
NUMETA G19%E, EMULSION FOR INFUSION

How to use NUMETA G19%E, EMULSION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
NUMETA G19%E Emulsion for Infusion
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts using this medicine, because it contains important information for them.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your child's doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- If your child experiences any side effects, talk to your child's doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet:
- What is Numeta G19%E and what is it used for
- What you need to know before Numeta G19%E is administered to your child
- How Numeta G19%E will be administered
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Numeta G19%E
- Package Contents and Additional Information
1. What is Numeta G19%E and what is it used for
Numeta G19%E is a specialized nutrition designed for children over 2 years and adolescents up to 18 years. It is administered through a tube connected to a vein in your child's arm or a large vein in their chest when they are unable to eat all their food by mouth.
Numeta comes in a three-compartment bag with three independent chambers containing:
a 50% glucose solution
a 5.9% pediatric amino acid solution with electrolytes
a 12.5% lipid (fat) emulsion
Depending on your child's needs, two (or three) of these solutions are mixed in the bag before administration to your child.
Numeta G19%E should only be used under medical supervision.
2. What you need to know before Numeta G19%E is administered to your child
Do not use Numeta G19%Ein the following cases:
With 2 solutions mixed in the bag (“2 in1”):
- If your child is allergic to any of the egg, soy, or peanut proteins or to the ingredients of the glucose or amino acid bag (listed in section 6).
- If your child's body has problems using the constituents of proteins.
- If your child has high concentrations of any of the electrolytes included in Numeta G19%E in their blood.
- If your child has hyperglycemia (especially high blood sugar levels).
With 3 solutions mixed in the bag (“3 in1”).
- All the situations mentioned in “2 in 1” plus the following
- If your child has a particularly high level of fat in their blood.
In all cases, your child's doctor will decide whether this medicine should be administered to your child based on factors such as age, weight, and medical condition, along with the results of all tests performed.
Warnings and Precautions
Talk to your child's doctor or nurse before Numeta G19%E is administered to your child.
Allergic Reactions
Infusion should be stopped immediately if any signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction appear (such as fever, sweating, chills, headache, skin rash, or difficulty breathing). This medicine contains soybean oil, which can rarely cause hypersensitivity reactions. In rare cases, it has been observed that some people who are allergic to peanut proteins are also allergic to soybean proteins.
Numeta G19%E contains glucose derived from cornstarch, so it should be used with caution in patients with known allergy to corn or its products.
Risk of Particle Formation with Ceftriaxone (Antibiotic):
Ceftriaxone, a specific antibiotic, should not be mixed or administered at the same time as a solution containing calcium (including Numeta G19%E) through an intravenous drip.
Your child's doctor is aware of this and will not administer them together, even through different lines or infusion sites.
However, your child's doctor may administer calcium and ceftriaxone sequentially, one after the other, if infusion lines are used at different points, or if the lines are replaced or thoroughly flushed with physiological saline solution to avoid precipitate formation.
Formation of Small Particles in the Blood Vessels of the Lungs:
Difficulty breathing can also be a sign of the formation of small particles that block the blood vessels in the lungs (pulmonary vascular precipitates). If your child experiences difficulty breathing, inform your child's doctor or nurse. They will decide on the measures to be taken.
Infection and Sepsis
Your child's doctor will closely monitor your child for any signs of infection. The use of an "aseptic technique" (germ-free technique) when placing and maintaining the catheter, as well as when preparing the nutrition formula, can reduce the risk of infection.
Occasionally, children may develop infections and sepsis (bacteria in the blood) when they have a tube connected to a vein (intravenous catheter). Certain medications and diseases can increase the risk of developing sepsis or infection. Patients who require parenteral nutrition (nutrition administered through a tube connected to a vein) are more likely to develop an infection due to their medical condition.
Fat Overload Syndrome
Cases of fat overload syndrome have been described with similar products. A reduced ability to eliminate the lipids contained in Numeta G19%E or an overdose can cause a "fat overload syndrome" (see sections 3 and 4).
