
VEJICUR POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INTRAVESICAL SUSPENSION

How to use VEJICUR POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INTRAVESICAL SUSPENSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Vejicur powder and solvent for intravesical suspension
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Vejicur and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Vejicur
- How to use Vejicur
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Vejicur
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Vejicur and what is it used for
The full name of this medicine is Vejicur powder and solvent for intravesical suspension. It will be referred to as Vejicur in the rest of this leaflet.
Vejicur contains weakened (attenuated) bacteria of the species Mycobacterium boviswith low infectious potential.
Vejicur stimulates the immune system and is used to treat various types of cancer in the urinary bladder. It is effective if the cancer is limited to the cells lining the inside of the bladder (urothelium) and has not invaded the inner tissues of the bladder.
Vejicur is administered directly into the bladder through instillation.
For the flat lesion form of bladder cancer (localized carcinoma), Vejicur is used to cure the disease limited to the bladder lining. There are different degrees of cancer that affect the bladder lining and the layers of cells close to the lining (lamina propria).
Vejicur is also used to prevent the recurrence of cancer (prophylactic treatment).
2. What you need to know before you use Vejicur
Do not use Vejicur
- if you are allergic to the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) viable bacterium or to any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you have a decreased activity of your immune system or if you suffer
from immunodeficiencies, whether due to a concurrent disease (e.g. positive HIV serology, leukemia, lymphoma), cancer treatment (e.g. cytostatic drugs, radiation) or immunosuppressive treatment (e.g. corticosteroids)
- if you have active tuberculosis
- if you have previously received radiation therapy in the bladder or adjacent areas
- if you are breastfeeding
- if you have had surgery through the urethra (TUR, transurethral resection), a tissue sample has been taken from your bladder (bladder biopsy), or you have suffered a catheter-related injury (traumatic catheterization) in the 2 or 3 weeks prior.
- if you have a bladder perforation
- if your urine contains visible blood (macrohematuria)
- if you have an acute urinary tract infection.
Vejicur must not be used for subcutaneous, intradermal, intramuscular, or intravenous administration, or for vaccination. It must be administered directly into the bladder through instillation.
Warnings and precautions
Your doctor will give you a patient alert card, which you should always carry with you (see also section 4).
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Vejicur
- if you have a fever or if there is blood in your urine. In this case, treatment with Vejicur should be postponed
- if you have a low bladder capacity, as it may decrease further after treatment
- if you are HLA-B27 (human leukocyte antigen B27) positive, as you may have an increased presence of joint inflammation (reactive arthritis)
- if you have arthritis with skin, eye, and urinary tract inflammation (Reiter's syndrome)
- if you have a localized dilation of a blood vessel (aneurysm) or a prosthesis. Your implants or grafts may become infected.
- if you have liver problems or are taking medications that may affect the liver. This is of particular importance if triple antibiotic treatment with antitubercular drugs is considered.
General hygiene
After instillation, sit down to urinate, in order to prevent urine splashing and avoid contaminating the surrounding area with the BCG bacterium.
It is recommended to wash your hands and genitals after urinating. This is especially important after urinating for the first time after BCG treatment. If skin lesions become contaminated, a suitable disinfectant should be used (ask your doctor or pharmacist).
Detection of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Detection of the BCG bacterium is usually difficult. A negative test result does not rule out a BCG infection outside the bladder.
Urinary tract infection
Your doctor will check that you do not have an acute urinary tract infection before each bladder treatment with BCG. If an acute urinary tract infection is diagnosed during BCG treatment, treatment should be interrupted until the urine analysis results are normal and antibiotic treatment is completed.
Patients in contact with immunocompromised individuals
If you receive treatment with Vejicur, you should follow the general hygiene rules listed above. This is of the utmost importance if you are in contact with immunocompromised individuals, as the BCG bacterium can be harmful to patients with a weakened immune system. However, to date, no person-to-person transmission of the bacterium has been reported.
Sexual transmission
A condom should be used during sexual intercourse during the week following BCG treatment to ensure that there is no transmission of the BCG bacterium.
Other medicines and Vejicur
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
This is especially important with the following medicines, as BCG bacteria are sensitive to:
- antitubercular drugs (e.g. ethambutol, streptomycin, p-aminosalicylic acid (PAS), isoniazid (INH), and rifampicin);
- antibiotics (fluoroquinolones, doxycycline, or gentamicin);
- antiseptics;
- lubricants.
BCG bacteria are resistant to pyrazinamide and cycloserine.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Pregnancy
You must not use Vejicur if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant.
Breastfeeding
Vejicur is contraindicated during breastfeeding.
Fertility
It has been observed that BCG negatively affects sperm production and may cause low or absent sperm count in semen. This effect was reversible in animals. However, men should seek advice on the possibility of preserving sperm before starting treatment.
Driving and using machines
This medicine may affect your ability to drive or use machines. Do not drive or use machines until you know what effect Vejicur has on you.
Consult your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist if you are unsure.
3. How to use Vejicur
Dosage
It will always be a healthcare professional with experience who prepares and administers Vejicur to you. The contents of one vial are needed for one bladder treatment.
Administration
Vejicur is introduced into the bladder at low pressure through a catheter.
The medicine should remain in the bladder for a period of 2 hours. For this, you should not drink during a period of 4 hours before treatment or in the 2 hours following treatment.
While the suspension remains in the bladder, you should maintain sufficient contact with the entire mucosal surface; moving from side to side helps the treatment. After 2 hours, you should urinate, in a sitting position to avoid splashing.
Unless you are on a low-fluid diet, it is recommended that you drink plenty of fluids during the 48 hours following each treatment.
Use in children
The safety and efficacy of the medicine in children have not been established.
Use in the elderly
There are no special instructions for use in the elderly. However, liver function should be considered before administering BCG.
Duration of treatment
As a standard treatment program (induction treatment), you will receive an intravesical treatment with Vejicur once a week for 6 consecutive weeks. After a period of 4 weeks without treatment, you may receive an additional intravesical administration, called maintenance treatment, for at least one year as described below. Your doctor will discuss this with you.
Induction treatment
- BCG treatment should be started 2-3 weeks after surgery through the urethra (TUR, transurethral resection) or after a tissue sample has been taken from your bladder (bladder biopsy) and without catheter-related injury (traumatic catheterization). It should be repeated at weekly intervals for 6 weeks.
- Subsequently, many people receive maintenance therapy, during which you may receive additional doses.
Maintenance treatment
- Maintenance therapy consists of 3 treatments at weekly intervals administered for a minimum of 1 year to a maximum of 3 years in months 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36. With this program, you will receive a total of 15 to 27 treatments over a period of one to three years.
Your doctor will discuss with you the need for maintenance therapy every 6 months after the first year of treatment, if necessary.
