ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão

Pergunte a um médico sobre a prescrição de ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão

Como usar ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão
Introdução
Prospecto: informação para o utilizador
Actilyse, pó e solvente para solução injectável e para perfusão
alteplase
Leia todo o prospecto atentamente antes de começar a usar este medicamento, porque contém informações importantes para si.
- Conserva este prospecto, porque pode ter que o ler novamente.
- Se tiver alguma dúvida, consulte o seu médico ou enfermeiro.
- Se experimentar efeitos adversos, consulte o seu médico ou enfermeiro, mesmo que se trate de efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Ver secção 4.
Conteúdo do prospecto:
- O que é Actilyse e para que é utilizado
- O que precisa saber antes de receber Actilyse
- Como é administrado Actilyse
- Possíveis efeitos adversos
- Conservação de Actilyse
- Conteúdo do envase e informação adicional
1. O que é Actilyse e para que é utilizado
O princípio ativo de Actilyse é a alteplase. Pertence a um grupo de medicamentos denominados trombolíticos. Estes medicamentos actuam dissolvendo os coágulos de sangue que se formaram nos vasos sanguíneos.
Actilyse 10 mg, 20 mg ou 50 mg é utilizado para tratar doenças causadas pela formação de coágulos de sangue dentro dos vasos sanguíneos, incluindo:
- ataques cardíacos causados por coágulos de sangue nas artérias do coração (infarto agudo de miocárdio)
- coágulos de sangue nas artérias dos pulmões (embolia pulmonar aguda maciça)
- acidente vascular cerebral causado por um coágulo de sangue numa artéria do cérebro (acidente vascular cerebral isquémico agudo)
2. O que precisa saber antes de receber Actilyse
Não deve receber Actilyse:
- se é alérgico (hipersensível) à alteplase ou a qualquer um dos outros componentes deste medicamento (incluídos na secção 6)
- se tem ou teve recentemente uma doença que aumenta o risco de hemorragia, incluindo:
- distúrbio hemorrágico ou predisposição ao sangramento
- hemorragia grave ou perigosa em qualquer parte do corpo
- hemorragia dentro do cérebro ou do crânio
- pressão arterial muito elevada não controlada
- infecção bacteriana ou inflamação do coração (endocardite), ou inflamação das membranas que envolvem o coração (pericardite)
- inflamação do pâncreas (pancreatite aguda)
- úlcera gástrica ou úlceras no intestino
- varizes no esófago (varizes esofágicas)
- anomalias dos vasos sanguíneos, como por exemplo o alargamento localizado de uma artéria (aneurisma)
- determinados tumores
- doença grave do fígado
- se está a tomar medicamentos para "diluir" a sangue (anticoagulantes orais), a menos que as provas apropriadas não mostrem atividade clinicamente relevante desse medicamento
- se foi submetido a cirurgia no cérebro ou na medula espinhal
- se foi submetido a cirurgia maior ou a um traumatismo importante durante os últimos 3 meses
- se recebeu uma punção recente num vaso sanguíneo maior
- se foi submetido a massagem cardíaca externa durante os últimos 10 dias
- se teve um bebé nos últimos 10 dias
O seu médico também não lhe administrará Actilyse para o tratamento de ataques cardíacos ou coágulos de sangue nas artérias dos pulmões
- se tem ou teve alguma vez um acidente vascular cerebral produzido por hemorragia no cérebro (acidente vascular cerebral hemorrágico)
- se tem ou teve alguma vez um acidente vascular cerebral de causa desconhecida
- se teve recentemente (nos últimos 6 meses) um acidente vascular cerebral causado por um coágulo de sangue numa artéria do cérebro (acidente vascular cerebral isquémico), a menos que seja o acidente vascular cerebral por que está a ser tratado agora
Além disso, o seu médico não lhe administrará Actilyse para o tratamento do acidente vascular cerebral causado por um coágulo de sangue numa artéria do cérebro (acidente vascular cerebral isquémico agudo)
- se os sintomas de acidente vascular cerebral começaram há mais de 4,5 horas ou se é possível que os sintomas tenham começado há mais de 4,5 horas porque desconhece quando começaram
- se o seu acidente vascular cerebral apresenta apenas sintomas muito leves
- se há sinais de hemorragia no cérebro
- se teve um acidente vascular cerebral nos últimos três meses
- se os sintomas melhoram rapidamente antes de ser administrado Actilyse
- se apresenta um acidente vascular cerebral muito grave
- se teve espasmos (convulsões) quando começou o acidente vascular cerebral
- se apresenta um tempo de tromboplastina (um teste para verificar como coagula a sua sangue) anormal. Este teste pode ser anormal se lhe foi administrado heparina (um medicamento utilizado para "diluir" a sangue) durante as últimas 48 horas
- se é diabético e teve um acidente vascular cerebral alguma vez
- se a quantidade de plaquetas (trombócitos) na sua sangue é muito baixa
- se a sua pressão arterial é muito elevada (acima de 185/110) e só pode ser reduzida quando lhe são administrados medicamentos
- se os níveis de açúcar (glicose) na sangue são muito baixos (menos de 50 mg/dl)
- se os níveis de açúcar (glicose) na sangue são muito altos (mais de 400 mg/dl)
- se tem menos de 16 anos. (Para adolescentes de 16 anos ou mais, ver secção “O seu médico terá especial cuidado com Actilyse”).
O seu médico terá especial cuidado com Actilyse
- se teve alguma reação alérgica diferente a uma reação alérgica repentina e potencialmente mortal (hipersensibilidade grave) ao princípio ativo alteplase ou a qualquer um dos outros componentes deste medicamento (incluídos na secção 6)
- se tem ou teve recentemente qualquer outro distúrbio que aumente o risco de hemorragia, tal como:
- traumatismo menor
- biópsia (um procedimento utilizado para obter amostras de tecidos)
- punção de vasos maiores
- injeção intramuscular
- massagem cardíaca externa
- se lhe foi administrado Actilyse alguma vez
- se tem mais de 65 anos de idade
- se tem mais de 80 anos de idade, pode ter um pior resultado independentemente do tratamento com Actilyse. No entanto, em geral o benefício-riesgo com Actilyse em pacientes de mais de 80 anos é positivo e a idade por si só não constitui uma barreira para o tratamento com Actilyse
- se é um adolescente de 16 anos ou mais, deve ser avaliada cuidadosamente a relação benefício-riesgo de forma individual para o tratamento de acidente vascular cerebral isquémico agudo
Outros medicamentos e Actilyse
Informa ao seu médico se está a utilizar ou utilizou recentemente outros medicamentos, mesmo os adquiridos sem receita. É especialmente importante que informe ao seu médico se está a utilizar ou utilizou recentemente:
- medicamentos utilizados para "diluir" a sangue, incluindo:
- ácido acetilsalicílico
- warfarina
- cumarina
- heparina
- alguns medicamentos utilizados para tratar a pressão arterial alta (inibidores do Enzima Conversor de Angiotensina, ECA)
Gravidez, lactação e fertilidade
Se está grávida ou em período de lactação, acha que pode estar grávida ou tem intenção de engravidar, consulte o seu médico. O seu médico lhe administrará Actilyse apenas se os benefícios esperados superarem o risco para o seu bebé.
3. Como é administrado Actilyse
Actilyse será preparado e administrado por um médico ou um profissional de saúde. Não está indicado para ser auto-administrado.
O tratamento com Actilyse deve ser iniciado o mais cedo possível após a apresentação dos sintomas.
Há três doenças para as quais Actilyse está indicado:
Ataque cardíaco (infarto agudo de miocárdio)
A dose que lhe será administrada dependerá do seu peso corporal. A dose máxima de Actilyse é 100 mg, mas será inferior se pesar menos de 65 kg.
Pode ser administrado de duas maneiras diferentes:
- Regime de dosificação de 90 minutos, para pacientes tratados durante as 6 horas posteriores à apresentação dos sintomas. Consiste em:
- uma injeção inicial de parte da dose de Actilyse numa veia
- perfusão do resto da dose durante os 90 minutos seguintes.
- Regime de dosificação de 3 horas, para pacientes tratados durante as 6-12 horas posteriores à apresentação dos sintomas. Consiste em:
- uma injeção inicial de parte da dose de Actilyse numa veia
- perfusão do resto da dose durante as 3 horas seguintes.
Além de Actilyse, o seu médico lhe administrará outro medicamento para impedir a formação de coágulos. Este medicamento lhe será administrado assim que possível após o início da dor no peito.
Coágulos de sangue nas artérias dos pulmões (embolia pulmonar aguda maciça)
A dose que lhe será administrada dependerá do seu peso corporal. A dose máxima de Actilyse é 100 mg, mas será inferior se pesar menos de 65 kg.
Normalmente o medicamento é administrado assim:
- uma injeção inicial de parte da dose numa veia
- perfusão do resto da dose durante as 2 horas seguintes.
Após o tratamento com Actilyse, o seu médico começará (ou continuará) o tratamento com heparina (um medicamento utilizado para "diluir" a sangue).
Acidente vascular cerebral causado por um coágulo de sangue numa artéria do cérebro (acidente vascular cerebral isquémico agudo)
Actilyse deve ser administrado durante as 4,5 horas posteriores à apresentação dos primeiros sintomas. Quanto mais cedo receber Actilyse, mais se pode beneficiar do tratamento e menor é a probabilidade de que apareçam efeitos adversos prejudiciais. A dose que lhe será administrada dependerá do seu peso corporal. A dose máxima deste medicamento é 90 mg, mas será inferior se pesar menos de 100 kg. Actilyse é administrado assim:
- uma injeção inicial de parte da dose numa veia
- perfusão do resto da dose durante os 60 minutos seguintes.
Não deve tomar ácido acetilsalicílico durante as primeiras 24 horas após ser tratado de um acidente vascular cerebral com Actilyse. O seu médico pode administrar-lhe uma injeção de heparina se for necessário.
Se tiver alguma outra dúvida sobre o uso deste produto, pergunte ao seu médico ou a um profissional de saúde.
4. Possíveis efeitos adversos
Como todos os medicamentos, este medicamento pode produzir efeitos adversos, embora nem todas as pessoas os sofram.
Os efeitos adversos descritos a seguir foram observados em pacientes a quem foi administrado Actilyse:
Muito frequentes (podem afetar mais de 1 de cada 10 pacientes)
- insuficiência cardíaca - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- hemorragia no cérebro (hemorragia cerebral) após o tratamento de um acidente vascular cerebral causado por um coágulo de sangue numa artéria do cérebro (acidente vascular cerebral isquémico agudo) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- líquido nos pulmões (edema pulmonar)
- sangramento no vaso sanguíneo danificado (como hematoma)
- pressão arterial baixa (hipotensão)
- dor no peito (angina de peito)
Frequentes (podem afetar até 1 de cada 10 pacientes)
- mais ataques cardíacos
- hemorragia no cérebro (hemorragia cerebral) após o tratamento de um ataque cardíaco (infarto de miocárdio) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- paragem dos batimentos cardíacos (paro cardíaco) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- choque (pressão arterial muito baixa) devido a insuficiência cardíaca - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- hemorragia na garganta
- hemorragia no estômago ou intestino, incluindo sangue nos vômitos (hematemese) ou sangue nas fezes (melena ou hemorragia retal), hemorragia nas gengivas
- hemorragia em tecidos corporais causando cardenais purpúreos (equimose)
- hemorragia no trato urinário ou nos órgãos reprodutivos, que pode originar a presença de sangue na urina (hematúria)
- hemorragia ou formação de cardenais (hematoma) no local de injeção
Pouco frequentes (podem afetar até 1 de cada 100 pacientes)
- hemorragia relacionada com o pulmão, como flema manchada com sangue (hemoptise) ou hemorragia no trato respiratório - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- hemorragias nasais (epistaxe)
- batimentos irregulares do coração após que o aporte de sangue ao coração se tenha restaurado
- lesões nas válvulas do coração (regurgitação mitral) ou nas paredes que dividem as cavidades do coração (defeito do tabique ventricular) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- bloqueio repentino de uma artéria dos pulmões (embolia pulmonar), do cérebro (embolia cerebral) e de outras áreas do corpo (embolia sistémica)
- hemorragia na orelha
- diminuição da pressão sanguínea
Raros (podem afetar até 1 de cada 1.000 pacientes)
- hemorragia na camada membranosa que envolve o coração (hemopericárdio) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- hemorragia interna na parte posterior do abdômen (hemorragia retroperitoneal) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- formação de coágulos de sangue em vasos sanguíneos que podem chegar a outros órgãos do corpo (embolismo). Os sintomas dependerão do órgão afetado
- reações alérgicas, por exemplo, erupções (urticária) e erupção, dificuldade para respirar até asma (broncoespasmo), líquido debaixo da pele e da membrana mucosa (angioedema), pressão arterial baixa ou choque – pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- hemorragia no olho (hemorragia ocular)
- desconforto no estômago (náuseas)
Muito raros (podem afetar até 1 de cada 10.000 pacientes)
- reações alérgicas graves (p. ex. anafilaxia que suponha uma ameaça para a vida) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- acontecimentos que afetam o sistema nervoso como por exemplo:
- espasmos (convulsões, ataques)
- dificuldade para falar
- confusão ou delírio (confusão muito grave)
- ansiedade acompanhada de inquietude (agitação)
- depressão
- pensamentos alterados (psicose)
Estes distúrbios costumam ocorrer frequentemente associados a um acidente vascular cerebral causado por um coágulo de sangue ou hemorragia no cérebro.
Frequência não conhecida (não pode ser estimada a partir dos dados disponíveis)
- hemorragia em órgãos internos, por exemplo hemorragia no fígado (hemorragia hepática) - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- formação de cristais de colesterol, que podem chegar a outros órgãos do corpo (embolização por cristais de colesterol). Os sintomas dependerão do órgão afetado - pode ser necessária a interrupção do tratamento
- hemorragia que possa requerer uma transfusão sanguínea
- vômitos
- aumento da temperatura do corpo (febre)
Os pacientes que sofreram uma hemorragia no cérebro ou outros acontecimentos de hemorragias graves podem morrer ou sofrer deficiência permanente.
Comunicação de efeitos adversos
Se experimentar qualquer tipo de efeito adverso, consulte o seu médico ou enfermeiro, mesmo que se trate de possíveis efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Também pode comunicá-los directamente através do Sistema Español de Farmacovigilância de Medicamentos de Uso Humano: www.notificaRAM.es. Mediante a comunicação de efeitos adversos, você pode contribuir para fornecer mais informações sobre a segurança deste medicamento.
5. Conservação de Actilyse
Não é habitual que você precise conservar Actilyse, pois será administrado pelo seu médico.
Mantenha este medicamento fora da vista e do alcance das crianças.
Não conserve a uma temperatura superior a 25 ºC. Conservar no embalagem original para protegê-lo da luz.
Não utilize Actilyse após a data de validade que aparece na etiqueta do frasco e no embalagem. A data de validade é o último dia do mês que se indica.
Solução reconstituída
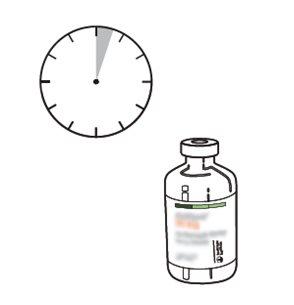
A solução reconstituída demonstrou ser estável durante 24 horas a 2 ºC-8 ºC e durante 8 horas a 25 ºC.
Do ponto de vista microbiológico, o produto deve ser utilizado imediatamente após a reconstituição. Se não for utilizado imediatamente, o período de conservação e as condições de uso antes da sua utilização serão responsabilidade da pessoa que o utilizar e não devem ser superiores a 24 horas a 2-8 ºC.
6. Conteúdo do envase e informação adicional
Composição de Actilyse
- O princípio ativo é alteplasa. Cada frasco contém 10 mg (equivalente a 5.800.000 UI), 20 mg (equivalente a 11.600.000 UI), ou 50 mg (equivalente a 29.000.000 UI) de alteplasa.
A alteplasa é produzida mediante a técnica de ADN recombinante, utilizando uma linha celular ovárica de hámster chinês. Os demais componentes são arginina, ácido fosfórico (para o ajuste do pH) e polissorbato 80.
- O dissolvente é água para preparações injetáveis.
Aspecto do produto e conteúdo do envase
Actilyse é pó e dissolvente para solução injetável e para perfusão. Cada envase contém um frasco com pó e um frasco com dissolvente.
Actilyse está disponível nos seguintes tamanhos de envases:
- um frasco de pó com 10 mg de alteplasa e um frasco com 10 ml de dissolvente.
- um frasco de pó com 20 mg de alteplasa, um frasco com 20 ml de dissolvente e uma cânula de transferência.
- um frasco de pó com 50 mg de alteplasa, um frasco com 50 ml de dissolvente e uma cânula de transferência.
Pode ser que apenas alguns tamanhos de envases estejam comercializados.
Titular da autorização de comercialização
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
55216 Ingelheim am Rhein
Alemanha
Representante local:
Boehringer Ingelheim España, S.A.
Prat de la Riba, 50
08174 Sant Cugat del Vallès (Barcelona)
Espanha
Responsável pela fabricação:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG
Birkendorfer Strasse 65
88397 Biberach/Riss
Alemanha
Boehringer Ingelheim France
100-104 avenue de France
75013 Paris
França
Data da última revisão deste prospecto:09/2024
A informação detalhada e atualizada deste medicamento está disponível na página web da Agência Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A seguinte informação está destinada apenas a profissionais de saúde:
Traçabilidade
Com o objetivo de melhorar a traçabilidade dos medicamentos biológicos, o nome e o número de lote do medicamento administrado devem estar claramente registrados.
Os frascos de 2 mg de alteplasa não estão indicados para serem usados nas indicações de infarto agudo de miocárdio, embolia pulmonar aguda maciça ou acidente vascular cerebral isquêmico agudo (devido ao risco de infra-dosificação maciça). Apenas os frascos de 10 mg, 20 mg e 50 mg estão indicados para serem usados nessas indicações.
Reconstituição
Para obter uma concentração final de 1 mg de alteplasa por ml após a reconstituição, deve-se transferir todo o volume do dissolvente fornecido para o frasco que contém o pó de Actilyse. Com este propósito, deve-se utilizar a cânula de transferência que é incluída nos tamanhos de envases de 20 mg e 50 mg. Para a apresentação de 10 mg, deve-se utilizar uma seringa.
Para obter uma concentração final de 2 mg de alteplasa por ml após a reconstituição, apenas deve-se utilizar a metade do dissolvente fornecido (segundo a tabela abaixo). Nesses casos, sempre deve-se utilizar uma seringa para transferir a quantidade necessária de dissolvente para o frasco que contém o pó de Actilyse.
O conteúdo de um frasco para injeção de Actilyse (10 mg, 20 mg ou 50 mg) deve ser dissolvido sob condições assépticas com água para preparações injetáveis, segundo a tabela seguinte, para obter uma concentração final de alteplasa de 1 mg/ml ou de 2 mg/ml:
Actilyse substância seca | 10 mg | 20 mg | 50 mg |
(a) Volume de água esterilizada para preparações injetáveis que deve ser adicionado à substância seca | 10 ml | 20 ml | 50 ml |
Concentração final: | 1 mg alteplasa/ml | 1 mg alteplasa/ml | 1 mg alteplasa/ml |
(b) Volume de água esterilizada para preparações injetáveis que deve ser adicionado à substância seca | 5 ml | 10 ml | 25 ml |
Concentração final: | 2 mg alteplasa/ml | 2 mg alteplasa/ml | 2 mg alteplasa/ml |
A solução reconstituída deve ser administrada a seguir por via intravenosa. A solução reconstituída de 1 mg/ml pode ser diluída adicionalmente com uma solução injetável estéril de cloreto de sódio 9 mg/ml (0,9%) até uma concentração mínima de 0,2 mg/ml, pois não se pode excluir a aparência de turbidez da solução reconstituída. Não se recomenda a diluição adicional da solução reconstituída de 1 mg/ml com água esterilizada para preparações injetáveis ou, em geral, o uso de soluções de carboidratos para perfusão, p. ex. dextrose, devido ao aumento da formação de turbidez na solução reconstituída. Actilyse não deve ser misturado com outros medicamentos no mesmo frasco de perfusão (nem mesmo com heparina).
Para condições de conservação, por favor, ver seção 5 do prospecto.
A solução reconstituída é de administração única. Qualquer fração de solução não utilizada deve ser descartada.
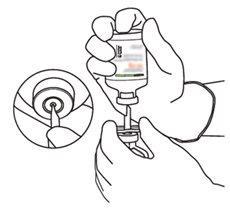
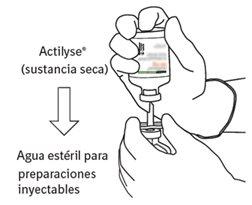
Instruções para reconstituir Actilyse
1 | Reconstituir imediatamente antes de sua administração. |
|
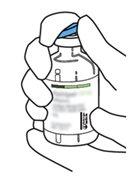
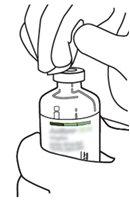
2 | Retirar as tampas protetoras dos dois frascos que contêm água estéril e Actilyse substância seca, respectivamente, puxando-as para cima com um dedo. |
|
3 | Limpar o tampão de borracha de cada um dos frascos com uma toalha com álcool. |
|
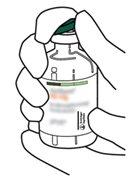
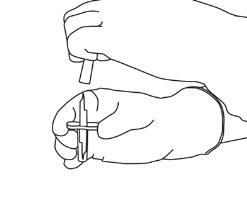
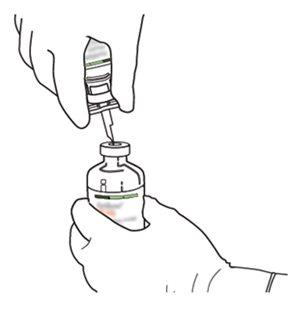
4 | Sacar a cânula de transferência* de seu envoltório. Não desinfetar nem esterilizar a cânula de transferência; é estéril. Retirar a tampa. |
|
5 | Mantenha o frasco de água estéril vertical sobre uma superfície estável. Diretamente de cima, perfure o tampão de borracha verticalmente no centro do tampão com a cânula de transferência, pressionando com cuidado, mas firmemente, sem girar. |
|
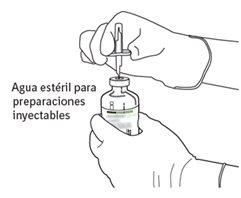
6 | Segure o frasco de água estéril e a cânula de transferência firmemente com uma mão, utilizando as duas solapas laterais. Retire a tampa restante da parte superior da cânula de transferência. |
|
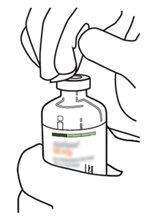
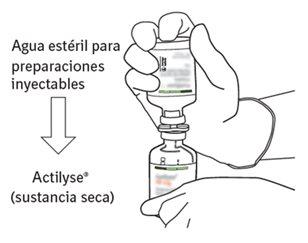
7 | Segure o frasco de água estéril e a cânula de transferência firmemente com uma mão, utilizando as duas solapas laterais. Segure o frasco com Actilyse substância seca verticalmente acima da cânula de transferência e posicione a ponta da cânula de transferência justo no centro do tampão. Pressione o frasco com a substância seca para baixo com a cânula de transferência diretamente de cima, perfurando o tampão de borracha verticalmente e com cuidado, mas firmemente, sem girar. |
|
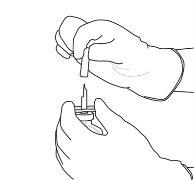
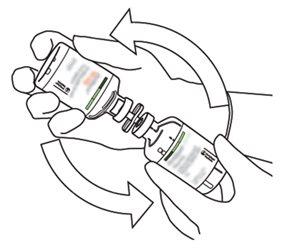
8 | Inverta os dois frascos e permita que a água drene completamente na substância seca. |
|
9 | Retire o frasco de água vazio junto com a cânula de transferência. Eles podem ser descartados. |
|
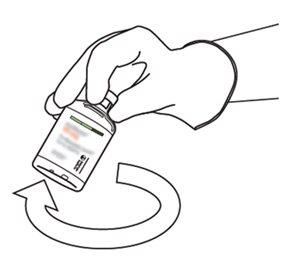
10 | Pegue o frasco com Actilyse reconstituído e gire-o com cuidado para dissolver qualquer pó restante, mas não agite, pois isso produzirá espuma. Se houver bolhas, mantenha a solução imóvel durante alguns minutos para permitir que desapareçam. |
|
11 | A solução reconstituída contém 1 mg/ml de alteplasa. Deve ser límpida e incolora a amarela clara e não deve conter nenhuma partícula. | |
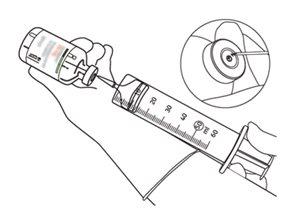
12 | Extraia a quantidade necessária apenas utilizando uma agulha e uma seringa. Não utilize a zona de punção da cânula de transferência para evitar perdas. |
|
13 | Utilize imediatamente. Descarte a solução não utilizada. |
(* Se incluída no kit uma cânula de transferência. A reconstituição também pode ser realizada com uma seringa e uma agulha.)
Posologia e forma de administração
Infarto agudo de miocárdio
Posologia
- Regime de dosificação de 90 minutos (acelerado) para pacientes com infarto agudo de miocárdio, nos quais possa ser iniciado o tratamento dentro de 6 horas após a apresentação dos sintomas.
Em pacientes com peso corporal ≥ 65 kg:
Volume a administrar em função da concentração de alteplasa | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
15 mg em forma de bolo intravenoso, imediatamente seguido de | 15 ml | 7,5 ml |
50 mg em forma de perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante os primeiros 30 minutos, imediatamente seguido de | 50 ml | 25 ml |
35 mg em forma de perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante 60 minutos, até uma dose máxima total de 100 mg | 35 ml | 17,5 ml |
Em pacientes com peso corporal <65 kg, a dose total deve ser ajustada ao peso da seguinte forma:< p>
Volume a administrar em função da concentração de alteplasa | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
15 mg em forma de bolo intravenoso, imediatamente seguido de | 15 ml | 7,5 ml |
0,75 mg/kg de peso corporal (p.c.) em forma de perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante os primeiros 30 minutos, imediatamente seguido de | 0,75 ml/kg p.c. | 0,375 ml/kg p.c. |
0,5 mg/kg de peso corporal (p.c.) em forma de perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante 60 minutos | 0,5 ml/kg p.c. | 0,25 ml/kg p.c. |
- Regime de dosificação de 3 horas para pacientes com infarto agudo de miocárdio nos quais possa ser iniciado o tratamento entre 6 e 12 horas após a apresentação dos sintomas.
Em pacientes com peso corporal ≥ 65 kg:
Volume a administrar em função da concentração de alteplasa | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg em forma de bolo intravenoso, imediatamente seguido de | 10 ml | 5 ml |
50 mg em forma de perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante a primeira hora, imediatamente seguido de | 50 ml | 25 ml |
40 mg em forma de perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante 2 horas, até uma dose máxima total de 100 mg | 40 ml | 20 ml |
Em pacientes com peso corporal <65 kg:< p>
Volume a administrar em função da concentração de alteplasa | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg em forma de bolo intravenoso, imediatamente seguido de | 10 ml | 5 ml |
uma perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante 3 horas até uma dose máxima total de 1,5 mg/kg p.c. | 1,5 ml/kg p.c. | 0,75 ml/kg p.c. |
Tratamento coadjuvante: Recomenda-se tratamento antitrombótico coadjuvante em conformidade com as diretrizes internacionais atuais para o tratamento de pacientes com infarto de miocárdio com elevação do ST.
Forma de administração
A solução reconstituída deve ser administrada por via intravenosa e é para uso imediato.
Os frascos de 2 mg de alteplasa não estão indicados para serem usados nesta indicação.
Embolia pulmonar aguda maciça
Posologia
Em pacientes com peso corporal ≥ 65 kg:
Deve ser administrada uma dose total de 100 mg de alteplasa em 2 horas. O seguinte regime de dosificação é com o qual se tem maior experiência:
Volume a administrar em função da concentração de alteplasa | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg em forma de bolo intravenoso durante 1-2 minutos, imediatamente seguido de | 10 ml | 5 ml |
90 mg como perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante 2 horas até uma dose máxima total de 100 mg | 90 ml | 45 ml |
Em pacientes com peso corporal <65 kg:< p>
Volume a administrar em função da concentração de alteplasa | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg em forma de bolo intravenoso durante 1-2 minutos, imediatamente seguido de | 10 ml | 5 ml |
uma perfusão intravenosa a velocidade constante durante 2 horas até uma dose máxima total de 1,5 mg/kg p.c. | 1,5 ml/kg p.c. | 0,75 ml/kg p.c. |
Tratamento coadjuvante: Após o tratamento com Actilyse, deve ser iniciado (ou retomado) um tratamento com heparina se os valores aPTT forem inferiores ao dobro do limite superior normal. A perfusão deve ser ajustada para manter os valores de aPTT no intervalo de 50 – 70 segundos (de 1,5 a 2,5 vezes o valor de referência).
Forma de administração
A solução reconstituída deve ser administrada por via intravenosa e é para uso imediato.
Os frascos de 2 mg de alteplasa não estão indicados para serem usados nesta indicação.
Acidente vascular cerebral isquêmico agudo
O tratamento só deve ser realizado sob a responsabilidade e supervisão de um médico treinado e com experiência em cuidados neurovasculares, ver Ficha técnica seção 4.3 contraindicações e 4.4 advertências e precauções especiais de emprego.
O tratamento com Actilyse deve ser iniciado o mais rápido possível dentro de 4,5 horas após a apresentação dos sintomas (ver Ficha técnica seção 4.4). Além de 4,5 horas após a apresentação dos sintomas de acidente vascular cerebral, há uma relação benefício-riesgo negativa associada ao tratamento com Actilyse e não deve ser administrado (ver Ficha técnica seção 5.1).
Posologia
A dose total recomendada é de 0,9 mg de alteplasa/kg de peso corporal (até um máximo de 90 mg) começando com um 10% da dose total em forma de bolo intravenoso inicial, imediatamente seguido do resto da dose total perfundida por via intravenosa durante 60 minutos.
TABELA DE DOSIFICAÇÃO PARA ACIDENTE VASCULAR CEREBRAL ISQUÊMICO AGUDO | |||
Utilizando a concentração padrão recomendada de 1 mg/ml, o volume (ml) a administrar é igual ao valor de dose recomendado (mg) | |||
Peso (kg) | Dose Total (mg) | Dose Bolo (mg) | Dose Perfusão* (mg) |
40 | 36,0 | 3,6 | 32,4 |
42 | 37,8 | 3,8 | 34,0 |
44 | 39,6 | 4,0 | 35,6 |
46 | 41,4 | 4,1 | 37,3 |
48 | 43,2 | 4,3 | 38,9 |
50 | 45,0 | 4,5 | 40,5 |
52 | 46,8 | 4,7 | 42,1 |
54 | 48,6 | 4,9 | 43,7 |
56 | 50,4 | 5,0 | 45,4 |
58 | 52,2 | 5,2 | 47,0 |
60 | 54,0 | 5,4 | 48,6 |
62 | 55,8 | 5,6 | 50,2 |
64 | 57,6 | 5,8 | 51,8 |
66 | 59,4 | 5,9 | 53,5 |
68 | 61,2 | 6,1 | 55,1 |
70 | 63,0 | 6,3 | 56,7 |
72 | 64,8 | 6,5 | 58,3 |
74 | 66,6 | 6,7 | 59,9 |
76 | 68,4 | 6,8 | 61,6 |
78 | 70,2 | 7,0 | 63,2 |
80 | 72,0 | 7,2 | 64,8 |
82 | 73,8 | 7,4 | 66,4 |
84 | 75,6 | 7,6 | 68,0 |
86 | 77,4 | 7,7 | 69,7 |
88 | 79,2 | 7,9 | 71,3 |
90 | 81,0 | 8,1 | 72,9 |
92 | 82,8 | 8,3 | 74,5 |
94 | 84,6 | 8,5 | 76,1 |
96 | 86,4 | 8,6 | 77,8 |
98 | 88,2 | 8,8 | 79,4 |
100+ | 90,0 | 9,0 | 81,0 |
*administrado numa concentração de 1mg/ml durante 60 min a uma velocidade de perfusão constante.
Tratamento coadjuvante:a segurança e eficácia deste regime com a administração concomitante de heparina ou inibidores da agregação plaquetária como o ácido acetilsalicílico durante as primeiras 24 horas após a apresentação dos sintomas não foram suficientemente investigadas. Por isso, a administração de heparina intravenosa ou inibidores da agregação plaquetária como o ácido acetilsalicílico deve ser evitada nas primeiras 24 horas após o tratamento com Actilyse devido a um aumento do risco de hemorragia. Se for necessária heparina para outras indicações (p. ex. prevenção da trombose venosa profunda) a dose não deve exceder as 10.000 UI por dia, administrada por via subcutânea.
Forma de administração
A solução reconstituída deve ser administrada por via intravenosa e é para uso imediato.
Os frascos de 2 mg de alteplase não estão indicados para ser usados nesta indicação.
População pediátrica
A experiência com o uso de Actilyse em crianças e adolescentes é limitada. Actilyse está contraindicado no tratamento do acidente vascular cerebral isquémico agudo em crianças e adolescentes menores de 16 anos (ver Ficha técnica seção 4.3). A dose em adolescentes entre 16 e 17 anos é a mesma que para os adultos (ver Ficha técnica seção 4.4 para ver as recomendações das técnicas de imagem prévias que devem ser utilizadas).
Os adolescentes de 16 anos ou mais devem ser tratados de acordo com as instruções de uso do prospecto para a população adulta após a obtenção de imagens mediante técnicas apropriadas para descartar falsos acidentes vasculares cerebrais e confirmar a oclusão arterial correspondente ao déficit neurológico.
- País de registo
- Substância ativa
- Requer receita médicaSim
- Fabricante
- Esta informação é apenas para referência e não constitui aconselhamento médico. Consulte sempre um médico antes de tomar qualquer medicamento. A Oladoctor não se responsabiliza por decisões médicas baseadas neste conteúdo.
- Alternativas a ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusãoForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 1500 UISubstância ativa: apadamtase alfa and cinaxadamtase alfaFabricante: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgRequer receita médicaForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 500 UISubstância ativa: apadamtase alfa and cinaxadamtase alfaFabricante: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgRequer receita médicaSubstância ativa: protein CFabricante: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgRequer receita médica
Alternativas a ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão noutros países
As melhores alternativas com o mesmo princípio ativo e efeito terapêutico.
Alternativa a ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão em Polónia
Alternativa a ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão em Ukraine
Médicos online para ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão
Avaliação de posologia, efeitos secundários, interações, contraindicações e renovação da receita de ACTILYSE pó e solvente para solução injetável e para perfusão – sujeita a avaliação médica e regras locais.