Changes in Blood Chemistry Levels
Your child's doctor will check and review the fluids in your child's body, blood chemistry levels, and other blood levels while your child is receiving this medicine, as refeeding someone who is severely malnourished can sometimes lead to changes in blood chemistry levels. Excess fluid in the tissues and swelling can also occur. It is recommended to start parenteral nutrition slowly and under supervision.
Monitoring and Adjustment
Your child's doctor will monitor and adjust the dose of Numeta G19%E to meet your child's individual needs if they have the following conditions:
- severe post-traumatic state
- severe diabetes mellitus
- shock
- infarction
- severe infection
- certain types of coma
Use with Caution:
Numeta should be used with caution if your child has:
- pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) or heart failure,
- severe liver problems,
- problems absorbing nutrients,
- high blood sugar levels,
- kidney problems,
- severe metabolic disorders (when the body cannot eliminate substances normally),
- blood coagulation disorders.
The levels of fluids in your child's body, liver test values, and blood values will be carefully monitored.
Use of Numeta G19%E with Other Medicines
Tell your child's doctor if your child is using, has recently used, or may need to use any other medicine.
Numeta G19%E must not be administered at the same time as:
- ceftriaxone(an antibiotic) even through separate infusion lines, due to the risk of particle formation.
- bloodthrough the same infusion line, due to the risk of pseudoagglutination (red blood cells pile up)
- ampicillin, phenytoin, and furosemidethrough the same infusion line, as there is a risk of particle formation.
Coumarin and Warfarin (Anticoagulants)
Your child's doctor will closely monitor your child if they are taking coumarin or warfarin. The olive and soybean oil in Numeta G19%E contain vitamin K1. Vitamin K1 can interfere with the action of medicines like coumarin and warfarin. These medicines are anticoagulants used to prevent blood clotting.
Laboratory Tests
The lipids included in this emulsion can interfere with the results of certain laboratory tests. Laboratory tests can be performed after a period of 5 to 6 hours if no more lipids are administered.
Interaction of Numeta G19%E with Medicines that May Affect Potassium Levels/Metabolism:
Numeta G19%E contains potassium. High potassium levels in the blood can cause an abnormal heart rhythm. Special attention should be paid to patients who take diuretics (medicines that reduce fluid retention), ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin II receptor antagonists (all of which are medicines used to treat high blood pressure) or immunosuppressants (medicines that can decrease the body's natural defenses). These types of medicines can increase potassium levels.
Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, and Fertility
There is not enough data on the use of Numeta in pregnant or breastfeeding women. Your child's doctor must carefully evaluate the benefits and potential risks in each specific patient before prescribing Numeta.
3. How Numeta G19%E will be administered
Numeta G19%E will always be administered to your child exactly as their doctor has indicated. Consult your child's doctor if you have any doubts.
Age Range
Numeta G19%E has been designed to meet the nutritional needs of children over 2 years and adolescents up to 18 years.
The doctor will decide if this medicine is suitable for your child.
Administration
This medicine is an emulsion for infusion. It is administered through a plastic tube connected to a vein in your child's arm or a large vein in their chest.
Your child's doctor may choose not to administer lipids to your child. The design of the Numeta G19%E bag allows the non-permanent seal between the amino acid/electrolyte and glucose chambers to be broken, if necessary. The seal between the amino acid and lipid chambers remains intact in this case. The contents of the bag can be infused without lipids.
Dosage and Duration of Treatment
Your child's doctor will decide on the dose your child needs and how long it will be administered. The dose depends on your child's nutritional needs and will be based on their weight, medical condition, and the body's ability to digest and absorb the ingredients of Numeta G19%E. Additional protein or nutrition may also be given orally or enterally.
If your child is given too much Numeta G19%E
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult the Toxicology Information Service. Phone 915.620.420
Symptoms
Receiving too much medicine or administering it too quickly could cause:
- nausea (feeling unwell)
- vomiting
- chills
- electrolyte disturbances (inappropriate amounts of electrolytes in the blood)
- signs of hypervolemia (increase in blood circulation volume)
- acidosis (increase in blood acidity)
In these cases, the infusion should be stopped immediately. Your child's doctor will decide if other actions are necessary.
An overdose of the fats contained in Numeta G19%E can cause a "fat overload syndrome", which is usually reversible once the infusion is interrupted. In newborns (neonates) and small children (infants), fat overload syndrome has been associated with respiratory disorders that cause a reduction in oxygen in the body (difficulty breathing) and conditions that cause an increase in blood acidity (acidosis).
To avoid these reactions, your child's doctor will regularly monitor your child's condition and analyze their blood levels during treatment.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not all children will experience them.
If you notice any change in the way your child feels during or after treatment, inform your child's doctor or nurse immediately.
The tests that your child's doctor will perform on your child while they are receiving this medicine should minimize the risk of side effects.
If symptoms of an allergic reaction occur, the infusion should be stopped and the doctor contacted immediately. This can be serious and symptoms may include:
- Sweating.
- Chills.
- Headache.
- Skin rash.
- Difficulty breathing.
Other side effects that have been observed are:
Frequent: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Low phosphate level in the blood (hypophosphatemia).
- High blood sugar level (hyperglycemia).
- High calcium level in the blood (hypercalcemia).
- High triglyceride level in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia).
- Electrolyte disturbances (hyponatremia).
Infrequent: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- High lipid level in the blood (hyperlipidemia).
- A disorder in which bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum (cholestasis). The duodenum is part of the intestine.
Unknown: frequency cannot be estimated from available data (these side effects have been reported with Numeta G13%E and G16%E when administered via peripheral route with insufficient dilution).
- Skin necrosis
- Soft tissue damage
- Extravasation
The following side effects have been reported with other parenteral nutrition products:
- The reduced or limited ability to eliminate the lipids contained in Numeta G19%E can lead to a "fat overload syndrome". The following signs and symptoms of this syndrome are usually reversible when the lipid emulsion infusion is stopped:
- Sudden and severe worsening of the patient's medical condition.
- High fat level in the blood (hyperlipidemia).
- Fever.
- Fatty infiltration of the liver (hepatomegaly).
- Worsening of liver function.
- Decreased red blood cell count, which can cause pale skin and weakness or difficulty breathing (anemia).
- Low white blood cell count, which can increase the risk of infection (leucopenia).
- Low platelet count, which can increase the risk of bruising and/or bleeding (thrombocytopenia).
- Blood coagulation disorders, which affect the blood's ability to clot
- Respiratory disorder that causes a reduction in oxygen in the body (difficulty breathing)
- Conditions that cause an increase in blood acidity (acidosis)
- Coma that requires hospitalization.
- Formation of small particles that can cause blockage of the blood vessels in the lungs (pulmonary vascular precipitates) or difficulty breathing.
Reporting Side Effects:
If your child experiences any side effects, talk to your child's doctor or nurse, even if it is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Numeta G19%E
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children when not in use.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the bag and outer packaging (MM/YYYY). The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not freeze.
Store in the overbag.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Product Appearance and Container Contents
Numeta G19%E is presented in a three-chamber bag. Each bag contains a sterile combination of a glucose solution, a pediatric amino acid solution with electrolytes, and a lipid emulsion, as described below:
Container Size | Glucose Solution 50% | Amino Acid Solution 5.9% with Electrolytes | Lipid Emulsion 12.5% |
1000 ml | 383 ml | 392 ml | 225 ml |
Appearance before reconstitution:
- The amino acid and glucose solutions in the chambers are clear, colorless, or slightly yellowish.
- The lipid emulsion chamber has a milky, white appearance.
Appearance after reconstitution:
- The "2 in 1" solution is clear, colorless, or slightly yellowish.
- The "3 in 1" emulsion for infusion has a uniform, milky, white appearance.