Although maintenance treatment reduces the likelihood of cancer recurrence and may reduce its ability to progress, the adverse effects and discomfort associated with treatment may outweigh the benefits in some patients. Therefore, it is essential that your doctor discusses the drawbacks of treatment and your preferences with you before starting or continuing maintenance treatment.
If you use more Vejicur than you should
Overdose is unlikely since one vial of Vejicur corresponds to a dose that is instilled into the bladder. There are no data to indicate that an overdose may produce any symptoms other than the adverse effects described (see section 4).
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine may cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
The adverse effects of BCG treatment are frequent, although they are usually mild and temporary. Adverse reactions normally increase with the number of BCG treatments.
However, the most serious adverse reaction is a severe systemic infection. Inform your doctor immediately if you suffer from the following symptoms, which may occur at any time, and often differ and may appear weeks, months, or even years after the last dose.
Show your patient alert card to the doctors who treat you.
- Fever above 39.5°C for at least 12 hours or fever above 38°C that lasts for weeks; night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Increasing discomfort
- Signs of inflammation may differ and present as:
- difficulty breathing or a cough that is not perceived as a common cold (miliary pneumonia),
- liver problems: feeling of pressure in the upper right abdomen or abnormalities in liver function tests (especially an enzyme called alkaline phosphatase), or
- eye pain and redness, vision problems or blurred vision; conjunctivitis
- A type of inflammation called granulomatous that has appeared in a biopsy.
BCG Systemic Reaction/Infection
An accidental injury to the bladder during BCG treatment or the administration of BCG into a muscle or vein can lead to a severe generalized BCG infection. A severe systemic BCG infection can cause BCG sepsis. BCG sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience a symptom or sign that concerns you, or contact a specialist in infectious diseases. However, the infection is not virulent. Your doctor will prescribe medication for your adverse reactions, and BCG treatment may be interrupted.
In contrast to a BCG infection, a BCG reaction often presents with a low-grade fever, flu-like symptoms, and general discomfort for 24-48 hours as the start of an immune reaction. Your doctor will prescribe medication to treat the symptoms. Talk to your doctor if your symptoms worsen.
Delayed BCG Infection
In individual cases, the BCG bacteria may remain in the body for years. This infection could occur at any time, and sometimes the symptoms and signs of an infection appear later, even years after the last dose of BCG was administered. The signs of inflammation could be similar to those of a severe BCG infection/reaction as mentioned previously. Other adverse effects of your BCG treatment may be problems with an implant or graft and require urgent treatment.
Therefore, it is of the utmost importance that you carry your personal alert card with you and give it to each doctor who treats you, to ensure appropriate treatment in case a delayed BCG infection appears. The doctor will also be able to assess whether the symptoms are an adverse reaction to your BCG treatment or not.
The following is a complete list of adverse reactions that may occur:
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- Nausea (feeling sick)
- Bladder inflammation (cystitis), inflammatory reactions (granulomas) of the bladder. These adverse effects may be an essential part of the antitumor activity.
- Frequent urination with discomfort and pain; may affect up to 90% of patients.
- Inflammatory reactions of the prostate (asymptomatic granulomatous prostatitis)
- Systemic and transient reactions to BCG, such as fever below 38.5°C, flu-like symptoms (discomfort, fever, chills), and general discomfort
- Fatigue
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Fever above 38.5°C
- Muscle pain (myalgia)
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of bladder control (urinary incontinence)
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Severe systemic BCG reaction/infection, BCG sepsis (see detailed information below)
- Blood cell deficiency (cytopenia)
- Anemia (decrease in blood hemoglobin)
- Reiter's syndrome (arthritis with skin, eye, and urinary tract inflammation)
- Lung inflammation (miliary pneumonia)
- Pulmonary inflammatory reactions (pulmonary granuloma)
- Liver inflammation (hepatitis)
- Skin abscess
- Skin rash, joint inflammation (arthritis), joint pain (arthralgia). In most cases, these adverse effects are signs of an allergic reaction (hypersensitivity) to BCG. In some cases, it may be necessary to discontinue treatment
- Urinary tract infection, presence of blood in the urine (macroscopic hematuria)
- Abnormally small bladder size (bladder contraction), abnormally low urine flow (urinary obstruction), bladder contracture
- Testicular inflammation (orchitis)
- Epididymal inflammation (epididymitis)
- Inflammatory reaction of the prostate (symptomatic granulomatous prostatitis)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Abnormal liver function test
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Vascular infection (e.g., infected localized dilation of a blood vessel)
- Kidney abscess
Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people
- BCG infection of implants and surrounding tissues (e.g., infection of the aortic graft, pacemaker, hip or knee arthroplasty)
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck (cervical lymphadenitis), infection of the regional lymph nodes
- Allergic reaction (hypersensitivity) (e.g., eyelid edema, cough)
- Inflammation of the inside of the eye (chorioretinitis)
- Conjunctivitis (red eyes), uveitis (inflammation of the eye's uvea)
- Vascular fistula
- Vomiting, intestinal fistula, inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis)
- Bone and bone marrow infection by bacteria (osteomyelitis)
- Bone marrow infection
- Abscess of the psoas muscle (abscess in the groin muscle)
- Inflammation of the testicles (orchitis) or epididymis (epididymitis) resistant to antitubercular treatment
- Infection of the glans
- Swelling in the arms and legs
Frequency not known: cannot be estimated from the available data
- Inflammation of blood vessels (can be in the brain)
- Genital disorders (e.g., vaginal pain)
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Severe immune reaction with fever, enlargement of the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes, jaundice, and skin rash (hemophagocytic syndrome)
- Kidney failure, inflammation of kidney tissue, calyces, and pelvis (pyelonephritis, nephritis [including tubulointerstitial nephritis, interstitial nephritis, and glomerulonephritis])
- Absence or low level of sperm in the semen (azoospermia, oligozoospermia)
- Elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA, a clinical analysis of the prostate)
Reporting ofadverse effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System for Human Use: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Vejicur
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the label and carton after CAD.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original packaging to protect it from light.
Physical and chemical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours when the medicine is stored protected from light at room temperature (between 20°C and 25°C) or in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C).
From a microbiological point of view, the medicine should be used immediately.
If not used immediately, the storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and normally should not exceed 24 hours between 2°C and 8°C, unless reconstitution has been performed under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Vejicur Composition
The active ingredient is the viable BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) bacteria (RIVM strain derived from strain 1173-P2).
After reconstitution, one vial contains:
RIVM strain of BCG derived from strain 1173-P2
2 x 10^8 to 3 x 10^9 viable units
The other components of the powder are: polygelin, anhydrous glucose, and polysorbate 80.
The other components of the solvent are: sodium chloride and water for injectables.
Product Appearance and Container Contents
Vejicur consists of a white or almost white powder, or a porous mass with yellow and gray tones, and a colorless and transparent solution used as a solvent. It is presented in packs of 1, 3, 5, or 6 vials with or without catheter(s) and Luer-Lock connector(s). Only certain pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
medac
Gesellschaft für
klinische Spezialpräparate mbH
Theaterstr. 6
22880 Wedel
Germany
For further information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Laboratorios Gebro Pharma, S.A.
Av. Tibidabo, 29
08022 Barcelona
Spain
Date of last revision of this leaflet: 03/2025
Detailed and up-to-date information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
Treatment of Symptoms, Signs, and Syndrome
Symptoms, Signs, or Syndrome | Treatment |
| Symptomatic treatment |
| Interrupt treatment with Vejicur and initiate treatment with quinolones. If after 10 days no complete resolution is observed, administer isoniazid (INH)* for 3 months. In case of antitubercular treatment, treatment with Vejicur should be definitively suspended |
| Postpone treatment with Vejicur until the urine analysis is normal and antibiotic treatment has been completed. |
| Interrupt treatment with Vejicur. Consider consulting an infectious disease specialist. Administer isoniazid (INH)* and rifampicin*, for 3-6 months depending on the severity. In case of antitubercular treatment, treatment with Vejicur should be definitively suspended |
| Symptomatic treatment with paracetamol |
| Suspend treatment with Vejicur. Consider consulting an infectious disease specialist. Administer antihistamines or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Corticosteroid treatment should be considered in case of an immune-mediated reaction. If there is no response, administer isoniazid* for 3 months. In case of antitubercular treatment, therapy with Vejicur should be definitively suspended. |
| Definitively suspend treatment with Vejicur. Consider consulting an infectious disease specialist. Administer antitubercular treatment with three drugs* for 6 months, and treatment with low-dose corticosteroids. |
| Definitively suspend treatment with Vejicur. Administer antitubercular treatment* with 3 drugs combined with fast-acting corticosteroids at high doses. Consult an infectious disease specialist. |
- Precaution: BCG bacteria are sensitive to all currently used antitubercular drugs, except pyrazinamide. If antitubercular treatment with 3 drugs is necessary, the generally recommended combination is isoniazid (INH), rifampicin, and ethambutol.
** see previous definition
Important Information on the Use of Vejicur
Vejicur should only be used by healthcare professionals with experience.
Ensure that storage is appropriate (see section 5) and confirm the integrity of the container.
Vejicur should be administered under the conditions required for intravesical endoscopy.
Vejicur should not be administered subcutaneously, intradermally, intramuscularly, or intravenously, nor for vaccination against tuberculosis.
The Luer-Lock catheter connector of the solvent bag should only be used for intravesical instillation!
Basic Principles and Protection Measures for the Use of Vejicur
In general, direct contact with Vejicur should be avoided. Vejicur is a medicinal product that can cause infection in humans and pose a risk to healthcare professionals. There may be a risk if the medicinal product enters the body through damaged skin, if aerosols are inhaled, if droplets enter the eyes, or if droplets come into contact with mucous membranes or are ingested. Do not eat, drink, or smoke in work areas, nor store food, drinks, or tobacco products in them. Vejicur should not be handled in a room where cytotoxic medicinal products are prepared for intravenous use, nor should it be handled by personnel who prepare cytotoxic medicinal products for intravenous use.
The medicinal product should not be handled by persons with known immunodeficiency.
It is recommended to use a closed, splash-proof protective gown, disposable gloves, an FFP2 respiratory mask, and safety glasses with side protectors as personal protective equipment during handling. Vejicur should only be transported in closed containers (for storage conditions after reconstitution, see section 5).
Once the work is finished, clean the work surfaces with a suitable disinfectant solution. After work and in case of skin contact, disinfect hands with a hand disinfectant, let them dry, wash them, and use skin care products.
Skin tests with tuberculin
Intravesical treatment with Vejicur may induce sensitivity to tuberculin and complicate the subsequent interpretation of the tuberculin skin test for the diagnosis of mycobacterial infections. Therefore, tuberculin reactivity should be measured before administration of Vejicur.
Preparation of the Reconstituted Intravesical Suspension
Before use, the medicinal product should be resuspended in aseptic conditions with a sterile 0.9% sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) (see instructions for use, step 7). The catheter should be placed with special care to avoid lesions in the urethral epithelium and the urinary bladder, which can cause a systemic BCG infection. It is recommended to use a lubricant to minimize the risk of traumatic catheterization and to make the procedure more comfortable. Women may require less lubricant than men. It has not been observed that a possible antiseptic effect of the lubricant can influence the efficacy of the medicinal product. Empty the bladder after catheterization to reduce the amount of lubricant that may have been introduced before administering Vejicur. The suspension is mixed by gently shaking it before use. Macroscopically visible particles do not affect the efficacy and safety of the medicinal product.
The contents of the vial are intended for single use only. The remaining suspension should be discarded.
The disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them should be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Procedure in Case of Emergencies and Spills of Vejicur
Wear protective clothing and avoid removing the powder.
Cover the spilled Vejicur suspension with cellulose and moisten it with a disinfectant with proven efficacy against mycobacteria. After cleaning the spilled Vejicur suspension, clean the surface again with a disinfectant solution and let it dry. Spills on the skin should be treated with a suitable disinfectant.
First Aid Measures
Always consult a doctor in case of contamination.
In case of skin contact: remove contaminated clothing. Disinfect and clean the skin and check for wound contamination.
In case of eye contact: rinse the affected eye with a sufficient amount of eye wash solution or, alternatively, with water. Remove contact lenses, if applicable.
In case of ingestion: rinse the mouth with plenty of water.
In case of inhalation: ensure a sufficient supply of fresh air.
For more information on the catheter, refer to the corresponding instructions for use.
Instructions for Users of Vejicur
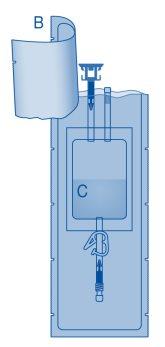
Components and Application of the Instillation Kit|
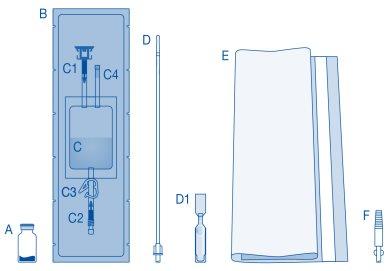
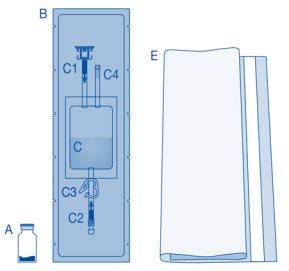
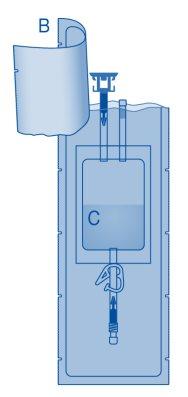
Main Components of the Instillation Kit
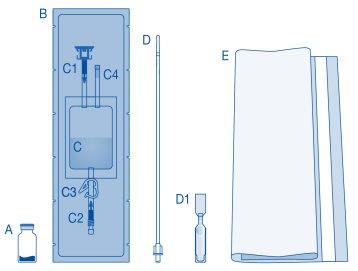
Main Component | Description |
A | Vial with powder |
B | Protective sleeve |
C | Solvent bag with 0.9% sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) |
C1 | Vial connector with protective cap and breakaway seal |
C2 | Catheter Luer-Lock connector with protective cap and breakaway seal |
C3 | Pressure clamp |
C4 | Filling port without application function |
D | Luer-Lock catheter |
D1 | Lubricant |
E | Bag for disposables |
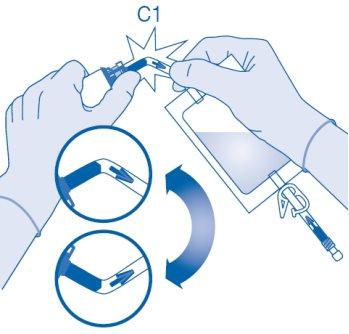
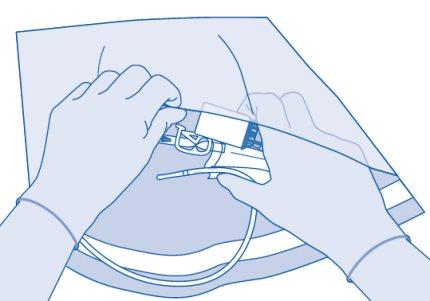
Connection of the Vial to the Solvent Bag
- Prepare the bag for disposables (E) for direct disposal of the kit after instillation to avoid contamination.
- Remove the removable closure cap from the vial (A) and disinfect the stopper according to local regulations.
- Open the protective sleeve (B) of the solvent bag (C) and completely remove the protective sleeve.
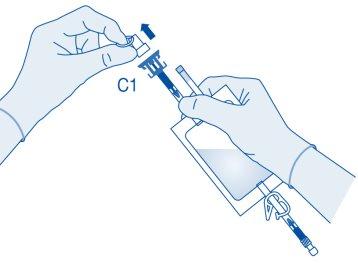
- Remove the protective cap from the vial connector (C1).
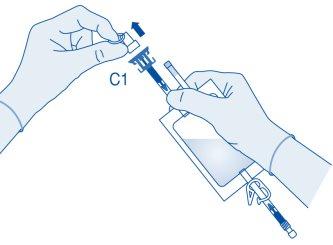
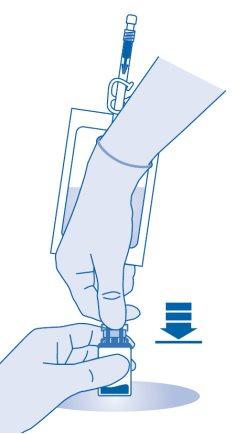
- Press the connector onto the vial until it stops.
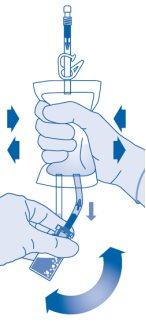
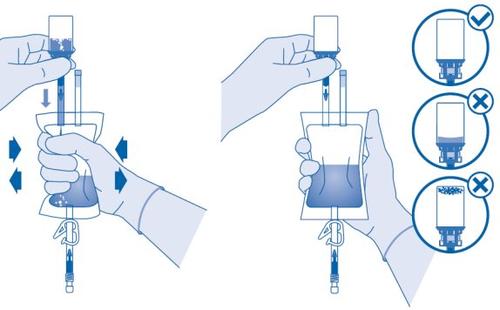
Mixing the Powder with the Solvent
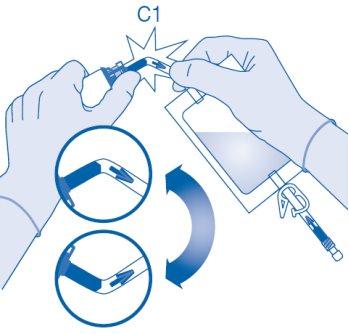
- Bend the breakaway seal inside the vial connector tube (C1) upwards and downwards several times to break the seal.
- Hold the solvent bag so that the vial is below it.
Compress the solvent bag several times to transfer sufficient solvent to the vial.
Make sure notto fill the vial completely to allow for subsequent transfer of the suspension to the solvent bag. Some solvent may remain inside the bag.
Remove the vial slowlyto minimize the formation of abundant foam when mixing the medicinal product with the solvent. If there is a lot of foam, let the vial rest briefly (several minutes).
The contents of the vial must form a homogeneous suspension. This may take several minutes.
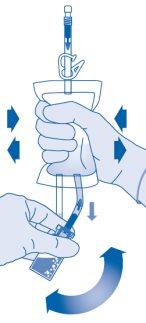
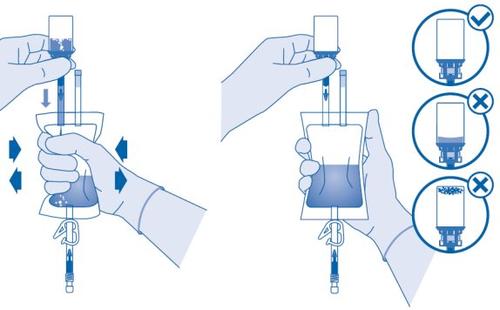
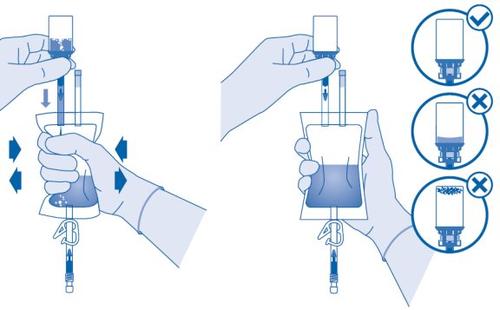
- Invert the solvent bag and hold it so that the vial is above it.
Hold the vial.
Compress the solvent bag several times until the vial is completely empty.
If powder remains inside the vial, repeat steps 7 and 8.
From a microbiological point of view, the medicinal product should be used immediately. If the medicinal product is not used immediately, refer to section 5 "Storage of Vejicur".
The suspension should not be instilled at refrigerator temperature to avoid the patient feeling the need to urinate, which would shorten the exposure time.
Catheterization
- Catheterize the patient according to local regulations and instructions for use using the Luer-Lock catheter (D) and the lubricant (D1) included or another suitable catheter and/or lubricant.
Empty the urinary bladder with the catheter.
