TRIAXIS SUSPENSION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE

How to use TRIAXIS SUSPENSION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
TRIAXIS injectable suspension in pre-filled syringe
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (acellular component) vaccine
(adsorbed, reduced antigen content)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you or your child are vaccinated because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you or your child only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you or your child get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Triaxis and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you or your child receive Triaxis
- How to use Triaxis
- Possible side effects
- Storing Triaxis
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Triaxis and what is it used for
Triaxis (Tdap) is a vaccine. Vaccines are used to protect against infectious diseases. Vaccines make the body produce its own protection against the bacteria that cause these infectious diseases.
This vaccine is used as a booster against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough) in children from 4 years of age, adolescents, and adults after completing the primary vaccination schedule.
The use of Triaxis during pregnancy allows the transfer of protection to the child in the womb against whooping cough during the first months of life.
Limitations of the protection provided
Triaxis will only prevent these diseases if they are caused by the bacteria used to produce the vaccine. You or your child may still get similar diseases caused by other bacteria or viruses.
Triaxis does not contain any live bacteria or virus and cannot cause any of the infectious diseases it protects against.
Remember that no vaccine can provide complete and long-lasting protection to all people who are vaccinated.
2. What you need to know before you or your child receive Triaxis
To ensure that Triaxis is suitable for you or your child, it is important that you tell your doctor or nurse if any of the following apply to you or your child. If there is anything you do not understand, ask your doctor or nurse.
Do not use Triaxis if you or your child
- have had an allergic reaction:
- to diphtheria, tetanus, or pertussis (whooping cough) vaccines
- to any other component (listed in section 6)
- to any residual component transferred during manufacturing (formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde) that may be present in small amounts.
- have had a severe reaction that affected the brain within one week of a previous dose of a pertussis vaccine.
- have a severe acute illness. Vaccination should be delayed until you or your child have recovered. A minor illness without fever is not usually a reason to delay vaccination. Your doctor will decide if you or your child should receive Triaxis.
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor or nurse before vaccination if you or your child:
- have received a booster dose of a diphtheria and tetanus vaccine in the last 4 weeks. In this case, you or your child should not receive Triaxis and your doctor will decide when you or your child can receive another injection according to official recommendations.
- have had Guillain-Barré syndrome (temporary loss of mobility and sensitivity in the whole body or part of it) within 6 weeks of receiving a previous dose of a vaccine containing tetanus antigen. Your doctor will decide if you or your child should receive Triaxis.
- have a progressive disease that affects the brain/nerves or uncontrolled seizures. Your doctor will start treatment and perform vaccination when the condition has stabilized.
- have a reduced or deficient immune system due to
- medicines (e.g., steroids, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy).
- HIV or AIDS infection.
- any other disease.
It is possible that the vaccine may not protect these individuals in the same way as it protects people with a healthy immune system. If possible, vaccination should be postponed until the end of such illness or treatment.
- have bleeding disorders that cause easy bruising or prolonged bleeding after minor cuts (e.g., due to a bleeding disorder such as hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, or treatment with anticoagulant medicines).
Fainting can occur after any injection with a needle, even before. Tell your doctor or nurse if you or your child have fainted after a previous injection.
Tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting to use Triaxis if you or your child have had any allergic reaction to latex. The pre-filled syringes (1.5 ml) with a soft stopper contain a derivative of natural rubber latex (latex) that may cause an allergic reaction.
Other medicines or vaccines and Triaxis
Tell your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist if you or your child are using or have recently used or might use any other medicines.
Since Triaxis does not contain any live bacteria, it can be administered at the same time as other vaccines or immunoglobulins, although in a different injection site. There are studies that have shown that Triaxis can be used at the same time as some of the following vaccines: hepatitis B vaccine, polio virus vaccine (oral or injectable), inactivated influenza vaccine, and human papillomavirus vaccine, respectively. Injections of more than one vaccine at the same time will be performed in different limbs.
If you or your child are receiving medical treatment that affects the blood or immune system (such as anticoagulants, steroids, or chemotherapy), see the previous section "Warnings and precautions".
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Ask your doctor or nurse if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding. Your doctor will help you decide if you should receive Triaxis during pregnancy.
Driving and using machines
No studies have been performed on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines. The vaccine has a negligible effect on the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Triaxis
When will you or your child receive the vaccine
Your doctor will decide if Triaxis should be administered to you or your child based on:
- which vaccines you or your child have received in the past.
- how many doses of similar vaccines you or your child have received in the past.
- when you or your child received the last dose of a similar vaccine.
Your doctor will decide what period to wait between vaccinations.
If you are pregnant, your doctor will help you decide if you should receive Triaxis during pregnancy.
Dosage and administration
Who will administer Triaxis to you?
Triaxis should be administered by healthcare professionals trained in the use of vaccines and in a clinic or outpatient setting with the necessary equipment to treat any severe allergic reaction to the vaccine.
Dosage
All age groups for which it is indicated will receive an injection (0.5 ml).
In case you or your child experience an injury that requires preventive action against tetanus, your doctor may decide to give you Triaxis with or without tetanus immunoglobulin.
Triaxis can be used for booster vaccination. Your doctor will recommend repeating the vaccination.
Administration
The doctor or nurse will administer the vaccine in a muscle of the upper outer arm (deltoid muscle).
The doctor or nurse will not administer the vaccine in a blood vessel, buttocks, or under the skin. In case of bleeding disorders, they may decide to inject under the skin, although this may cause more local side effects, including a small lump under the skin.
If you have any doubts about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Triaxis can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Severe allergic reactions
If any of these symptoms occur after leaving the place where you or your child received the injection, see a doctor IMMEDIATELY.
- difficulty breathing
- blue discoloration of the tongue or lips
- a rash
- swelling of the face or throat
- low blood pressure causing dizziness or fainting (collapse)
When these signs or symptoms occur, they usually develop very quickly after the injection and while you or your child are still in the doctor's office. Severe allergic reactions are a very rare possibility (may affect 1 in 10,000 people) after receiving any vaccine.
Other side effects
The following side effects were observed during clinical studies conducted in specific age groups.
In children from 4 to 6 years of age
Very common (may occur in more than 1 in 10 people):
- loss of appetite
- headache
- diarrhea
- fatigue
- pain
- redness
- swelling at the injection site
Common (may occur in up to 1 in 10 people):
- nausea
- vomiting
- rash
- body pain or muscle weakness
- joint pain or swelling
- fever
- chills
- lymph node disorder in the armpit
In adolescents from 11 to 17 years of age
Very common (may occur in more than 1 in 10 people):
- headache
- diarrhea
- nausea
- body pain or muscle weakness
- joint pain or swelling
- fatigue/weakness
- malaise
- chills
- pain
- redness and swelling at the injection site
Common (may occur in up to 1 in 10 people):
- vomiting
- skin rash
- fever
- lymph node disorder in the armpit
In adults from 18 to 64 years of age
Very common (may occur in more than 1 in 10 people):
- headache
- diarrhea
- body pain or muscle weakness
- fatigue/weakness
- malaise
- pain
- redness and swelling at the injection site
Common (may occur in up to 1 in 10 people):
- nausea
- vomiting
- skin rash
- joint pain or swelling
- fever
- chills
- lymph node disorder in the armpit
The following additional adverse events have been reported in the recommended age groups during commercial use of Triaxis. It is not possible to calculate the frequency of these events, as they are based on voluntary reports of notification in relation to the estimated number of people vaccinated.
- allergic reactions/severe allergic reactions (for information on how to recognize such a reaction, see the beginning of section 4), muscle aches or numbness, paralysis of part or all of the body (Guillain-Barré syndrome), inflammation of the nerves in the arm (brachial neuritis), loss of function in the nerve that transmits the impulse to the facial muscles (facial paralysis), seizures, fainting, inflammation of the spinal cord (myelitis), inflammation of the muscular part of the heart (myocarditis), itching (pruritus), hives, inflammation of a muscle (myositis), extensive swelling of the limbs associated with redness, heat, pain to the touch, or pain at the injection site, bruising, swelling, or a small lump at the injection site.
Reporting of side effects
If you or your child experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is possible that they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Triaxis
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use Triaxis after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and label after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C). Do not freeze. Discard the vaccine if it freezes.
Keep the pre-filled syringe in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Triaxis
The active principles of each dose (0.5 ml) of the vaccine are:
Diphtheria toxoid not less than 2 international units (2 Lf) Tetanus toxoid not less than 20 international units (5 Lf) Pertussis antigens: Pertussis toxoid 2.5 micrograms Filamentous hemagglutinin 5 micrograms Pertactin 3 micrograms Fimbriae types 2 and 3 5 micrograms It is adsorbed on aluminum phosphate 1.5 mg (0.33 mg of Al3+)
Aluminum phosphate is included in the vaccine as an adjuvant. Adjuvants are substances included in certain vaccines to accelerate, enhance and/or prolong the protective effects of the vaccines.
The other components are: phenoxylethanol, water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
Triaxis is presented as an injectable suspension in a pre-filled syringe (0.5 ml):
- without needle - packaging of 1 or 10
- with 1 or 2 separate needles - packaging of 1 or 10
- with separate safety needle – packaging of 1 or 10
It contains a derivative of natural rubber latex (latex rubber) in the plug at the end of the pre-filled syringe.
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
The normal appearance of the vaccine is a white and turbid suspension, which may sediment during storage and form lumpy or scaly aggregates. After correct agitation, the liquid has a uniform white appearance. If there are aggregates, the product can be shaken again until a uniform suspension is obtained.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
The marketing authorization holder is:
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
82 avenue Raspail
94250 Gentilly
France
The manufacturer is:
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
1541 avenue Marcel Mérieux
Marcy l'Etoile - 69280 - France
or
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
Voie de l’Institut – Parc Industriel d’Incarville
B.P 101
27100 Val de Reuil
France
or
SANOFI-AVENTIS ZRT
Campona U.1 (Harbor Park ) - Budapest - 1225 - Hungary
Local Representative
sanofi-aventis, S.A.
