shock (skin rash, swelling, fever, difficulty breathing, and fainting) during treatment on the skin, genital mucosa, or leg ulcers.
- Methemoglobinemia (blood disorder) during treatment of the skin.
- Minor pinpoint bleeding in the treated area (particularly in children with eczema after long periods of application), during treatment on the skin.
- Eye irritation if EMLA accidentally comes into contact with the eyes during treatment on the skin.
Frequency Not Known(cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Chemical burns to the eyes if EMLA accidentally comes into contact with them during treatment.
Other Adverse Effects in Children
Methemoglobinemia, a blood disorder that is usually observed more frequently in newborns and infants from 0 to 12 months, often associated with overdose.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es/. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of EMLA
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the carton and tube after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not freeze.
Keep the tube tightly closed.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packaging and any unused medicines in the SIGRE collection point at your pharmacy. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicines. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of EMLA
- The active ingredients are: lidocaine and prilocaine.
- 1 g of cream contains 25 mg of lidocaine and 25 mg of prilocaine.
- The other ingredients are carbomers, macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate, sodium hydroxide, and purified water.
Appearance of EMLA and Package Contents
Homogeneous white cream.
It is presented in an aluminum tube with a polypropylene cap equipped with a piercing device.
EMLA is available in packages of:
1 tube containing 5 g of cream
1 tube containing 5 g of cream + 2 dressings
1 tube containing 5 g of cream + 3 dressings
3 tubes containing 5 g of cream + 8 dressings
5 tubes containing 5 g of cream
5 tubes containing 5 g of cream + 10 dressings
5 tubes containing 5 g of cream + 12 dressings
1 tube containing 30 g of cream
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Aspen Pharma Trading Limited
3016 Lake Drive,
Citywest Business Campus,
Dublin 24, Ireland
Tel: +34 952 010 137
Manufacturer:
Recipharm Karlskoga AB
Björkbornsvägen 5
S-69133 – Karlskoga
Sweden
O
Aspen Bad Oldesloe GmbH,
32-36 Industriestrasse,
23843 Bad Oldesloe,
Germany
Local Representative:
Aspen Pharmacare España S.L.
Avenida Diagonal, 512,
Planta Interior 1, Oficina 4,
Barcelona, 08006, Spain
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria | Emla 5% - Cream |
Belgium | Emla 25mg/25mg cream |
Cyprus | Emla Cream 5% |
Finland | EMLA |
France | EMLA 5 POUR CENT, cream |
Greece | EMLA |
Iceland | Emla |
Ireland | EMLA 5% w/w Cream |
Italy | EMLA |
Luxembourg | Emla 25mg/25mg cream |
Malta | EMLA 5% w/w Cream |
Norway | Emla |
Poland | EMLA |
Spain | EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g cream |
Sweden | EMLA |
Netherlands | Emla |
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet:July 2024
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price10.02 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g CREAMDosage form: CREAM, 25 mg/g + 25 mg/gActive substance: combinationsManufacturer: Glenmark Arzneimittel GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: CREAM, 25 mg/g + 25 mg/gActive substance: combinationsManufacturer: Galenicum Derma S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: CREAM, Lidocaine 25 mg/g + Prilocaine 25 mg/gActive substance: combinationsManufacturer: Mesoestetic Pharma Group S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g CREAM
Discuss questions about EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g CREAM, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