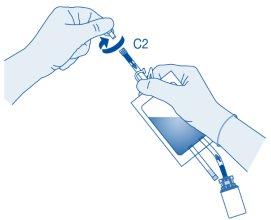
Connection of the Catheter to the Solvent Bag
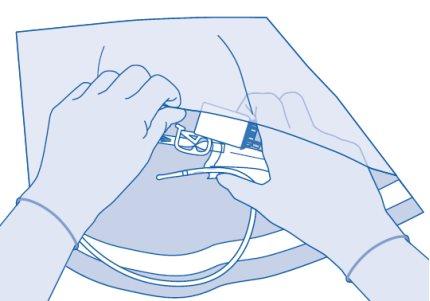
- To mix any sediment that may be present, rotate and shake the bag before connecting it.
Do not administer the suspension at refrigerator temperature.
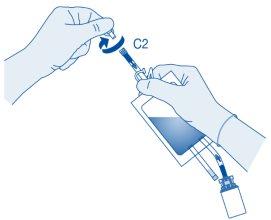
Remove the protective cap from the catheter connector (C2).
Connect the patient's Luer-Lock catheter (D) to the catheter connector (C2) of the solvent bag.
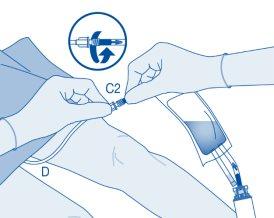
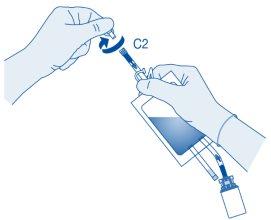
Instillation
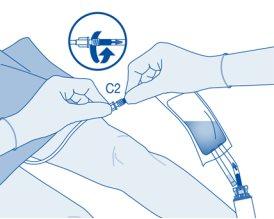
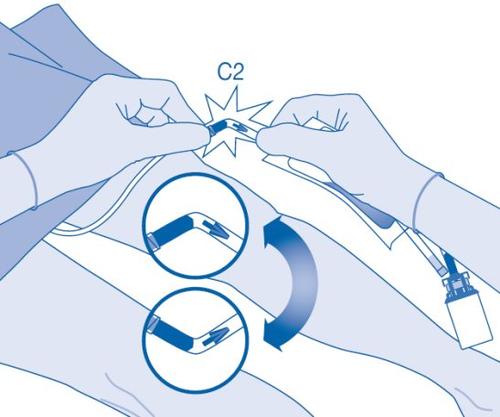
- Bend the breakaway seal inside the catheter connector tube (C2) upwards and downwards several times to break the seal.
Hold the patient's catheter firmly while doing so.
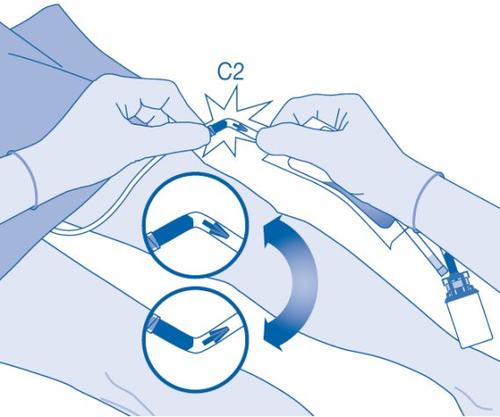
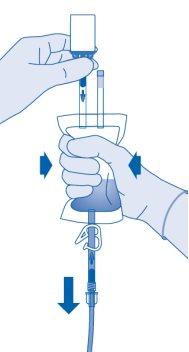
- Hold the solvent bag with the inverted vial above the bag.
Compress the solvent bag gentlywith the other hand to instill the medicinal product slowlyinto the patient's urinary bladder.
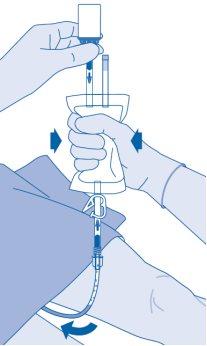
Continue compressing the solvent bag until it and the vial are empty.
- Compress the solvent bag to expel the remaining air and empty the catheter as much as possible.
After Instillation
- The closure of the pressure clamp (C3) prevents liquid backflow into the catheter and minimizes the risk of contamination. Alternatively, you can keep the solvent bag compressed while performing steps 15 and 16.
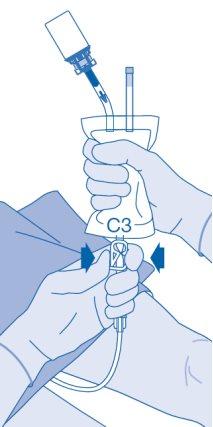
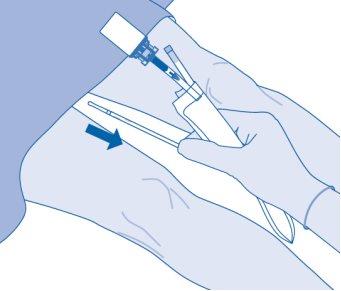
- Carefully remove the catheter from the bladder without disconnecting the solvent bag from the catheter. Avoid splashing contamination.
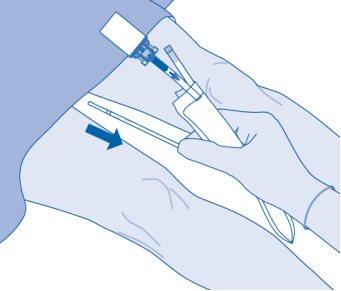
- Dispose of the product according to national regulations using the bag for disposables.
The contents of the vial are intended for single use only. The remaining suspension should be discarded.
Instructions for Users of Vejicur
Components and Application of the Instillation Kit|
Main Components of the Instillation Kit
Main Component | Description |
A | Vial with powder |
B | Protective sleeve |
C | Solvent bag with 0.9% sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) |
C1 | Vial connector with protective cap and breakaway seal |
C2 | Catheter Luer-Lock connector with protective cap and breakaway seal |
C3 | Pressure clamp |
C4 | Filling port without application function |
D | Luer-Lock catheter |
D1 | Lubricant |
E | Bag for disposables |
F | Luer-Lock to conic connector |
Connection of the vial to the solvent bag
- Prepare the disposable bag (E) for direct disposal of the kit after instillation to avoid contamination.
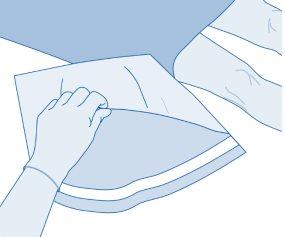
- Remove the removable closure cap from the vial (A) and disinfect the stopper according to local regulations.
- Open the protective sleeve (B) of the solvent bag (C) and completely remove the protective sleeve.
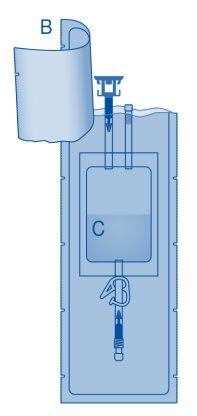
- Remove the protective cap from the vial connector (C1).
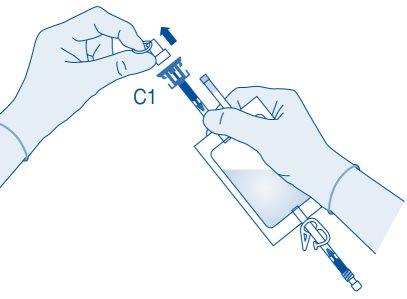
- Press the connector onto the vial until it stops.
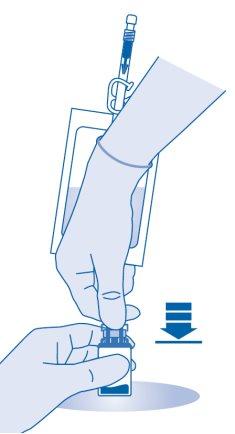
Mixing the powder with the solvent
- Bend the breakable seal inside the vial connector tube (C1) up and down several times to break the seal.
- Hold the solvent bag so that the vial is below it.
Compress the solvent bag several times to transfer sufficient amount of solvent to the vial.
Make sure notto fill the vial completely to allow for the subsequent transfer of the suspension to the solvent bag. Some solvent may remain inside the bag.
Remove the vial slowlyto minimize the formation of excessive foam when mixing the medication with the solvent. If there is a lot of foam, let the vial rest briefly (several minutes).
The vial contents must form a homogeneous suspension. This may take several minutes.
- Invert the solvent bag and hold it so that the vial is above it.
Hold the vial.
Compress the solvent bag several times until the vial is completely empty.
If powder remains inside the vial, repeat steps 7 and 8.
From a microbiological point of view, the medication should be used immediately.
If the medication is not used immediately, refer to section 5 "Storage of Vejicur".
The suspension should not be instilled at refrigerator temperature to avoid the patient feeling the need to urinate, which would shorten the exposure time.
Sounding
- Sound the patient according to local regulations and instructions for use using the Luer-Lock catheter (D) and lubricant (D1) included or another suitable catheter and/or lubricant.
Empty the urinary bladder with the catheter.
Note for use with a self-selected catheter with a conic connector:
The Luer-Lock to conic connector (F) included should be used to connect the bag to the self-selected catheter (not shown).
To do this, perform the following additional steps:
- Remove the protective cap from the catheter connector (C2, see step 10).
- Turn and remove the bag before connecting it to remix any sediment that may be present.
- Connect the Luer-Lock to conic connector (F) to the catheter connector (C2) of the bag.
- Connect the bag with connector (F) to the patient's catheter carefully.
- Then, proceed to step 11.
Connection of the catheter to the solvent bag
- To mix any sediment that may be present, turn and remove the bag before connecting it.
Do not administer the suspension at refrigerator temperature.
Remove the protective cap from the catheter connector (C2).
Connect the patient's Luer-Lock catheter (D) to the catheter connector (C2) of the solvent bag.
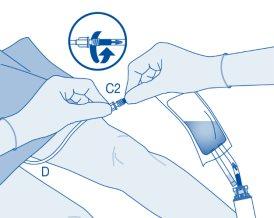
Instillation
- Bend the breakable seal inside the catheter connector tube (C2) up and down several times to break the seal.
Hold the patient's catheter firmly while doing so.
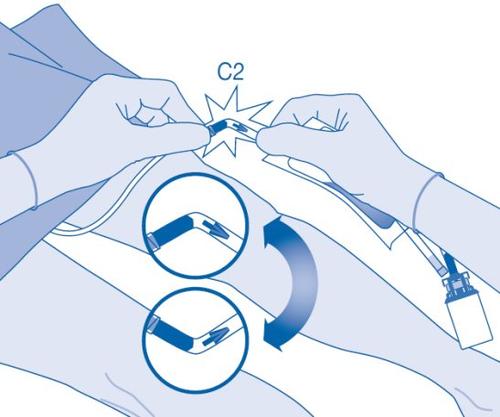
- Hold the solvent bag with the vial inverted above the bag.
Compress the solvent bag gentlywith the other hand to instill the medication slowlyinto the patient's urinary bladder.
Continue compressing the solvent bag until it and the vial are empty.
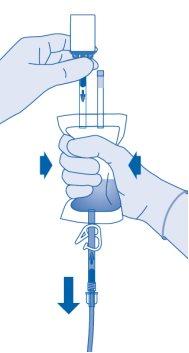
- Compress the solvent bag to expel the remaining air to empty the catheter as much as possible.
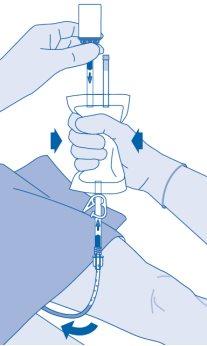
After instillation
- The closure of the pressure clamp (C3) prevents liquid reflux to the catheter and minimizes the risk of contamination. Alternatively, you can keep the solvent bag compressed while performing steps 15 and 16.
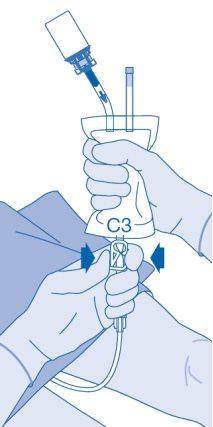
- Carefully remove the catheter from the bladder without disconnecting the solvent bag from the catheter. Avoid splashing contamination.
- Dispose of the product according to national regulations using the disposable bag.
The vial contents are intended for single use only. Discard any remaining suspension.
Instructions for Vejicur users
Components and application of the instillation kit|
Main components of the instillation kit
Main component | Description |
A | Vial with powder |
B | Protective sleeve |
C | Solvent bag with 0.9% sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) |
C1 | Vial connector with protective cap and breakable seal |
C2 | Luer-Lock catheter connector with protective cap and breakable seal |
C3 | Pressure clamp |
C4 | Fill port without application function |
E | Disposable bag |
Connection of the vial to the solvent bag
- Prepare the disposable bag (E) for direct disposal of the kit after instillation to avoid contamination.
- Remove the removable closure cap from the vial (A) and disinfect the stopper according to local regulations.
- Open the protective sleeve (B) of the solvent bag (C) and completely remove the protective sleeve.
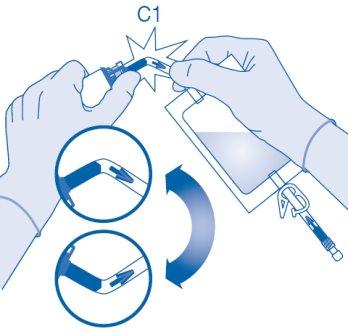
- Remove the protective cap from the vial connector (C1).
- Press the connector onto the vial until it stops.
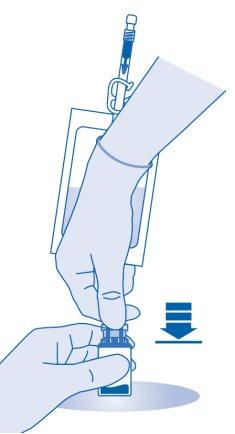
Mixing the powder with the solvent
- Bend the breakable seal inside the vial connector tube (C1) up and down several times to break the seal.
- Hold the solvent bag so that the vial is below it.
Compress the solvent bag several times to transfer sufficient amount of solvent to the vial.
Make sure notto fill the vial completely to allow for the subsequent transfer of the suspension to the solvent bag. Some solvent may remain inside the bag.
Remove the vial slowlyto minimize the formation of excessive foam when mixing the medication with the solvent. If there is a lot of foam, let the vial rest briefly (several minutes).
The vial contents must form a homogeneous suspension. This may take several minutes.
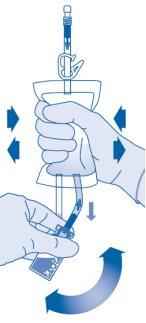
- Invert the solvent bag and hold it so that the vial is above it.
Hold the vial.
Compress the solvent bag several times until the vial is completely empty.
If powder remains inside the vial, repeat steps 7 and 8.
From a microbiological point of view, the medication should be used immediately.
If the medication is not used immediately, refer to section 5 "Storage of Vejicur".
The suspension should not be instilled at refrigerator temperature to avoid the patient feeling the need to urinate, which would shorten the exposure time.
Sounding
- Sound the patient according to local regulations and instructions for use using a suitable catheter and lubricant.
Empty the urinary bladder with the catheter.
Connection of the catheter to the solvent bag
- To mix any sediment that may be present, turn and remove the bag before connecting it.
Do not administer the suspension at refrigerator temperature.
Remove the protective cap from the catheter connector (C2).
Connect the patient's catheter to the catheter connector (C2) of the solvent bag.
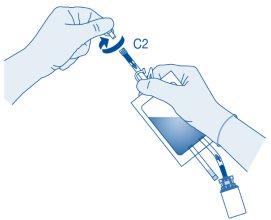
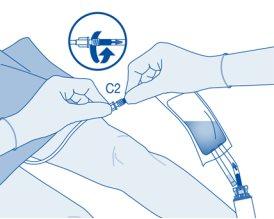
Instillation
- Bend the breakable seal inside the catheter connector tube (C2) up and down several times to break the seal.
Hold the patient's catheter firmly while doing so.
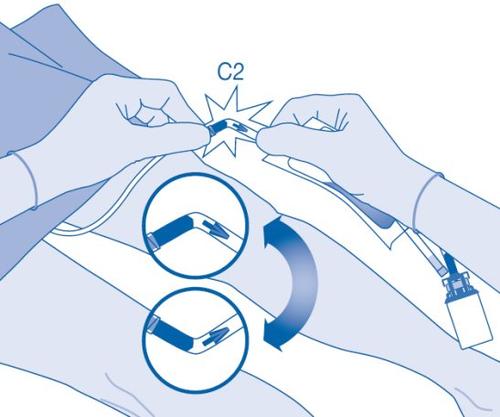
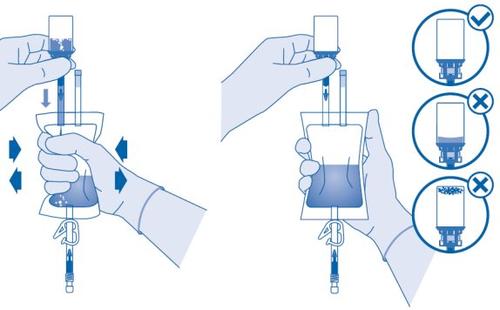
- Hold the solvent bag with the vial inverted above the bag.
Compress the solvent bag gentlywith the other hand to instill the medication slowlyinto the patient's urinary bladder.
Continue compressing the solvent bag until it and the vial are empty.
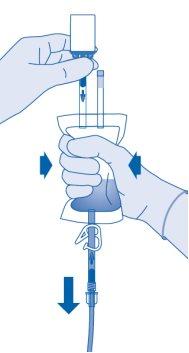
- Compress the solvent bag to expel the remaining air to empty the catheter as much as possible.
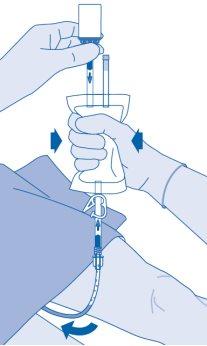
After instillation
- The closure of the pressure clamp (C3) prevents liquid reflux to the catheter and minimizes the risk of contamination. Alternatively, you can keep the solvent bag compressed while performing steps 15 and 16.
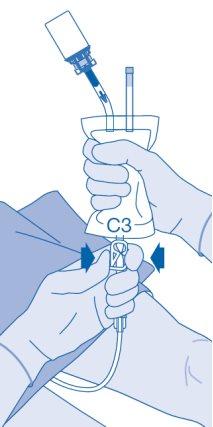
- Carefully remove the catheter from the bladder without disconnecting the solvent bag from the catheter. Avoid splashing contamination.
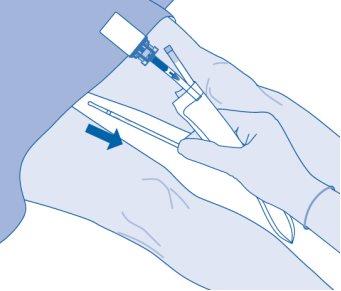
- Dispose of the product according to national regulations using the disposable bag.
The vial contents are intended for single use only. Discard any remaining suspension.
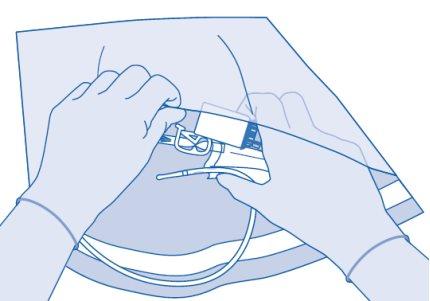
Instructions for Vejicur users
Components and application of the instillation kit|
Main components of the instillation kit
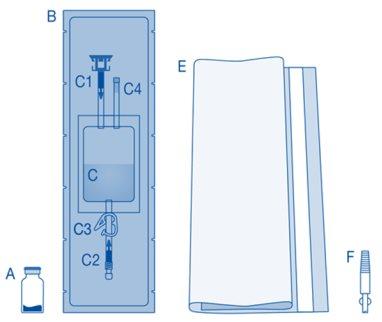
Main component | Description |
A | Vial with powder |
B | Protective sleeve |
C | Solvent bag with 0.9% sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) |
C1 | Vial connector with protective cap and breakable seal |
C2 | Luer-Lock catheter connector with protective cap and breakable seal |
C3 | Pressure clamp |
C4 | Fill port without application function |
E | Disposable bag |
F | Luer-Lock to conic connector |
Connection of the vial to the solvent bag
- Prepare the disposable bag (E) for direct disposal of the kit after instillation to avoid contamination.
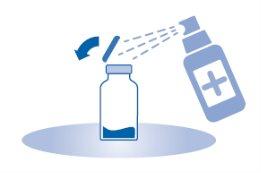
- Remove the removable closure cap from the vial (A) and disinfect the stopper according to local regulations.
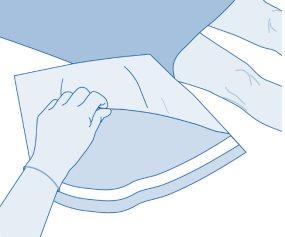
- Open the protective sleeve (B) of the solvent bag (C) and completely remove the protective sleeve.
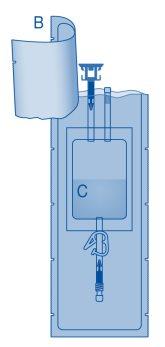
- Remove the protective cap from the vial connector (C1).
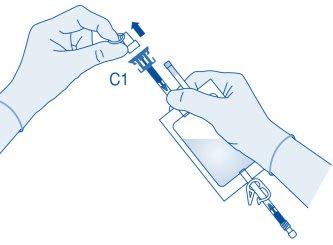
- Press the connector onto the vial until it stops.
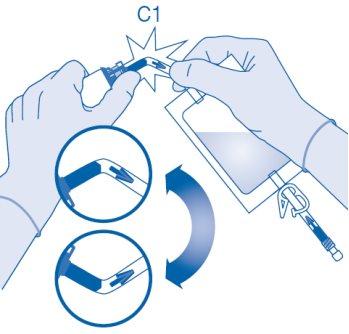
Mixing the powder with the solvent
- Bend the breakable seal inside the vial connector tube (C1) up and down several times to break the seal.
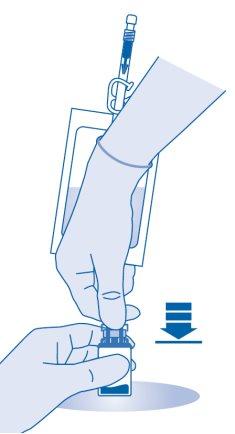
- Hold the solvent bag so that the vial is below it.
Compress the solvent bag several times to transfer sufficient amount of solvent to the vial.
Make sure notto fill the vial completely to allow for the subsequent transfer of the suspension to the solvent bag. Some solvent may remain inside the bag.
Remove the vial slowlyto minimize the formation of excessive foam when mixing the medication with the solvent. If there is a lot of foam, let the vial rest briefly (several minutes).
The vial contents must form a homogeneous suspension. This may take several minutes.
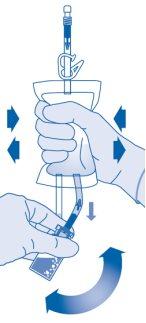
- Invert the solvent bag and hold it so that the vial is above it.
Hold the vial.
Compress the solvent bag several times until the vial is completely empty.
If powder remains inside the vial, repeat steps 7 and 8.
From a microbiological point of view, the medication should be used immediately.
If the medication is not used immediately, refer to section 5 "Storage of Vejicur".
The suspension should not be instilled at refrigerator temperature in order to avoid the patient feeling the need to urinate, which would shorten the exposure time.
Sounding
- Sound the patient according to local regulations and instructions for use using a suitable catheter and lubricant.
Empty the urinary bladder with the catheter.
This container does not include a catheter. Use the included connector (F) to connect the bag to the patient's catheter with a conical connector (not shown).
To do this, the following additional steps must be performed:
- Remove the protective cap from the catheter connector (C2, see step 10).
- Connect the connector (F) to the catheter connector (C2) of the bag.
- Carefully connect the bag with connector (F) to the patient's catheter.
- Then, proceed to step 11.
Connection of the catheter to the solvent bag
- To mix any sediment that may be present, turn and shake the bag before connecting it.
Do not administer the suspension at refrigerator temperature.
Remove the protective cap from the catheter connector (C2).
Connect the patient's catheter to the catheter connector (C2) of the solvent bag.
Instillation
- Double the break seal inside the catheter connector tube (C2) up and down several times to break the seal.
Hold the patient's catheter firmly while doing so.
- Hold the solvent bag with the vial inverted above the bag.
Compress the solvent bag gentlywith the other hand to instill the medication slowlyinto the patient's urinary bladder.
Continue compressing the solvent bag until it and the vial are empty.
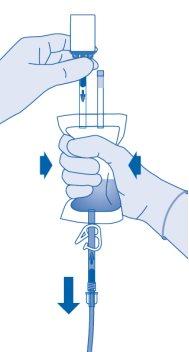
- Compress the solvent bag to expel the remaining air and empty the catheter as much as possible.
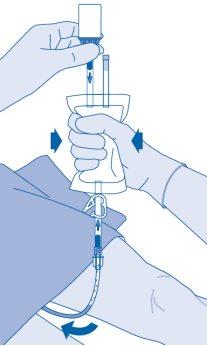
After instillation
- The closure of the pressure clamp (C3) prevents liquid reflux to the catheter and minimizes the risk of contamination. Alternatively, you can keep the solvent bag compressed while performing steps 15 and 16.
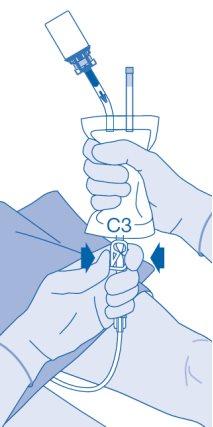
- Carefully withdraw the catheter from the bladder without disconnecting the solvent bag from the catheter. Avoid splash contamination of droplets.
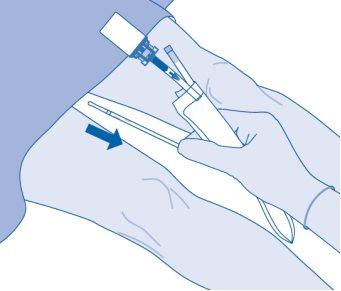
- Dispose of the product according to national regulations using the bag for disposables.
The contents of the vial are intended for single use/single dose only. The remaining suspension should be discarded.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to VEJICUR POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INTRAVESICAL SUSPENSIONDosage form: VESICAL IRRIGATION SOLUTION, BCG (LYOPHILIZED LIVE CULTURE) 2-8 x 10(8) CFUActive substance: BCG vaccineManufacturer: Merck Sharp & Dohme De Espana S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, UnknownActive substance: tasonerminManufacturer: Belpharma S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5 mg histamine dihydrochloride/0.5 mLActive substance: histamine dihydrochlorideManufacturer: Laboratoires DelbertPrescription required
Online doctors for VEJICUR POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INTRAVESICAL SUSPENSION
Discuss questions about VEJICUR POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INTRAVESICAL SUSPENSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