The three-chamber bag is a multilayer plastic bag.
To prevent contact with air, Numeta is packaged in an oxygen barrier overbag containing an oxygen absorber packet and an oxygen indicator.
Container Sizes
1000 ml bag: 6 units per box
1 bag of 1000 ml
Not all container sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Baxter, S.L.
Pouet de Camilo 2, 46394 Ribarroja del Turia (Valencia)
Manufacturer
Baxter S.A.
Boulevard Rene Branquart, 80
7860 Lessines
Belgium
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria Germany | Numeta G19 % E Emulsion zur Infusion |
Belgium Luxembourg | Numetzah G19%E, émulsion pour perfusion |
France | Numetah G19 %E émulsion pour perfusion |
Denmark Norway Sweden | Numeta G19E |
Czech Republic Greece | Numeta G19 % E |
Netherlands | Numeta G19%E emulsie voor infusie |
Ireland United Kingdom | Numeta G19%E, Emulsion for Infusion |
Italy | Numeta G19%E emulsione per infusione |
Finland | Numeta G19E infuusioneste, emulsio |
Poland | Numeta G19 % E |
Portugal | Numeta G19%E |
Spain | Numeta G19%E, emulsión para perfusión |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: May 2024
Detailed and updated information on this product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended solely for healthcare professionals:
(*) Please note that in certain cases, these medications may be administered at home by parents or other caregivers. In these cases, parents/caregivers should read the following information.
No medication should be added to the bag without first checking compatibility. Particles may form or the lipid emulsion may break down, which could block blood vessels.
Numeta G19%E should be at room temperature before use.
Before administering Numeta G19%E, you should prepare the bag as follows.
Make sure the bag is not damaged and use it only if it is not damaged. An undamaged bag has the following appearance:
- The non-permanent seals are intact. This is observed because there is no mixing of the three chambers.
- The amino acid and glucose solutions are clear, colorless, or slightly yellowish and without visible particles.
- The lipid emulsion is a liquid with a milky, white appearance.
Before opening the overbag, examine the color of the oxygen absorber.
- Compare it to the reference color printed next to the OK symbol and shown in the printed area of the indicator label.
- Do not use the product if the color of the oxygen absorber does not match the reference color printed next to the OK symbol.
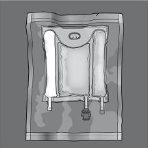
Figures 1 and 2 illustrate how to remove the overbag. Discard it along with the oxygen indicator and oxygen absorber.
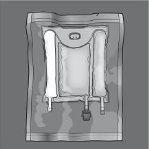
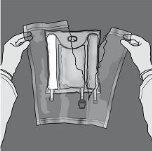
Figure 1 Figure 2
Mixture Preparation
- Make sure the product is at room temperature before breaking the non-permanent seals.
- Place the bag on a clean, flat surface.
Activation of the 3-chamber bag (breaking of the two non-permanent seals)
Step 1: Roll the bag from the hanger side in D
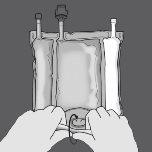
Step 2: Press until the non-permanent seals open.
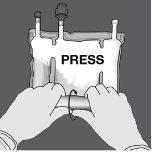
Step 3: Change direction and roll the bag towards the hanger in D until the seal is completely open. Follow the same steps to open the second non-permanent seal.
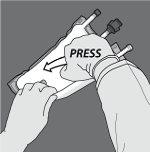
Step 4: Turn the bag at least three times to mix the contents well. The appearance of the mixed solution should be a white, milky emulsion.
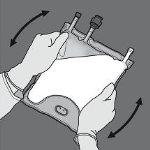
Step 5: Remove the protective cap from the administration point and insert the intravenous administration equipment.
