
SODIUM OXIBATE NORMON 500 MG/ML ORAL SOLUTION

How to use SODIUM OXIBATE NORMON 500 MG/ML ORAL SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Sodium Oxybate Normon 500 mg/ml Oral Solution EFG
Sodium Oxybate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Sodium Oxybate Normon is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Sodium Oxybate Normon
- How to take Sodium Oxybate Normon
- Possible side effects
- Storing Sodium Oxybate Normon
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Sodium Oxybate Normon is and what it is used for
Sodium Oxybate Normon contains the active substance sodium oxybate. Sodium Oxybate Normon acts by consolidating nocturnal sleep, although its exact mechanism of action is unknown.
Sodium Oxybate Normon is used to treat narcolepsy with cataplexy in adults, adolescents, and children from 7 years of age.
Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder that can include sleep attacks during hours when you are normally awake, as well as cataplexy, sleep paralysis, hallucinations, and insomnia. Cataplexy is the sudden appearance of muscle weakness or paralysis without loss of consciousness, in response to a sudden emotional reaction such as anger, fear, joy, laughter, or surprise.
2. What you need to know before you take Sodium Oxybate Normon
Do not take Sodium Oxybate Normon
- if you are allergic to sodium oxybate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if you have a deficiency of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (a rare metabolic disorder);
- if you have severe depression;
- if you are receiving treatment with opioid or barbiturate medicines.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to take Sodium Oxybate Normon.
- if you have respiratory or pulmonary problems (and especially if you are obese), as Sodium Oxybate Normon has the potential to cause breathing difficulties;
- if you have or have had depression, suicidal thoughts, anxiety, psychosis (a mental disorder that can involve hallucinations, incoherent speech, or disorganized and agitated behavior) or bipolar disorder;
- if you have heart failure, high blood pressure, liver or kidney problems, you may need to have your dose adjusted;
- if you have previously used drugs or abused medicines;
- if you have epilepsy, as the use of Sodium Oxybate Normon is not recommended in this disease;
- if you have porphyria (a rare metabolic disorder).
If you have any of these problems, inform your doctor before taking Sodium Oxybate Normon.
If while taking Sodium Oxybate Normon, you experience nocturnal urine loss and incontinence (both urinary and fecal), confusion, hallucinations, sleepwalking episodes, or abnormal thinking, you must immediately inform your doctor. Although these effects are rare, if they appear, they are usually mild to moderate in nature.
In elderly patients, the doctor will carefully monitor their progress to check if Sodium Oxybate Normon produces the desired effects.
Sodium Oxybate Normon has a well-known potential for abuse. There have been cases of dependence after illicit use of sodium oxybate.
Your doctor will ask you if you have used any drugs before starting to take Sodium Oxybate Normon and while you are taking this medicine.
Children and adolescents
Sodium Oxybate Normon can be taken by adolescents and children from 7 years of age who weigh more than 15 kg.
Sodium Oxybate Normon must not be taken by children under 7 years of age or who weigh less than 15 kg.
If you are a child or adolescent, your doctor will regularly check your body weight.
While the doctor is adjusting the dose, which can take several weeks, parents/caregivers must carefully monitor the child's breathing during the first 2 hours after taking sodium oxybate to assess if there is any breathing anomaly; for example, interruption of breathing during short periods while sleeping, noisy breathing, and a bluish color on the lips and face. If breathing anomalies are observed, medical assistance should be sought and the doctor should be informed as soon as possible. If any anomaly is observed after the first dose, the second dose should not be administered. If no anomaly is observed, the second dose can be administered. The second dose should not be administered before 2.5 hours or after 4 hours after the administration of the first dose.
If you have had or are having unpleasant feelings, especially if you feel very sad or have lost interest in life, it is important that you inform your doctor or caregiver.
Using Sodium Oxybate with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
In particular, Sodium Oxybate Normon must not be used with medicines that induce sleep and medicines that reduce the activity of the Central Nervous System (the Central Nervous System is the part of the body composed of the brain and spinal cord):
You must also inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are using any of the following types of medicines:
- medicines that increase the activity of the central nervous system
- antidepressants
- medicines that can be metabolized in a similar way by the body (e.g., valproate, phenytoin, or ethosuximide, which are used to treat epileptic seizures)
- topiramate (used to treat epilepsy)
If you are taking valproate, your daily dose of Sodium Oxybate Normon will need to be adjusted (see section 3) as it may lead to interactions.
Taking Sodium Oxybate with food, drinks, and alcohol
You must not drink alcohol while taking Sodium Oxybate Normon, as its effects may be increased.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
There have been very few women who have taken Sodium Oxybate Normon during pregnancy, and some of them have had miscarriages. The risk of taking Sodium Oxybate Normon during pregnancy is not known, so it is not recommended for use in pregnant women or women who are trying to become pregnant.
Patients taking Sodium Oxybate Normon must stop breastfeeding, as Sodium Oxybate Normon passes into breast milk. Changes in sleep have been observed in breastfed infants of exposed mothers.
Driving and using machines
Sodium Oxybate Normon may affect you if you drive or use machines. Do not drive, do not use heavy machinery, or do not perform any activity that may be dangerous or that requires mental alertness, for at least 6 hours after taking Sodium Oxybate Normon. When you first start taking Sodium Oxybate Normon and until you know if it makes you sleepy the next day, be extra careful when driving, operating heavy machinery, or doing any other activity that could be dangerous or requires complete mental alertness.
In pediatric patients, doctors, parents, or caregivers are warned that the waiting time for performing activities that require a state of mental alertness, motor coordination, or activities that may have a physical risk may be more than 6 hours, depending on individual sensitivity.
Sodium Oxybate contains sodium
This medicine contains 182.24 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt/cooking salt) per gram. This is equivalent to 9.11% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you need 2 g of Sodium Oxybate Normon or more per day for a prolonged period, especially if you have been advised to follow a low-salt diet (sodium).
This is also relevant for children, where the maximum daily intake is considered proportional to that of adults and is based on energy needs.
3. How to take Sodium Oxybate Normon
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medicine given by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
It is important that you only use the syringe included in the box during the preparation of the doses of Sodium Oxybate Normon. The Sodium Oxybate Normon syringe has a measuring scale in grams; you will see which one has the exact mark for your dose.
Adults: taking Sodium Oxybate Normon alone
- For adults, the recommended initial dose is 4.5 g/day, divided into two separate doses of 2.25 g.
- Your doctor may gradually increase your dose up to a maximum of 9 g/day divided into two separate doses of 4.5 g.
- Take Sodium Oxybate Normon orally twice each night.
- Take the first dose when going to bed and the second dose 2.5 to 4 hours later. You may need an alarm clock to make sure you wake up to take your second dose.
- Food reduces the amount of Sodium Oxybate Normon absorbed by your body. Therefore, it is best to take Sodium Oxybate Normon always at a set time 2-3 hours after meals.
- Prepare both doses before going to bed.
- Take the doses within 24 hours after preparation.
Adolescents and children from 7 years who weigh 15 kg or more: taking Sodium Oxybate Normon alone
For children from 7 years who weigh 15 kg or more, the doctor will calculate the suitable dose based on body weight.
The doctor will calculate the suitable dose for you. Do not exceed the dose that has been prescribed for you.
Adults: taking Sodium Oxybate Normon with valproate
If you are taking valproate with Sodium Oxybate Normon, your doctor will adjust the dose of Sodium Oxybate Normon.
- For adults, the recommended initial dose of Sodium Oxybate Normon when used with valproate is 3.6 g/day, divided into two separate doses of 1.8 g.
- Take the first dose when going to bed and the second dose 2.5 to 4 hours later.
Adolescents and children from 7 years who weigh 15 kg or more: taking Sodium Oxybate Normon with valproate
If you are taking valproate with Sodium Oxybate Normon, your doctor will adjust the dose of Sodium Oxybate Normon.
Liver or kidney problems
- If you have kidney problems, you should take into account the dietary recommendations to reduce sodium intake (salt).
- If you have liver problems, the initial dose should be reduced by half. Your doctor may gradually increase your dose.
Instructions for diluting Sodium Oxybate Normon
The following instructions explain how to prepare Sodium Oxybate Normon. Read the instructions carefully and follow them step by step. Do not let children prepare Sodium Oxybate Normon.
To help you, the Sodium Oxybate Normon package contains 1 bottle of medicine, a graduated syringe, and two dosing cups with child-resistant caps.
Step 1
- Remove the cap from the bottle by pressing down and twisting counterclockwise (to the left).
- After removing the cap, place the bottle upright on a table.
- Keeping the bottle upright, insert the pressure adapter into the neck of the bottle. This should only be done the first time the bottle is opened. The adapter can be left on the bottle for subsequent uses.
- Then, insert the tip of the graduated syringe into the center of the bottle opening and press firmly (See Figure 1).

Step 2
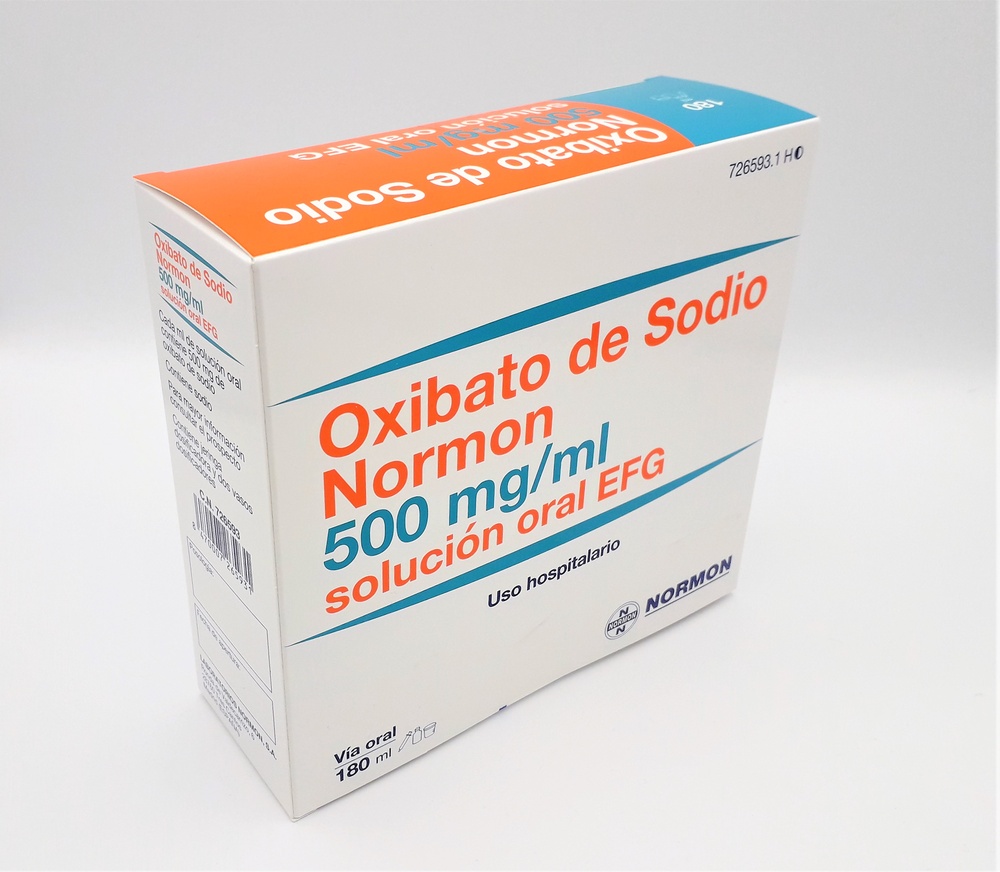
- Keeping the bottle and syringe in one hand, prepare the prescribed dose with the other hand by pulling the plunger. NOTE: The medicine will not flow into the syringe unless you keep the bottle upright (See Figure 2).
Step 3
- Remove the syringe from the center of the bottle opening.
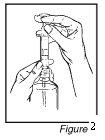
- Empty the medicine from the syringe into one of the provided dosing cups by pushing the plunger (See Figure 3). Repeat this step for the second dosing cup.
- Then add approximately 60 ml of water to each dosing cup (60 ml is approximately 4 tablespoons).
Step 4
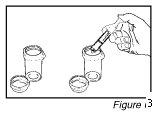
- Put the caps on the dosing cups and turn each cap clockwise (to the right) until you feel the click and close it in the child-resistant position (See Figure 4).
- Rinse the syringe with water.
Just before going to bed:
- Adult patients should place their second dose near their bed.
- Parents or caregivers of adolescents and children from 7 years should not leave the second dose near the child's bed or within their reach.
- You may need an alarm clock to make sure you wake up to take your second dose, no earlier than 2.5 hours and no later than 4 hours after your first dose.
Then:
- Remove the cap from the first dosing cup by pressing on the child-resistant cap and twisting counterclockwise (to the left).
- Drink the first dose sitting in bed, cap the cup, and then lie down immediately. In the case of children who sleep more than 8 hours but less than 12, the first dose can be administered after the child has slept for 1 to 2 hours.
- When you wake up or wake the child between 2.5 and 4 hours later, remove the cap from the second dosing cup. Sitting in bed, drink the second dose just before lying down to continue sleeping. Cap the second cup.
If you think that the effect of Sodium Oxybate Normon is too strong or too weak, tell your doctor or pharmacist.
If you take more Sodium Oxybate Normon than you should
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount taken.
The symptoms of overdose by Sodium Oxybate Normon may include agitation, confusion, altered mobility, breathing difficulties, blurred vision, excessive sweating, headache, vomiting, decreased consciousness that can lead to coma and epileptic seizure, excessive thirst, muscle cramps, and weakness. If you take more Sodium Oxybate Normon than you should, or take it by accident, seek immediate medical help. You should take the medicine box with you, even if it is empty.
If you forget to take Sodium Oxybate Normon
If you forget to take the first dose, take it as soon as you remember and continue with the procedure described previously. If you miss the second dose, skip that dose and do not take Sodium Oxybate Normon again until the next night. Do not take a double dose to make up for the forgotten doses.
If you are not sure if you have taken Sodium Oxybate Normon
In case of doubt about the administration of a dose, do not administer the dose again to reduce the risk of overdose.
If you stop taking Sodium Oxybate Normon
You should continue taking Sodium Oxybate Normon while your doctor continues to prescribe it for you. If the medication is stopped, cataplexy attacks may return, and you may experience insomnia, headache, anxiety, dizziness, sleep disorders, somnolence, hallucinations, and abnormal thinking.
If you stop treatment with Sodium Oxybate Normon for more than 14 days, you should consult your doctor, as you may need to restart treatment with Sodium Oxybate Normon from a lower dose.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them. These are often of mild to moderate intensity.
Adults: most frequent adverse effects observed in clinical studies(occurring in 10% to 20% of patients):
- dizziness
- nausea
- headache.
If you experience any of these adverse effects, inform your doctor immediately.
Children and adolescents: most frequent adverse effects observed in a clinical study:
- bedwetting (18.3%)
- nausea (12.5%)
- vomiting (8.7%)
- weight loss (8.7%)
- decreased appetite (6.7%)
- headache (5.8%)
- dizziness (5.8%)
- suicidal thoughts (1%)
- feeling mentally unwell (loss of contact with reality) (1%)
If you experience any of these adverse effects, inform your doctor immediately.
The adverse effects in adults and children are the same. If you experience any of these adverse effects, inform your doctor immediately:
Very frequent (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- nausea
- dizziness
- headache.
Frequent (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- sleep problems such as insomnia, abnormal dreams, sleep paralysis, somnolence, nightmares, sleepwalking, bedwetting, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty falling asleep in the middle of the night,
- feeling of drunkenness, tremors, confusion or disorientation, blurred vision, balance disorder, falls, feeling of "dizziness" (vertigo),
- feeling heartbeats, increased blood pressure, shortness of breath
- vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea
- anorexia, decreased appetite, weight loss
- weakness, fatigue, sedation
- sweating
- depression
- muscle cramps, swelling
- joint pain, back pain
- attention disorder, sensitivity disorder especially to touch, abnormal touch sensation, abnormal taste
- anxiety, nervousness
- urinary incontinence
- snoring, nasal congestion
- rash
- breast inflammation, nasal and throat inflammation
Infrequent (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- psychosis (a mental disorder that can include hallucinations, incoherent speech or disorganized and agitated behavior)
- paranoia, abnormal thinking, hallucinations, agitation, attempted suicide,
- difficulty falling asleep, restless legs,
- amnesia (memory loss),
- myoclonus (involuntary muscle contractions),
- involuntary bowel movements,
- hypersensitivity
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- seizure
- decrease in depth or frequency of breathing, short cessation of breathing during sleep
- urticaria
- suicidal thoughts, delirium, thoughts of committing violent acts (including harming others)
- irritability, aggression
- euphoric mood
- panic attack
- mania/bipolar disorder
- dry mouth, dehydration
- facial swelling (angioedema)
- bruxism (bruxism and jaw clenching)
- pollakiuria/urinary urgency (increased need to urinate)
- tinnitus (noise in the ears, such as ringing or buzzing)
- sleep-related eating disorder
- increased appetite
- loss of consciousness
- discinesia (e.g., abnormal and uncontrolled movements of the limbs)
- dandruff
- increased sexual desire
- nocturia (excessive urination at night)
- feeling of suffocation
If you experience any of these side effects, inform your doctor immediately.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this prospectus. You can also report it directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Oxibato de sodio Normon
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the bottle after (CAD). The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
After dilution in the dosing cups, the preparation should be used within 24 hours.
Once the Oxibato de sodio Normon bottle is opened, any unused content should be discarded after 40 days.
Medicines should not be thrown away in drains or trash. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Oxibato de sodio Normon
- The active ingredient is oxibato de sodio. Each ml contains 500 mg of oxibato sódico.
- The other components are malic acid, sodium hydroxide, and purified water.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
Oxibato de sodio Normon is presented in a 200 ml amber plastic bottle containing 180 ml of oral solution, closed with a child-resistant cap. Each package contains a bottle, a pressure adapter (PIBA), a graduated plastic syringe (graduated from 0.25 to 0.25 grams with horizontal marks showing doses of 1.5g, 2.25g, 3.0g, 3.75g, and 4.5g) and two dosing cups with child-resistant caps.
Oxibato de sodio Normon is a clear and colorless solution.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
LABORATORIOS NORMON, S.A.
Ronda de Valdecarrizo, 6
28760 Tres Cantos- Madrid (SPAIN)
Your doctor should have given you a package of information about Oxibato de sodio Normon, which includes a leaflet on how to take the medicine, a patient information sheet with Frequently Asked Questions, and a patient alert card.
Date of the Last Revision of this Prospectus: November 2021
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information about this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SODIUM OXIBATE NORMON 500 MG/ML ORAL SOLUTIONDosage form: ORAL SOLUTION/SUSPENSION, 300 mg/mlActive substance: sodium oxybateManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: ORAL SOLUTION/SUSPENSION, 500 mg/mlActive substance: sodium oxybateManufacturer: Zentiva K.S.Prescription requiredDosage form: ORAL SOLUTION/SUSPENSION, 500 mg/mlActive substance: sodium oxybateManufacturer: Laboratorio Reig Jofre, S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for SODIUM OXIBATE NORMON 500 MG/ML ORAL SOLUTION
Discuss questions about SODIUM OXIBATE NORMON 500 MG/ML ORAL SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions













