
XEOMIN 200 Units Powder for Injectable Solution

How to use XEOMIN 200 Units Powder for Injectable Solution
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
XEOMIN 50 units powder for solution for injection
XEOMIN 100 units powder for solution for injection
XEOMIN 200 units powder for solution for injection
Botulinum toxin type A (150 kD), a neurotoxin without complexing proteins
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What XEOMIN is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use XEOMIN
- How to use XEOMIN
- Possible side effects
- Storage of XEOMIN
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What XEOMIN is and what it is used for
XEOMIN is a medicine that contains the active substance botulinum toxin type A, which relaxes the muscles into which it is injected or reduces saliva production at the site of administration.
XEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of the following conditions in adults:
- eyelid spasms (blepharospasm) and spasms affecting one side of the face (hemifacial spasm)
- neck twisting (cervical dystonia)
- increased muscle tension/uncontrollable muscle stiffness in shoulders, arms, and/or hands (upper limb spasticity)
- chronic drooling (sialorrhea) due to neurological disorders
XEOMIN is indicated for the treatment of chronic drooling (sialorrhea) in children and adolescents aged 2 to 17 years and weighing 12 kg or more due to neurological disorders/developmental neurological disorders.
2. What you need to know before you use XEOMIN
Do not use XEOMIN
? if you are allergic to botulinum toxin type A or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
? if you have a generalized disorder of muscle activity (e.g., myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome)
? if you have an infection or inflammation at the proposed injection site
Warnings and precautions
Side effects can occur due to misplaced injections of botulinum toxin type A that temporarily paralyze nearby muscle groups. Very rare reports of side effects have been produced that may be related to the spread of the botulinum toxin outside the injection site to produce symptoms consistent with the effects of botulinum toxin type A (e.g., excessive muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, or accidental ingestion of food or drink into the airways). Patients who receive the recommended doses may experience excessive muscle weakness.
If the dose is too high or the injections are too frequent, the risk of antibody formation may increase. Antibody formation can cause treatment with botulinum toxin type A to fail, regardless of the indication for which it is intended.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist before using XEOMIN:
? if you have any bleeding disorder
? if you are taking substances that prevent blood clotting (e.g., coumarin, heparin, acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel)
? if the muscles to be injected show pronounced weakness or decreased muscle volume
? if you have amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), which can lead to muscle tissue loss
? if you have any disease that alters the interaction between nerves and skeletal muscles (peripheral neuromuscular disorder)
? if you have difficulty swallowing
? if you have had seizures
? if you have had problems with botulinum toxin type A injections in the past
? if you are going to undergo surgery
If you experience any of the following symptoms, contact your doctor and seek immediate medical attention:
- difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking
- hives, swelling including swelling of the face or throat, wheezing,
feeling of fainting and difficulty breathing (possible symptoms of severe allergic reactions)
Repeated injections with XEOMIN
If you receive repeated injections with XEOMIN, the effect may increase or decrease. The possible reasons are:
? your doctor may follow a different procedure when preparing the solution for injection
? different treatment intervals
? injections into a different muscle
? marginal variation in the efficacy of the active substance of XEOMIN
? absence of response/failure of therapy during treatment.
Eyelid spasms (blepharospasm) and spasms affecting one side of the face (hemifacial spasm)
Tell your doctor before using XEOMIN if:
? you have had previous eye surgery. Your doctor will take the necessary precautions
? you are at risk of developing a disease called narrow-angle glaucoma. This disease can cause an increase in the internal pressure of the eye and can lead to damage to the optic nerve. Your doctor will know if you are at risk.
During treatment, small hemorrhagic spots may occur in the soft tissues of the eyelid. Your doctor can limit this risk by applying gentle compression to the injection site immediately after injection.
After receiving an injection of XEOMIN into the eye muscle, a decrease in blinking may occur, which can lead to prolonged exposure of the front transparent part of the eye (cornea). This exposure can cause surface damage and inflammation (corneal ulceration).
Neck twisting (cervical dystonia)
After injection, you may develop difficulty swallowing, which can lead to breathing problems and may pose a greater risk of inhaling liquids or foreign substances. Foreign substances in your lungs can cause inflammation or infection (pneumonia). Your doctor will provide special treatment if needed (e.g., artificial nutrition).
Difficulty swallowing may last from two to three weeks after injection, but a case has been described where it lasted up to five months.
If you have been inactive for a long period, you should gradually resume activity after XEOMIN injection.
Increased muscle tension and/or uncontrollable muscle stiffness
XEOMIN can be used to treat muscle tension and stiffness in different parts of the upper limb, for example, your arm or hand. XEOMIN is effective in combination with usual treatment methods. XEOMIN should be used in conjunction with these other methods.
It is unlikely that this medicine can increase the range of motion of joints where the surrounding muscle has lost its ability to stretch.
If you have been inactive for a long period, you should gradually resume activity after XEOMIN injection.
Chronic drooling (sialorrhea)
Some medications (e.g., clozapine, aripiprazole, pyridostigmine) can cause excessive saliva production. First, consider replacing, reducing, or even interrupting this medication before using XEOMIN as treatment for drooling. The use of XEOMIN to reduce medication-induced drooling has not been investigated.
Your doctor will consider a dose reduction if "dry mouth" cases develop in association with XEOMIN administration.
When your saliva flow is reduced by XEOMIN, oral health problems such as tooth decay may occur or existing problems may worsen. Contact a dentist when you start using XEOMIN for the treatment of chronic drooling. If necessary, your dentist may decide to take measures for caries prevention.
Children and adolescents
Do not use this medicine in children under 2 years of age, with a weight below 12 kg, or in children and adolescents for treatments other than chronic drooling, as the use of XEOMIN has not been established in this population and is not recommended.
Other medicines and XEOMIN
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
The effect of XEOMIN may be enhanced:
? by medicines used to treat certain infectious diseases (e.g., spectinomycin or aminoglycoside antibiotics [e.g., neomycin, kanamycin, tobramycin])
? by other medicines that relax muscles (e.g., tubocurarine-type muscle relaxants) These medicines are used, for example, for general anesthesia. Before undergoing surgery, tell your anesthesiologist if you have received XEOMIN.
? when used for the treatment of chronic drooling: with other medicines that reduce saliva flow by themselves (e.g., anticholinergics such as atropine, glycopyrrolate, or scopolamine) or by therapeutic radiation to the head and neck, including the salivary glands. Tell your doctor if you are receiving or plan to receive radiation therapy.
In these cases, XEOMIN should be used with caution.
The effect of XEOMIN may be reduced by the use of certain medicines for malaria and rheumatism (known as aminoquinolines).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
XEOMIN should not be used during pregnancy, unless your doctor decides that the need and potential benefit justify the possible risk to the fetus.
XEOMIN is not recommended during breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or perform other potentially hazardous activities if you have drooping eyelids, weakness (asthenia), muscle weakness, dizziness, or vision disturbances.
If you are unsure, consult your doctor.
3. How to use XEOMIN
XEOMIN can only be administered by healthcare professionals with adequate knowledge and experience in the application of botulinum toxin type A.
Your doctor will choose the best dosage for you, frequency, and optimal number of injection points. The result of the initial treatment with XEOMIN should be evaluated, which may lead to a dose adjustment until the desired therapeutic effect is achieved. The treatment intervals will be determined by your doctor based on your actual clinical need.
If you feel that the effect of XEOMIN is too strong or too weak, tell your doctor. In cases where no therapeutic effect is observed, alternative treatments should be considered.
Eyelid spasms (blepharospasm) and spasms affecting one side of the face (hemifacial spasm)
The recommended initial dose is up to 25 units per eye, and the recommended total dose in subsequent treatment sessions is up to 50 units per eye. The initial effect usually occurs within four days of injection. The effect of each treatment lasts approximately 3 to 5 months; however, the duration can be significantly longer or shorter. Treatments at intervals of less than 12 weeks are not recommended.
Normally, treatment used with a frequency greater than every three months does not confer any additional beneficial effect.
If you have spasms affecting one side of your face (hemifacial spasm), your doctor will follow the treatment recommendations for eyelid spasms (blepharospasm) restricted to one side of the face. Hemifacial spasm will be treated only in the upper part of the face, as XEOMIN injections in the lower part of the face can increase the risk of side effects such as pronounced local weakness.
Neck twisting (cervical dystonia)
The recommended dose per injection site is up to 50 units, and the maximum dose for the first treatment session is 200 units. Your doctor may administer doses of up to 300 units in subsequent sessions depending on the response. The initial effect usually occurs within seven days of injection. The effect of each treatment lasts approximately 3 to 4 months; however, the duration can be significantly longer or shorter. The period between each treatment session should be at least 10 weeks.
Increased muscle tension and/or uncontrollable muscle stiffness in shoulders, arms, or hands (upper limb spasticity)
The recommended dose is up to 500 units per treatment session, and no more than 250 units should be administered in the shoulder muscles. Patients reported the onset of effect at 4 days after the start of treatment. Improvement in muscle tone was observed at 4 weeks. In general, the effect of the treatment lasted 12 weeks. However, the duration can be significantly longer or shorter. The period between each treatment session should be at least 12 weeks.
Chronic drooling (sialorrhea, adults)
The recommended dose is 100 units per treatment session. This maximum dose should not be exceeded. The period between each treatment session should be at least 16 weeks.
Chronic drooling (sialorrhea, children/adolescents)
The recommended dose per treatment session depends on body weight. The maximum dose should not exceed 75 units. The period between each treatment session should be at least 16 weeks.
Method of administration
XEOMIN dissolved is intended for intramuscular injection and injection into the salivary glands (intraglandular use) (see information for healthcare professionals at the end of this leaflet). With regard to the location of the salivary glands in adults, both anatomical landmarks and ultrasound guidance are possible; however, ultrasound guidance should be the preferred method for reasons of efficacy. For children and adolescents, ultrasound guidance should be used. Before injection, local anesthetics (e.g., anesthetic creams), sedation, or combined anesthesia with sedation can be used.
If you are given too much XEOMIN
Overdose symptoms
Overdose symptoms may not be apparent immediately after injection and may include general weakness, drooping eyelids, double vision, difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking, and paralysis of the respiratory muscles or difficulty swallowing that could cause pneumonia.
Measures to be taken in case of overdose
In the event of overdose symptoms, seek immediate medical attention or ask your family members to do so, and try to be hospitalized. Medical supervision may be necessary for several days, and the use of assisted ventilation may be required.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Generally, adverse effects are observed in the first week after treatment and are transient. These effects may be related to the medicine, injection technique, or both. Adverse effects may be restricted to the area surrounding the injection site (e.g., localized muscle weakness, local pain, inflammation, tingling (paresthesia), reduced sensation to touch (hypoesthesia), pain on palpation, inflammation (general), soft tissue inflammation (edema), redness (erythema), itching, localized infection, hematoma, bleeding, and/or bruising).
The injection of the needle can cause pain. This pain or the anxiety caused by needles can lead to fainting, nausea, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), or a drop in blood pressure.
Adverse effects such as excessive muscle weakness or difficulty swallowing may be caused by the relaxation of muscles distant from the XEOMIN injection site. Difficulty swallowing can cause the inhalation of foreign bodies, leading to pulmonary inflammation and, in some cases, death.
An allergic reaction can occur with XEOMIN. Rarely, immediate and/or severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) or allergic reactions to the product's serum (serum sickness) have been reported, causing, for example, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), hives (urticaria), or soft tissue inflammation (edema). Some of these reactions have been observed after the use of the conventional complex of botulinum toxin type A. They occurred when the toxin was administered alone or in combination with other medicines known to cause similar reactions. An allergic reaction can cause any of the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking due to inflammation of the face, lips, mouth, or throat
- inflammation of the hands, feet, or ankles
If you observe any of these adverse effects, please inform your doctor immediately or ask your family members to do so and go to the emergency department of your nearest hospital.
The following adverse effects have been reported with XEOMIN:
Eye Lid Spasm (Blepharospasm)
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
Eye lid drooping (ptosis)
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Dry eyes, blurred vision, difficulty seeing, dry mouth, pain at the injection site
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
Headache, facial muscle weakness (facial paralysis), double vision (diplopia), increased tearing, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), fatigue, muscle weakness, hives
Facial Spasm Affecting One Side of the Face (Hemifacial Spasm)
Similar adverse effects are expected when treating facial spasm affecting one side of the face as for eye lid spasm.
Neck Spasm (Spasmodic Torticollis)
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Neck pain, muscle weakness, musculoskeletal pain (myalgia), musculoskeletal stiffness, muscle spasms, headache, dizziness, pain at the injection site, weakness (asthenia), dry mouth, nausea, increased sweating (hyperhidrosis), upper respiratory tract infection, feeling of fainting (presyncope)
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
Speech disorders (dysphonia), difficulty breathing (dyspnea), hives
Treatment of neck spasm may cause difficulty swallowing, with varying degrees of intensity. This may lead to the inhalation of foreign materials, which may require medical intervention. Difficulty swallowing may persist for two to three weeks after injection, but in one case, it was reported to last five months. Difficulty swallowing appears to depend on the dose.
Increased Muscle Tension and/or Uncontrollable Muscle Stiffness in Shoulders, Arms, or Hands (Upper Limb Spasticity)
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Dry mouth
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
Headache, reduced sensation to touch (hypoesthesia), muscle weakness, pain in the limbs, weakness (asthenia), musculoskeletal pain (myalgia), difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), nausea
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
Pain at the injection site
Chronic Drooling (Sialorrhea) in Adults
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Dry mouth, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), tingling sensation (paresthesia)
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
Thick saliva, speech disorder, taste disorder (dysgeusia)
Persistent dry mouth (> 110 days) of severe intensity has been reported, which could cause additional complications such as gum inflammation (gingivitis), difficulty swallowing, and tooth decay.
Chronic Drooling (Sialorrhea) in Children/Adolescents
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
Dry mouth, thick saliva, oral pain, tooth decay
Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported without a known frequency for the use of XEOMIN since its launch, regardless of the treatment area:
Flu-like symptoms, contraction of the injected muscle, and hypersensitivity reactions such as swelling, soft tissue inflammation (edema, also distant from the injection site), redness, itching, rash (local and generalized), and difficulty breathing.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of XEOMIN
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the box and on the label of the vial after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Unopened vial: Do not store at a temperature above 25°C.
Reconstituted solution: Chemical and physical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the product must be used immediately. If not used immediately, the in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user and normally should not exceed 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C, unless the reconstitution has been carried out under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Your healthcare professional should not use XEOMIN if the solution has a cloudy appearance or contains flocculated or particulate material.
For instructions on disposal, see information for healthcare professionals at the end of this prospectus.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of XEOMIN
- The active ingredient is botulinum toxin type A (150 kD) from Clostridium botulinum,
without complexing proteins.
XEOMIN 50 units powder for solution for injection
A vial contains 50 units of botulinum toxin type A (150 kD) from Clostridium botulinum, without complexing proteins*.
XEOMIN 100 units powder for solution for injection
A vial contains 100 units of botulinum toxin type A (150 kD) from Clostridium botulinum, without complexing proteins*.
XEOMIN 200 units powder for solution for injection
A vial contains 200 units of botulinum toxin type A (150 kD) from Clostridium botulinum, without complexing proteins*.
- Botulinum toxin type A, purified from Clostridium botulinumcultures (Hall strain)
- The other ingredients are: human albumin, sucrose.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
XEOMIN is presented as a powder for solution for injection. The powder is white.
When reconstituted, a clear and colorless solution is produced.
XEOMIN 50 units powder for solution for injection: packs of 1, 2, 3, or 6 vials
XEOMIN 100 units powder for solution for injection: packs of 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 vials
XEOMIN 200 units powder for solution for injection: packs of 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 vials
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbH
Eckenheimer Landstr. 100
D-60318 Frankfurt/Main
Germany
Manufacturer
Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KgaA
Legal address:
Eckenheimer Landstraße 100
60318 Frankfurt/Main
P.O. Box 11 13 53
60048 Frankfurt/Main
Germany
Phone: +49-69/15 03-1
Fax: +49-69/15 03-200
Manufacturing address:
Ludwigstraße 22
64354 Reinheim
Germany
Local representative
Merz Therapeutics Iberia, S.L.U.
Avenida de Bruselas 6
28108 Alcobendas - Madrid
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area with the following names:
XEOMIN: Austria, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Germany, Greece, Finland, France, Hungary, Ireland, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden,
XEOMEEN: Belgium
Date of the last revision of this prospectus:February 2022
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es)
__________________________________________________________________________
The following information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Instructions for Reconstitution of the Solution for Injection:
XEOMIN is reconstituted before use with sodium chloride solution for injection, at a concentration of 9 mg/ml (0.9%).
XEOMIN can only be used for its intended purpose to treat a patient in one session.
It is recommended to carry out the reconstitution of the vial and the preparation of the syringe on plastic-coated paper towels to collect any possible spilled material. With a syringe, an appropriate amount of sodium chloride solution is drawn up (see the dilution table). A 20-27 G needle is recommended for reconstitution. After the vertical insertion of the needle through the rubber stopper, the solvent should be carefully injected into the vial to avoid foam formation. Discard the vial if the vacuum does not aspirate the solvent into the vial. Separate the syringe from the vial and mix XEOMIN with the solvent by carefully rotating/inverting the vial, do not shake vigorously. If necessary, the reconstitution needle should remain in the vial, and the required amount of solution should be drawn up with a new sterile needle suitable for injection.
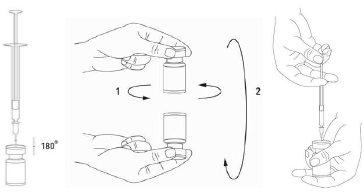
Reconstituted XEOMIN is a clear and colorless solution.
XEOMIN should not be used if the reconstituted solution (prepared as mentioned above) has a cloudy appearance or contains particles.
Care should be taken to use the correct volume of solvent to prevent accidental overdose. If different presentations of XEOMIN are to be used as part of an injection procedure, care should be taken to use the correct amount of solvent when reconstituting a certain number of units per 0.1 ml. The amount of solvent varies between XEOMIN 50 units, XEOMIN 100 units, and XEOMIN 200 units. Each syringe should be labeled accordingly.
Possible concentrations of XEOMIN 50, 100, and 200 units are indicated in the following table:
Resulting Dose (in units per 0.1 ml) | Solvent Added (sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) solution for injection) | ||
Vial with 50 units | Vial with 100 units | Vial with 200 units | |
20 units | 0.25 ml | 0.5 ml | 1 ml |
10 units | 0.5 ml | 1 ml | 2 ml |
8 units | 0.625 ml | 1.25 ml | 2.5 ml |
5 units | 1 ml | 2 ml | 4 ml |
4 units | 1.25 ml | 2.5 ml | 5 ml |
2.5 units | 2 ml | 4 ml | Not applicable |
2 units | 2.5 ml | 5 ml | Not applicable |
1.25 units | 4 ml | Not applicable | Not applicable |
Instructions for Disposal
Any unused solution for injection should be discarded after 24 hours and any unused solution for injection.
Procedure for safe disposal of vials, syringes, and materials used
Any unused vial or remainder, solution in the vial, and/or syringes should be subjected to an autoclave sterilization process. Alternatively, the remaining XEOMIN can be inactivated by adding one of the following solutions: 70% ethanol, 50% isopropanol, 0.1% SDS (anionic detergent), diluted sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH 0.1 N), or diluted sodium hypochlorite solution (NaOCl at least 0.1%).
After inactivation, the vials, syringes, and materials used should not be emptied but discarded in appropriate containers and disposed of according to local procedures.
Recommendations in case of any incident that may occur during handling with botulinum toxin type A
?? Any remaining product should be cleaned, using absorbent material impregnated with any of the solutions mentioned above in the case of powder, or with dry absorbent material if it is the reconstituted product.
?? Contaminated surfaces should be cleaned with absorbent material soaked in any of the above solutions and then dried.
?? If a vial is broken, proceed as mentioned above, carefully collecting the broken glass fragments and cleaning the spilled product, avoiding skin cuts.
?? If the product comes into contact with the skin, rinse the affected area with plenty of water.
?? If the product comes into contact with the eyes, rinse with plenty of water or with an ophthalmic washing solution.
?? If the product comes into contact with a wound, cut, or non-intact skin, rinse with plenty of water and take appropriate medical measures according to the injected dose.
These instructions for use, handling, and disposal must be strictly followed.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to XEOMIN 200 Units Powder for Injectable SolutionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 200 U/mlActive substance: botulinum toxinManufacturer: Ipsen PharmaPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 125 Speywood UnitsActive substance: botulinum toxinManufacturer: Ipsen Pharma S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 unitsActive substance: botulinum toxinManufacturer: Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for XEOMIN 200 Units Powder for Injectable Solution
Discuss questions about XEOMIN 200 Units Powder for Injectable Solution, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















