
DIFLUCAN 40 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION POWDER


How to use DIFLUCAN 40 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION POWDER
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Diflucan 10 mg/ml Powder for Oral Suspension
Diflucan 40 mg/ml Powder for Oral Suspension
fluconazole
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information:
- What is Diflucan and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you take Diflucan
- How to take Diflucan
- Possible side effects
- Storing Diflucan
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Diflucan and what is it used for
Diflucan is one of a group of medicines called “antifungals”. The active substance is fluconazole.
Diflucan is used to treat infections caused by fungi, and it can also be used to prevent fungal infections from occurring. The most common cause of fungal infections is a yeast called Candida.
Adults
Your doctor may prescribe this medicine for you to treat the following types of fungal infections:
- Cryptococcal meningitis – a fungal infection in the brain.
- Coccidioidomycosis – a disease of the bronchopulmonary system.
- Candidainfections located in the bloodstream, in body organs (e.g. heart, lungs) or in the urinary tract.
- Mucosal candidiasis – an infection that affects the lining of the mouth, throat, or associated with dental prostheses.
- Genital candidiasis – an infection of the vagina or penis.
- Skin infections – e.g. athlete's foot, ringworm, jock itch, nail infection.
They may also prescribe Diflucan for you to:
- prevent cryptococcal meningitis from coming back.
- prevent Candidamucosal infections from coming back.
- reduce the repeated occurrence of Candidavaginal infections.
- prevent the spread of Candidainfections (if your immune system is weak and not working properly).
Children and adolescents (0 to 17 years)
Your doctor may prescribe this medicine for you to treat the following types of fungal infections:
- Mucosal candidiasis – an infection that affects the lining of the mouth or throat.
- Candidainfections located in the bloodstream, in body organs (e.g. heart, lungs) or in the urinary tract.
- Cryptococcal meningitis – a fungal infection in the brain.
They may also prescribe Diflucan for you to:
- prevent the spread of Candidainfections (if your immune system is weak and not working properly).
prevent cryptococcal meningitis from coming back.
2. What you need to know before you take Diflucan
Do not take Diflucan
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to fluconazole, to other medicines you have taken to treat fungal infections, or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). The symptoms can include itching, redness of the skin, or difficulty breathing.
- if you are taking astemizole, terfenadine (antihistamine medicines for treating allergies).
- if you are taking cisapride (used for stomach upset).
- if you are taking pimozide (used for treating mental illness).
- if you are taking quinidine (used for treating heart arrhythmias).
- if you are taking erythromycin (an antibiotic for treating infections).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you start taking Diflucan
- if you have liver or kidney problems.
- if you have a heart condition, including problems with your heart rhythm.
- if you have abnormal levels of potassium, calcium, or magnesium in your blood.
- if you experience severe skin reactions (itching, redness of the skin, or difficulty breathing).
- if you experience signs of “adrenal insufficiency”, in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough of certain hormones, such as cortisol (chronic or prolonged fatigue, muscle weakness, loss of appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain).
- if you have ever had a severe skin rash or peeling of the skin, blisters, and/or sores in the mouth after taking Diflucan.
- Severe skin reactions, including drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), have been reported in relation to treatment with Diflucan. Stop taking Diflucan and seek immediate medical attention if you notice any of the symptoms related to these severe skin reactions described in section 4.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if the fungal infection does not improve. You may need an alternative antifungal treatment.
Taking Diflucan with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Tell your doctor immediatelyif you are taking astemizole, terfenadine (an antihistamine for treating allergies), cisapride (used for stomach upset), pimozide (used for treating mental illness), quinidine (used for treating heart arrhythmias), or erythromycin (an antibiotic for treating infections), as these medicines should not be taken with Diflucan (see section: “Do not take Diflucan”).
There are some medicines that can interact with Diflucan. Make sure your doctor knows if you are taking any of the following medicines, as your dose may need to be adjusted or you may need to be monitored to check that the medicines are still working:
- Rifampicin or rifabutin (antibiotics for infections).
- Alfentanil, fentanyl (used as anesthetics).
- Abrocitinib (used to treat atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema).
- Amitriptyline, nortriptyline (used as antidepressants).
- Amphotericin B, voriconazole (antifungals).
- Medicines that make the blood less viscous, to prevent the formation of clots (warfarin or similar medicines).
- Benzodiazepines (midazolam, triazolam, or similar medicines) used to help you sleep or for anxiety.
- Carbamazepine, phenytoin (used to treat seizures).
- Nifedipine, isradipine, amlodipine, verapamil, felodipine, and losartan (for high blood pressure).
- Olaparib (used to treat ovarian cancer).
- Ciclosporin, everolimus, sirolimus, or tacrolimus (to prevent transplant rejection).
- Cyclophosphamide, vinca alkaloids (vincristine, vinblastine, or similar medicines) used to treat cancer.
- Halofantrine (used to treat malaria).
- Statins (atorvastatin, simvastatin, and fluvastatin or similar medicines) used to lower high cholesterol levels.
- Methadone (used for pain relief).
- Celecoxib, flurbiprofen, naproxen, ibuprofen, lornoxicam, meloxicam, diclofenac (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs - NSAIDs).
- Oral contraceptives.
- Prednisone (steroid).
- Zidovudine, also known as AZT; saquinavir (used in patients infected with HIV).
- Medicines for diabetes, such as chlorpropamide, glibenclamide, glipizide, or tolbutamide.
- Theophylline (used to control asthma).
- Tofacitinib (used to treat rheumatoid arthritis).
- Tolvaptan (used to treat hyponatremia [low sodium levels in the blood] or to slow down the worsening of kidney function).
- Vitamin A (nutritional supplement).
- Ivacaftor (alone or in combination with medicines used to treat cystic fibrosis).
- Amiodarone (used to treat irregular heartbeats [arrhythmias]).
- Hydrochlorothiazide (diuretic).
- Ibrutinib (used to treat blood cancer).
- Lurasidone (used to treat schizophrenia).
Taking Diflucan with food and drinks
You can take the medicine with or without food.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
If you are planning to become pregnant, it is recommended that you wait one week after a single dose of fluconazole before becoming pregnant.
For longer treatment cycles with fluconazole, consult your doctor about the need to use adequate contraceptive methods during treatment, which should be continued for one week after the last dose.
Do not take Diflucan if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to become pregnant, unless your doctor has told you to. If you become pregnant while taking this medicine or in the week following the last dose, talk to your doctor.
Fluconazole taken during the first or second trimester of pregnancy may increase the risk of miscarriage. Fluconazole during the first trimester may increase the risk of a baby being born with congenital anomalies affecting the heart, bones, and/or muscles.
There have been reports of babies born with congenital anomalies affecting the skull, ears, and bones of the thigh and elbow in women treated for three months or more with high doses (400-800 mg daily) of fluconazole for coccidioidomycosis. The relationship between fluconazole and these cases is unclear.
You can continue breastfeeding after taking a single dose of 150 mg of Diflucan. You should not continue breastfeeding if you are taking repeated doses of Diflucan.
Driving and using machines
When you are going to drive or use machines, you should bear in mind that occasionally dizziness or seizures may occur.
Diflucan oral suspension contains sucrose (sugar), sodium benzoate, and sodium (salt)
If your doctor has told you that you have an intolerance to some sugars, consult them before taking this medicine.
Patients with diabetes mellitus should note that this medicine contains 5.5 g or more of sucrose per 10 ml.
It may damage teeth if used for more than 2 weeks.
The 60 ml bottle contains 83 mg of sodium benzoate per bottle, which is equivalent to 2.38 mg/ml.
Sodium benzoate may increase the risk of jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) in newborns (up to 4 weeks of age).
Once reconstituted, 1 ml of Diflucan 10 mg/ml oral suspension contains 1.13 mg of sodium per ml. This is equivalent to 4.5% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
Once reconstituted, a dose of 20 ml (the maximum recommended dose) of Diflucan 40 mg/ml oral suspension contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg); this is, essentially “sodium-free”.
3. How to Take Diflucan
Follow your doctor's instructions for taking this medication exactly. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
It is best to take your medications at the same time every day.
The following are the recommended doses of this medication for different types of infections:
Adults
Condition | Dose |
To treat cryptococcal meningitis | 400 mg on the first day and then 200 mg to 400 mg once a day for 6 to 8 weeks or longer if necessary. The dose may be increased to 800 mg in some cases. |
To prevent the recurrence of cryptococcal meningitis | 200 mg once a day until your doctor tells you to stop. |
To treat coccidioidomycosis | 200 mg to 400 mg once a day for 11 months to 24 months or longer if necessary. The dose may be increased to 800 mg in some cases. |
To treat internal fungal infections caused by Candida | 800 mg on the first day and then 400 mg once a day until your doctor tells you to stop. |
To treat mucosal infections that affect the lining of the mouth, throat, or are associated with dental prostheses. | 200 mg to 400 mg on the first day and then 100 mg to 200 mg once a day until your doctor tells you to stop. |
To treat mucosal candidiasis - the dose depends on the location of the infection | 50 mg to 400 mg once a day for 7 to 30 days until your doctor tells you to stop. |
To prevent the recurrence of mucosal infections that affect the lining of the mouth and throat | 100 mg to 200 mg once a day, or 200 mg 3 times a week, while the risk of developing an infection continues. |
To treat genital candidiasis | 150 mg in a single dose. |
To reduce the recurrence of vaginal candidiasis | 150 mg every 3 days for a total of 3 doses (days 1, 4, and 7) and then once a week, while the risk of developing an infection continues. |
To treat fungal infections of the skin or nails | Depending on the location of the infection, 50 mg once a day, 150 mg once a week, 300 to 400 mg once a week for 1 to 4 weeks (for athlete's foot, up to 6 weeks may be necessary, and for nail infections, treatment should continue until a healthy nail grows). |
To prevent the transmission of a Candidainfection (if your immune system is weak and not functioning properly) | 200 mg to 400 mg once a day while the risk of developing an infection continues. |
Adolescents 12 to 17 years of age
Follow the dose indicated by your doctor (either the adult or pediatric dose).
Children up to 11 years of age
The maximum daily dose for children is 400 mg per day.
The dose will be based on the child's weight in kilograms.
Condition | Daily dose |
Mucosal candidiasis and throat infections caused by Candida- the dose and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and its location. | 3 mg per kg of body weight once a day (on the first day, 6 mg per kg of body weight may be given). |
Cryptococcal meningitis or internal fungal infections caused by Candida | 6 mg to 12 mg per kg of body weight once a day. |
To prevent the recurrence of cryptococcal meningitis | 6 mg per kg of body weight once a day. |
To prevent the child from contracting a Candidainfection (if their immune system is not functioning properly) | 3 mg to 12 mg per kg of body weight once a day. |
Use in children from 0 to 4 weeks of age
Use in children from 3 to 4 weeks of age:
- The same dose as described in the table, but administered once every 2 days. The maximum dose is 12 mg per kg of body weight every 48 hours.
Use in children under 2 weeks of age:
- The same dose as described in the table, but administered once every 3 days. The maximum dose is 12 mg per kg of body weight every 72 hours.
Elderly patients
The usual adult dose, unless you have kidney problems.
Patients with kidney problems
Your doctor may change your dose, depending on how well your kidneys are functioning.
Instructions for preparing the suspension:
It is recommended that your pharmacist reconstitute the powder for oral suspension before giving it to you. However, if the pharmacist does not reconstitute this product, the instructions are provided at the end of this prospectus in the section: "The following information is provided only for healthcare professionals or for patients (in case the pharmacist does not reconstitute this product)".
Instructions for use:
Shake the suspension bottle with the cap closed before each use.
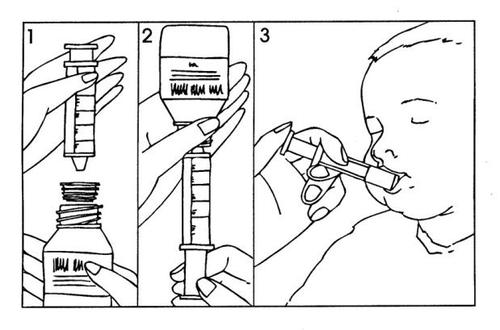
Instructions for using the oral syringe:
- Shake the prepared suspension well.
- Open the bottle (safety cap);
- Insert the oral syringe into the adapter on the neck of the bottle (Figure 1);
- Turn the bottle upside down with the oral syringe and withdraw the amount of suspension indicated by your doctor (Figure 2). The marks on the syringe indicate the ml.
Do not exceed the maximum dose of 400 mg per day in children (see section 3 "How to take Diflucan").
- Turn the bottle right side up with the oral syringe and remove the syringe from the bottle.
- The medication can be administered directly into the mouth with the oral syringe. The patient should remain upright during administration. Aim the oral syringe at the inside of the cheek; release the suspension slowly into the patient's mouth (Figure 3).
- Rinse the oral syringe.
- Close the bottle with the safety cap; the adapter should remain on the neck of the bottle.
To convert the dose of the oral suspension powder from mg/ml to ml/kg of body weight for pediatric patients, see section 6.
In adult patients, calculate the dose in ml to administer according to the recommended posology in mg and the concentration of the product.
If you take more Diflucan than you should
Taking too much Diflucan can make you feel unwell. Contact your doctor immediately or go to the nearest hospital. You can also call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount taken.
The symptoms of a possible overdose may include hearing, seeing, feeling, and thinking things that are not real (hallucinations and paranoid behavior). It may be appropriate to initiate symptomatic treatment (with supportive measures and stomach lavage if necessary).
If you forget to take Diflucan
Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses. If you have forgotten to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, do not take the forgotten dose.
If you have any doubts about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
Stop taking Diflucan and seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- widespread rash, high body temperature, and swollen lymph nodes (DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome).
Some people develop allergic reactions,although severe allergic reactions are rare. If you experience any side effect, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effect not mentioned in this prospectus. If you experience any of the following symptoms, inform your doctor immediately.
- sudden ringing in the ears, difficulty breathing, or chest tightness.
- swelling of the eyelids, face, or lips.
- itching all over the body, redness of the skin, or red spots with itching.
- skin rash.
- severe skin reactions, such as a rash that causes blisters (this can affect the mouth and tongue).
Diflucan may affect your liver. Signs of liver problems include:
- fatigue.
- loss of appetite.
- nausea and vomiting.
- yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes (jaundice).
If you experience any of these symptoms, stop taking Diflucan and tell your doctor immediately.
Other side effects:
Additionally, if you consider that any of the side effects you are experiencing is serious or if you notice any side effect not mentioned in this prospectus, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 patients) are:
- headache.
- stomach upset, diarrhea, discomfort, nausea and vomiting.
- elevated blood test results indicating liver function.
- rash.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients) are:
- reduction of red blood cells, which can make your skin pale and cause weakness or difficulty breathing.
- decreased appetite.
- insomnia, feeling of numbness.
- seizures, dizziness, feeling of spinning, tingling, pinching, or numbness, changes in taste.
- constipation, indigestion, gas, dry mouth.
- muscle pain.
- liver damage and yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
- hives, blisters (hives), itching, increased sweating.
- fatigue, general feeling of discomfort, fever.
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients) are:
- white blood cells in the blood that help defend against infections and blood cells that help stop bleeding, lower than normal.
- red or purple discoloration of the skin, which may be due to a low platelet count, other changes in blood cells.
- changes in blood tests (high cholesterol, fats).
- low potassium levels in the blood.
- tremors.
- abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG), changes in heart rate or rhythm.
- liver failure.
- allergic reactions (sometimes severe), including widespread rash with blisters and peeling of the skin, severe allergic reactions, swelling of the lips or face.
- hair loss.
Frequency not known, but may occur (cannot be estimated from available data):
- hypersensitivity reaction with skin rash, fever, swollen glands, increased eosinophils, and inflammation of internal organs (liver, lungs, heart, kidneys, and large intestine) (drug reaction or rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms [DRESS]).
Reporting side effects:
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible side effect not mentioned in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Diflucan
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date stated on the bottle and the outer carton after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Powder before reconstitution: Store below 25°C. Keep the bottle tightly closed.
After reconstitution: Store below 30°C. Do not freeze. The validity period of the reconstituted suspension is 28 days. Write the expiration date of the reconstituted suspension on the label of the bottle.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Any remaining suspension should be discarded 28 days after reconstitution. Deposit the packaging and unused medication in the pharmacy's SIGRE point. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medication you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Diflucan Composition
- The active ingredient is fluconazole, 1 ml of reconstituted suspension contains 10 mg or 40 mg of fluconazole.
- The other components (excipients) are sucrose, anhydrous colloidal silica, titanium dioxide (E 171), xanthan gum (E415), sodium citrate, anhydrous citric acid, sodium benzoate (E211), and natural orange flavor (contains orange essential oil and maltodextrin (contains glucose and corn starch)) (see section 2, Diflucan powder for oral suspension contains sucrose (sugar), glucose (sugar), sodium benzoate) and sodium (salt).
Product Appearance and Container Content
Oral suspension powder 10 mg/ml in a 60 ml capacity bottle: 35 ml of suspension after reconstitution:
- Diflucan 10 mg/ml oral suspension powder is presented in a 60 ml capacity bottle containing 24.4 g of powder that yields 35 ml of suspension once reconstituted.
- Diflucan 10 mg/ml oral suspension powder is a dry powder of white or almost white color. After adding water to the powder (following the detailed instructions later in the prospectus), a white or almost white suspension with an orange flavor is obtained.
- In each bottle, the mixture of powder with water produces 35 ml of suspension.
- The 35 ml suspension is supplied with a 5 ml graduated oral syringe and a pressure adapter for the bottle to measure the correct dose.
Oral suspension powder 40 mg/ml in a 60 ml capacity bottle: 35 ml of suspension after reconstitution:
- Diflucan 40 mg/ml oral suspension powder is presented in 60 ml capacity bottles containing 24.4 g of powder that yields 35 ml of suspension once reconstituted.
- Diflucan 40 mg/ml oral suspension powder is a dry powder of white or almost white color. After adding water to the powder (following the detailed instructions later in the prospectus), a white or almost white suspension with an orange flavor is obtained.
- In each bottle, the mixture of powder with water produces 35 ml of suspension.
- It is supplied with a 5 ml graduated oral syringe with a pressure adapter for the bottle to measure the correct dose.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Vinci Farma S.A. Avda de Europa, 20B. Parque Empresarial La Moraleja. 28108, Alcobendas (Madrid). Spain
Local Representative:
Pfizer, S.L. Avda de Europa, 20B. Parque Empresarial La Moraleja. 28108, Alcobendas (Madrid). Spain
Manufacturer:
Fareva Amboise. Zone Industrielle. 29 Route des Industries. 37530, Pocé-sur-Cisse. France.
Date of Last Revision of this Prospectus:February 2024
Detailed and updated information on this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS): http://www.aemps.gob.es/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended for healthcare professionals and patients (in case the pharmacist does not reconstitute this product):
Instructions for Preparing the Suspension:
The reconstituted suspension will consist of a white or almost white suspension with an orange flavor.
Oral suspension powder 10 mg/ml or 40 mg/ml in a 60 ml capacity bottle: 35 ml of suspension after reconstitution:
- Tap the bottle gently to release the powder.
- Reconstitute by adding 24 ml of water. First, add a small amount of water and shake vigorously. Then, add water up to the marked fill level (?) on the bottle (this corresponds to a total of 24 ml of water required).
- Shake well for 1 or 2 minutes to obtain a homogeneous suspension.
- After reconstitution, there will be a useful volume of 35 ml.
- Write the expiration date of the reconstituted suspension on the bottle label (the validity period of the reconstituted suspension is 28 days). The leftover suspension should not be used after this date and should be returned to your pharmacist.
Conversion of the Dose of the Oral Suspension Powder from mg/ml to ml/kg of Body Weight:
Diflucan and associated denominations 10 mg/ml powder for oral suspension:
In children, the dose of Diflucan oral suspension powder should be measured as accurately as possible according to the following equation:
The increments of the oral syringe graduation are 0.2 ml. Therefore, for intermediate weights and dosages, the dose to be administered in ml should be calculated and rounded up or down to the nearest graduation of the syringe:
For example, a child of 11 kg who has been prescribed 3 mg/kg/day of Diflucan should receive 33 mg/day, which is equivalent to 3.3 ml of the 10 mg/ml oral suspension. The dose can be rounded to 3.4 ml, the nearest graduation of the oral syringe to provide the complete dose.
The maximum dose of 400 mg per day should not be exceeded in the pediatric population (see table *). The use of Diflucan 10 mg/ml powder for oral suspension is not recommended for doses > 15.0 ml (highlighted in gray in the table). If the doses exceed 15.0 ml, the use of Diflucan 40 mg/ml powder for oral suspension is recommended.
Dosage Table with Examples
Dosage (corresponding dose in ml/day) | |||
Weight in kg | 3 mg/kg/day | 6 mg/kg/day | 12 mg/kg/day |
3 kg | 1.0 ml | 1.8 ml | 3.6 ml |
5 kg | 1.6 ml | 3.0 ml | 6.0 ml |
7.5 kg | 2.2 ml | 4.6 ml | 9.0 ml |
10 kg | 3.0 ml | 6.0 ml | 12.0 ml |
12.5 kg | 3.8 ml | 7.6 ml | 15.0 ml |
15 kg | 4.6 ml | 9.0 ml | 18.0 ml |
20 kg | 6.0 ml | 12.0 ml | 24.0 ml |
25 kg | 7.6 ml | 15.0 ml | 30.0 ml |
30 kg | 9.0 ml | 18.0 ml | 36.0 ml |
35 kg | 10.6 ml | 21.0 ml | 40.0 ml* |
40 kg | 12.0 ml | 24.0 ml | 40.0 ml* |
45 kg | 13.6 ml | 27.0 ml | 40.0 ml* |
Diflucan and associated denominations 40 mg/ml powder for oral suspension:
In children, the dose of Diflucan oral suspension powder should be measured as accurately as possible according to the following equation:
The increments of the oral syringe graduation are 0.2 ml. Therefore, for intermediate weights and dosages, the dose to be administered in ml should be calculated and rounded up or down to the nearest graduation of the syringe:
For example, a child of 23 kg who has been prescribed 6 mg/kg/day of Diflucan should receive 138 mg/day, which is equivalent to 3.45 ml of the 40 mg/ml oral suspension. The dose can be rounded to 3.4 ml, the nearest graduation of the oral syringe to provide the complete dose.
The maximum dose of 400 mg per day should not be exceeded in the pediatric population (see table *). The use of Diflucan 40 mg/ml powder for oral suspension is not recommended for weights below 15 kg. For weights below 15 kg, the use of Diflucan 10 mg/ml powder for oral suspension is recommended.
Dosage Table with Examples
Dosage (corresponding dose in ml/day) | |||
Weight in kg | 3 mg/kg/day | 6 mg/kg/day | 12 mg/kg/day |
15 kg | 1.2 ml | 2.2 ml | 4.6 ml |
20 kg | 1.6 ml | 3.0 ml | 6.0 ml |
25 kg | 1.8 ml | 3.8 ml | 7.6 ml |
30 kg | 2.2 ml | 4.6 ml | 9.0 ml |
35 kg | 2.6 ml | 5.2 ml | 10.0 ml* |
40 kg | 3.0 ml | 6.0 ml | 10.0 ml* |
50 kg | 3.8 ml | 7.6 ml | 10.0 ml* |
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price30 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DIFLUCAN 40 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION POWDERDosage form: CAPSULE, 150 mg fluconazoleActive substance: fluconazoleManufacturer: Arafarma Group S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: ORAL SOLUTION/SUSPENSION, 10 mg/mlActive substance: fluconazoleManufacturer: Vinci Farma, S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 100 mgActive substance: fluconazoleManufacturer: Vinci Farma, S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for DIFLUCAN 40 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION POWDER
Discuss questions about DIFLUCAN 40 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION POWDER, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















