VAXIGRIP INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE

How to use VAXIGRIP INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Vaxigrip injectable suspension in a pre-filled syringe
Influenza vaccine (trivalent, inactivated, split virion)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you or your child are vaccinated because it contains important information for you or your child.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This vaccine has been prescribed to you or your child, do not pass it on to others, even if their symptoms are the same as yours, as it may harm them.
- If you or your child experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet
- What is Vaxigrip and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you or your child start using Vaxigrip
- How to use Vaxigrip
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Vaxigrip
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Vaxigrip and what is it used for
Vaxigrip is a vaccine.
This vaccine is given to you or your child from 6 months of age, it is indicated to protect you or your child against influenza.
When Vaxigrip vaccine is injected into a person, the immune system (the body's natural defense system) will produce protection (antibodies) against infection. When the vaccine is administered during pregnancy, it also protects the baby from birth to 6 months of age through the transmission of protection from mother to baby during pregnancy (see also sections 2 and 3).
None of the components of the vaccine can cause influenza.
The use of Vaxigrip should be based on official recommendations.
Influenza is a disease that can spread rapidly and is caused by different types of strains that can change every year. Due to this potential change in circulating strains each year, as well as the duration of the protection provided by the vaccine, vaccination is recommended every year. There is a higher risk of getting influenza during the cold months between October and March. If you or your child did not get vaccinated in the autumn, it is possible to get vaccinated until spring, since you or your child are at risk of getting infected with influenza during that period. Your doctor will be able to recommend the best date for vaccination.
The objective of Vaxigrip is to protect you or your child against the three strains of the virus contained in the vaccine after about 2 to 3 weeks of injection.
Additionally, the incubation period of influenza is a few days, so if you or your child are exposed to influenza immediately before or after vaccination, you or your child may develop the disease.
The vaccine will not protect you or your child against the common cold, even if some of the symptoms are similar to influenza.
2. What you need to know before you start using Vaxigrip
To ensure that Vaxigrip is suitable for you or your child, it is important that you consult your doctor or pharmacist if any of the points described below apply to you or your child. If there is anything you do not understand, consult your doctor or pharmacist to clarify it.
Do not use Vaxigrip
- If you or your child are allergic to:
- The active substances, or
- Any of the other components of this vaccine (listed in section 6), or
- Any of the components that may be present in minimal amounts, such as eggs (ovoalbumin or chicken proteins), neomycin, formaldehyde, or octoxinol-9.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Vaxigrip.
Consult your doctor before getting vaccinated if you or your child have:
- A weakened immune system (immunodeficiency or treatment with medicines that affect the immune system),
- Bleeding problems or bruising easily.
If you or your child have an acute illness with fever, vaccination should be postponed until the fever has disappeared.
Your doctor will decide if you or your child should receive the vaccine.
Fainting (syncope) may occur after any injection, especially in adolescents, so you should inform your doctor or nurse if you or your child have fainted after a previous injection.
Like all vaccines, Vaxigrip may not provide complete protection to all individuals who are vaccinated.
Not all babies under 6 months of age born to vaccinated pregnant women during pregnancy will be protected.
Children
Vaxigrip is not recommended for use in children under 6 months of age.
Use of Vaxigrip with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you or your child are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines or vaccines.
- Vaxigrip can be administered at the same time as other vaccines in different injection sites.
- The immune response may be reduced in the case of immunosuppressive treatments, such as corticosteroids, cytotoxic medicines, or radiotherapy.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this vaccine.
Vaxigrip can be used in all stages of pregnancy.
Vaxigrip can be used during breast-feeding.
Your doctor/pharmacist will decide if you should be vaccinated with Vaxigrip.
Driving and using machines
Vaxigrip has a negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Vaxigrip contains potassium and sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of potassium (39 mg) and less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose; i.e., it is essentially "potassium-free" and "sodium-free".
3. How to use Vaxigrip
Dosage
Adults: 1 dose of 0.5 ml.
Use in children and adolescents
Children from 6 months to 17 years of age receive a dose of 0.5 ml.
If your child is under 9 years of age and has not been previously vaccinated against influenza, a second dose of 0.5 ml should be administered after an interval of at least 4 weeks.
If you are pregnant, a dose of 0.5 ml administered during pregnancy may protect your baby from birth to 6 months of age. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How Vaxigrip is administered
Your doctor or nurse will administer the recommended dose of the vaccine with an injection into the muscle or under the skin.
If you or your child receive more Vaxigrip than you should
In some cases, more doses than recommended were accidentally administered.
In these cases, when adverse events were reported, they were in line with those described after administration of the recommended dose (see section 4).
If you have any doubts about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this vaccine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you experience an allergic reaction, contact your doctor or healthcare professional or go immediately to the emergency department of the nearest hospital.
Allergic reactions
Can occur immediately after administration of the vaccine and can be life-threatening.
Symptoms may include:
- rash, itching, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, swelling of the face, lips, throat, or tongue, low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, and weak pulse, cool and clammy skin, dizziness, weakness, or fainting (anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, shock).
- Other symptoms may include:
- itchy areas, redness, swelling, and cracking of the skin (atopic dermatitis), flushing, hot flush, blood in the white of the eye (ocular hyperaemia), redness and irritation of the eye (conjunctivitis), throat irritation, sore throat, irritation inside the nose, runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion, or throat congestion, numbness or tingling sensation in the mouth (oral paresthesia), rash in the mouth (oral mucosal rash), asthma.
These allergic reactions were reported as uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people) to rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people).
Additional side effects in adults and the elderly
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- headache, muscle pain, general feeling of being unwell (malaise) (1), pain at the injection site.
(1) Common in the elderly
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- fever (2), chills, reactions at the injection site: redness (erythema), hardness (induration), swelling.
(2) Uncommon in the elderly
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpit, or groin (lymphadenopathy) (3), unusual weakness (3), fatigue, drowsiness (4), dizziness (4), increased sweating (hyperhidrosis) (3), joint pain (3), diarrhea, feeling sick (nausea), reactions at the injection site: bruising, itching, heat, and discomfort.
(3) Rare in the elderly (4) Rare in adults
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- numbness or tingling sensation (paresthesia), vomiting, decreased appetite, flu-like illness.
- decreased sensitivity (hypoesthesia), abdominal pain, allergy at the injection site: only observed in adults.
- skin peeling (exfoliation) at the injection site: only observed in the elderly.
Additional side effects in children from 3 to 17 years of age
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- headache, muscle pain, general feeling of being unwell, chills, reactions at the injection site: pain, redness, swelling, hardness (5).
(5) Common in children from 9 to 17 years of age
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- fever, bruising at the injection site.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- fatigue, dizziness, diarrhea, reactions at the injection site: itching, heat.
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin, abdominal pain, vomiting, irritability, crying, joint pain, rash: only observed in children from 3 to 8 years of age.
- reduced number of certain types of particles in the blood called platelets; a low number of these can cause bruising or bleeding (thrombocytopenia): only observed in a 3-year-old child.
- unusual weakness, discomfort at the injection site: only observed in children from 9 to 17 years of age.
Additional side effects in children from 6 to 35 months of age
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- irritability (6), vomiting (7), muscle pain (8), general feeling of being unwell (8), fever, decreased appetite (6), reactions at the injection site; sensitivity, redness.
- abnormal crying, drowsiness: only observed in children under 24 months of age.
- headache: only observed in children from 24 months of age.
(6) Rare in children from 24 to 35 months of age
(7) Uncommon in children from 24 to 35 months of age
(8) Rare in children from 6 to 23 months of age
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- diarrhea, reactions at the injection site: hardness, bruising, swelling.
- chills: only observed in children from 24 months of age.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- flu-like illness, reactions at the injection site: itching, rash.
In children from 6 months to 8 years of age who receive 2 doses, the side effects are similar after both the first and second doses. Some side effects may occur after the administration of the second dose in children from 6 months to 35 months of age.
Most side effects occurred generally within 3 days after vaccination and resolved within 1 to 3 days without treatment. The intensity of most of these side effects was mild to moderate.
The frequency of the following side effects is unknown (cannot be estimated from the available data) in the whole population, except for the population for which the side effect is indicated above:
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin.
- numbness or tingling sensation (paresthesia), nerve pain (neuralgia) (9), seizures (convulsions), neurological disorders that can cause stiff neck, confusion, numbness, pain, and weakness of the limbs, loss of balance, loss of reflexes, paralysis of a part or all of the body (encephalomyelitis, neuritis (9), Guillain-Barré Syndrome (9)).
- inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) that can cause skin rashes and, in very rare cases, temporary kidney problems.
- temporary reduction in the number of certain types of particles in the blood called platelets; a low number of these can cause bruising or bleeding (transient thrombocytopenia).
(9) Not reported in children from 6 to 35 months of age
Reporting of side effects
If you or your child experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly to the Spanish Medicines Agency: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Vaxigrip
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this vaccine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the syringe in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Container contents and additional information
Vaxigrip composition
The active ingredients are: Influenza virus (fractionated, inactivated) of the following strains*:
- Strain similar to A/Victoria/4897/2022 (H1N1)pdm09: (IVR-238)....... 15 micrograms HA**
- Strain similar to A/Croatia/10136RV/2023(H3N2): (X-425A)............. 15 micrograms HA**
- Strain similar to B/Austria/1359417/2021: B/Michigan/01/2021 ..…... 15 micrograms HA**
Per 0.5 ml dose
- grown in embryonated chicken eggs from healthy chickens
** hemagglutinin
This vaccine complies with the recommendations of the World Health Organization (Northern Hemisphere) and the decision of the European Union for the 2025-2026 campaign.
The other components are: a buffer solution containing sodium chloride, disodium phosphate dihydrate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, potassium chloride, and water for injectable preparations.
Some components such as eggs (ovoalbumin, chicken proteins), neomycin, formaldehyde, or octoxinol-9 may be present in very small quantities (see section 2).
Appearance of the product and container contents
After careful shaking, the vaccine is a slightly colorless and opalescent liquid.
Vaxigrip is presented in a pre-filled syringe containing 0.5 ml of injectable suspension, with a fixed needle, a separate needle, or a safety needle, or without a needle, in packs of 1 or 10. Only some pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder:
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
82 avenue Raspail
94250 Gentilly
France
Manufacturer:
The manufacturer responsible for batch release is:
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
1541 avenue Marcel Mérieux
69280 Marcy l’Etoile
France
or
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
Voie de l’Institut – Parc Industriel d’Incarville
B.P 101
27100 Val de Reuil
France
or
Sanofi-Aventis Zrt.
Building Dc5 - Campona Utca 1
Budapest XXII,1225
Hungary
Local representative
sanofi-aventis, S.A.
C/ Rosselló i Porcel, 21
08016 Barcelona
Spain
Tel: +34 93 485 94 00
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Member State | Name |
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Germany, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Sweden, Slovenia, Slovakia, Spain | Vaxigrip |
Cyprus, Greece | Vaxigrip TIV |
Date of the last revision of thisleaflet: June 2025
Other sources of information
You can access detailed and updated information about this medicinal product by scanning the QR code included in the packaging with your mobile phone (smartphone). You can also access this information at the following internet address: https://vaxigrip-nh.info.sanofi.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
As with all injectable vaccines, medical treatment and appropriate supervision should be available in case of an anaphylactic reaction following administration of the vaccine.
The vaccine should reach room temperature before use.
Shake before use. Inspect visually before administration.
The vaccine should not be used if it contains foreign particles in the suspension.
It should not be mixed with other medicinal products in the same syringe.
This vaccine should not be injected directly into any blood vessel.
See also section 3. How to use Vaxigrip.
Instructions for use of the safety needle with the pre-filled Luer Lock syringe:
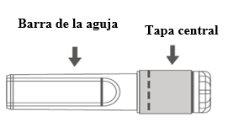
Image A: Safety needle (inside the bar) | Image B: Components of the safety needle (prepared for use) |
|
|
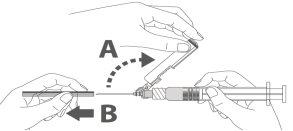
Step 1:To attach the needle to the syringe, remove the central cap to expose the needle bar and gently turn the needle on the Luer Lock adapter of the syringe until you feel a slight resistance. |
Step 2:Remove the protector from the safety needle. The needle is covered by the safety device and the protector. |
Step 3: A:Separate the safety device from the needle towards the body of the syringe at the angle shown. B:Remove the protector in a straight line. |
|
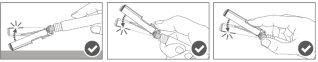
Step 4:Once the injection is complete, lock (activate) the safety device using one of the three techniques illustrated (3) with one hand: activation with a surface, with the thumb, or with the index finger. Note: Activation is verified by an audible and/or tactile "click". |
|
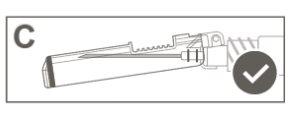
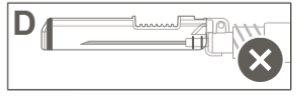
Step 5:Visually inspect the activation of the safety device. The safety device should be completely locked (activated)as shown in figure C. Figure D shows that the safety device is NOTcompletely locked (not activated). |
|
Caution: Do not attempt to unlock (deactivate) the safety device by forcing the needle out of the safety device.> |
Disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them should be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to VAXIGRIP INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGEDosage form: INJECTABLE, 3.75 microgramsActive substance: influenza, inactivated, split virus or surface antigenManufacturer: Glaxosmithkline BiologicalsPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5 mlActive substance: influenza, inactivated, split virus or surface antigenManufacturer: Sanofi Winthrop IndustriePrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 60 micrograms of HAActive substance: influenza, inactivated, split virus or surface antigenManufacturer: Sanofi Winthrop IndustriePrescription required
Online doctors for VAXIGRIP INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Discuss questions about VAXIGRIP INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions