
RATIOGRASTIM 48 MU/0.8 ml SOLUTION FOR INJECTION OR INFUSION

How to use RATIOGRASTIM 48 MU/0.8 ml SOLUTION FOR INJECTION OR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Ratiograstim 30 MUI/0.5 ml Solution for Injection and Infusion
Ratiograstim 48 MUI/0.8 ml Solution for Injection and Infusion
filgrastim
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Ratiograstim and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Ratiograstim
- How to use Ratiograstim
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Ratiograstim
- Package Contents and Further Information
- Information for Self-Injection
- This information is intended only for healthcare professionals
1. What is Ratiograstim and what is it used for
What is Ratiograstim
Ratiograstim is a white blood cell growth factor (granulocyte-colony stimulating factor) and belongs to a group of medicines called cytokines. Growth factors are proteins that are produced naturally in the body, but can also be produced using genetic engineering for use as a medicine. Ratiograstim works by making the bone marrow produce more white blood cells.
What is Ratiograstim used for
A reduction in the number of white blood cells (neutropenia) can occur for several reasons and makes your body less effective at fighting infections. Ratiograstim stimulates the bone marrow to produce new white blood cells quickly.
Ratiograstim can be used:
- to increase the number of white blood cells after chemotherapy to help prevent infections;
- to increase the number of white blood cells after a bone marrow transplant to help prevent infections;
- before high-dose chemotherapy to make the bone marrow produce more stem cells, which can be collected and returned to your body after treatment. These cells can be collected from you or a donor. The stem cells will then return to the bone marrow and produce blood cells;
- to increase the number of white blood cells if you have severe chronic neutropenia to help prevent infections;
- to help reduce the risk of infection in patients with advanced HIV infection.
2. What you need to know before you use Ratiograstim
Do not use Ratiograstim
- if you are allergic to filgrastim or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and Precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment with Ratiograstim.
Tell your doctor before starting treatment if you have:
- sickle cell anaemia, as this medicine may cause sickle cell crisis;
- osteoporosis (bone disease).
Tell your doctor immediately during treatment with Ratiograstim if:
- you have sudden signs of allergy, such as rash, itching, or hives on the skin, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or other parts of the body, shortness of breath, wheezing, or difficulty breathing, as these may be signs of a severe allergic reaction (hypersensitivity);
- you have swelling in your face or ankles, blood in your urine, or urine that is brown in colour, or if you notice that you are urinating less often than usual (glomerulonephritis);
- you have pain in the upper left side of your abdomen (abdominal pain), pain below the left side of your rib cage, or pain in the left shoulder tip (these may be symptoms of an enlarged spleen [splenomegaly] or a possible rupture of the spleen);
- you notice unusual bleeding or bruising (these may be symptoms of a decrease in platelets in the blood [thrombocytopenia], with a reduced ability of the blood to clot);
- you have symptoms of inflammation of the aorta (the large blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body), this has rarely been reported in patients with cancer and in healthy donors. The symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, general feeling of being unwell, back pain, and increased inflammatory markers. Tell your doctor if you have these symptoms.
Loss of Response to Filgrastim
If you experience a loss of response or if you are unable to maintain a response to treatment with filgrastim, your doctor will investigate the causes, including whether you have developed antibodies that may neutralize the activity of filgrastim.
Your doctor may want to closely monitor you, see section 4 of the package leaflet.
If you are a patient with severe chronic neutropenia, you may be at risk of developing blood cancer (leukaemia, myelodysplastic syndrome [MDS]). Talk to your doctor about the risks of developing blood cancer and the tests that should be performed. If you develop or are likely to develop blood cancer, you should not use Ratiograstim unless your doctor says so.
If you are a stem cell donor, you must be between 16 and 60 years of age.
Be careful with other products that stimulate white blood cells
Ratiograstim belongs to a group of medicines that stimulate the production of white blood cells. Your doctor should always record the exact product you are using.
Other Medicines and Ratiograstim
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Ratiograstim has not been studied in pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Ratiograstim is not recommended during pregnancy.
It is important that you tell your doctor if you:
- are pregnant or breastfeeding;
- think you may be pregnant; or
- are planning to have a baby.
If you become pregnant during treatment with Ratiograstim, tell your doctor. Unless your doctor tells you otherwise, you must stop breastfeeding if you use Ratiograstim.
Driving and Using Machines
Ratiograstim has a minor influence on your ability to drive and use machines. This medicine may cause dizziness. It is recommended that you wait and see how you feel after administration of the medicine before driving or operating machinery.
Ratiograstim contains Sorbitol
This medicine contains 50 mg of sorbitol in each ml.
For intravenous administration
Sorbitol is a source of fructose. If you (or your child) have hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI), a rare genetic disorder, you (or your child) should not receive this medicine. Patients with HFI cannot break down fructose, which can cause serious side effects. Consult your doctor before receiving this medicine if you (or your child) have HFI or if your child cannot take sweet foods or drinks because they cause nausea, vomiting, or unpleasant effects such as bloating, stomach cramps, or diarrhoea.
Ratiograstim contains Sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per pre-filled syringe; this is essentially “sodium-free”.
3. How to use Ratiograstim
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as told by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
How is Ratiograstim administered and how much should you take?
Ratiograstim is usually administered once a day as an injection into the tissue just under the skin (known as a subcutaneous injection). It can also be administered once a day as a slow injection into a vein (known as an intravenous infusion). The usual dose varies depending on your disease and weight. Your doctor will tell you how much Ratiograstim you should take.
Patients with bone marrow transplant after chemotherapy:
You will usually receive your first dose of Ratiograstim at least 24 hours after chemotherapy and at least 24 hours after receiving your bone marrow transplant.
You or the people caring for you may be taught how to administer subcutaneous injections so that you can continue treatment at home. However, you should not attempt to do this unless you have been properly trained by a healthcare professional.
How long will you need to take Ratiograstim?
You will need to take Ratiograstim until your white blood cell count is normal. You will have regular blood tests to monitor the number of white blood cells in your body. Your doctor will tell you how long you need to take Ratiograstim.
Use in Children
Ratiograstim is used to treat children who are receiving chemotherapy or who have a low white blood cell count (neutropenia). The dose given to children receiving chemotherapy is the same as for adults.
If you use more Ratiograstim than you should
Do not increase the dose that your doctor has prescribed. If you have used more Ratiograstim than you should, contact your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible.
If you forget to use Ratiograstim
If you have missed an injection or if you have injected less dose, contact your doctor as soon as possible. Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Important side effects
It is important that you contact your doctor immediately:
- if you experience an allergic reaction, including weakness, low blood pressure, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face (anaphylaxis), skin rash, itchy skin rash (urticaria), swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat (angioedema), and shortness of breath (dyspnoea);
- if you experience cough, fever, and difficulty breathing (dyspnoea), as this may be a sign of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS);
- if you experience kidney damage (glomerulonephritis). Kidney damage has been observed in patients receiving filgrastim. Contact your doctor immediately if you notice swelling in your face or ankles, blood in your urine, or urine that is brown in colour, or if you notice that you are urinating less often than usual;
- if you experience any or a combination of the following side effects:
- swelling that may be associated with urinating less often, difficulty breathing, swelling, and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, and a general feeling of tiredness. These symptoms usually develop quickly.
These may be symptoms of a condition called “capillary leak syndrome” and can cause blood to leak from small blood vessels into other parts of your body and may require urgent medical attention.
- if you experience a combination of the following symptoms:
- fever, chills, or feeling very cold, rapid heartbeat, confusion or disorientation, difficulty breathing, severe pain or discomfort, and sweaty skin.
These could be symptoms of a condition called “sepsis” (also called “blood poisoning”), a serious infection with a whole-body inflammatory response that can be life-threatening and requires urgent medical attention;
- if you experience pain in the upper left side of your abdomen (abdominal pain), pain below the left side of your rib cage, or pain in the left shoulder tip, as this may be a problem with your spleen (enlarged spleen [splenomegaly] or rupture of the spleen);
- if you are being treated for severe chronic neutropenia and have blood in your urine (haematuria). Your doctor will perform regular urine tests if you experience this side effect or if protein is found in your urine (proteinuria).
A common side effect of using Ratiograstim is pain in the muscles or bones (musculoskeletal pain), which can be relieved by taking usual pain-relieving medicines (analgesics). In patients undergoing stem cell or bone marrow transplantation, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) may occur. This is a reaction of the donor cells against the patient receiving the transplant; signs and symptoms include rashes on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet, and ulcers and sores in the mouth, intestine, liver, skin, eyes, lungs, vagina, and joints.
In healthy donors of stem cells, an increase in white blood cells (leucocytosis) and a decrease in platelets that can reduce the ability of the blood to clot (thrombocytopenia) may be observed. These effects will be monitored by your doctor.
You may experience the following side effects:
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Decrease in platelets, which reduces the ability of the blood to clot (thrombocytopenia)
- Low red blood cell count (anaemia)
- Headache
- Diarrhoea
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Unusual hair loss or thinning (alopecia)
- Fatigue
- Irritation and swelling of the lining of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus (mucosal inflammation)
- Fever (pyrexia)
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Inflammation of the lungs (bronchitis)
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Urinary tract infection
- Decreased appetite
- Sleep disorders (insomnia)
- Dizziness
- Decreased sensitivity, especially in the skin (hypoesthesia)
- Numbness or tingling of the hands or feet (paraesthesia)
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Cough
- Coughing up blood (haemoptysis)
- Pain in the mouth and throat (oropharyngeal pain)
- Nosebleeds (epistaxis)
- Constipation
- Mouth pain
- Enlargement of the liver (hepatomegaly)
- Rash
- Redness of the skin (erythema)
- Muscle cramp
- Pain when urinating (dysuria)
- Chest pain
- Pain
- General weakness (asthenia)
- Feeling unwell (malaise)
- Swelling in hands and feet (peripheral oedema)
- Increased levels of certain enzymes in the blood
- Changes in blood biochemistry tests
- Transfusion reaction
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Increased white blood cells in the blood (leucocytosis)
- Allergic reaction (hypersensitivity)
- Rejection of bone marrow transplant (graft-versus-host disease)
- High levels of uric acid in the blood, which can cause gout (hyperuricaemia) (elevated uric acid in blood)
- Liver damage caused by blockage of small veins in the liver (veno-occlusive disease)
- Lungs not working as they should, causing shortness of breath (respiratory failure)
- Swelling or fluid in the lungs (pulmonary oedema)
- Inflammation of the lungs (interstitial lung disease)
- Abnormal chest X-rays (pulmonary infiltration)
- Bleeding in the lungs (pulmonary haemorrhage)
- Lack of oxygen absorption in the lungs (hypoxia)
- Irregular skin rash (maculopapular rash)
- Disease that causes bones to lose density, making them weaker, more fragile, and prone to breaking (osteoporosis)
- Reaction at the injection site
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Severe pain in the bones, chest, intestines, or joints (sickle cell crisis)
- Sudden, life-threatening allergic reactions (anaphylactic reaction)
- Swelling and pain in the joints, similar to gout (pseudogout)
- A change in the way your body regulates body fluids, which can result in swelling (fluid volume changes)
- Inflammation of the blood vessels in the skin (cutaneous vasculitis)
- Painful, inflamed, dark red ulcers on the limbs and sometimes on the face and neck, accompanied by fever (Sweet's syndrome)
- Worsening of rheumatoid arthritis
- Unusual changes in urine
- Decrease in bone density
- Inflammation of the aorta (the large blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body), see section 2
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Ratiograstim
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and on the pre-filled syringe after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month shown.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2 °C and 8 °C).
