PROMETAX 4.6 mg/24H TRANSDERMAL PATCH

How to use PROMETAX 4.6 mg/24H TRANSDERMAL PATCH
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Prometax 4.6mg/24h transdermal patch
Prometax 9.5mg/24h transdermal patch
Prometax 13.3mg/24h transdermal patch
rivastigmine
Read the entire package leaflet carefully before starting to use this medication, as it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any questions, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medication has been prescribed to you only, and you should not give it to others, even if they have the same symptoms as you, as it may harm them.
- If you experience side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this package leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Prometax and what is it used for
- What you need to know before starting to use Prometax
- How to use Prometax
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Prometax
- Package contents and additional information
1. What is Prometax and what is it used for
The active substance of Prometax is rivastigmine.
Rivastigmine belongs to the group of cholinesterase inhibitors. In patients with Alzheimer's dementia, certain nerve cells die in the brain, causing low levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (a substance that allows nerve cells to communicate with each other). Rivastigmine acts by blocking the enzymes that break down acetylcholine: acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. By blocking these enzymes, Prometax allows the increase of acetylcholine in the brain, helping to reduce the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
Prometax is used for the treatment of adult patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia, a progressive brain disorder that gradually affects memory, intellectual ability, and behavior.
2. What you need to know before starting to use Prometax
Do not use Prometax
- if you are allergic to rivastigmine (the active substance of Prometax) or to any of the other components of this medication (listed in section 6).
- if you have ever had an allergic reaction to a similar medication (carbamate derivatives).
- if you have a skin reaction that extends beyond the size of the patch, if there is a more intense local reaction (such as blisters, increasing skin inflammation, swelling) and if there is no improvement within 48 hours after removing the transdermal patch.
If you are in any of these situations, inform your doctor and do not use Prometax transdermal patches.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor before starting to use Prometax:
- if you have or have ever had any heart problems, such as irregular or slow heart rhythm, QTc prolongation, family history of QTc prolongation, torsades de pointes, or if you have low blood levels of potassium or magnesium.
- if you have or have ever had an active stomach ulcer.
- if you have or have ever had difficulty urinating.
- if you have or have ever had seizures.
- if you have or have ever had asthma or severe respiratory disease.
- if you suffer from tremors.
- if you have low body weight.
- if you have gastrointestinal reactions such as a feeling of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. You may become dehydrated (lose a large amount of fluid) if vomiting or diarrhea is prolonged.
- if you have liver problems (liver failure).
If you are in any of these situations, your doctor may consider it necessary to monitor you more closely while you are being treated.
If you have not used the patches for more than three days, do not put on another one without consulting your doctor first.
Children and adolescents
Prometax should not be used in the pediatric population for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Other medications and Prometax
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or may need to take any other medication.
Prometax may interfere with anticholinergic medications, some of which are medications used to relieve stomach cramps or spasms (e.g., dicyclomine), for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (e.g., amantadine), or to prevent motion sickness (e.g., diphenhydramine, scopolamine, or meclizine).
Prometax transdermal patches should not be administered at the same time as metoclopramide (a medication used to relieve or prevent nausea and vomiting). Taking the two medications together may cause problems such as stiffness in the limbs and hand tremors.
In case you need to undergo surgery while using Prometax transdermal patches, inform your doctor that you are using it, as it may potentiate the effects of some muscle relaxants used in anesthesia.
Caution should be exercised when using Prometax transdermal patches with beta blockers (medications such as atenolol used to treat hypertension, angina, and other heart conditions). Taking the two medications together may cause complications such as a decrease in heart rate (bradycardia) that can lead to fainting or loss of consciousness.
Caution should be exercised when using Prometax with other medications that may affect heart rhythm or the heart's electrical system (QT prolongation).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
If you are pregnant, it is necessary to evaluate the benefits of using Prometax against the possible adverse effects for the fetus. Prometax should not be used during pregnancy unless it is clearly necessary.
