
RAPAMUNE 1 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION

How to use RAPAMUNE 1 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Rapamune 1 mg/ml Oral Solution
sirolimus
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
|
Contents of the pack
- What is Rapamune and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you take Rapamune
- How to take Rapamune
- Possible side effects
- Storing Rapamune
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Rapamune and what is it used for
Rapamune contains the active substance sirolimus, which belongs to a group of medicines called immunosuppressants. It helps to control your body's immune system after you have received a kidney transplant.
Rapamune is used in adults to prevent rejection of transplanted kidneys and is normally used in combination with other immunosuppressive medicines called corticosteroids, and initially (for the first 2 to 3 months) with cyclosporin.
Rapamune is also used to treat patients with sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis (S-LAM) with moderate to severe lung disease or declining lung function. S-LAM is a rare, progressive lung disease that mainly affects women of childbearing age. The most common symptom of S-LAM is difficulty breathing.
2. What you need to know before you take Rapamune
Do not take Rapamune
- if you are allergic to sirolimus or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you are allergic to peanuts or soya.
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor or pharmacist before you start taking Rapamune.
- If you have any liver problems or have had any disease that may have affected your liver, tell your doctor as this may affect the dose of Rapamune you receive and may mean you have other blood tests.
- Rapamune, like other immunosuppressant medicines, may reduce your ability to fight infections and may increase the risk of developing cancer of the lymphoid tissues and skin.
- If you have a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or more, you may have a higher risk of abnormal wound healing.
- If you are considered to be at high risk of rejecting your kidney transplant, for example if you have had a previous transplant that was rejected.
Your doctor will do tests to monitor your blood levels of Rapamune. Your doctor will also do tests to check your kidney function, to measure your lipid (cholesterol and/or triglyceride) levels in your blood, and possibly your liver function, during treatment with Rapamune.
Exposure to sunlight and UV light should be limited by covering your skin with clothing and using a sunscreen with a high sun protection factor, due to the increased risk of skin cancer.
Children and adolescents
Experience with the use of Rapamune in children and adolescents under 18 years of age is limited. The use of Rapamune in this population is not recommended.
Taking Rapamune with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
Some medicines may interfere with the action of Rapamune and may require a dose adjustment. In particular, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- any other immunosuppressant medicine
- antibiotics or antifungal medicines used to treat infections, such as clarithromycin, erythromycin, telithromycin, troleandomycin, rifabutin, clotrimazole, fluconazole, and itraconazole. You should not take Rapamune with rifampicin, ketoconazole, or voriconazole.
- any medicine used to treat high blood pressure or heart problems, including nicardipine, verapamil, and diltiazem
- antiepileptic medicines, including carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin
- medicines used to treat ulcers or other gastrointestinal problems, such as cisapride, cimetidine, or metoclopramide
- bromocriptine (used to treat Parkinson's disease and various hormonal disorders), danazol (used to treat gynaecological disorders), or protease inhibitors (for example, for HIV and hepatitis C, such as ritonavir, indinavir, boceprevir, and telaprevir)
- St John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- letermovir (an antiviral medicine to prevent illness from cytomegalovirus)
- cannabidiol (its use includes, among others, the treatment of epileptic seizures)
Vaccines containing live organisms should be avoided during treatment with Rapamune. Before vaccination, tell your doctor or pharmacist that you are receiving Rapamune.
Treatment with Rapamune may lead to increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood (blood fats) that may require treatment. Medicines known as "statins" and "fibrates" used to treat high cholesterol and triglycerides have been associated with an increased risk of muscle fibre breakdown (rhabdomyolysis). Tell your doctor if you are taking medicines to lower your blood fats.
The combined use of Rapamune and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (a type of medicine used to lower blood pressure) may cause allergic reactions. Tell your doctor if you are taking these medicines.
Taking Rapamune with food and drink
Always take Rapamune the same way, with or without food. If you prefer to take Rapamune with food, you should always take it with food. If you prefer to take Rapamune without food, you should always take it without food. Food can affect the amount of medicine that gets into your blood and, therefore, taking your medicine the same way each time will help keep your blood levels of Rapamune more stable.
Do not take Rapamune with grapefruit juice.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Rapamune should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary. You should use effective contraception during treatment with Rapamune and for 12 weeks after stopping treatment. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
It is not known whether Rapamune passes into breast milk. Patients who take Rapamune should not breastfeed.
A reduction in sperm count has been associated with the use of Rapamune, which usually returns to normal after stopping treatment.
Driving and using machines
Although treatment with Rapamune is not expected to affect your ability to drive, if you are unsure, consult your doctor.
Rapamune contains ethanol (alcohol)
Rapamune contains up to 3.17% ethanol (alcohol). An initial dose of 6 mg contains up to 150 mg of alcohol, which is equivalent to 3.80 ml of beer or 1.58 ml of wine. This amount of alcohol may be harmful for individuals with alcoholism, as well as for pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and high-risk groups, such as patients with liver disease or epilepsy. Alcohol may modify or increase the effect of other medicines.
Maintenance doses of 4 mg or less contain small amounts of ethanol (100 mg or less), amounts that are probably too low to be harmful.
3. How to take Rapamune
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, check with your doctor or pharmacist.
Your doctor will decide the exact dose of Rapamune that you should take and how often you should take it. Always follow your doctor's instructions and never change the dose yourself.
Rapamune is for oral use only. Tell your doctor if you have difficulty taking the oral solution.
Always take Rapamune the same way, with or without food.
Kidney transplant
Your doctor will give you an initial dose of 6 mg as soon as possible after your kidney transplant operation. After this, you will need to take 2 mg of Rapamune every day until your doctor tells you otherwise. Your dose will be adjusted depending on your blood levels of Rapamune. Your doctor will need to do blood tests to measure the levels of Rapamune in your blood.
If you are also taking cyclosporin, you should take the two medicines approximately 4 hours apart.
It is recommended that you first take Rapamune in combination with cyclosporin and corticosteroids. After 3 months, your doctor may stop Rapamune or cyclosporin, as it is not recommended to take these medicines together after this time.
Sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis (S-LAM)
Your doctor will give you 2 mg of Rapamune per day, until further notice. Your dose will be adjusted according to your blood levels of Rapamune. Your doctor will need to do blood tests to measure the levels of Rapamune in your blood.
Instructions on how to dilute Rapamune
- Remove the cap from the bottle by pressing the tabs on the cap and twisting. Insert the syringe adapter into the bottle until it is even with the top of the bottle. Do not attempt to remove the adapter from the bottle once it is inserted.
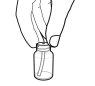
- With the plunger fully depressed, insert one of the dosing syringes into the adapter opening.
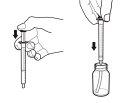
- Withdraw the exact amount of Rapamune oral solution prescribed by your doctor by gently pulling the dosing syringe plunger until the solution level is equal to the appropriate mark on the dosing syringe. The bottle should remain in an upright position while withdrawing the solution. If air bubbles form in the oral solution in the dosing syringe during withdrawal, return the solution to the bottle and repeat the withdrawal procedure. You may need to repeat step 3 more than once to obtain your dose.
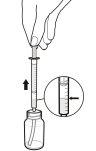
- You may need to take the oral solution of Rapamune at a specific time of day. If you need to carry your medicine with you, fill the dosing syringe to the appropriate mark and place the cap on securely – the cap should click into place. Then, put the dosing syringe in the box provided for transport. Once in the syringe, the medicine can be stored at room temperature (not above 25°C) or refrigerated and should be used within 24 hours.
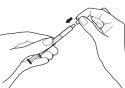
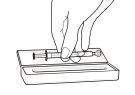
- Empty the contents of the dosing syringe into a glass or plastic cup containing at least 60 ml of water or orange juice. Stir well for 1 minute and drink immediately. Refill the cup with at least 120 ml of water or orange juice, stir well, and drink immediately. You should not use any other liquid for dilution, including grapefruit juice. The dosing syringe and its cap should be used once and then discarded.

When refrigerated, the solution in the bottle may become slightly cloudy. If this happens, simply leave the Rapamune oral solution at room temperature and gently shake. The presence of this cloudiness does not affect the quality of Rapamune.
If you take more Rapamune than you should
If you have taken more medicine than you should, contact your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department immediately. Always take the bottle and label with you, even if it is empty.
If you forget to take Rapamune
If you forget to take Rapamune, take it as soon as you remember, but not within 4 hours of your cyclosporin dose. After this, continue taking your medicine as usual. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose, and always take Rapamune and cyclosporin with an interval of approximately 4 hours. If you have forgotten to take a dose of Rapamune, you should inform your doctor.
If you stop taking Rapamune
Do not stop taking Rapamune unless your doctor tells you to, as you may be at risk of losing your transplant.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Allergic Reactions
You should see yourdoctor immediatelyif you experience symptoms such as swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat (angioedema) and/or difficulty breathing, or skin peeling (exfoliative dermatitis). These could be symptoms of a severe allergic reaction.
Kidney Damage withLow Blood Cell Counts (Thrombocytopenic Purpura/Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome)
When taken with medicines called calcineurin inhibitors (cyclosporine or tacrolimus), Rapamune may increase the risk of a condition that combines kidney damage with low blood cell counts, with or without skin irritation (thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome). If you experience symptoms such as bruising, skin rash, changes in urine, mood changes, or any other symptom that you consider serious, unusual, or prolonged, contact your doctor.
Infections
Rapamune decreases your body's defense mechanisms. As a result, your body will not be as good at fighting infections. Therefore, if you are taking Rapamune, you may get more infections than usual, such as skin, mouth, stomach, and intestinal infections, lung and urinary tract infections (see list below). You should contact your doctor if you experience symptoms that you consider serious, unusual, or prolonged.
Frequency of Adverse Effects
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- fluid accumulation around the kidney
- body swelling, including hands and feet
- pain
- fever
- headache
- increased blood pressure
- stomach pain, diarrhea, constipation, nausea
- decrease in red blood cell count, decrease in platelet count
- increase in blood fats (cholesterol and/or triglycerides), increase in blood sugar, decrease in blood potassium, decrease in blood phosphorus, increase in blood lactate dehydrogenase, increase in blood creatinine
- joint pain
- acne
- urinary tract infection
- pneumonia and other infections caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi
- decrease in white blood cells that fight infections
- diabetes
- abnormal liver function tests, elevated liver enzymes AST and/or ALT
- skin rash
- increased protein in urine
- menstrual disorders (including absent, infrequent, or heavy periods)
- slow wound healing (this may include separation of surgical wound layers or suture lines)
- increased heart rate
- there is a general tendency for fluids to accumulate in various tissues
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- infections (including potentially life-threatening infections)
- blood clots in legs
- blood clots in lungs
- mouth sores
- fluid accumulation in abdomen
- kidney damage with decreased platelet and red blood cell count, with or without skin rash (hemolytic uremic syndrome)
- decrease in a type of white blood cell called neutrophils
- bone damage
- inflammation that can lead to lung damage, fluid accumulation around lungs
- nasal bleeding
- skin cancer
- kidney infection
- ovarian cysts
- fluid accumulation in the membrane surrounding the heart, which can decrease the heart's ability to pump blood
- pancreatitis
- allergic reactions
- herpes
- cytomegalovirus infection
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- lymph tissue cancer (lymphoma/post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder), combined decrease in red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
- bleeding in lungs
- protein in urine, sometimes severe and associated with adverse effects such as swelling
- kidney scarring that can reduce kidney function
- excess fluid in tissues due to irregular lymphatic function
- decrease in platelet count, with or without skin rash (thrombocytopenic purpura)
- severe allergic reactions that can cause skin peeling
- tuberculosis
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- infectious diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile
- severe liver damage
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- protein deposits in lung air sacs that can interfere with breathing
- severe allergic reactions that can affect blood vessels (see allergic reactions section)
Frequency not known: cannot be estimated from available data
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES), a severe nervous system disorder with symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion, seizures, and vision loss. If you experience more than one of these symptoms, contact your doctor.
Patient with S-LAM experienced adverse effects similar to those of patients with kidney transplant, with the addition of weight loss, which may affect more than 1 in 10 people.
Reporting Adverse Effects
If you experience any adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Rapamune
Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the packaging after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C).
Keep Rapamune oral solution in its original bottle to protect it from light.
Once the bottle is opened, the contents must be refrigerated and used within 30 days. If necessary, the bottle can be stored at room temperature up to 25°C for a short period, but no more than 24 hours.
Once the dosing syringe has been filled with Rapamune oral solution, it must be stored at room temperature, but not above 25°C, for a maximum of 24 hours.
Once the contents of the dosing syringe have been diluted with water or orange juice, the preparation must be consumed immediately.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Rapamune Composition
The active substance is sirolimus. Each ml of Rapamune oral solution contains 1 mg of sirolimus.
The other ingredients are:
Polysorbate 80 (E433) and Phosal 50 PG (phosphatidylcholine, propylene glycol [E1520], mono- and diglycerides, ethanol, soybean fatty acids, and ascorbyl palmitate).
This medicine contains approximately 350 mg of propylene glycol (E1520) per ml.
Product Appearance and Packaging Contents
Rapamune oral solution is a pale yellow to yellow oral solution presented in 60 ml bottles.
Each pack contains: 1 bottle (topaz glass) containing 60 ml of Rapamune solution, a syringe adapter, 30 dosing syringes (topaz plastic), and a carrying case for the syringe.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder: Pfizer Europe MA EEIG Boulevard de la Plaine 17 1050 Brussels Belgium | Manufacturer: Pfizer Service Company BV Hoge Wei 10 1930 Zaventem Belgium |
You can obtain more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
België/Belgique/BelgienLuxembourg/Luxemburg Pfizer NV/SA Tel/Tel: +32 (0)2 554 62 11 | Lietuva Pfizer Luxembourg SARL filialas Lietuvoje Tel: +3705 2514000 |
България Пфайзер България ЕООД Тел: +359 2 970 4333 | Magyarország Pfizer Kft. Tel: +36 1 488 3700 |
Česká Republika Pfizer, spol. s r.o. Tel: +420 283 004 111 | Malta Vivian Corporation Ltd. Tel: +35621 344610 |
Danmark Pfizer ApS Tlf: +45 44 201 100 | Nederland Pfizer bv Tel: +31 (0)800 63 34 636 |
Deutschland Pfizer Pharma GmbH Tel: +49 (0)30 550055-51000 | Norge Pfizer AS Tlf: +47 67 52 61 00 |
Eesti Pfizer Luxembourg SARL Eesti filiaal Tel: +372 666 7500 | Österreich Pfizer Corporation Austria Ges.m.b.H. Tel: +43 (0)1 521 15-0 |
Ελλάδα Πφайζερ Ελλάς Α.Ε. Τηλ.: +30 210 6785 800 | Polska Pfizer Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel.: +48 22 335 61 00 |
España Pfizer, S.L. Tel:+34914909900 | Portugal Laboratórios Pfizer, Lda. Tel: +351 21 423 5500 |
France Pfizer Tél: +33 (0)1 58 07 34 40 | România Pfizer Romania S.R.L Tel: +40 (0)21 207 28 00 |
Hrvatska Pfizer Croatia d.o.o. Tel: + 385 1 3908 777 | Slovenija Pfizer Luxembourg SARL, Pfizer, podružnica za svetovanje s podrocja farmacevtske dejavnosti, Ljubljana Tel: +386 (0)1 52 11 400 |
Ireland Pfizer Healthcare Ireland Unlimited Company Tel: +1800 633 363 (toll free) Tel: +44 (0)1304 616161 | Slovenská Republika Pfizer Luxembourg SARL, organizacná zložka Tel: + 421 2 3355 5500 |
Ísland Icepharma hf Tel: +354 540 8000 | Suomi/Finland Pfizer Oy Puh/Tel: +358 (0)9 430 040 |
Italia Pfizer S.r.l. Tel: +39 06 33 18 21 | Sverige Pfizer AB Tel: +46 (0)8 550 520 00 |
Κύπρος Πφайζερ Ελλάς Α.Ε. (Κύπρος) Τηλ.: +357 22 817690 | |
Latvija Pfizer Luxembourg SARL filiale Latvija Tel. +371 67035775 |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: 01/2025.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to RAPAMUNE 1 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTIONDosage form: TABLET, 0.5 mgActive substance: sirolimusManufacturer: Pfizer Europe Ma EeigPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 1 mgActive substance: sirolimusManufacturer: Pfizer Europe Ma EeigPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 2 mgActive substance: sirolimusManufacturer: Pfizer Europe Ma EeigPrescription required
Online doctors for RAPAMUNE 1 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION
Discuss questions about RAPAMUNE 1 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






