
ROPSINE 5 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use ROPSINE 5 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Ropsine5 mg/ml solution for injection EFG
Ropivacaine hydrochloride
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What Ropsine is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Ropsine
- How to use Ropsine
- Possible side effects
- Storing Ropsine
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Ropsine is and what it is used for
Ropsine contains the active substance ropivacaine hydrochloride, which belongs to a class of medicines called local anesthetics.
Ropsine is used in adults to numb(anesthetize) the area of the body where surgery is to be performed. It is injected into the lower part of the spine. This quickly stops pain from the waist down for a limited period (usually 1 to 2 hours). This is known as a "spinal block" (or "spinal").
Ropsine is used in children aged 1-12 years to numb (anesthetize) parts of the body. It is used to calm pain or to relieve pain.
2. What you need to know before you use Ropsine
Do not useRopsine
- if you are allergic(hypersensitive) to ropivacaine hydrochloride, or any other amide-type local anesthetic or any of the other ingredients of Ropsine (listed in section 6),
- if you have a reduced blood volume(hypovolemia). This will be measured by healthcare staff,
- to inject it into a blood vesselto numb a specific area of your body,
- to inject it into the neck of the wombto relieve pain during childbirth.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you start using Ropsine
- In children under 1 year, as the use of Ropsine injections to numb parts of the body has not been established.
- In children, as the use of Ropsine injections in the lower part of the spine has not been established.
Special care should be taken to avoid any injectionof Ropsine directly into a blood vesselto prevent any immediate toxic effect. The injection should not be performed in an inflamed area.
Tell your doctor:
- if you have a poor general conditiondue to age or other factors,
- if you have heart problems(partial or complete heart block),
- if you have an advanced liver problem,
- if you have severe kidney problems.
Tell your doctor if you have any of these problems as your doctor will need to adjust your dose of Ropsine.
Tell your doctor:
- if you have acute porphyria(problems with the production of red blood cell pigments, sometimes resulting in neurological symptoms).
Tell your doctor if you or a family member has porphyria as your doctor may need to use a different anesthetic.
Using Ropsine with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Caution should be taken if you are receiving:
- Other local anesthetics(e.g. lidocaine) or structurally related agents to amide-type local anesthetics, e.g. certain medicines used to treat irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia), such as mexiletine or amiodarone
- General anestheticsor opioids, such as morphine or codeine
- Medicines used to treat depression(e.g. fluvoxamine)
- Certain antibiotics(e.g. enoxacin)
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine. It is not known if ropivacaine hydrochloride affects pregnancy or if it passes into breast milk.
Children
Intrathecal administration (injection into the lower part of the spinal cord) has not been studied in infants or children under 12 years.
Driving and using machines
Ropsine may cause drowsiness and affect your reaction speed. Do not drive or use tools or machines after taking Ropsine, until the next day.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any doubts.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Ropsine
This medicine contains 3.2 mg of sodium (main component of cooking/table salt) per ml. This is equivalent to 0.2% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
3. How to use Ropsine
Method of administration
Ropsine will be administered to you by your doctor. It will be given to you by injection.
Dose
The recommended dose will depend on what it is being used for and also on your health, age, and weight.
The smallest dose that can produce a numbing effect (anesthesia) of the required area should be used.
The usual dose
- for adultsand adolescents over 12 yearsis between 15 mg and 25 mgof ropivacaine hydrochloride.
Duration of treatment
The administration of ropivacaine hydrochloride usually lasts between2 and 6 hoursin the case of anesthesiabefore certain surgeries.
It is administered by injection into the lower part of the spinal cord (intrathecal administration).
If you are given too much Ropsine
The first symptoms of being given too much ropivacaine hydrochloride are usually problems related to:
- hearing and vision,
- numbness around the mouth,
- dizziness or fainting,
- tingling,
- speech disorder characterized by poor articulation (dysarthria),
- muscle stiffness, muscle spasms, seizures (convulsions),
- low blood pressure,
- slow or irregular heartbeat.
These symptoms may precede a heart attack, respiratory arrest, or severe seizures.
If you experience any of these symptoms or think you may have been given too much Ropsine, tell your doctor or healthcare staff immediately.
In case of acute toxicity, the appropriate corrective measures will be taken immediately by healthcare staff.
Due to the low dose administered during injection into the lower part of the spinal cord (intrathecal administration), it is not expected that side effects affecting the whole body will occur.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Ropsine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Important side effects to look out for:
Sudden and potentially life-threatening allergic reactions (e.g. anaphylaxis, including anaphylactic shock) are rare and affect 1 to 10 people in 10,000. Possible symptoms include:
- sudden onset of rash, itching, or hives (urticaria);
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or other parts of the body;
- shortness of breath, wheezing, or difficulty breathing;
- and a feeling of loss of consciousness.
If you think you are having an allergic reaction to Ropsine, tell your doctor or healthcare staff immediately.
Other possible side effects:
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension). This may make you feel dizzy or faint.
- Feeling sick (nausea).
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Headache, tingling (paresthesia), feeling dizzy.
- Slow or fast heartbeat (bradycardia, tachycardia).
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Feeling sick (vomiting).
- Difficulty urinating (urinary retention).
- Back pain, high temperature, muscle stiffness.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Anxiety.
- Some symptoms may occur if the injection was accidentally given into a blood vessel, or if you have been given too much Ropsine (see also section 3 "If you are given too much Ropsine" above). These include seizures (convulsions), feeling dizzy or faint, numbness of the lips and around the mouth, numbness of the tongue, hearing problems, vision problems (vision), speech problems (dysarthria), muscle stiffness, and tremor, decreased sense of touch (hypoesthesia).
- Fainting (syncope).
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea).
- Low body temperature.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Heart attack, irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias).
Side effects that have been reported with other local anesthetics that may also be caused by Ropsine include:
- Numbness, due to irritation of the nerves caused by the needle or the injection. This usually does not last long.
- Nerve damage. This can rarely cause permanent problems.
- If too much Ropsine is administered into the spinal fluid, it can numb the whole body (anesthetize).
Additional side effects in children
In children, the side effects are the same as in adults, except for low blood pressure, which is less common in children (affecting less than 1 in 10 children), and feeling sick, which is more common in children (affecting more than 1 in 10 children).
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the Spanish Medicines Agency's website: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Ropsine
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use Ropsine after the expiry date which is stated on the ampoule or carton. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Do not freeze.
Do not use Ropsine if you notice any precipitation in the solution for injection.
Normally, your doctor or hospital will store Ropsine and are responsible for the quality of the product if it is not used immediately after opening. They are also responsible for disposing of any unused Ropsine correctly.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition ofRopsine
- The active ingredient is ropivacaine hydrochloride 5 mg/ml. Each 10 ml polypropylene ampoule contains 50 mg of ropivacaine (as hydrochloride).
- The other components are sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
Ropsine injectable solution is a clear, colorless, sterile, isotonic, isobaric aqueous solution.
Ropsine 5 mg/ml injectable solution EFG is available in 10 ml transparent polypropylene ampoules.
Container size:
10 sterile ampoules in a plastic blister pack.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Sintetica GmbH
Albersloher Weg 11
48155 Münster
Germany
Manufacturer:
Sintetica GmbH
Albersloher Weg 11
48155 Münster
Germany
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:September 2023.
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended solely for doctors or healthcare professionals:
Handling
Ropsine should be used by, or under the supervision of, experienced physicians in regional anesthesia (see section 3)
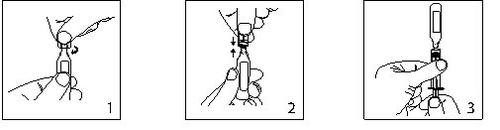
- Keep the ampoule in a vertical position and twist the neck to eliminate any remaining solution.
Open by twisting the top of the ampoule sharply.
- The ampoule can be connected directly to the syringe as shown in fig.2.
The ampoules are suitable for both Luerfit and LuerLock syringes.
- Hold the syringe with the ampoule upwards. Without squeezing the ampoule, withdraw the solution. Maintain downward pressure on the syringe plunger once the solution has been withdrawn and until the empty ampoule is discarded.
Shelf Life before Opening
3 years
Shelf Life after Opening
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, the storage conditions during use and before administration are the responsibility of the user and generally should not exceed 24 hours at 2-8°C.
Ropsine medicines are preservative-free products intended for single use. Discard any unused solution.
The medicinal product should be inspected visually before use. The solution should only be used if the solution is clear, practically free of particles, and if the container is intact.
The intact container should not be re-introduced into the autoclave.
Posology
Adults and adolescents over 12 years of age
The table below is a guide to the most commonly used doses in different types of block. The smallest dose required to produce an effective block should be used. Clinical experience and knowledge of the patient's clinical condition are important factors in deciding the dose.
Indication | Concentration mg/ml | Volume ml | Dose mg | Onset of Action minutes | Duration hours |
Surgical Anesthesia | |||||
Intrathecal Administration | |||||
Surgery | 5.0 | 3-5 | 15-25 | 1-5 | 2-6 |
The doses shown in the table are those considered necessary to produce an adequate block and should be considered as recommendations for use in adults. There are individual variations in the onset and duration of action. The figures in the "Dose" column reflect the average dose range expected. Adequate literature should be consulted for factors affecting specific block techniques and the requirements of each patient. |
Dose foruse in infants from 1 yearand children up to12 years.Intrathecal administration has not been investigated in infants or children.
Concentration | Volume | Dose (mg/kg) | |
ACUTE PAIN TREATMENT (pre- and post-operative) | |||
Single InjectionforPeripheral Nerve Block(for exampleilioinguinal nerve block,brachial plexus block) | 5.0 mg/ml | 0.5 – 0.6 ml/kg | 2.5 – 3.0 mg/kg |
Continuous InfusionforPeripheral Nerve Block1 | 2.0 mg/ml | 0.1 – 0.3 ml/kg/h | 0.2 – 0.6 mg/kg/h |
1 Recommended duration of infusion was up to 72 hours |
Method of Administration
Intrathecal injection.
Before and during injection, careful aspiration is recommended to prevent intravascular injection. Accidental intravascular injection can be recognized by a temporary increase in heart rate.
Aspiration should be performed before and during administration of the main dose, which should be injected slowly at a rate of 25-50 mg/minute, while constantly monitoring the patient's vital functions and maintaining verbal contact with them. If toxic symptoms appear, administration of the medicinal product should be interrupted immediately.
Intrathecal injection will be performed once the subarachnoid space has been identified and the clear cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is observed coming out of the spinal needle, or detected by aspiration.
Incompatibilities
No compatibility with other solutions has been investigated, so this medicinal product should not be mixed with other medicinal products.
Precipitation may occur in alkaline solutions since ropivacaine hydrochloride shows poor solubility at pH > 6.0.
Elimination
Elimination of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them should be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ROPSINE 5 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 mgActive substance: ropivacaineManufacturer: Altan Pharmaceuticals SaPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 2 mg/mlActive substance: ropivacaineManufacturer: Altan Pharmaceuticals SaPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 75 mgActive substance: ropivacaineManufacturer: Altan Pharmaceuticals SaPrescription required
Online doctors for ROPSINE 5 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about ROPSINE 5 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