You should not breastfeed while being treated with Prometax transdermal patches.
Driving and using machines
Your doctor will inform you if your condition allows you to drive or use machinery safely. Prometax transdermal patches may cause dizziness and severe confusion. If you feel dizzy or confused, do not drive or use machinery, and do not perform other tasks that require your attention.
3. How to use Prometax
Follow the instructions for administration of Prometax transdermal patches exactly as indicated by your doctor. If in doubt, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse again.
IMPORTANT:
- Remove the previous patch before applying a NEW patch.
- Only ONE patch per day.
- Do not cut the patch into pieces.
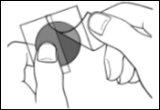
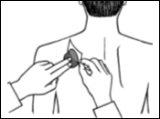
- Press the patch firmly against the skin with the palm of your hand for at least 30 seconds.
How to start treatment
Your doctor will indicate the most suitable dose of Prometax transdermal patch for your case.
- Normally, treatment is started with Prometax 4.6 mg/24 h.
- The recommended daily dose is Prometax 9.5 mg/24 h. If this dose is well tolerated, the doctor treating you may consider increasing the dose to 13.3 mg/24 h.
- Wear only one Prometax patch at a time and replace the patch with a new one after 24 hours.
During treatment, your doctor may adjust the dose depending on your individual needs.
If you have not used the patches for more than three days, do not put on another one without consulting your doctor first. Treatment with the transdermal patch can be restarted at the same dose if treatment is not interrupted for more than three days. Otherwise, your doctor will have you restart your treatment with Prometax 4.6 mg/24 h.
Prometax can be used with food, drink, and alcohol.
Where to apply your Prometax transdermal patch
- Before applying a patch, make sure the skin is clean, dry, and hairless, without powders, oils, moisturizers, or lotions that may prevent the patch from sticking well to the skin, without cuts, redness, or irritation.
- Remove any existing patch carefully before applying a new one.Wearing multiple patches on your body could expose you to an excessive amount of this medication, which could be potentially dangerous.
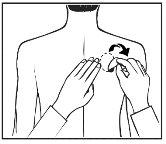
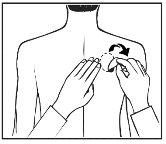
- Apply ONLY ONEpatch per day to ONLY ONEof the possible areas, as shown in the following diagrams:
- upper left orupper right arm
- upper left orupper right chest (avoiding the breasts in women)
- upper left orupper right back
- lower left orlower right back
Every 24 hours, remove the previous patch before applying a NEW patch to ONLY ONE of the following possible areas. |
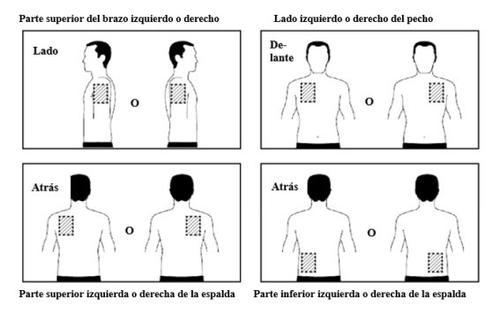
Each time you change the patch, remove the previous day's patch before applying a new patch to a different area of the skin (e.g., one day on the right side of the body and the next day on the left side; or one day on the upper part of the body and the next day on the lower part). Wait at least 14 days before applying a new patch to the same area of skin again.
How to apply your Prometax transdermal patch
Prometax patches are thin, opaque plastic and stick to the skin. Each patch is in a pouch that protects it until you are ready to apply it. Do not open the pouch or remove the patch until you are ready to apply it.
|
|
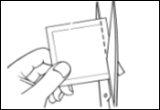
Only open the pouch when you are ready to apply the patch. Cut the pouch along the dotted line with scissors and remove the patch from the pouch. |
|
|
|
|
|
If it helps, you can write on the patch, for example, the day of the week, with a fine-tipped pen. |
|
You should wear the patch continuously until it is time to change it for a new one. When you apply a new patch, you can try different areas to find the ones that are most comfortable and where clothing does not rub against the patch.
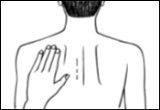
How to remove your Prometax transdermal patch
Gently pull one of the edges of the patch to slowly detach it from the skin. If adhesive residues remain on the skin, soak the area with warm water and mild soap or use baby oil to remove it. Do not use alcohol or other solvents (nail polish removers or other solvents).
After removing the patch, wash your hands with soap and water. If you get the patch in your eyes or if your eyes become red after handling the patch, rinse them immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice if the symptoms do not resolve.
Can you wear your Prometax transdermal patch while bathing, swimming, or exposing yourself to the sun?
- Bathing, swimming, or showering should not affect the patch. Make sure it does not come off partially while performing these activities.
- Do not expose the patch to an external heat source (e.g., excessive sunlight, sauna, sunbed) for long periods.
What to do if a patch falls off
If a patch falls off, apply a new one for the rest of that day and change it the next day at the usual time.
When and for how long should you wear your Prometax transdermal patch
- To benefit from your treatment, you should apply a new patch every day, preferably at the same time.
- Wear only one Prometax patch at a time and replace the patch with a new one after 24 hours.
If you use more Prometax than you should
If you accidentally apply more than one patch, remove all patches from the skin and inform your doctor. You may need medical attention. Some people who have accidentally taken too high doses of Prometax orally have experienced nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, high blood pressure, and hallucinations. A slowing of the heart rate and fainting may also occur.
If you forget to use Prometax
If you realize you have forgotten to apply a patch, apply it immediately. The next day, apply the next patch at the usual time. Do not apply two patches to make up for the one you forgot.
If you interrupt treatment with Prometax
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you stop using the patches.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, Prometax transdermal patches can cause adverse effects, although not all people will experience them.
You may have adverse effects more frequently when starting your treatment or when your dose is increased. Generally, the adverse effects will slowly disappear as your body gets used to the medicine.
If you notice any of the following adverse effects that may be serious, remove the patch and inform your doctor immediately.
Frequent(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Lack of appetite
- Dizzy sensation
- Restlessness
- Urinary incontinence (inability to stop urine properly)
- Urinary tract infection
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Confusion
- Headache
- Fainting
- Stomach problems such as dizzy sensation (nausea), vomiting, diarrhea
- Heartburn
- Stomach pain
- Rash
- Allergic reaction where the patch was applied, such as blisters or skin inflammation
- Feeling of tiredness or weakness
- Weight loss
- Fever
Infrequent(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Heart rhythm problems such as slow heart rate
- Stomach ulcer
- Dehydration (loss of large amounts of fluid)
- Hyperactivity (high level of activity, restlessness)
- Aggressiveness
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Falls
Very Rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Stiffness of arms or legs and tremors in hands
Unknown(cannot be estimated from available data)
- Worsening of Parkinson's disease symptoms – such as tremors, stiffness, and difficulty moving
- Pancreatitis – signs include severe pain in the upper abdomen, often accompanied by dizzy sensation (nausea) or vomiting
- Fast or irregular heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Seizures (convulsions)
- Liver disorders (yellowing of skin, yellowing of whites of eyes, abnormal darkening of urine, or unexplained nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and loss of appetite)
- Changes in tests showing liver function
- Feeling of restlessness
- Nightmares
- Pisa syndrome (a condition involving involuntary muscle contraction and abnormal tilting of the body and head to one side)
- Seeing things that do not exist (hallucinations)
- Tremors
- Somnolence
- Skin rash, itching
- Redness of skin
- Blisters
If you notice any of the adverse effects listed above, remove the patch and inform your doctor immediately.
Other Adverse Effects Experienced with Prometax Capsules or Oral Solution and that May Occur with Patches:
Frequent(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Excessive saliva
- Restlessness
- Feeling of general discomfort
- Tremors
- Increased sweating
Infrequent(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Irregular heart rate (e.g., fast heart rate)
- Difficulty sleeping
- Accidental falls
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Seizures (convulsions)
- Ulcer in the intestine
- Chest pain – probably caused by spasm in the heart
Very Rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- High blood pressure
- Pancreatitis – signs include severe pain in the upper abdomen, often with dizzy sensation (nausea) or vomiting
- Gastrointestinal bleeding – manifested as blood in stool or when vomiting
- Seeing things that do not exist (hallucinations)
- Some people who have been intensely dizzy (vomiting) have had tears in part of the digestive tube connecting their mouth to their stomach (esophagus)
Reporting Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Prometax
- Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiration date shown on the box and on the pouch after CAD/EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Do not store at a temperature above 25°C.
- Store the transdermal patch in the pouch until use.
- Do not use any patch if you observe that it is damaged or shows signs of tampering.
- After removing a patch, fold it in half with the adhesive side facing in and press. After placing it in the original pouch, make sure to dispose of the patch in a way that it is out of reach of children. After removing the patch, do not touch your eyes, and wash your hands well with soap and water. Medicines should not be thrown down the drain or into the trash. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines that you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Prometax Composition
- The active ingredient is rivastigmine.
- Prometax 4.6 mg/24 h transdermal patch: Each patch releasing 4.6 mg of rivastigmine in 24 hours, measures 5 cm2 and contains 9 mg of rivastigmine.
- Prometax 9.5 mg/24 h transdermal patch: Each patch releasing 9.5 mg of rivastigmine in 24 hours, measures 10 cm2 and contains 18 mg of rivastigmine.
- Prometax 13.3 mg/24 h transdermal patch: Each patch releasing 13.3 mg of rivastigmine in 24 hours, measures 15 cm2 and contains 27 mg of rivastigmine.
- The other components are polyethylene terephthalate lacquered foil, alpha-tocopherol, poly-(butylmethacrylate, methylmethacrylate), acrylic copolymer, silicone oil, dimeticone, fluoropolymer-coated polyester film.
Product Appearance and Package Contents
Thin transdermal patch composed of three layers. The outer layer is beige and marked with:
- "Prometax", "4.6 mg/24 h", and "AMCX".
- "Prometax", "9.5 mg/24 h", and "BHDI".
- "Prometax", "13.3 mg/24 h", and "CNFU".
Each pouch contains one transdermal patch. Patches are available in packages containing 7 or 30 pouches and in multi-packs containing 60 or 90 pouches. Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Almirall, S.A.
Ronda General Mitre, 151
08022 Barcelona
Spain
Manufacturer
LTS Lohmann Therapie-Systeme AG
Lohmannstrasse 2
56626 Andernach
Germany
You can request more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien, ???????, Ceská republika, Danmark, Deutschland, Eesti, Ελλάδα, España, France, Hrvatska, Ireland, Ísland, Italia, Κύπρος, Latvija, Lietuva, Luxembourg/Luxemburg, Magyarország, Malta, Nederland, Norge, Österreich, Polska, Portugal, România, Slovenija, Slovenská republika, Suomi/Finland, Sverige
Almirall, S.A.
Tel: +34 93 306 42 00
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information about this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: https://www.ema.europa.eu
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to PROMETAX 4.6 mg/24H TRANSDERMAL PATCHDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 13.3 mg/24 hActive substance: rivastigmineManufacturer: Esteve Pharmaceuticals S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 4.6 mg/24 hActive substance: rivastigmineManufacturer: Esteve Pharmaceuticals S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 9.5 mg/24 hActive substance: rivastigmineManufacturer: Esteve Pharmaceuticals S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for PROMETAX 4.6 mg/24H TRANSDERMAL PATCH
Discuss questions about PROMETAX 4.6 mg/24H TRANSDERMAL PATCH, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions