
APIDRA 100 UNIDADES/ML,SOLOSTAR SOLUCION INYECTABLE EN PLUMA PRECARGADA


Cómo usar APIDRA 100 UNIDADES/ML,SOLOSTAR SOLUCION INYECTABLE EN PLUMA PRECARGADA
Traducción generada por IA
Este contenido ha sido traducido automáticamente y se ofrece solo con fines informativos. No sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
Ver originalContenido del prospecto
Introducción
Prospecto: información para el usuario
Apidra SoloStar100 Unidades/ml solución inyectable en pluma precargada
Insulina glulisina
Lea todo el prospecto detenidamente y las Instrucciones de Uso de Apidra SoloStar, pluma precargada, antes de empezar a usar este medicamento, porque contiene información importante para usted.
- Conserve este prospecto, ya que puede tener que volver a leerlo.
- Si tiene alguna duda, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero.
- Este medicamento se le ha recetado solamente a usted, y no debe dárselo a otras personas aunque tengan los mismos síntomas, ya que puede perjudicarles.
- Si experimenta efectos adversos, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero, incluso si se trata de efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. Ver sección 4.
Contenido del prospecto
- Qué es Apidra y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a usar Apidra
- Cómo usar Apidra
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Apidra
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
1. Qué es Apidra y para qué se utiliza
Apidra es un agente antidiabético, utilizado para reducir el nivel alto de azúcar en sangre en pacientes con diabetes mellitus. Se puede administrar a adultos, adolescentes y niños a partir de los 6 años. La diabetes mellitus es una enfermedad en la que su cuerpo no produce insulina suficiente para controlar el nivel de azúcar en sangre.
Se obtiene por biotecnología. Tiene un rápido comienzo de acción en 10-20 minutos y una corta duración de acción, de alrededor de 4 horas.
2. Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a usar Apidra
No use Apidra
- Si es alérgico a insulina glulisina o a cualquiera de los demás componentes de este medicamento (incluidos en la sección 6).
- Si su nivel de azúcar es demasiado bajo (hipoglucemia), siga la guía de la hipoglucemia (vea el recuadro al final de este prospecto).
Advertencias y precauciones
Apidra en pluma precargada sólo está indicado para inyectarse justo debajo de la piel (ver también sección 3). Consulte con su médico si necesita inyectarse la insulina por otro método.
Consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero antes de empezar a usar Apidra.
Siga atentamente las instrucciones de dosificación, control (pruebas de la sangre), dieta y actividad física (trabajo físico y ejercicio) tal y como le indicó su médico.
Grupos especiales de pacientes
Si tiene problemas de hígado o riñón, consulte con su médico ya que puede necesitar una dosis más baja.
No existe información clínica suficiente sobre el uso de Apidra en niños menores de 6 años.
Cambios en la piel en el punto de inyección.
Se debe rotar el punto de inyección para evitar cambios en la piel, como bultos bajo la piel. La insulina puede no funcionar muy bien si se inyecta en una zona abultada (ver Cómo usar Apidra). Póngase en contacto con su médico si actualmente está inyectándose en una zona abultada, antes de comenzar a inyectarse en una zona distinta. Su médico puede indicarle que compruebe sus niveles de azúcar en sangre más de cerca, y que ajuste la insulina o la dosis de sus otras medicaciones antidiabéticas.
Viajes
Antes de viajar, consulte con su médico. Tal vez tenga que consultar sobre
- la disponibilidad de su insulina en el país que va a visitar,
- reservas de insulina, agujas, etc.,
- el almacenamiento correcto de la insulina durante el viaje,
- el horario de las comidas y de la administración de insulina durante el viaje,
- los posibles efectos del traslado a zonas con diferencias horarias,
- los posibles nuevos riesgos para la salud en los países que va a visitar,
- qué debe hacer en situaciones de urgencia cuando se encuentre mal o se ponga enfermo.
Enfermedades y lesiones
El manejo de su diabetes puede necesitar un cuidado especial en las siguientes situaciones:
- Si está enfermo o sufre una lesión mayor, puede aumentar su nivel de azúcar en sangre (hiperglucemia).
- Si no come lo suficiente, el nivel de azúcar en sangre puede bajar demasiado (hipoglucemia).
En la mayoría de los casos necesitará un médico. Asegúrese de consultar inmediatamente a un médico.
Si padece usted diabetes tipo 1 (diabetes mellitus dependiente de insulina), no deje de administrarse su insulina y de seguir tomando suficientes hidratos de carbono. Informe siempre a las personas que se ocupan de su cuidado o tratamiento de que necesita insulina.
Algunos pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 de larga duración y enfermedad cardíaca o accidente cerebrovascular previo que fueron tratados con pioglitazona e insulina sufrieron desarrollo de insuficiencia cardíaca. Informe a su médico lo antes posible si sufre síntomas de insuficiencia cardíaca como falta de aliento poco corriente o aumento rápido de peso o hinchazón localizada (edema).
Uso de Apidra con otros medicamentos
Algunos medicamentos producen cambios en los niveles de azúcar en sangre (aumento, descenso o ambos dependiendo de la situación). En cada caso, puede ser necesario ajustar su dosis de insulina para evitar niveles de azúcar en sangre tanto demasiado bajos como demasiado altos. Hay que tener cuidado cuando empiece a tomar otro medicamento y también cuando deje de tomarlo.
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si está tomando, ha tomado recientemente o podría tener que tomar otros medicamentos. Pregunte a su médico, antes de tomar un medicamento, si éste puede afectar a su nivel de azúcar en sangre, y qué medidas debe adoptar, en su caso.
Entre los medicamentos que pueden provocar un descenso de su nivel de azúcar en sangre (hipoglucemia) se incluyen:
- todos los demás medicamentos para tratar la diabetes,
- los inhibidores de la enzima conversora de la angiotensina (ECA) (utilizados para tratar ciertas enfermedades del corazón o la hipertensión),
- la disopiramida (utilizada para tratar ciertas enfermedades del corazón),
- la fluoxetina (utilizada para tratar la depresión),
- los fibratos (utilizados para reducir los niveles elevados de lípidos en sangre),
- los inhibidores de la monoaminoxidasa (MAO) (utilizados para tratar la depresión),
- la pentoxifilina, el propoxifeno, los salicilatos (como la aspirina, utilizada para aliviar el dolor y la fiebre moderada),
- los antibióticos del grupo de las sulfamidas.
Entre los medicamentos que pueden provocar un aumento de su nivel de azúcar en sangre (hiperglucemia) se incluyen:
- los corticosteroides (como “cortisona” utilizada para tratar la inflamación),
- el danazol (medicamento que actúa sobre la ovulación),
- el diazóxido (utilizado para tratar la hipertensión),
- los diuréticos (utilizados para tratar la hipertensión y el exceso de retención de líquidos),
- el glucagón (hormona pancreática utilizada para tratar la hipoglucemia grave),
- la isoniazida (utilizada para tratar la tuberculosis),
- los estrógenos y progestágenos (como la píldora anticonceptiva utilizada para el control de la natalidad),
- los derivados de la fenotiazina (utilizados para tratar trastornos psiquiátricos),
- la somatotropina (hormona del crecimiento),
- los medicamentos simpaticomiméticos (como la epinefrina [adrenalina], el salbutamol, la terbutalina, utilizados para tratar el asma),
- las hormonas tiroideas (utilizadas para tratar trastornos de la glándula tiroidea),
- inhibidores de la proteasa (utilizados para tratar el VIH),
- medicamentos antipsicóticos atípicos (como la clozapina y olanzapina).
Su nivel de azúcar en sangre puede subir o bien bajar si toma:
- betabloqueantes (utilizados para tratar la hipertensión),
- clonidina (utilizada para tratar la hipertensión),
- sales de litio (utilizadas para tratar trastornos psiquiátricos).
La pentamidina (utilizada para tratar algunas infecciones causadas por parásitos) puede causar una hipoglucemia, que algunas veces puede ir seguida de una hiperglucemia.
Los betabloqueantes, al igual que otros medicamentos simpaticolíticos (como clonidina, guanetidina y reserpina) pueden atenuar o suprimir por completo los primeros síntomas de aviso que podrían ayudarle a reconocer una hipoglucemia.
Si no está usted seguro de si está tomando alguno de estos medicamentos, pregunte a su médico o farmacéutico.
Uso de Apidra con alcohol
Sus niveles de azúcar en sangre pueden subir o bajar si bebe alcohol.
Embarazo y lactancia
Si está embarazada o en periodo de lactancia, cree que podría estar embarazada o tiene intención de quedarse embarazada, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de utilizar este medicamento.
Informe a su médico si está planeando quedarse embarazada o si ya lo está. Su dosis de insulina puede requerir cambios durante el embarazo y tras el parto. Un control cuidadoso de su diabetes, y la prevención de la hipoglucemia, son importantes para la salud de su bebé.
No hay datos o éstos son limitados relativos al uso de Apidra en mujeres embarazadas.
Si usted se encuentra en periodo de lactancia, consulte a su médico ya que puede necesitar ajustes en sus dosis de insulina y en su dieta.
Conducción y uso de máquinas
Su capacidad de concentración o de reacción puede verse reducida si:
- tiene usted hipoglucemia (bajos niveles de azúcar en sangre),
- tiene usted hiperglucemia (altos niveles de azúcar en sangre).
Esté atento a este posible problema, considerando todas las situaciones que pueden ser causa de riesgo para usted o para otros (como conducir un vehículo o utilizar máquinas).
Debe pedir a su médico que le aconseje sobre la capacidad para conducir si:
- tiene usted episodios frecuentes de hipoglucemia,
- han disminuido o no aparecen los primeros síntomas de aviso que pueden ayudarle a reconocer una hipoglucemia.
Información importante sobre algunos de los componentes de Apidra
Este medicamento contiene menos de 1 mmol (23 mg) de sodio por dosis, esto es, esencialmente “exento de sodio”.
Apidra contiene metacresol
Apidra contiene metacresol, el cual puede causar reacciones alérgicas.
3. Cómo usar Apidra
Dosis
Siga exactamente las instrucciones de administración de este medicamento indicadas por su médico. En caso de duda, consulte de nuevo a su médico o farmacéutico.
Su médico además determinará la dosis de Apidra que necesite en función de su estilo de vida y de los resultados de sus controles de azúcar (glucosa) en sangre y de su anterior tratamiento con insulina.
Apidra es una insulina de acción corta. Su médico le puede indicar que la use en combinación con una insulina de acción intermedia, de acción larga, una insulina basal o con comprimidos utilizados para tratar los niveles altos de azúcar en sangre.
Si usted pasa de otra insulina a insulina glulisina, su dosis podría tener que ser ajustada por su médico.
Muchos factores pueden influir en su nivel de azúcar en sangre. Debe conocer estos factores ya que así podrá reaccionar correctamente ante cambios de su nivel de azúcar en sangre, y para evitar que suba o baje demasiado. Vea el recuadro que aparece al final del prospecto para más información.
Forma de administración
Apidra se inyecta bajo la piel (subcutáneamente).
Su médico le mostrará en qué área de la piel debe usted inyectarse Apidra. Apidra puede inyectarse en la pared abdominal, el muslo o la parte alta del brazo, o por perfusión continua en la pared abdominal. El efecto será ligeramente más rápido si se inyecta la insulina en su abdomen. Al igual que con las demás insulinas, los lugares de inyección y perfusión dentro de un área de inyección (abdomen, muslo o parte alta del brazo) deben rotar de una inyección a otra.
Frecuencia de administración
Apidra debe administrarse poco tiempo (0-15 min) antes o poco tiempo después de las comidas.
Instrucciones para la correcta utilización
Cómo manejar SoloStar
SoloStar es una pluma desechable precargada que contiene insulina glulisina. Apidra en pluma precargada sólo está indicado para inyectarse justo debajo de la piel. Consulte con su médico si necesita inyectarse la insulina por otro método.
Lea cuidadosamente las “Instrucciones de uso de SoloStar” incluidas en este prospecto. Debe utilizar la pluma tal y como se describe en estas Instrucciones de uso.
Para prevenir la posible transmisión de una enfermedad, cada pluma debe ser utilizada por un solo paciente.
Antes de utilizarla inserte siempre una aguja nueva y realice la prueba de seguridad. Utilice solo agujas compatibles con SoloStar (ver “Instrucciones de uso de SoloStar”).
Inspeccione el cartucho sellado en la pluma inyector desechable, antes de usarlo. Sólo se debe usar si la solución es transparente, incolora y no contiene partículas visibles. No agitar ni mezclar antes de su uso.
Utilice siempre una pluma nueva si nota que su control de azúcar en sangre empeora de manera inexplicable. Si piensa que podría tener un problema con SoloStar, por favor consulte a su profesional sanitario.
Si usa más Apidra del que debe
- Si se ha inyectado demasiado Apidra, su nivel de azúcar en sangre puede llegar a ser muy bajo (hipoglucemia).
Compruebe su nivel de azúcar en sangre frecuentemente. En general, para prevenir la hipoglucemia debe comer más y controlar su nivel de azúcar en sangre. Para más información sobre el tratamiento de la hipoglucemia, vea el recuadro que aparece al final del prospecto.
Si olvidó usar Apidra
- Si ha olvidado una dosis de Apidra o si no se ha inyectado suficiente insulina, su nivel de azúcar en sangre puede aumentar mucho (hiperglucemia). Compruebe su nivel de azúcar en sangre frecuentemente. Para más información sobre el tratamiento de la hiperglucemia, vea el recuadro que aparece al final del prospecto.
- No use una dosis doble para compensar las dosis olvidadas.
Si interrumpe el tratamiento con Apidra
Esto podría producir hiperglucemia grave (niveles muy altos de azúcar en sangre) y cetoacidosis (aumento del ácido en sangre porque el organismo degrada las grasas en lugar del azúcar). No interrumpa su tratamiento con Apidra sin consultar con su médico, él le dirá lo que debe hacer.
Si tiene cualquier otra duda sobre el uso de este medicamento, pregunte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero.
Confusiones entre insulina
Debe comprobar siempre la etiqueta de insulina antes de cada inyección para evitar confusiones entre Apidra y otras insulinas.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, este medicamento puede producir efectos adversos, aunque no todas las personas los sufran.
Efectos adversos graves
La hipoglucemia (niveles bajos de azúcar en sangre) puede ser muy grave.La hipoglucemia es un efecto adverso observado muy frecuentemente (puede afectar a más de 1 de cada 10 pacientes).
La hipoglucemia (niveles bajos de azúcar en sangre) significa que no tiene suficiente azúcar en sangre.Si su nivel de azúcar en sangre baja mucho, puede perder el conocimiento. Una hipoglucemia grave puede provocar daños en el cerebro y puede ser amenazante para la vida. Si tiene síntomas de niveles bajos de azúcar en sangre, actúe inmediatamentepara subir su nivel de azúcar en sangre. Vea el recuadro al final de este prospecto, donde encontrará más información importante acerca de la hipoglucemia y su tratamiento.
Si usted experimenta los siguientes síntomas, contacte inmediatamente con su médico:
Las reacciones alérgicas sistémicasson efectos adversos poco frecuentemente observados (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 pacientes).
Alergia generalizada a insulina:los síntomas relacionados pueden incluir reacciones cutáneas a gran escala (erupción cutánea y picor en todo el cuerpo), hinchazón grave de la piel o de las membranas mucosas (angioedema), dificultad para respirar, descenso de la tensión arterial con latido cardíaco rápido y sudoración. Estos pueden ser los síntomas de casos graves de alergia generalizada a las insulinas, incluyendo reacción anafiláctica que puede ser amenazante para la vida.
Hiperglucemia (niveles altos de azúcar en sangre) significa que hay demasiado azúcar en sangre.
La frecuencia de la hiperglucemia no puede estimarse. Si su nivel de azúcar en sangre es demasiado alto, esto le indica que puede necesitar más insulina de la que se ha inyectado. Esto puede ser grave si su nivel de azúcar en sangre se vuelve muy alto.
Para más información sobre los signos y síntomas de la hiperglucemia, vea el recuadro al final de este prospecto.
Otros efectos adversos
- Cambios en la piel en el punto de inyección.
Si se inyecta insulina con demasiada frecuencia en el mismo lugar, el tejido graso se puede encoger (lipoatrofia) o hacerse más grueso (lipohipertrofia) (puede afectar hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas). Los bultos bajo la piel también pueden producirse por la acumulación de una proteína denominada amiloide (amiloidosis cutánea; no se sabe con qué frecuencia se produce esto). La insulina puede no funcionar muy bien si se inyecta en una zona abultada. Cambie el punto de inyección para ayudar a evitar estos cambios en la piel.
Efectos adversos frecuentes(pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 pacientes)
- Reacciones alérgicas y de la piel en el lugar de la inyección
Se pueden experimentar reacciones en el lugar de inyección (como enrojecimiento, dolor intenso poco habitual al inyectar, picor, urticaria, hinchazón o inflamación). Estas reacciones también pueden extenderse alrededor del lugar de inyección. La mayor parte de las reacciones menores a la insulina se resuelven habitualmente en unos días o en pocas semanas.
Efectos adversoscuya frecuencia no puede estimarse a partir de los datos disponibles
- Reacciones oculares
Un cambio significativo (mejoría o empeoramiento) del control de su nivel de azúcar en sangre puede provocar un empeoramiento temporal de su visión. Si padece una retinopatía proliferativa (una enfermedad del ojo relacionada con la diabetes) los ataques hipoglucémicos graves pueden provocar una pérdida temporal de la visión.
Comunicación de efectos adversos
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del sistema nacional de notificación incluido en el Apéndice V. Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Conservación de Apidra
Mantener este medicamento fuera de la vista y del alcance de los niños.
No utilice este medicamento después de la fecha de caducidad que aparece en el envase y en la etiqueta de la pluma después de CAD/EXP. La fecha de caducidad es el último día del mes que se indica.
Plumas sin utilizar
Conservar en nevera (entre 2ºC y 8ºC).
No congelar.
No colocar SoloStar cerca del compartimento del congelador o junto a un acumulador de frío.
Conservar la pluma precargada en el embalaje exterior para protegerla de la luz.
Plumas en uso
Las plumas precargadas en uso (o para llevarlas como reserva) pueden conservarse durante un máximo de 4 semanas por debajo de 25ºC y protegidas del calor directo o de la luz directa. La pluma en uso no debe conservarse en nevera.
No la utilice después de este periodo de tiempo.
No utilice este medicamento si no está incoloro y transparente.
Los medicamentos no se deben tirar por los desagües ni a la basura. Pregunte a su farmacéutico cómo deshacerse de los envases y de los medicamentos que ya no necesita. De esta forma, ayudará a proteger el medio ambiente.
6. Contenido del envase e información adicional
Composición de Apidra
- El principio activo es insulina glulisina. Cada ml de solución contiene 100 Unidades de insulina glulisina (equivalente a 3,49 mg).
- Los demás componentes son: metacresol (ver sección 2 “Apidra contiene metacresol”), cloruro de sodio (ver sección 2 “Información importante sobre algunos de los componentes de Apidra”), trometamol, polisorbato 20, ácido clorhídrico concentrado, hidróxido de sodio, agua para preparaciones inyectables.
Aspecto del producto y contenido del envase
Apidra SoloStar 100 Unidades/ml solución inyectable en pluma precargada. Es una solución acuosa transparente, incolora, sin partículas visibles.
Cada pluma contiene 3 ml de solución, equivalente a 300 Unidades. Existen envases de 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 y 10 plumas precargadas. Puede que solamente estén comercializados algunos tamaños de envase.
Titular de la autorización de comercialización y responsable de la fabricación
Titular de la autorización de comercialización:
Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH
D-65926 Frankfurt am Main
Alemania
Responsable de la fabricación:
Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH
Industriepark Höchst, D-65926 Frankfurt
Alemania
Puede solicitar más información respecto a este medicamento dirigiéndose al representante local del titular de la autorización de comercialización.
België/Belgique/Belgien Sanofi Belgium Tél/Tel: +32 (0)2 710 54 00 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg Sanofi Belgium Tél/Tel: +32 (0)2 710 54 00 (Belgique/Belgien) |
| Magyarország SANOFI-AVENTIS Zrt. Tel.: +36 1 505 0050 |
Ceská republika Sanofi s.r.o. Tel: +420 233 086 111 | Malta Sanofi S.r.l. Tel: +39 02 39394275 |
Danmark Sanofi A/S Tlf: +45 45 16 70 00 | Nederland Sanofi B.V. Tel: +31 20 245 4000 |
Deutschland Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH Tel.: 0800 52 52 010 Tel. aus dem Ausland: +49 69 305 21 131 | Norge sanofi-aventis Norge AS Tlf: +47 67 10 71 00 |
Eesti Swixx Biopharma OÜ Tel: +372 640 10 30 | Österreich sanofi-aventis GmbH Tel: +43 1 80 185 – 0 |
Ελλ?δα Sanofi-Aventis Μονοπρ?σωπη AEBE Τηλ: +30 210 900 16 00 | Polska Sanofi Sp. z o.o. Tel.: +48 22 280 00 00 |
España sanofi-aventis, S.A. Tel: +34 93 485 94 00 | Portugal Sanofi - Produtos Farmacêuticos, Lda. Tel: +351 21 35 89 400 |
France Sanofi Winthrop Industrie Tél: 0 800 222 555 Appel depuis l’étranger : +33 1 57 63 23 23 Hrvatska Swixx Biopharma d.o.o. Tel: +385 1 2078 500 | România Sanofi Romania SRL Tel: +40 (0) 21 317 31 36 |
Ireland sanofi-aventis Ireland Ltd. T/A SANOFI Tel: +353 (0) 1 403 56 00 | Slovenija Swixx Biopharma d.o.o. Tel: +386 1 235 51 00 |
Ísland Vistor hf. Sími: +354 535 7000 | Slovenská republika Swixx Biopharma s.r.o. Tel: +421 2 208 33 600 |
Italia Sanofi S.r.l. Tel: 800 13 12 12 (domande di tipo tecnico) 800 536389 (altre domande) | Suomi/Finland Sanofi Oy Puh/Tel: +358 (0) 201 200 300 |
Κ?προς C.A. Papaellinas Ltd. Τηλ: +357 22 741741 | Sverige Sanofi AB Tel: +46 (0)8 634 50 00 |
Latvija Swixx Biopharma SIA Tel: +371 6 616 47 50 | United Kingdom(Northern Ireland) sanofi-aventis Ireland Ltd. T/A SANOFI Tel: +44 (0) 800 035 2525 |
Lietuva Swixx Biopharma UAB Tel: +370 5 236 91 40 |
Fecha de la última revisión de este prospecto:
Otra fuente de información
La información detallada de este medicamento está disponible en la página web de la Agencia Europea de Medicamentos: http://www.ema.europa.eu/
HIPERGLUCEMIA E HIPOGLUCEMIA
Lleve siempre consigo algo de azúcar (al menos 20 gramos).
Lleve consigo alguna información que indique que es una persona diabética.
HIPERGLUCEMIA (altos niveles de azúcar en sangre)
Si tiene el nivel de azúcar en sangre muy alto (hiperglucemia), puede que no haya inyectado suficiente insulina.
¿Por qué ocurre la hiperglucemia?
Algunos ejemplos son:
- no se ha inyectado su insulina o no se ha inyectado la cantidad suficiente, o si su efecto ha disminuido, por ejemplo, debido a un almacenamiento incorrecto,
- está haciendo menos ejercicio que de costumbre, tiene estrés (angustia emocional, excitación), o sufre una lesión, una operación, infección o fiebre,
- está tomando o ha tomado ciertos medicamentos (ver la sección 2, “Uso de Apidra con otros medicamentos”).
Síntomas de aviso de hiperglucemia
La sed, el aumento de la necesidad de orinar, el cansancio, la piel seca, el enrojecimiento de la cara, la pérdida del apetito, la tensión arterial baja, el latido rápido del corazón y la presencia de glucosa y cuerpos cetónicos en la orina. El dolor de estómago, la respiración profunda y rápida, la somnolencia o incluso la pérdida del conocimiento pueden ser signos de una afección grave (cetoacidosis) debida a la falta de insulina.
¿Qué hacer en caso de hiperglucemia?
Debe analizar su nivel de azúcar en sangre y su nivel de acetona en orina tan pronto se produzca cualquiera de los síntomas arriba descritos. La hiperglucemia o la cetoacidosis graves deben ser tratadas siempre por un médico, normalmente en un hospital.
HIPOGLUCEMIA (bajos niveles de azúcar en sangre)
Si su nivel de azúcar en sangre disminuye de forma excesiva puede perder el conocimiento. La hipoglucemia grave puede producir un ataque al corazón o daño cerebral y puede poner en peligro su vida. Normalmente debe ser capaz de reconocer cuándo su nivel de azúcar en sangre está disminuyendo demasiado para poder tomar las medidas adecuadas.
¿Por qué ocurre la hipoglucemia?
Algunos ejemplos son:
- se inyecta demasiada insulina,
- omite comidas o las retrasa,
- no come lo suficiente, o come alimentos que contienen menos hidratos de carbono de lo normal (el azúcar y las sustancias similares al azúcar se llaman hidratos de carbono; sin embargo, los edulcorantes artificiales NO son hidratos de carbono),
- pierde hidratos de carbono por vómitos o diarrea,
- bebe alcohol, especialmente si no está comiendo mucho,
- está haciendo más ejercicio de lo habitual o un tipo diferente de actividad física,
- se está recuperando de una lesión, de una operación o de otros tipos de estrés,
- se está recuperando de una enfermedad o fiebre,
- está tomando o ha dejado de tomar determinados medicamentos (ver la sección 2, “Uso de Apidra con otros medicamentos”).
También es más probable que se produzca una hipoglucemia si:
- acaba de empezar un tratamiento con insulina o cambia a otra preparación de insulina,
- sus niveles de azúcar en sangre son casi normales o son inestables,
- cambia el sitio de la piel en la que se inyecta la insulina (por ejemplo del muslo a la parte alta del brazo),
- padece una enfermedad del riñón o del hígado grave, o alguna otra enfermedad como el hipotiroidismo.
Síntomas de aviso de la hipoglucemia
- En su cuerpo
Ejemplos de síntomas que le indican que su nivel de azúcar en sangre está bajando mucho o muy deprisa: sudor, piel húmeda y pegajosa, ansiedad, latido rápido del corazón, tensión arterial alta, palpitaciones y latido irregular del corazón. Estos síntomas se producen a menudo antes de que aparezcan los síntomas de un bajo nivel de azúcar en el cerebro.
- En su cerebro
Ejemplos de síntomas que le indican que existe un nivel bajo de azúcar en el cerebro: dolores de cabeza, hambre intensa, náuseas, vómitos, cansancio, sopor, trastornos del sueño, inquietud, comportamiento agresivo, fallos de concentración, reacciones alteradas, depresión, confusión, trastornos del habla (a veces, pérdida total del habla), trastornos visuales, temblor, parálisis, sensaciones de hormigueo (parestesias), sensaciones de entumecimiento y hormigueo en la zona de la boca, mareos, pérdida del autocontrol, incapacidad para cuidar de sí mismo, convulsiones y pérdida del conocimiento.
Los primeros síntomas de alerta de hipoglucemia (“síntomas de aviso”) pueden cambiar, atenuarse o faltar por completo si:
- es una persona de edad avanzada,
- ha padecido diabetes durante mucho tiempo,
- sufre cierto tipo de enfermedad nerviosa (neuropatía diabética autónoma),
- ha sufrido recientemente un episodio de hipoglucemia (por ejemplo, el día antes) o si ésta se desarrolla gradualmente,
- tiene niveles casi normales o, al menos, niveles muy mejorados de azúcar en sangre,
- está tomando o ha tomado ciertos medicamentos (ver la sección 2, “Uso de Apidra con otros medicamentos”).
En este caso, puede desarrollar una hipoglucemia grave (e incluso desmayarse) antes de darse cuenta del problema. Esté siempre familiarizado con sus síntomas de aviso. Si fuera necesario, la realización con más frecuencia de un análisis del azúcar en sangre puede ayudar a identificar episodios hipoglucémicos leves, que en caso contrario podrían pasar inadvertidos. Si no está seguro de poder reconocer sus síntomas de aviso, evite situaciones (como conducir un coche) que puedan ponerle en peligro a usted o a otras personas como consecuencia de la hipoglucemia.
¿Qué debe hacer si sufre una hipoglucemia?
- No se inyecte insulina. Ingiera inmediatamente de 10 a 20 g de azúcar, como glucosa, terrones de azúcar o una bebida endulzada con azúcar. Aviso: los edulcorantes artificiales y los productos alimenticios con edulcorantes artificiales en lugar de azúcar (como bebidas dietéticas) no sirven de ayuda para tratar la hipoglucemia.
- Después coma algo que tenga un efecto de acción larga en el aumento de su azúcar en sangre (como pan o pasta). Su médico o enfermero deben haber comentado este tema con usted.
- Si la hipoglucemia reaparece, tome de nuevo otros 10 a 20 g de azúcar.
- Consulte de inmediato con un médico si no es capaz de controlar la hipoglucemia o si ésta reaparece.
Indiquele a sus familiares, amigos y personas cercanas lo siguiente:
Si no es capaz de tragar o si pierde el conocimiento, necesitará una inyección de glucosa o de glucagón (un medicamento que incrementa el nivel de azúcar en sangre). Estas inyecciones están justificadas aun cuando no tenga la certeza de que padece hipoglucemia.
Es recomendable analizar su nivel de azúcar en sangre inmediatamente después de la ingestión de glucosa para confirmar que padece realmente hipoglucemia.
Apidra SoloStar solución inyectable en pluma precargada. INSTRUCCIONES DE USO
SoloStar es una pluma precargada para la inyección de insulina. Su médico ha decidido que SoloStar es adecuado para usted en base a su habilidad para manejar SoloStar. Antes de usar SoloStar, hable con su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero sobre la técnica de inyección adecuada.
Lea estas instrucciones detenidamente antes de usar su SoloStar. Si usted no está capacitado para utilizar SoloStar o seguir completamente las instrucciones por sí solo, debe usar SoloStar solo si cuenta con la ayuda de una persona que pueda seguir completamente las instrucciones. Sujete la pluma tal y como se muestra en este prospecto. Para asegurar que lee la dosis correctamente, sujete la pluma horizontalmente, con la aguja en la izquierda y el selector de dosis a la derecha según se muestra en el dibujo de abajo.
Usted puede fijar dosis de 1 a 80 unidades en pasos de 1 unidad. Cada pluma contiene múltiples dosis.
Guarde este prospecto para futuras consultas.
Si tiene alguna duda sobre SoloStar o sobre la diabetes, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero o llame al teléfono local de sanofi-aventis que aparece en la parte delantera de este prospecto.


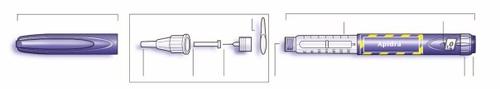
Esquema de la pluma
Información importante para utilizar SoloStar:
- Inserte siempre una aguja nueva antes de cada uso. Utilice únicamente las agujas compatibles con SoloStar.
- No se debe seleccionar una dosis ni presionar el botón si no hay una aguja insertada.
- Realice siempre la prueba de seguridad antes de cada inyección (ver Paso 3).
- Esta pluma es para su uso exclusivo. No la debe compartir con nadie.
- Si su inyección la realiza otra persona, se debe tener especial precaución para evitar daños de forma accidental con la aguja y la transmisión de infecciones.
- Nunca utilice SoloStar si está dañado o si no está seguro de que está funcionando correctamente.
- Tenga siempre un recambio de SoloStar, por si acaso su SoloStar se pierde o está dañado.
Paso 1.Comprobación de la insulina
- Compruebe la etiqueta de su SoloStar para asegurarse de que contiene la insulina correcta. Apidra SoloStar es azul. Tiene un botón de inyección azul oscuro con un anillo que sobresale en el extremo.
- Retire el capuchón de la pluma.
- Compruebe el aspecto de su insulina. Apidra es una insulina transparente. No utilice SoloStar si la insulina es opaca, con color o contiene partículas.
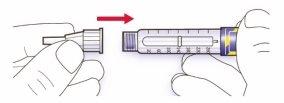
Paso 2.Colocación de la aguja
Utilice siempre una aguja nueva y estéril para cada inyección. Esto ayuda a prevenir contaminaciones y posibles bloqueos de la aguja.
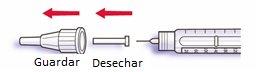
- Retire el sello protector de la nueva aguja.
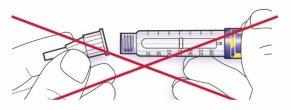
- Alinee la aguja con la pluma, y manténgala recta mientras la inserta (enrósquela o empújela dependiendo del tipo de aguja).
- Si la aguja no se mantiene recta mientras se inserta, el sello de goma puede romperse y dar lugar a pérdidas o a la rotura de la aguja.
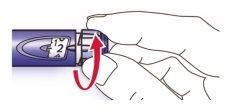
Paso 3.Prueba de seguridad
Antes de cada inyección realice siempre la prueba de seguridad. Ésta garantiza que usted recibe la dosis exacta ya que:
- se asegura que la pluma y la aguja funcionan perfectamente
- se eliminan las burbujas de aire
- Seleccione una dosis de 2 unidades girando el selector de la dosis.
- Retire el protector exterior de la aguja y guárdelo para retirar la aguja utilizada después de cada inyección. Retire el protector interior de la aguja y deséchelo.
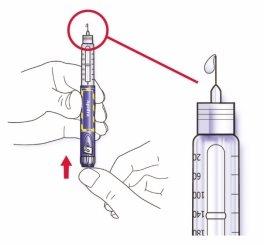
- Sujete la pluma con la aguja apuntando hacia arriba.
- Golpee ligeramente el reservorio de insulina para que las burbujas de aire suban hacia la aguja.
- Presione el botón de inyección completamente. Compruebe que la insulina aparece en el extremo de la aguja.
Puede realizar la prueba de seguridad varias veces hasta que aparezca insulina.
- Si no sale insulina, compruebe las burbujas de aire y repita la prueba de seguridad dos veces más hasta eliminarlas.
- Si aún así no sale insulina, la aguja podría estar bloqueada. Cambie de aguja e inténtelo de nuevo.
- Si no sale insulina después de cambiar la aguja, su SoloStar podría estar estropeado. No use este SoloStar.
Paso 4.Selección de la dosis
Puede seleccionar la dosis en pasos de 1 unidad, desde un mínimo de 1 unidad hasta un máximo de 80 unidades. Si usted necesita una dosis superior a 80 unidades, deberá administrarse dos o más inyecciones.
- Compruebe que en la ventana de la dosis aparece “0” después de la prueba de seguridad.
- Seleccione su dosis (en el siguiente ejemplo, la dosis seleccionada es de 30 unidades). Si usted gira demasiado el selector de la dosis, puede volver hacia atrás.
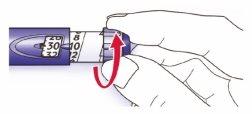
- No presione el botón de inyección mientras gira, ya que la insulina podría salir.
- No podrá girar el selector de la dosis si el número de unidades supera las que quedan en la pluma. No fuerce el selector de la dosis. En este caso usted puede inyectarse lo que queda en la pluma y completar su dosis con un nuevo SoloStar o utilizar un SoloStar nuevo para la dosis completa.
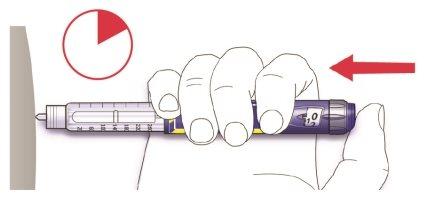
Paso 5.Inyectar la dosis
- Utilice el método de inyección que le enseñó su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero.
- Inserte la aguja en la piel.
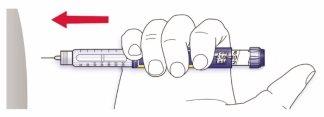
- Libere la dosis presionando el botón de inyección por completo. El número que aparece en la ventana de la dosis volverá a “0” cuando se inyecte.
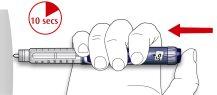
- Mantenga el botón de inyección presionado por completo. Lentamente cuente hasta 10 antes de retirar la aguja de la piel. Esto garantiza que se libera la dosis completa.
El émbolo de la pluma se mueve con cada dosis. El émbolo alcanzará el final del cartucho cuando se haya utilizado el total de las 300 unidades de insulina.
Paso 6.Retirada y eliminación de la aguja
Después de cada inyección elimine la aguja y conserve SoloStar sin la aguja.
Esto ayuda a prevenir:
- Contaminaciones y/o infecciones,
- Entrada de aire en el reservorio de insulina y pérdida de insulina que pueden dar lugar a una dosis inexacta.
- Coloque el protector exterior de la aguja en la aguja, y utilícelo para desenroscar la aguja de la pluma. Para reducir el riesgo de accidentes con la aguja, no recoloque nunca el protector interior.
- Si su inyección es administrada por otra persona, o si usted está administrando una inyección a otra persona, debe tener especial cuidado al retirar y desechar la aguja. Siga las medidas recomendadas de seguridad para la retirada y eliminación de las agujas (contacte con su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero) con el fin de reducir el riesgo de accidentes con la aguja y la transmisión de enfermedades infecciosas.
- Deseche la aguja de forma segura, tal y como le enseñó su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero.
- Coloque el capuchón de pluma siempre después de cada inyección y guarde la pluma hasta su próxima inyección.
Instrucciones de conservación
Revise la parte de atrás de este prospecto para seguir las instrucciones de cómo conservar SoloStar.
Si SoloStar está conservado en lugar fresco, debe sacarse de 1 a 2 horas antes de la inyección para dejar que se atempere a temperatura ambiente. La inyección de insulina fría es más dolorosa.
SoloStar debe desecharse tal y como indiquen sus autoridades locales.
Mantenimiento
Proteja SoloStar del polvo y de la suciedad.
Puede limpiar la parte exterior de su SoloStar con un trapo húmedo.
No ponga en remojo, lave o lubrique la pluma, podría estropearla.
SoloStar está diseñado para funcionar con precisión y seguridad. Debe manipularse con cuidado. Evite situaciones en las que SoloStar pueda estropearse. Si le preocupa que su SoloStar pueda estar estropeado, utilice uno nuevo.
- País de registro
- Precio medio en farmacia46.97 EUR
- Principio activo
- Requiere recetaSí
- Fabricante
- Esta información es de carácter general y no sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
- Alternativas a APIDRA 100 UNIDADES/ML,SOLOSTAR SOLUCION INYECTABLE EN PLUMA PRECARGADAForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE, 100 U/mlPrincipio activo: insulina glulisinaFabricante: Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbhRequiere recetaForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE, 100 U/mlPrincipio activo: insulina glulisinaFabricante: Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbhRequiere recetaForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE, 100 U/mlPrincipio activo: insulina humanaFabricante: Novo Nordisk A/SRequiere receta
Médicos online para APIDRA 100 UNIDADES/ML,SOLOSTAR SOLUCION INYECTABLE EN PLUMA PRECARGADA
Comenta la dosis, los posibles efectos secundarios, interacciones, contraindicaciones o la revisión de receta de APIDRA 100 UNIDADES/ML,SOLOSTAR SOLUCION INYECTABLE EN PLUMA PRECARGADA, sujeto a valoración médica y a la normativa local.
Preguntas frecuentes
