C/ Rosselló i Porcel, 21
08016 Barcelona
Spain
Tel: +34 93 485 94 00
This medicinal product has been authorized in the EEA Member States under the following names:
Austria, Germany: | Covaxis |
Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Netherlands: | Triaxis |
Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): | Adacel |
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet:March 2023
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
In the absence of compatibility studies, Triaxis should not be mixed with other medicinal products.
Preparation for Administration
The pre-filled syringe may be supplied with a Luer Lock closure with a soft tip cap (Image A) or with a rigid tip cap (Image B). The syringe with the injectable suspension should be visually inspected before administration. In case of foreign particles, leaks, premature plunger activation, or defective tip sealing, discard the pre-filled syringe. The syringe is for single use and should not be reused.
Instructions for use of the Luer Lock pre-filled syringe:
Image A: Luer Lock Syringe with Soft Tip Cap
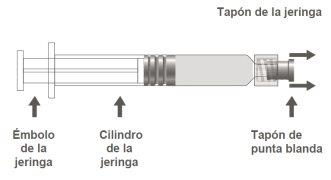
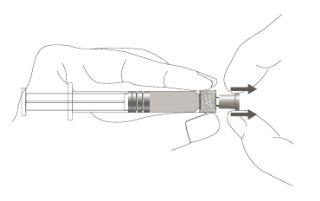
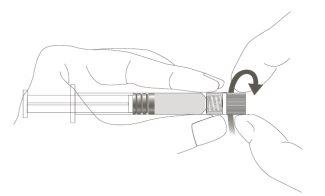
Step 1:Holding the syringe cap with one hand (avoid holding the plunger or the syringe cylinder), remove the tip cap. |
|
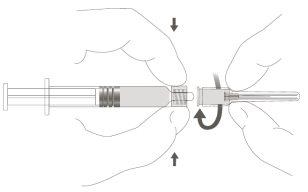
Step 2:To attach the needle to the syringe, gently turn it clockwise until you feel a slight resistance. |
|
Image B: Luer Lock Syringe with Rigid Tip Cap
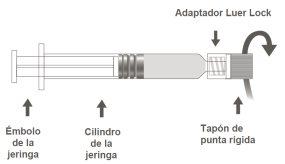
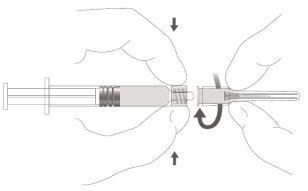
Step 1:Holding the Luer Lock adapter with one hand (avoid holding the plunger or the syringe cylinder), unscrew the tip cap by turning it. |
|
Step 2:To attach the needle to the syringe, gently turn the needle in the Luer Lock adapter of the syringe until you feel a slight resistance. |
|
Instructions for use of the safety needle with the Luer Lock pre-filled syringe:
Follow steps 1 and 2 above to prepare the Luer Lock syringe and needle for placement.
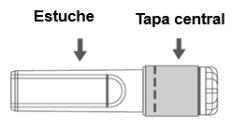
Image C: Safety Needle (Inside the Case) | Image D: Components of the Safety Needle (Prepared for Use) |
|
|
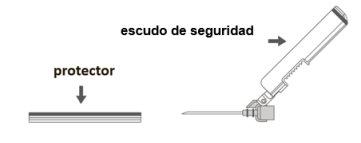
Step 3:Remove the safety needle cover. The needle is covered by the safety shield and the protector. | |
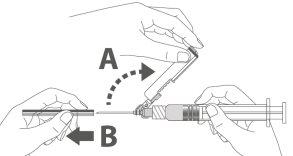
Step 4: A:Move the safety shield away from the needle and towards the syringe at the indicated angle. B:Remove the protector in a straight line. |
|
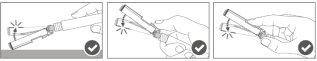
Step 5:Once the injection is complete, lock (activate) the safety shield using oneof the three one-handed activation techniques illustrated: surface activation, with the thumb, or with the finger. Note: Activation is verified by an audible and/or tactile "click". |
|
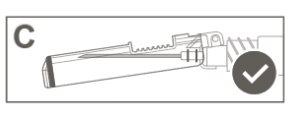
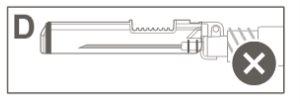
Step 6:Visually inspect the activation of the safety shield. The safety shield must be completely locked (activated)as shown in Figure C. Figure D shows that the safety shield is NOT completely locked (not activated). |
|
Caution: Do not attempt to unlock (deactivate) the safety device by forcing the needle out of the safety shield. |
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
The cap should not be replaced on the needles.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to TRIAXIS SUSPENSION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGEDosage form: INJECTABLE, -Active substance: pertussis, purified antigen, combinations with toxoidsManufacturer: Glaxosmithkline S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5 ml single doseActive substance: meningococcus B, multicomponent vaccineManufacturer: Glaxosmithkline Vaccines S.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5 ml single doseActive substance: meningococcus B, multicomponent vaccineManufacturer: Glaxosmithkline Vaccines S.R.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for TRIAXIS SUSPENSION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Discuss questions about TRIAXIS SUSPENSION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions