
Bcg - medac

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Bcg - medac

How to use Bcg - medac
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
BCG-medac, powder and solvent for solution for bladder instillation
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell the doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is BCG-medac and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using BCG-medac
- 3. How to use BCG-medac
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store BCG-medac
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is BCG-medac and what is it used for
The full name of the medicine is BCG-medac, powder and solvent for solution for bladder instillation. In the rest of the leaflet, this medicine is referred to as BCG-medac.
BCG-medac contains weakened (attenuated) Mycobacterium bovis bacteria with low infectious potential.
BCG-medac stimulates the immune system and is used to treat several types of bladder cancer. The medicine is effective if the cancer is limited to the cells lining the inner surface of the bladder (transitional epithelium) and does not infiltrate the inner tissues of the bladder.
BCG-medac is administered directly into the bladder in the form of an instillation.
In the case of flat bladder tumors (carcinoma in situ), BCG-medac is used to cure the disease limited to the epithelium lining the bladder surface. There are different degrees of malignancy of cancer that can occur in the bladder epithelium and the adjacent cell layer (called the lamina propria).
BCG-medac is also used to prevent cancer recurrence (prophylaxis).
2. Important information before using BCG-medac
When not to use BCG-medac
BCG-medac should never be administered subcutaneously, intradermally, intramuscularly, intravenously, or as a vaccine. The medicine must be administered directly into the bladder in the form of an instillation.
Warnings and precautions
The doctor will give the patient a warning card, which should always be carried with them (see also section 4).
Before starting treatment with BCG-medac, discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist
General recommendations for personal hygiene
After instillation, sit down before urinating to prevent splashing of urine and contamination of the area with BCG bacteria.
After urinating, it is recommended to wash your hands and genital area. This is especially important after the first urination after BCG instillation. If skin lesions become contaminated, a suitable disinfectant should be used (consult a doctor or pharmacist).
Tests for the presence of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin bacilli
Detecting BCG bacteria is usually difficult. A negative test result does not rule out BCG infection outside the bladder.
Urinary tract infection
Before each intravesical administration of BCG, the doctor should ensure that the patient does not have an acute urinary tract infection. If an acute urinary tract infection is diagnosed during BCG therapy, treatment should be discontinued until the urine test results normalize and antibiotic treatment is completed.
Patients in contact with people with weakened immunity
Patients treated with BCG-medac should follow the hygiene rules described above. This is especially important when in contact with people with weakened immunity, as BCG bacteria can be harmful to patients with impaired immune systems.
So far, no cases of human-to-human transmission of BCG bacteria have been reported.
Sexual transmission
It is recommended to use condoms during sexual intercourse for one week after BCG administration.
BCG-medac and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
This is especially important when using the following medicines that interact with BCG bacteria:
- Antitubercular drugs (e.g. ethambutol, streptomycin, p-aminosalicylic acid (PAS), isoniazid (INH), and rifampicin)
- Antibiotics (fluoroquinolones, doxycycline, gentamicin)
- Antiseptics
- Lubricants
BCG bacteria are resistant to pyrazinamide and cycloserine.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Pregnancy
If the patient is pregnant or thinks she may be pregnant, she should not use BCG-medac.
Breastfeeding
BCG-medac should not be used during breastfeeding.
Fertility
It has been found that BCG bacteria affect sperm production, and their administration may cause a decrease in the number of sperm or their absence in the semen. This symptom was reversible in animals. However, before starting treatment, men should consult about the possibility of storing semen.
Driving and operating machinery
The medicine may affect the ability to drive and operate machinery. The patient should not drive or operate machinery until they know how BCG-medac affects their body.
In case of doubts about using this medicine, consult a doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.
3. How to use BCG-medac
Dosage of the medicine
BCG-medac is prepared and administered only by experienced medical personnel. The contents of one vial are intended for single use.
Administration of the medicine
BCG-medac is administered under low pressure using a catheter into the bladder.
The medicine should remain in the bladder for 2 hours. To achieve this, the patient should not drink any fluids for 4 hours before administration and for 2 hours after administration.
Inside the bladder, the medicine should be distributed over the entire surface of the mucous membrane, and movement helps the effectiveness of the treatment. After two hours, the bladder should be emptied while sitting down to avoid splashing of urine.
Patients who are not on a fluid-restricted diet should drink plenty of fluids for 48 hours after each administration of the medicine.
Use in children
The safety and efficacy of the medicinal product BCG-medac in children have not been established.
Use in the elderly
There are no special recommendations for the use of the medicine in the elderly. However, liver function should be considered before administering BCG.
Duration of treatment
In the standard treatment schedule (induction therapy), BCG-medac is administered intravesically once a week for 6 consecutive weeks. Four weeks after the end of treatment, maintenance therapy (so-called maintenance therapy) can be started, which involves administering the medicine intravesically for at least 1 year, according to the description below. The attending physician will discuss this with the patient.
Induction therapy
- BCG administration can be started about 2-3 weeks after surgical procedures through the urethra (TUR; transurethral resection) or after taking a bladder tissue sample (bladder biopsy), provided that the patient did not suffer an injury during catheterization. The medicine is administered once a week for 6 weeks.
- After this therapy, many people receive maintenance therapy, during which additional doses of the medicine can be administered.
Maintenance therapy
- Maintenance therapy consists of 3 procedures at weekly intervals, administered for at least 1 year to 3 years, in months 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36. In this treatment schedule, the patient receives a total of 15 to 27 procedures over a period of 1 to 3 years. If necessary, the doctor will discuss with the patient the need for maintenance therapy every 6 months after the first year of treatment.
Although maintenance therapy reduces the likelihood of disease recurrence and may reduce the ability of the tumor to progress, some patients may experience side effects and discomfort associated with treatment, which may outweigh the benefits of treatment. Therefore, it is essential to discuss the disadvantages of treatment and take into account the patient's treatment preferences before starting or continuing maintenance therapy.
Use of a higher dose of BCG-medac than recommended
Overdose is unlikely, as one vial of BCG-medac contains a single dose administered as an instillation into the bladder. There are no data indicating that overdose may cause any symptoms other than the adverse reactions listed below (see section 4).
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects of BCG treatment are common, but they are usually mild and temporary. The number of adverse reactions usually increases with the number of BCG doses administered.
The most serious side effect is severe systemic infection. You should immediately inform your doctor if you experience any of the following, which may occur at any time and sometimes with a delay, and may appear weeks, months, or even years after the last dose of BCG-medac.
The patient warning card should be shown to the treating physicians.
- fever above 39.5°C for at least 12 hours or fever above 38°C lasting for weeks
- unexplained weight loss
- worsening condition
- inflammation symptoms, which may vary and occur as: o difficulty breathing or cough that does not resemble a common cold (miliary pneumonia) o liver problems: feeling of pressure in the right upper abdomen or abnormalities in liver function tests (especially the enzyme alkaline phosphatase) or o eye problems: pain and redness of the eye, vision problems or blurred vision; conjunctivitis (so-called "pink eye")
- granulomatous inflammation, which was found in a biopsy.
Systemic BCG infection/reaction
If the bladder is accidentally damaged during treatment with BCG-medac or BCG-medac is administered into a muscle or vein, it may cause severe systemic BCG infection. Severe systemic BCG infection can lead to BCG sepsis. BCG sepsis is a life-threatening condition. If worrying symptoms or signs occur, you should immediately consult the attending physician or contact a doctor specializing in infectious diseases! This infection is not caused by virulent bacteria. The doctor will prescribe medications for the side effects, and BCG treatment may be discontinued.
In contrast to BCG infection, a reaction to BCG often manifests as a mild fever, flu-like symptoms, and general malaise 24-48 hours after the initial immune response. The doctor may prescribe some medications to treat the symptoms. If the symptoms worsen, you should consult a doctor.
Delayed BCG infection
In individual cases, BCG bacteria may remain in the body for years. Infection may occur at any time, and sometimes symptoms and signs of infection appear late, even years after the last dose of BCG-medac. Inflammation symptoms may be similar to severe BCG infection/reaction, as mentioned above. Problems with implants or transplants may also be side effects of BCG treatment and require immediate treatment.
Therefore, it is extremely important to carry the patient warning card and show it to every treating physician to ensure proper treatment in case of delayed BCG infection. The doctor will also be able to assess whether the symptoms are
a side effect of BCG treatment or not.
Below is a complete list of side effects that may occur:
Very common (may occur in more than 1 in 10 people)
- Nausea (vomiting)
- Bladder inflammation and other bladder inflammatory conditions (granulomatous inflammation). These side effects may be an essential element of the antitumor effect.
- Frequent urination, accompanied by discomfort and pain. These symptoms may occur in up to 90% of patients.
- Prostate inflammation (asymptomatic granulomatous prostatitis)
- Transient, systemic reactions to BCG bacteria, such as fever below 38.5°C, flu-like symptoms (malaise, fever, chills), and general discomfort.
- Fatigue
Common (may occur in up to 1 in 10 people)
- Fever above 38.5°C
- Muscle pain
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Urinary incontinence
Uncommon (may occur in up to 1 in 100 people)
- Severe systemic BCG infections/reactions, BCG sepsis (more detailed information is provided below)
- Blood cell deficiency (cytopenia)
- Anemia (decrease in hemoglobin level in the blood)
- Reiter's syndrome (arthritis associated with skin, eye, and urinary tract inflammation)
- Lung inflammation (miliary pneumonia)
- Pulmonary inflammatory reactions (pulmonary granulomatosis)
- Hepatitis
- Skin abscess
- Rash, arthritis (arthralgia), joint pain (arthralgia). In most cases, these symptoms are the result of an allergic reaction (hypersensitivity) to BCG. In some cases, it may be necessary to discontinue treatment.
- Urinary tract infection, presence of blood in the urine (macroscopic hematuria)
- Abnormal bladder size (contraction), abnormal urine flow (urinary tract obstruction), bladder shrinkage
- Orchitis
- Epididymitis
- Prostate inflammation (symptomatic granulomatous prostatitis)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Abnormal liver function test results
Rare (may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Vascular infection (e.g. infection at the site of vascular enlargement)
- Kidney abscess
Very rare (may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Infection of the implant and surrounding tissue with BCG bacteria (e.g. infection of an aortic prosthesis, pacemaker, hip or knee arthroplasty)
- Cervical lymph node inflammation, regional lymph node infection
- Allergic reactions (hypersensitivity), e.g. eyelid swelling, cough
- Eye inflammation (retinitis and uveitis)
- Conjunctivitis, eye membrane inflammation
- Vascular fistula
- Vomiting, intestinal fistula, peritonitis
- Bacterial infection of bone and bone marrow tissue
- Bone marrow infection
- Psoas muscle abscess
- Prostate or epididymitis resistant to antitubercular drugs
- Glans penis infection
- Arm or leg swelling
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Vascular inflammation (possibly in the brain)
- Genital organ disorders (e.g. vaginal pain)
- Pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Severe immune reactions with fever, liver enlargement, spleen enlargement, and lymph node enlargement, jaundice, and rash (hemophagocytic syndrome)
- Kidney failure, kidney tissue inflammation, pyelonephritis (pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis, including tubulointerstitial nephritis and glomerulonephritis)
- Absence or low sperm count in the semen (azoospermia, oligospermia)
- Increased prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocides of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocides:
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49-21-301, Fax: +48 22 49-21-309, Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store BCG-medac
Store the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton after the expiration date.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light.
The stability of the prepared product has been demonstrated for 24 hours when stored away from light at room temperature (20°C – 25°C) or in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
From a microbiological point of view, the medicinal product should be used immediately.
If the medicinal product is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the storage conditions before use, and usually, it should not be longer than 24 hours at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C, unless the reconstitution was performed in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
6. Package contents and other information
What BCG-medac contains
The active substance of the medicine is live BCG bacteria (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin, RIVM strain derived from strain 1173-P2).
1 vial contains after reconstitution:
BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin), RIVM strain derived from strain 1173-P2
from 2 x 10 to 3 x 10 live units.
The other ingredients of the powder are: polygelin, anhydrous glucose, polysorbate 80
The other ingredients of the solvent are: sodium chloride and water for injection
What BCG-medac looks like and what the package contains
BCG-medac is a white or almost white powder or a porous disk with yellow and gray hues and a colorless, clear solution serving as a solvent. The package contains 1, 3, or 5 vials, a bag with a solvent and a connector to the vial and a connector to the catheter, a catheter, and a Luer-Lock connector for conical connections. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
medac
Gesellschaft für
klinische Spezialpräparate mbH
Theaterstr. 6
22880 Wedel
Germany
e-mail:
[email protected]
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 03/2025.
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Treatment of symptoms, signs, and symptom complexes
| Symptoms, signs, and symptom complexes | Treatment |
| Symptomatic treatment |
| Discontinue BCG-medac treatment and start treatment with quinolones. If there is no complete cure after 10 days, administer isoniazid (INH)* for 3 months. When using antitubercular drugs, BCG-medac treatment should be discontinued. |
| Postpone BCG-medac treatment until the urine test results normalize and antibiotic treatment is completed. |
| Discontinue BCG-medac treatment. Consider consulting an infectious disease specialist. Administer isoniazid (INH)* and rifampicin* for 3 to 6 months, depending on the severity of symptoms. When using antitubercular drugs, BCG-medac treatment should be discontinued. |
| Symptomatic treatment with paracetamol. |
| Discontinue BCG-medac treatment. Consider consulting an infectious disease specialist. Administer antihistamines or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of an immune reaction, consider treatment with corticosteroids. If there is no response, administer isoniazid (INH)* for 3 months. |
| When using antitubercular drugs, BCG-medac treatment should be discontinued. | |
| Discontinue BCG-medac treatment. Consider consulting an infectious disease specialist. Administer three antitubercular drugs* for 6 months and low-dose corticosteroids. |
| Discontinue BCG-medac treatment immediately. Administer three antitubercular drugs* in combination with high-dose fast-acting corticosteroids. Consult an infectious disease specialist. |
*Note: BCG bacteria are susceptible to currently used antitubercular medicinal products, with the exception of pyrazinamide. If it is necessary to use three antitubercular drugs, the usually recommended drugs are: isoniazid (INH), rifampicin, and ethambutol.
**Definition - see: BCG infection/reaction
Important information about using BCG-medac
BCG-medac can only be used by experienced medical personnel.
Ensure proper storage conditions (see section 5) and package integrity.
BCG-medac should be administered under conditions required for endoscopy of the bladder.
The product BCG-medac cannot be administered subcutaneously, intradermally, intramuscularly, intravenously, or for vaccination against tuberculosis.
The Luer-Lock catheter connector in the solvent bag can only be used for intravesical instillation!
Basic principles and safety precautions for using BCG-medac
Generally, avoid direct contact with BCG-medac. BCG-medac is a medicinal product that can cause infection in humans and poses a risk to medical personnel. The risk may occur if the medicinal product enters the body through damaged skin, if aerosols are inhaled, droplets get into the eyes, or come into contact with mucous membranes, or are swallowed. Do not eat, drink, or smoke in work areas, and do not store food, drinks, or tobacco products there. BCG-medac cannot be prepared in a room where cytotoxic medicinal products for intravenous use are prepared, or by personnel preparing cytotoxic medicinal products for intravenous use.
The medicinal product cannot be prepared by persons with a known immune deficiency.
It is recommended to wear a surgical, zip-up, splash-resistant protective gown, single-use gloves, an FFP2 respiratory mask, and protective glasses with side shields as personal protective equipment when preparing the medicine. BCG-medac can only be transported in closed containers (storage conditions after reconstitution, see section 6.3).
After completing the work, wipe the work surfaces with a suitable disinfectant. After completing the work and in case of skin contact, disinfect your hands with a disinfectant, let them dry, wash them, and use skin care products.
BCG skin tests
Bladder instillation treatment with BCG-medac may cause increased sensitivity to tuberculin and complicate the later interpretation of tuberculin skin tests in the diagnosis of tuberculosis infections. Therefore, tuberculin sensitivity should be determined before administering BCG-medac.
Preparing the bladder suspension after reconstitution
Before use, the medicinal product must be mixed with aseptic precautions with sterile 0.9% (9 mg/ml) sodium chloride solution (see instructions for use, step 7). The catheter should be inserted with particular care to avoid damaging the urethral mucosa and bladder, which may lead to systemic BCG infection. It is recommended to use a lubricant to minimize the risk of traumatic catheterization and increase comfort during the procedure. In women, the amount of lubricant required may be less than in men. No interaction has been observed between the possible antiseptic effect of the lubricant and the effectiveness of BCG-medac. The bladder should be emptied after catheterization to reduce the amount of potentially introduced lubricant before administering BCG-medac. Before using the medicinal product, shake the suspension gently. Visible particles do not affect the effectiveness and safety of the medicinal product.
Discard any unused medicinal product or waste in accordance with local regulations.
Emergency procedures and BCG-medac spillage
Wear protective clothing and avoid raising dust.
Cover the spilled BCG-medac suspension with absorbent cellulose material and moisten it with a disinfectant with proven effectiveness against tubercle bacilli. After wiping the spilled BCG-medac suspension, clean the surface again with a disinfectant and let it dry. In case of skin contact, use a suitable disinfectant.
First aid
In case of contamination, always consult a doctor.
In case of skin contact: remove contaminated clothing. Disinfect and clean the skin and check for wounds.
In case of eye contact: rinse the affected eye with a suitable amount of eye wash or, alternatively, water. If necessary, remove contact lenses.
In case of ingestion: rinse the mouth with a large amount of water.
In case of inhalation: ensure adequate ventilation.
For more information on the catheter, see the relevant instructions for use.
Instructions for BCG-medac users
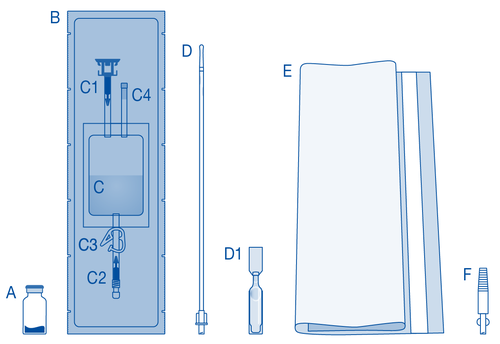
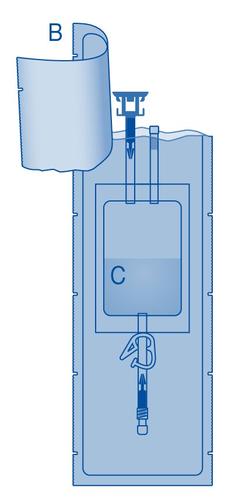
Components and use of the instillation setwith catheter and Luer-Lock connector for conical connection
Main components of the instillation set
Connecting the vial to the solvent bag
- 1. Prepare a waste bag (E) for disposal of the set after instillation to prevent contamination.
| Main component | Description |
| A | Vial with powder |
| B | Protective cover |
| C | Solvent bag 0.9% (9 mg/ml) sodium chloride solution |
| C1 | Vial connector with plug and flow blocker |
| C2 | Catheter Luer-Lock connector with plug and flow blocker |
| C3 | Clamp |
| C4 | Fill port without administration function |
| D | Catheter Luer-Lock |
| D1 | Lubricant |
| E | Waste bag |
| F | Luer-Lock connector for conical connection |
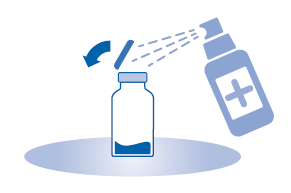
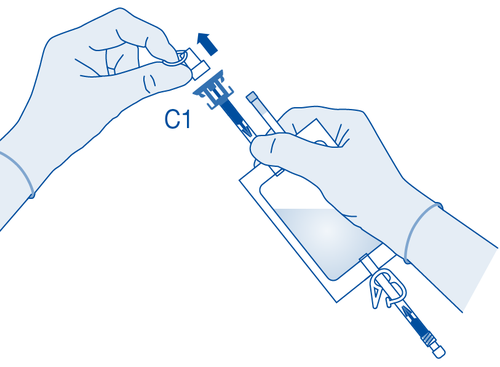
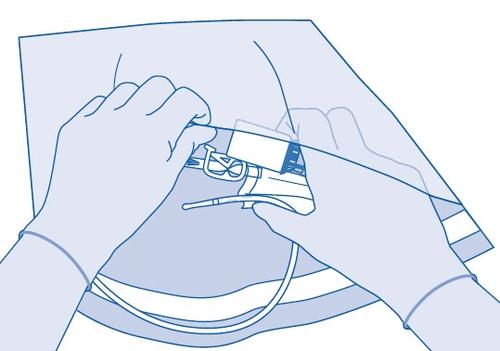
- 2. Remove the cap from the vial (A) and disinfect the stopper according to local regulations.
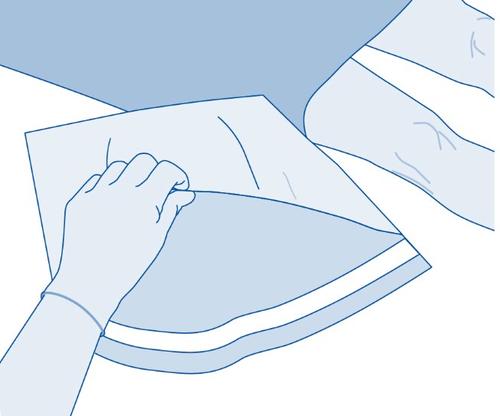
- 3. Tear off the protective cover (B) of the solvent bag (C) and completely remove the protective cover.
- 4. Remove the protective plug from the vial connector (C1).
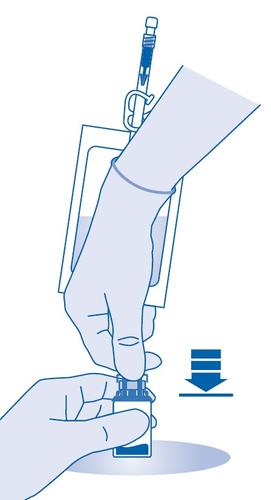
- 5. Press the connector into the rubber stopper of the vial until it stops.
Mixing the powder with the solvent
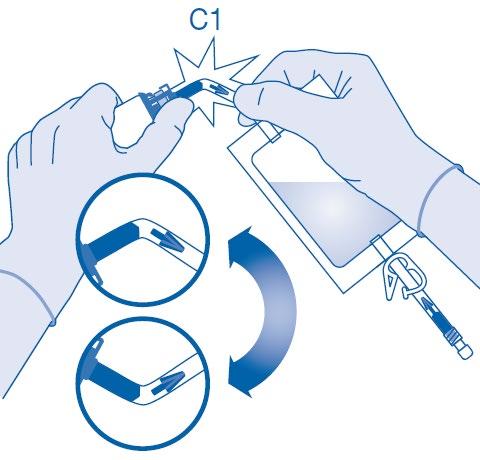
- 6. Break the flow blocker in the vial connector (C1) by bending it several times up and down.
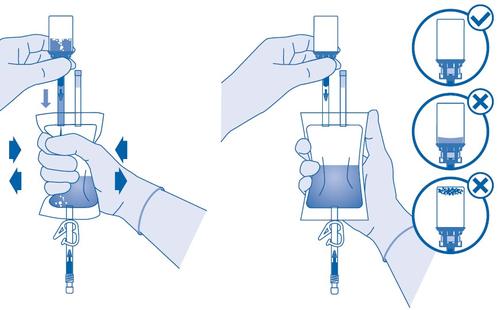
- 7. Hold the solvent bagso that the vial is below it.
Squeeze the solvent bag several times to transfer a sufficient amount of solvent to the vial.
Make sure the vial is notcompletely filled to allow for later transfer of the suspension to the solvent bag. Some solvent may remain in the bag.
While mixing the medicinal product with the solvent, slowlymove the vial to minimize intense foaming. If a large amount of foam appears, set the vial aside for a short time (a few minutes).
The vial contents must form a uniform suspension. This may take several minutes.
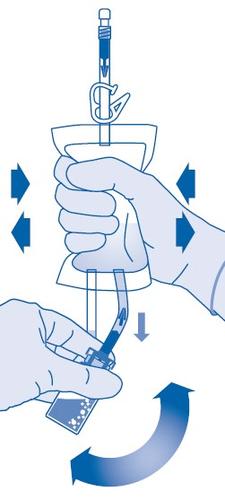
- 8. Invert the solvent bagand hold it so that the vial is above it, upside down.
Hold the vial.
Squeeze the solvent bag several times until the vial is empty.
If some powder remains in the vial, repeat steps 7 and 8.
From a microbiological point of view, the medicinal product should be used immediately.
If the medicinal product is not used immediately, refer to section 5 "How to store BCG-medac".
Do not administer the suspension at refrigerator storage temperature to prevent the patient from feeling the need to urinate, which results in a shortened exposure time.
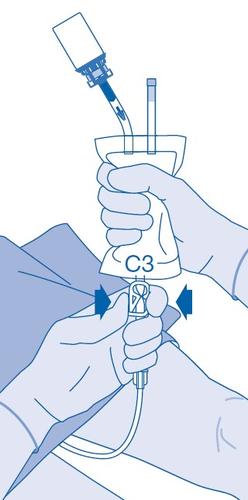
After injection
- 14. Closing the clamp (C3) prevents the fluid from flowing back into the catheter and minimizes the risk of contamination. Alternatively, you can squeeze the solvent bag while performing steps 15 and 16.
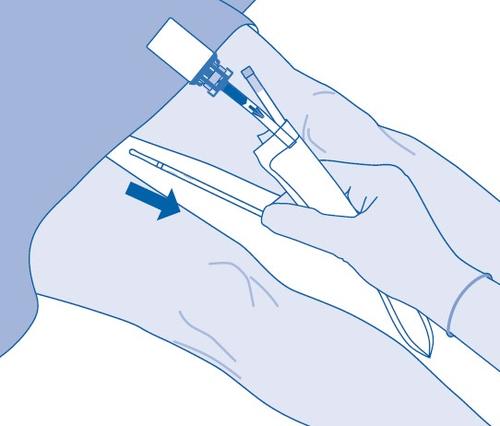
- 15. Carefully remove the catheter from the bladder without disconnecting the emptied solvent bag from the catheter. Avoid contamination from splashing droplets of suspension.
- 16. Place the catheter set in a waste bag and dispose of it in accordance with national regulations.
The contents of the vial are intended for single-use/one dose only. Any remaining suspension should be disposed of.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Importermedac Gesellschaft fuer klinische Spezialpraeparate mbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Bcg - medacDosage form: Powder, 2-8 x 108 CFU live, attenuated BCG bacilli/vialActive substance: BCG vaccinePrescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 100 mg (not less than 300 million and not more than 1.2 billion live BCG bacilli)/mlActive substance: BCG vaccinePrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 50 mg (not less than 150 million and not more than 600 million live BCG bacilli)/mlActive substance: BCG vaccinePrescription required
Alternatives to Bcg - medac in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Bcg - medac in Ukraine
Alternative to Bcg - medac in Spain
Online doctors for Bcg - medac
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Bcg - medac – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














