
PREGABALIN ARISTO 20 mg/mL ORAL SOLUTION

How to use PREGABALIN ARISTO 20 mg/mL ORAL SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Pregabalin Aristo20 mg/ml oral solution EFG
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of thepackage leaflet
- What is Pregabalin Aristo and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you take Pregabalin Aristo
- How to take Pregabalin Aristo
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Pregabalin Aristo
- Package contents and further information
1. What is Pregabalin Aristo and what is it used for
Pregabalin Aristo belongs to a group of medicines used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults.
Peripheral and central neuropathic pain:pregabalin is used to treat long-lasting pain caused by damage to the nerves. There are several diseases that can cause peripheral neuropathic pain, such as diabetes or herpes. The feeling of pain can be described as heat, burning, throbbing, shooting, stabbing, sharp, spasms, continuous, tingling, numbness, and a feeling of pins and needles. Peripheral and central neuropathic pain may also be associated with mood changes, sleep disturbances, fatigue (tiredness), and can have an impact on physical and social activity and overall quality of life.
Epilepsy:pregabalin is used in the treatment of certain types of epilepsy (partial seizures with or without secondary generalization) in adults. Your doctor will prescribe pregabalin for you to treat epilepsy when your current treatment is not controlling the condition. You should take pregabalin in addition to your current treatment. This medicine should not be taken on its own, but should always be used in combination with other antiepileptic treatments.
Generalized anxiety disorder:pregabalin is used in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The symptoms of GAD are excessive and prolonged worry and anxiety that are difficult to control. GAD can also cause restlessness or a feeling of being "on edge" or nervous, feeling tired easily, having difficulty concentrating or having a blank mind, irritability, muscle tension, or sleep disturbances. This is different from everyday stress and strain.
2. What you need to know before you take Pregabalin Aristo
Do not takePregabalin Aristo
If you are allergic to pregabalin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
- Some patients treated with pregabalin have reported symptoms that suggest an allergic reaction. These symptoms include swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, as well as the appearance of a diffuse rash. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should see your doctor immediately.
- Severe skin reactions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported with pregabalin treatment. Stop taking pregabalin and seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of the symptoms related to these severe skin reactions described in section 4.
- Pregabalin has been associated with dizziness and somnolence, which may increase the risk of accidental injury (falls) in elderly patients. Therefore, you should be cautious until you are used to the effects of the medicine.
- Pregabalin may cause blurred vision, loss of vision, or other changes in vision, many of which are transient. If you experience any changes in your vision, you should inform your doctor immediately.
- Diabetic patients who gain weight while taking pregabalin may need a change in their diabetes medicines.
- Certain side effects, such as somnolence, may be more frequent because patients with spinal cord injury may be taking other medicines for treatment, for example, for pain or spasticity (stiff or rigid muscles), with similar side effects to those of pregabalin, so the intensity of these effects may increase when taken together.
- There have been reports of heart failure in some patients treated with pregabalin. Most of these patients were elderly with cardiovascular diseases. Before using this medicine, you should tell your doctor if you have a history of heart disease.
- There have been reports of kidney failure in some patients treated with pregabalin. If, during treatment with this medicine, you notice a decrease in your ability to urinate, you should inform your doctor, as stopping treatment may improve this situation.
- Some patients taking antiepileptics, such as pregabalin, have had thoughts of harming themselves or suicidal thoughts or have shown suicidal behavior. If at any time you have these thoughts or have shown such behavior, contact your doctor as soon as possible.
- When pregabalin is taken with other medicines that can cause constipation (such as some types of painkillers), gastrointestinal problems (e.g., constipation and intestinal blockage or paralysis) may occur. Inform your doctor if you suffer from constipation, especially if you are prone to this problem.
- Before taking this medicine, inform your doctor if you have ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines, or illegal drugs; this may mean you have a greater risk of becoming dependent on pregabalin.
- There have been reports of seizures during treatment with pregabalin or shortly after stopping treatment with pregabalin. If you have seizures, contact your doctor immediately.
- There have been reports of reduced brain function (encephalopathy) in some patients taking pregabalin who had other illnesses. Tell your doctor if you have a history of any serious illness, including liver or kidney disease.
- There have been reports of difficulty breathing. If you have nervous system disorders, respiratory disorders, kidney failure, or are over 65 years old, your doctor may prescribe a different dose. Contact your doctor if you experience breathing problems or shallow breathing.
Dependence
Some people may become dependent on pregabalin (need to keep taking the medicine). They may have withdrawal effects when they stop using pregabalin (see section 3, “How to take Pregabalin Aristo”and “If you stop taking pregabalin”). If you are concerned that you may become dependent on pregabalin, it is important that you consult your doctor.
If you notice any of the following signs while taking pregabalin, it could be a sign that you have become dependent:
- You need to take the medicine for longer than recommended by your doctor.
- You feel you need to take more than the recommended dose.
- You are using the medicine for reasons other than those prescribed.
- You have made repeated unsuccessful attempts to stop or control the use of the medicine.
- When you stop taking the medicine, you feel unwell and feel better once you take the medicine again.
If you notice any of these signs, talk to your doctor to discuss the best care plan for you, including when it is appropriate to stop treatment and how to do it safely.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy in children and adolescents (under 18 years) have not been established, so pregabalin should not be used in this age group.
Other medicines and pregabalin
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Pregabalin and certain medicines can affect each other (interact). When pregabalin is used with certain sedative medicines (including opioids), these effects may be increased, which can lead to respiratory failure, coma, and death. The degree of dizziness, somnolence, and decreased concentration may increase if pregabalin is taken with other medicines that contain:
Oxicodone – (used as a painkiller)
Lorazepam – (used to treat anxiety)
Alcohol
This medicine can be taken with oral contraceptives.
Taking pregabalin with food, drinks, and alcohol
Pregabalin can be taken with or without food.
It is advised not to drink alcohol during treatment with this medicine.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Do not take pregabalin during pregnancy or breastfeeding, unless your doctor has told you to do so. The use of pregabalin during the first 3 months of pregnancy may cause congenital malformations in the fetus that require medical treatment. In a study that reviewed data from women in Nordic countries who took pregabalin during the first 3 months of pregnancy, 6 babies out of 100 had such congenital malformations. This compares with 4 babies out of 100 born to women not treated with pregabalin in the study. There have been reports of malformations of the face (clefts), eyes, nervous system (including the brain), kidneys, and genitals.
An effective contraceptive method should be used in women of childbearing age. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Pregabalin may cause symptoms such as dizziness, somnolence, and decreased concentration. These effects, as well as the underlying disease, may impair your ability to drive vehicles or operate machines. Therefore, you should not drive, operate machinery, or engage in other potentially hazardous activities until you know whether this medicine affects your ability to perform these activities.
This medicine contains methylparahydroxybenzoate (E-218)
It may cause allergic reactions (possibly delayed) because it contains methylparahydroxybenzoate (E-218).
This medicine contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 23 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per ml; this is essentially “sodium-free”.
3. How to take Pregabalin Aristo
Follow exactly the instructions for administration of this medicine given by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again. Do not take more medicine than prescribed.
Your doctor will determine the dose that is right for you.
Peripheral and central neuropathic pain, epilepsy, or generalized anxiety disorder:
- Take the solution as your doctor has told you.
- The dose, which has been adjusted for you and your condition, will generally be between 150 mg (7.5 ml) and 600 mg (30 ml) per day.
- Your doctor will tell you to take this medicine twice or three times a day. In the case of twice a day, take this medicine once in the morning and once in the evening, approximately at the same time every day. In the case of three times a day, take this medicine in the morning, at noon, and in the evening, approximately at the same time every day.
If you think the effect of this medicine is too strong or too weak, tell your doctor or pharmacist.
If you are an elderly patient (over 65 years old), you should take this medicine normally, unless you have kidney problems.
Your doctor may prescribe a different dosing regimen and/or different doses if you have kidney problems.
Continue taking this medicine until your doctor tells you to stop.
Administration:
Instructions for use
Pregabalin is for oral use only.
- Open the bottle: press down the cap and turn it clockwise (Figure 1).
- Only the first time you use it: Along with the oral syringe, a bottle adapter is provided. This adapter should be placed on the neck of the bottle to facilitate the extraction of the solution using the syringe. If the adapter is not on the bottle, remove the adapter and the 5 ml syringe from the transparent bag. Place the bottle on a firm surface and proceed to place the adapter on the neck of the bottle with the flat part facing you and press it down (Figure 2).
- Press the plunger of the syringe towards the end of the syringe cylinder (towards the tip) to eliminate excess air. Insert the syringe into the bottle adapter with a slight rotary motion (Figure 3).
- Invert the bottle (with the syringe in place) and load the syringe with the liquid by pulling the plunger down until just past the graduation mark corresponding to the prescribed amount in milliliters (ml) by your doctor (Figure 4). Eliminate air bubbles from the syringe by moving the plunger up to the correct graduation mark.
- Put the bottle back in the normal position, without removing the syringe from the bottle adapter (Figure 5).
- Remove the syringe from the bottle adapter (Figure 6).
- Empty the contents of the syringe directly into the mouth by pressing the plunger towards the end of the syringe cylinder (Figure 7).
Note:Steps 4-7 may need to be repeated up to three times to obtain the total dose (Table 1).
[For example, a dose of 150 mg (7.5 ml) will require withdrawing the volume from the bottle twice to reach the complete dose. Using the syringe, withdraw 5 ml first, empty the contents directly into the mouth, and then take another 2.5 ml, emptying the remaining contents into the mouth.]
- Rinse the syringe by taking water with the help of the plunger and expelling it from the syringe by pressing the plunger towards the tip, at least three times (Figure 8).
- Put the cap back on the bottle (leaving the adapter on the neck of the bottle) (Figure 9).
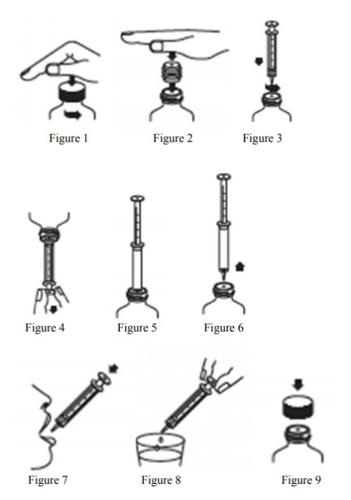
Table 1. Volume to be extracted with the syringe to obtain the prescribed dose of pregabalin
Pregabalin dose (mg) | Total volume of the solution (ml) | First extraction with the syringe (ml) | Second extraction with the syringe (ml) | Third extraction with the syringe (ml) |
25 | 1.25 | 1.25 | Not required | Not required |
50 | 2.5 | 2.5 | Not required | Not required |
75 | 3.75 | 3.75 | Not required | Not required |
100 | 5 | 5 | Not required | Not required |
150 | 7.5 | 5 | 2.5 | Not required |
200 | 10 | 5 | 5 | Not required |
225 | 11.25 | 5 | 5 | 1.25 |
300 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
If you take more Pregabalin Aristo than you should
Call your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room immediately. Take the package or bottle of the oral solution with you. As a result of taking more medicine than you should, you may feel drowsy, confused, agitated, or restless. There have also been reports of seizures and unconsciousness (coma).
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, telephone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount taken.
If you forget to take Pregabalin Aristo
It is important that you take the Pregabalin Aristo oral solution regularly at the same time every day. If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it is time for the next dose. In that case, continue with the next dose as normal. Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If you stop taking Pregabalin Aristo
Do not stop taking this medicine suddenly. If you want to stop taking this medicine, talk to your doctor first. If you are going to stop treatment, it should be done gradually over a minimum of one week.
Once you have finished treatment with this medicine for a long or short time, you should know that you may experience certain side effects, called withdrawal effects. These effects include sleep problems, headache, nausea, feeling anxious, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, seizures, nervousness, depression, thoughts of harming yourself or suicidal thoughts, pain, sweating, and dizziness.
These effects may occur more frequently or severely if you have been taking this medicine for a longer period. If you experience withdrawal effects, you should see your doctor.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Very Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Dizziness, drowsiness, headache.
Common: May affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Increased appetite.
- Feeling of euphoria, confusion, disorientation, decreased sexual appetite, irritability.
- Alteration of attention, clumsiness, memory impairment, memory loss, tremors, difficulty speaking, tingling sensation, numbness, sedation, lethargy, insomnia, fatigue, abnormal sensation.
- Blurred vision, double vision.
- Dizziness, balance problems, falls.
- Dry mouth, constipation, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea, bloated abdomen.
- Difficulty getting an erection.
- Swelling of the body including the limbs.
- Feeling of drunkenness, gait disturbances.
- Weight gain.
- Muscle cramp, joint pain, back pain, pain in the limbs.
- Sore throat.
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Loss of appetite, weight loss, low blood sugar levels, high blood sugar levels.
- Change in self-perception, restlessness, depression, agitation, mood changes, difficulty finding words, hallucinations, strange dreams, anxiety attacks, apathy, aggression, elevated mood, mental deterioration, difficulty thinking, increased sexual appetite, sexual relationship problems including inability to reach climax, delayed ejaculation.
- Changes in vision, unusual eye movements, changes in vision including tunnel vision, flashes of light, spasmodic movements, reduced reflexes, hyperactivity, dizziness when standing up, sensitive skin, loss of taste, burning sensation, tremor when moving, decreased consciousness, loss of consciousness, fainting, increased sensitivity to noise, general malaise.
- Dry eyes, swollen eyes, eye pain, tired eyes, teary eyes, eye irritation.
- Alterations in heart rhythm, increased heart rate, low blood pressure, high blood pressure, changes in heart rhythm, heart failure.
- Flushing, hot flashes.
- Difficulty breathing, dry nose, nasal congestion.
- Increased saliva production, heartburn, numbness around the mouth.
- Sweating, rash, chills, fever.
- Muscle spasms, swollen joints, muscle stiffness, pain including muscle pain, neck pain.
- Breast pain.
- Difficulty or pain when urinating, incontinence.
- Weakness, thirst, chest tightness.
- Changes in blood and liver test results (elevated creatine phosphokinase in blood, elevated alanine aminotransferase, elevated aspartate aminotransferase, decreased platelet count, neutropenia, increased creatinine in blood, decreased potassium in blood).
- Hypersensitivity, facial swelling, itching, hives, runny nose, nosebleeds, cough, snoring.
- Painful menstrual periods.
- Feeling of cold in hands and feet.
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Altered sense of smell, oscillating vision, altered depth perception, visual glare, loss of vision.
- Dilated pupils, strabismus.
- Cold sweat, throat tightness, swollen tongue.
- Pancreatitis.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Slow or reduced body mobility.
- Difficulty writing correctly.
- Increased fluid in the abdominal area.
- Fluid in the lungs.
- Seizures.
- Changes in the electrocardiogram (ECG) corresponding to heart rhythm disorders.
- Muscle damage.
- Milk secretion, abnormal breast growth, increased breast size in men.
- Menstrual period interruption.
- Kidney failure, reduced urine output, urine retention.
- Decreased white blood cell count.
- Inappropriate behavior, suicidal behavior, suicidal thoughts.
- Allergic reactions that may include difficulty breathing, eye inflammation (keratitis), and a severe skin reaction characterized by reddish patches, not elevated, or circular or coin-shaped patches on the chest, often with central blisters, skin peeling, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes. These severe skin reactions may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
- Jaundice (yellow color of the skin and eyes).
- Parkinsonism, symptoms similar to Parkinson's disease, such as tremors, bradykinesia (decreased ability to move), and muscle stiffness.
Very Rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people
- Liver failure.
- Hepatitis (liver inflammation).
Frequency Not Known: cannot be estimated from the available data
- Becoming dependent on pregabalin ("drug dependence").
Once you have finished a short or long-term treatment with pregabalin, you should know that you may experience certain adverse effects, called withdrawal effects (see "If you stop taking pregabalin").
If you experience swelling in the face or tongue, or if your skin turns red and has blisters or peeling, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Certain adverse effects, such as drowsiness, may be more frequent since patients with spinal cord injury may be taking other medications to treat, for example, pain or spasticity (stiff or rigid muscles), with similar adverse effects to those of this medicine, so the intensity of these effects may increase when taken together.
The following adverse reaction has been reported in post-marketing experience: difficulty breathing, shallow breathing.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Conservation of Pregabalina Aristo
Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the packaging or bottle, after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store below 25°C.
Validity period once opened: 3 months.
Medicines should not be thrown away through the sewers or in the trash. Deposit the packaging and medicines you no longer need in the SIGRE Point of the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Pregabalina Aristo:
- The active ingredient is pregabalin. Each ml contains 20 mg of pregabalin.
- The other components are: sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, disodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous, sucralose, methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218), strawberry flavor (containing propylene glycol (E 1520) and purified water.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
Pregabalina Aristo 20 mg/ml oral solution is a clear and colorless solution presented in a 500 ml high-density polyethylene bottle with a child-resistant HDPE screw cap, containing 473 ml of oral solution. 5 ml PP cylindrical syringe and HDPE plunger, graduated in 1.25, 2.5, 3.75, and 5 mL) with an LDPE adapter.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Aristo Pharma Iberia, S.L.
C/ Solana, 26
28850, Torrejón de Ardoz
Madrid, Spain
Manufacturer
Aristo Pharma GmbH
Wallenroder Straße 8-10,
13435 Berlin,
Germany
Or
Chanelle Medical Unlimited Company
Ida Business Park, Dublin Road
Loughrea, Co. H62 FH90 Galway
Ireland
Date of the Last Revision of this Prospectus: February 2024
Detailed information about this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to PREGABALIN ARISTO 20 mg/mL ORAL SOLUTIONDosage form: CAPSULE, 150 mgActive substance: pregabalinManufacturer: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 25 mgActive substance: pregabalinManufacturer: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 300 mgActive substance: pregabalinManufacturer: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for PREGABALIN ARISTO 20 mg/mL ORAL SOLUTION
Discuss questions about PREGABALIN ARISTO 20 mg/mL ORAL SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