Within its validity period and for ambulatory use, the medicine can be taken out of the refrigerator (2 °C - 8 °C) and stored at a temperature of up to 25 °C for a single period of up to 4 days. If the medicine has not been used within these 4 days, it must be refrigerated again (2 °C - 8 °C) until the expiry date. Pre-filled syringes stored at more than 8 °C for more than 4 days must be discarded.
Do not use this medicine if you notice turbidity or particles in the interior.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Ratiograstim Composition
- The active substance is filgrastim. Each milliliter of injectable solution and infusion contains 60 million international units (MIU) (600 micrograms) of filgrastim.
Ratiograstim 30 MIU/0.5 ml: each pre-filled syringe contains 30 million international units [MIU] (300 micrograms) of filgrastim in 0.5 ml of solution.
Ratiograstim 48 MIU/0.8 ml: each pre-filled syringe contains 48 million international units [MIU] (480 micrograms) of filgrastim in 0.8 ml of solution.
- The other components are: sodium hydroxide, glacial acetic acid, sorbitol, polysorbate 80, water for injectable preparations.
Product Appearance and Package Contents
Ratiograstim is an injectable and infusion solution in a pre-filled syringe with or without a safety device. Ratiograstim is a clear and colorless solution. Each pre-filled syringe contains 0.5 ml or 0.8 ml of solution.
Ratiograstim is supplied in packs of 1, 5, or 10 pre-filled syringes or in multipacks containing 10 pre-filled syringes (2 packs of 5). Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
ratiopharm GmbH
Graf-Arco-Strasse 3
89079 Ulm
Germany
Manufacturer
Teva Biotech GmbH
Dornierstrasse 10
89079 Ulm
Germany
Merckle GmbH
Graf-Arco-Straße 3
89079 Ulm
Germany
You can request more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Belgium/Belgique/Belgien Teva Pharma Belgium N.V./S.A./AG Tel: +32 38207373 | Lithuania UAB Teva Baltics Tel: +370 52660203 |
| Luxembourg/Luxemburg ratiopharm GmbH Germany/Deutschland Tel: +49 73140202 |
Czech Republic Teva Pharmaceuticals CR, s.r.o. Tel: +420 251007111 | Hungary Teva Gyógyszergyár Zrt. Tel: +36 12886400 |
Denmark Teva Denmark A/S Tlf: +45 44985511 | Malta Teva Pharmaceuticals Ireland Ireland Tel: +44 2075407117 |
Germany ratiopharm GmbH Tel: +49 73140202 | Netherlands Teva Nederland B.V. Tel: +31 8000228400 |
Estonia UAB Teva Baltics Eesti filiaal Tel: +372 6610801 | Norway Teva Norway AS Tlf: +47 66775590 |
Greece Specifar Α.Β.Ε.Ε. Τηλ: +30 2118805000 | Austria ratiopharm Arzneimittel Vertriebs-GmbH Tel: +43 1970070 |
Spain Teva Pharma, S.L.U. Tel: +34 913873280 | Poland Teva Pharmaceuticals Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 223459300 |
France Laboratoires Biogaran Tél: +33 800970109 | Portugal ratiopharm - Comércio e Indústria de Produtos Farmacêuticos, Lda. Tel: +351 214767550 |
Croatia Pliva Hrvatska d.o.o. Tel: +385 13720000 | Romania Teva Pharmaceuticals S.R.L. Tel: +40 212306524 |
Ireland Teva Pharmaceuticals Ireland Tel: +44 2075407117 | Slovenia Pliva Ljubljana d.o.o. Tel: +386 15890390 |
Iceland Teva Pharma Iceland ehf. Sími: +354 5503300 | Slovakia TEVA Pharmaceuticals Slovakia s.r.o. Tel: +421 257267911 |
Italy Teva Italia S.r.l. Tel: +39 028917981 | Finland Teva Finland Oy Puh/Tel: +358 201805900 |
Cyprus Specifar Α.Β.Ε.Ε. Ελλάδα Τηλ: +30 2118805000 | Sweden Teva Sweden AB Tel: +46 42121100 |
Latvia UAB Teva Baltics filiale Latvija Tel: +371 67323666 | United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) Teva Pharmaceuticals Ireland Ireland Tel: +44 2075407117 |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
- Information for Self-Administration
This section contains information on how to administer Ratiograstim to yourself. It is essential that you do not attempt to administer an injection without having received the necessary training from your doctor or nurse. If you are unsure about administering an injection or have any doubts, consult your doctor or nurse.
How to Self-Administer Ratiograstim
You must inject it into the tissue just under the skin. This is known as a subcutaneous injection. The injection should be administered every day at approximately the same time.
Equipment Needed for Administration
For subcutaneous injection administration, you will need:
- a pre-filled syringe of Ratiograstim,
- cotton or similar with alcohol.
What Should I Do Before Administering a Subcutaneous Injection of Ratiograstim
- Try to administer the injection at approximately the same time every day.
- Remove the pre-filled syringe of Ratiograstim from the refrigerator.
- Check the expiry date on the pre-filled syringe (EXP). Do not use it if the date is later than the last day of the month shown.
- Check the appearance of Ratiograstim. It should be a clear and colorless liquid. If there are particles in the interior, do not use it.
- For a more comfortable injection, let the pre-filled syringe stand at room temperature for 30 minutes or gently hold the pre-filled syringe in your hands for a few minutes. Do not heat Ratiograstim in any other way (e.g., do not heat it in a microwave or hot water)
- Do notremove the cap from the syringe until you are ready for the injection
- Wash your hands carefully.
- Find a comfortable and well-lit place and put everything you need within reach (the pre-filled syringe of Ratiograstim and the cotton).
How to Prepare Your Ratiograstim Injection
Before injecting Ratiograstim, you must:
- Take the syringe and remove the protective cap from the needle gently without tilting it. Separate as indicated in images 1 and 2. Do not touch the needle or push the plunger.
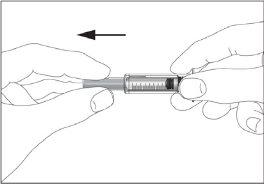 1
1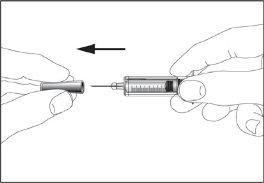 2
2
- A small air bubble may appear in the pre-filled syringe. If there are bubbles, tap the syringe gently with your fingers until the bubbles go to the end of the syringe. With the syringe pointing upwards, extract the air from the syringe by pushing the plunger.
- The syringe has a scale. Push the plunger until the number (ml) on the syringe corresponds to the prescribed dose of Ratiograstim by your doctor.
- Check again that the dose of Ratiograstim is correct.
- Now you can use the pre-filled syringe.
Where Should I Put the Injection
The most suitable injection sites are:
- the top of the thighs; and
- the abdomen, except the area around the navel (see image 3).
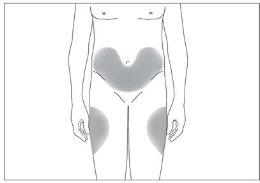 3
3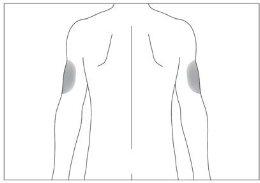 4
4
If someone else administers the injection, they can also use the back of your upper arms (see image 4)
To avoid the risk of pain at a given point, it is best to change the injection site every day.
How to Inject Myself
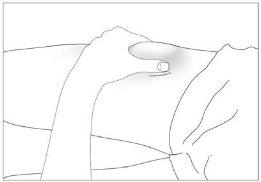
- Disinfect your skin using cotton with alcohol and pinch the skin between your thumb and index finger, without squeezing (see image 5).
- Insert the needle completely into the skin as your nurse or doctor indicated (see image 6).
- Gently pull the plunger to ensure that you have not punctured a vein. If you see blood in the syringe, remove the needle and insert it into another area.
- Inject the liquid slowly and regularly, keeping the skin pinched.
- Inject only the dose prescribed by your doctor.
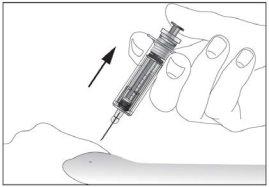
- Remove the needle from the injection site while keeping your finger on the plunger (see image 7). Direct the needle away from you and those around you and activate the safety device by pressing the plunger firmly (see image 8). You will hear a "click," which confirms the activation of the safety device. The needle will be covered with a protective sheath so that you cannot prick yourself.
 5
5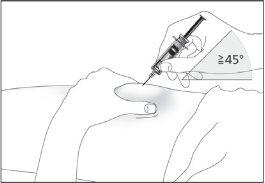 6
6
 7
7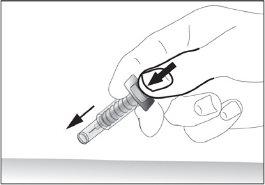 8
8
Remember
If you have any doubts, ask for help or advice from your doctor or nurse.
How to Dispose of Used Syringes
- The safety device prevents needlestick injuries after use, so no special disposal precautions are necessary. Dispose of the syringes with the safety device according to the instructions of your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.
- This information is intended only for healthcare professionals
Ratiograstim does not contain preservatives. In view of the potential risk of microbial contamination, Ratiograstim pre-filled syringes are for single use only.
Accidental exposure to freezing temperatures does not negatively affect the stability of Ratiograstim.
Ratiograstim should not be diluted with sodium chloride. This medicine should not be mixed with other medicines except those mentioned below. The dilution of filgrastim may be adsorbed by glass and plastic materials except if diluted as mentioned below.
Ratiograstim can be diluted, if necessary, in a glucose 50 mg/ml (5%) solution for infusion. It is not recommended to dilute to final concentrations below 0.2 MIU (2 μg) per ml. The solution should be inspected visually before use. Only clear solutions without particles should be used. In patients treated with filgrastim diluted to concentrations below 1.5 MIU (15 μg) per ml, human serum albumin (HSA) should be added to a final concentration of 2 mg/ml. Example: if the final injection volume is 20 ml and the total dose of filgrastim is below 30 MIU (300 μg), 0.2 ml of a 200 mg/ml (20%) human albumin solution should be administered. When Ratiograstim is diluted in a glucose 50 mg/ml (5%) solution for infusion, it is compatible with glass and various plastics such as PVC, polyolefin (copolymer of polypropylene and polyethylene), and polypropylene.
After dilution: the chemical and physical stability of the diluted infusion solution has been demonstrated for 24 hours stored between 2 and 8 °C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, the storage time and conditions of the diluted solution are the responsibility of the user and normally should not exceed 24 hours between 2 and 8 °C, unless the dilution has been made under validated and controlled aseptic conditions.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to RATIOGRASTIM 48 MU/0.8 ml SOLUTION FOR INJECTION OR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 12 IU/0.2 mlActive substance: filgrastimManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.3 mg / prefilled syringeActive substance: filgrastimManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.3 mg / prefilled syringeActive substance: filgrastimManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for RATIOGRASTIM 48 MU/0.8 ml SOLUTION FOR INJECTION OR INFUSION
Discuss questions about RATIOGRASTIM 48 MU/0.8 ml SOLUTION FOR INJECTION OR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions







