
FOSCARNET KABI 24 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION

How to use FOSCARNET KABI 24 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Foscarnet Kabi 24 mg/ml Solution for Infusion EFG
foscarnet sodium hexahydrate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Foscarnet Kabi and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Foscarnet Kabi
- How to use Foscarnet Kabi
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Foscarnet Kabi
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Foscarnet Kabi and what is it used for
This medicine belongs to a group of medicines called antivirals. It works on certain viruses [all viruses belonging to the herpes group and some retroviruses such as cytomegalovirus (CMV)]. It prevents the virus from reproducing in infected cells.
Foscarnet is used in people with a weakened immune system:
- To treat CMV retinitis in patients with AIDS.
- To treat herpes infection (of the lips, nose, eyes, and genitals).
- Foscarnet is given to people with CMV infection after a bone marrow transplant. This is also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Sometimes, the infection can be detected before the patient starts to show symptoms. This is known as CMV viremia.
2. What you need to know before you use Foscarnet Kabi
Do not use Foscarnet Kabi:
- If you are allergic to foscarnet or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
ASK YOUR DOCTOR OR PHARMACIST IF YOU ARE NOT SURE.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or nurse before you start using this medicine:
- If you have kidney problems. In this case, your doctor may adjust the dose according to your condition.
- If you have low calcium levels in your blood before receiving this medicine, and if you are taking a medicine that reduces calcium levels in your blood.
- If you have heart problems.
- If you have tingling in your hands or lips, and nausea. In this case, your nurse will reduce the infusion rate.
- In case of accidental contact with the product, rinse the exposed skin or mucous membranes (inside the mouth, nose, ears, or genitals) with water.
It is recommended to pay close attention to personal hygiene after urinating: wash the penis (or vulva) with running water to avoid genital lesions (genital ulcers),
Blood tests
Before and during treatment, your doctor may ask you to have blood and urine tests. These tests are intended to check kidney function and mineral levels in the blood.
Other medicines and Foscarnet Kabi
Tell your doctor or nurse if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines, including those bought without a prescription and herbal medicines. This is because foscarnet can affect how some medicines work and some medicines can have effects on foscarnet.
In particular, tell your doctor or nurse if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Pentamidine (for infections).
- Amphotericin B (for fungal infections).
- Aciclovir (for viral infections).
- Antibiotics called aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin or streptomycin (for infections).
- Cyclosporin A, methotrexate, or tacrolimus (used to suppress the immune system).
- Protease inhibitors, such as ritonavir and saquinavir.
- Quinidine, amiodarone, sotalol, or other medicines that can affect your heart rate and rhythm.
- Anxiolytics (neuroleptics).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
- Foscarnet is not recommended during pregnancy.
- You should avoid becoming pregnant during treatment with foscarnet and should use effective contraceptive methods while being treated with foscarnet and for 7 months after the end of treatment.
- Men treated with foscarnet are advised to use effective contraceptive measures and should not father a child during or up to 4 months after treatment.
- Do not take foscarnet during breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Foscarnet may affect your ability to drive or use machines. This is due to the risk of seizures, abnormal movements, and dizziness reported with this medicine. Consult your doctor before performing these activities.
Foscarnet Kabi contains sodium
This medicine contains 240 micromoles (5.5 mg) of sodium (the main component of table/cooking salt) per ml. This should be taken into account by patients on a controlled sodium diet, so please inform your doctor or nurse if you are on a low-sodium diet.
The maximum recommended dose of this medicine contains 2.89 grams of sodium (present in table salt).
This is equivalent to 144.5% of the maximum daily sodium intake recommended for an adult.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you need foscarnet daily for a prolonged period, especially if you have been advised to follow a low-salt diet.
3. How to use Foscarnet Kabi
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as told by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor again.
- Foscarnet will be given to you by a doctor or nurse. It will be given as an intravenous infusion. It can be given through a central line in your chest if you already have one in place.
- Each infusion will last at least 1 hour. Do not interfere with the drip during the infusion.
- The dose of foscarnet that you are given will depend on your weight and kidney function.
- It is important to keep a good fluid intake during the infusion, which will also help prevent kidney problems. If necessary, your doctor or nurse will give you the necessary hydration regimen at the same time as the foscarnet infusion.
Personal hygiene
Wash your genitals carefully after urinating. This will help prevent the development of ulcers.
If the foscarnet solution comes into contact with the skin or eyes
If the foscarnet solution accidentally comes into contact with the skin or eyes, wash the affected area immediately with water.
If you use more Foscarnet Kabi than you should
If you are given a very high dose of foscarnet, tell your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
If you think you have been given too much foscarnet, inform your doctor immediately.
In case of overdose, consult your doctor or pharmacist or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount administered.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be serious and need immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions, including low blood pressure, shock, and skin swelling (angioedema). These are known as hypersensitivity, anaphylactic, or anaphylactoid reactions.
- Severe skin rashes. These rashes can be associated with redness, swelling, and blisters on the skin, mouth, throat, eyes, and other areas inside the body, and can sometimes be fatal. They are called erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
If you experience any of the above side effects, tell your doctor immediately or go to the nearest emergency unit.
Other side effects include:
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- Reduced red blood cell count (shown in blood tests). You may feel tired or look pale.
- Low white blood cell count (granulocytopenia). Signs include infections and high temperature (fever).
- Low potassium levels in the blood.
- Low magnesium levels in the blood.
- Low calcium levels in the blood.
- Dizziness.
- Headache.
- Tingling.
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Feeling weak or tired.
- High temperature or chills.
- Skin rash.
- Changes in kidney function (shown in blood tests), such as increased creatinine, decreased hemoglobin concentration.
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Low white blood cell count (leucopenia and/or neutropenia). Signs include infections and high temperature (fever).
- Low platelet count in the blood. This can make you bruise more easily.
- Generalized infection (sepsis).
- Increased or decreased phosphate levels in the blood.
- Low sodium levels in the blood.
- High calcium levels in the blood.
- Dehydration.
- Abnormal liver function.
- Elevated liver enzymes (gamma-GT, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), LDH).
- Mood changes. These include aggression, agitation, anxiety, confusion, depression, nervousness.
- Abnormal movement coordination.
- Seizures.
- Reduced skin sensitivity.
- Abnormal heartbeats (palpitations).
- Fast heart rate (tachycardia).
- Nerve disorders that can cause sensory changes or muscle weakness (neuropathy).
- Tremors.
- High blood pressure.
- Low blood pressure, which can cause dizziness.
- Swelling, pain, and redness along a vein.
- Abdominal pain, constipation, and indigestion.
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) or changes in pancreatic function. Signs include severe stomach pain and changes in blood tests (elevated lipase).
- Itching of the skin.
- Muscle pain.
- Kidney disorders, such as kidney pain (lower back pain), kidney failure, protein in the urine.
- Pain when urinating.
- Genital ulcers. These are isolated or multiple lesions that resolve when treatment is stopped (see "Warnings and precautions").
- General discomfort.
- Pain and inflammation at the injection site.
- Swelling of hands and feet.
- Changes in heart function tests (ECG).
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Reduced red, white, and platelet blood cell count.
- Too much acid in the blood. This can make you breathe faster.
- Itchy rash (urticaria)
- Kidney and urinary disorders (renal tubular disorder, glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome).
- Increased levels of certain blood enzymes, such as amylase, creatine, and phosphokinase.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Abnormal heartbeats.
- Diabetes. Signs include urinating more often than usual. More rarely, you may also feel extremely thirsty.
- High sodium levels in the blood.
- Encephalopathy.
- Abnormal heartbeats or changes in heart rate, such as torsade de pointes.
- Muscle problems: muscle weakness, muscle tissue destruction (rhabdomyolysis: abnormal urine color and severe muscle stiffness, sensitivity, or weakness).
- Kidney problems, such as pain, blood in urine, tubular necrosis, crystal nephropathy.
- Extravasation.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System for Human Use: https://www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Foscarnet Kabi
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
- Do not refrigerate or freeze. If stored in the refrigerator or exposed to temperatures below freezing point, it may precipitate. This precipitate can be redissolved by keeping the vial at room temperature and shaking repeatedly.
- Chemical and physical stability in use of the product has been demonstrated for 9 days at 25 °C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately unless opening and dilution have been carried out under aseptic conditions. If not used immediately, the in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
- Foscarnet can be mixed with another liquid by a pharmacist. This is to provide you with a ready-to-use medicine. The pharmacist will inform you about how to store and when to use the medicine.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Foscarnet Kabi
The active ingredient is foscarnet.
Each ml contains 24 mg of foscarnet sodium hexahydrate
The other components are water for injectable preparations and hydrochloric acid.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
Foscarnet is a sterile solution for infusion.
The solution is transparent and colorless.
Foscarnet is presented in 250 ml vials.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U
Torre Mapfre – Vila Olímpica
Marina 16-18
08005 Barcelona
Spain
Manufacturer
Fresenius Kabi Austria GmbH
Hafnerstrasse 36
A-8055 Graz
Austria
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Belgium: Foscarnet Fresenius Kabi 24 mg/ml oplossing voor infusie; Foscarnet Fresenius Kabi 24 mg/ml solution pour perfusion; Foscarnet Fresenius Kabi 24 mg/ml Infusionslösung
France: FOSCARNET KABI 24 mg/ml, solution pour perfusion
Germany: Foscarnet Kabi 24 mg/ml Infusionslösung
Italy: Foscarnet Kabi
Luxembourg: Foscarnet Sodium 24 mg/ml Solution for Infusion
Portugal: Foscarneto sódico Kabi
Spain: Foscarnet Kabi 24 mg/ml solución para perfusión EFG
United Kingdom: Foscarnet Sodium 24 mg/ml Solution for Infusion
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet:August 2022
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
Be especially careful with Foscarnet Kabi
- In patients with impaired renal function:
- Serum creatinine must be regularly monitored.
- A dose adjustment should be anticipated in patients with altered renal function. To avoid changes in renal function that may occur during treatment, adequate hydration should be maintained.
- Do not use solutions that may contain calcium.
- In case of accidental contact, rinse the exposed skin or mucous membranes with water.
Method of Administration
Foscarnet must be administered solely by the intravenous route, either through a central venous line (catheter) or in a peripheral vein.
Precaution: Do not administer foscarnet by rapid intravenous injection.
Do not administer foscarnet without a hydration regimen.
Do not use solutions that may contain calcium, 30% glucose, amphotericin B, sodium acyclovir, ganciclovir, pentamidine isethionate, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and vancomycin hydrochloride.
As with all infusions, strict aseptic conditions must be observed during handling.
When using peripheral veins, the foscarnet 24 mg/ml solution must be diluted. Hospital pharmacy services must aseptically transfer the individually dispensed foscarnet doses to plastic infusion bags and dilute them in equal parts of 0.9% sodium chloride (9 mg/ml) or 5% dextrose (50 mg/ml). The physicochemical stability of foscarnet, foscarnet dilutions, and their dilutions in PVC bags is 9 days. The diluted solutions should be used as soon as possible after preparation but can be stored for up to 24 hours if kept refrigerated.
The renal toxicity of foscarnet can be reduced with adequate patient hydration. See the "Hydration" section below.
If a Y-infusion system is used, simultaneously infuse 0.5 to 1 liter of 0.9% NaCl or 5% glucose.
Do not administer other products in the same infusion. When the product is administered by infusion in a peripheral vein, simultaneous intravenous hydration serves as dilution (see "Hydration" section).
Diagram of a Y-infusion system
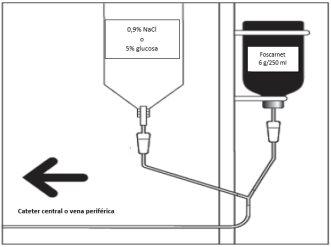
Hydration:
Special attention should be paid to the importance of preventing foscarnet's renal toxicity by ensuring that patients receive adequate hydration.
If a Y-infusion system is used, 0.5 to 1 liter of 0.9% NaCl or 5% glucose should be infused simultaneously. In patients who meet the requirements, oral hydration with similar hydration regimens has been used. Clinically dehydrated patients should have their condition corrected before starting treatment with foscarnet.
Each vial of foscarnet should only be used to treat a single patient with a single infusion.
Accidental contact of the foscarnet sodium solution with the skin or eyes may cause local irritation and a burning sensation. In case of accidental contact, the affected area should be rinsed with water.
Foscarnet that has been refrigerated or exposed to temperatures below the freezing point may precipitate. By keeping the vial at room temperature with constant agitation, the precipitate can be converted back into a solution.
Disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FOSCARNET KABI 24 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 24 mg/mlActive substance: foscarnetManufacturer: Laboratorios Tillomed Spain S.L.UPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 24 mg foscarnet sodium/mlActive substance: foscarnetManufacturer: Clinigen Healthcare B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 300 mgActive substance: abacavirManufacturer: Tarbis Farma S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for FOSCARNET KABI 24 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about FOSCARNET KABI 24 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