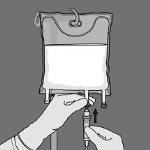
Activation of the 2-chamber bag (breaking of the non-permanent seal between the amino acid and glucose chambers)
Step 1: To break only the non-permanent seal of amino acids/glucose, start rolling the bag from the corner of the hanger in D of the seal that separates the amino acid and glucose chambers and press to open the seal that separates both compartments.

Step 2: Place the bag so that the compartment with lipid emulsion is facing the operator and roll the bag while protecting the compartment with lipid emulsion in the palms of the hands.
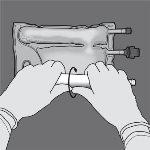
Step 3: With one hand, apply pressure by rolling the bag towards the tubes.
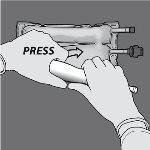
Step 4: Then, change direction and roll the bag towards the hanger in D, pressing with the other hand until the seal that separates the amino acid and glucose solutions is completely open.
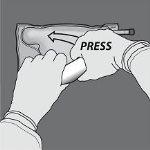
Step 5: Turn the bag at least three times to mix the contents well. The appearance of the mixed solution should be clear, colorless, or slightly yellowish.
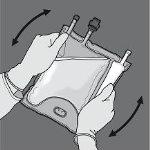
Step 6: Remove the protective cap from the administration point and insert the intravenous administration equipment.
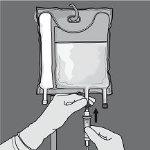
The administration rate should be gradually increased during the first hour and adjusted based on the following factors:
The dose to be administered
Daily volume intake
Infusion duration
Administration Method
The emulsion (in the bag and in the administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure from the point of administration of the mixture and throughout administration.
The use of a 1.2 micras filter is recommended for the administration of Numeta G19%E.
Due to its high osmolarity, Numeta G19%E can only be administered undiluted through a central vein; however, appropriate dilution of Numeta G19%E with water for injectable preparations reduces osmolarity and allows peripheral infusion.
The following formula indicates the impact of dilution on the osmolarity of the bags.
Final Osmolarity | = | Bag Volume x Initial Osmolarity |
Added Water + Bag Volume |
The following table shows examples of osmolarity for the activated 3-chamber bag (B3C) after adding water for injectable preparations:
Amino Acids, Glucose, and Lipids (B3C Activated) | |
Initial Volume in Bag (ml) | 1000 |
Initial Osmolarity (mOsm/l approx) | 1460 |
Volume of Added Water (ml) | 1000 |
Final Volume after Addition (ml) | 2000 |
Osmolarity after Addition (mOsm/l approx) | 730 |
Medication Addition
Mixtures containing oligoelements and vitamins should be protected from light, from the point of administration of the mixture and during administration. Exposure to ambient light generates peroxides and other degradation products, which can be reduced with photoprotection.
Compatible medications can be added to the reconstituted mixture (after opening the non-permanent seals and mixing the contents of the two or three chambers) through the injection point.
Vitamins can also be added to the glucose chamber before reconstituting the mixture (before opening the non-permanent seals and mixing the solutions and emulsion).
Tables 1-6 show the possible additions of commercially available oligoelement solutions (identified as TE1, TE2, and TE4), vitamins (identified as lyophilized V1 and emulsion V2), and electrolytes in defined quantities.
1 Compatibility with TE4, V1, and V2
Table 1: Compatibility of 3-in-1 (B3C Activated) with or without Water Dilution
Per 1000 ml (3-in-1 mixture with lipids) | ||||||
Undiluted Mixture | Diluted Mixture | |||||
Additives | Included Level | Maximum Addition | Maximum Total Level | Included Level | Maximum Addition | Maximum Total Level |
Sodium (mmol) | 45.8 | 105 | 151 | 45.8 | 105 | 151 |
Potassium (mmol) | 32.0 | 118 | 150 | 32.0 | 118 | 150 |
Magnesium (mmol) | 2.6 | 7.8 | 10.4 | 2.6 | 7.8 | 10.4 |
Calcium (mmol) | 3.8 | 20.5 | 24.3 | 3.8 | 20.5 | 24.3 |
Phosphate* (mmol) | 9.4 | 14.6 | 24.0 | 9.4 | 14.6 | 24.0 |
Oligoelements and Vitamins | - | 34 ml TE4 + 3.4 vials V1 + 38 ml V2 | 34 ml TE4 + 3.4 vials V1 + 38 ml V2 | - | 34 ml TE4 + 3.4 vials V1 + 38 ml V2 | 34 ml TE4 + 3.4 vials V1 + 38 ml V2 |
Water for Injectable Preparations | 1450 ml | 1450 mL |
- Organic Phosphate
Table 2: Compatibility of 2-in-1 (B2C Activated)
Per 775 ml (2-in-1 mixture without lipids) | |||
Additives | Included Level | Maximum Addition | Maximum Total Level |
Sodium (mmol) | 45.1 | 32.0 | 77.1 |
Potassium (mmol) | 32.0 | 45.6 | 77.6 |
Magnesium (mmol) | 2.6 | 5.2 | 7.8 |
Calcium (mmol) | 3.8 | 19.4 | 23.2 |
Phosphate* (mmol) | 7.2 | 16.0 | 23.2 |
Oligoelements and Vitamins | - | 10 ml TE4 + 1 vial V1 | 10 ml TE4 + 1 vial V1 |
- Organic Phosphate
2 Compatibility with TE1, V1, and V2
Table 3: Compatibility of 3-in-1 (B3C Activated)
Per 1000 ml (3-in-1 mixture with lipids) | |||
Additives | Included Level | Maximum Addition | Maximum Total Level |
Sodium (mmol) | 45.8 | 0 | 45.8 |
Potassium (mmol) | 32.0 | 0 | 32.0 |
Magnesium (mmol) | 2.6 | 0 | 2.6 |
Calcium (mmol) | 3.8 | 6.4 | 10.2 |
Phosphate* (mmol) | 9.4 | 0 | 9.4 |
Oligoelements and Vitamins | - | 15 ml TE1 + 1 vial V1 + 10 ml V2 | 15 ml TE1 + 1 vial V1 + 10 ml V2 |
- Organic Phosphate
Table 4: Compatibility of 2-in-1 (B2C Activated)
Per 775 ml (2-in-1 mixture without lipids) | |||
Additives | Included Level | Maximum Addition | Maximum Total Level |
Sodium (mmol) | 45.1 | 32.0 | 77.1 |
Potassium (mmol) | 32.0 | 45.6 | 77.6 |
Magnesium (mmol) | 2.6 | 5.2 | 7.8 |
Calcium (mmol) | 3.8 | 19.4 | 23.2 |
Phosphate* (mmol) | 7.2 | 16.0 | 23.2 |
Oligoelements and Vitamins | - | 10 ml TE1 + 1 vial V1 | 10 ml TE1 + 1 vial V1 |
- Organic Phosphate
3 Compatibility with TE2, V1, and V2
Table 5: Compatibility of 2-in-1 (B2C Activated)
Per 775 ml (2-in-1 mixture without lipids) | |||
Additives | Included Level | Maximum Addition | Maximum Total Level |
Sodium (mmol) | 45.1 | 32.0 | 77.1 |
Potassium (mmol) | 32.0 | 45.6 | 77.6 |
Magnesium (mmol) | 2.6 | 5.2 | 7.8 |
Calcium (mmol) | 3.8 | 19.4 | 23.2 |
Phosphate* (mmol) | 7.2 | 16.0 | 23.2 |
Oligoelements and Vitamins | 15 ml TE2 + 1 vial V1 | 15 ml TE2 + 1 vial V1 |
- Organic Phosphate
Table 6: Compatibility of 3-in-1 (B3C Activated)
Per 1000 ml (3-in-1 mixture with lipids) | |||
Additives | Included Level | Maximum Addition | Maximum Total Level |
Sodium (mmol) | 45.8 | 0 | 45.8 |
Potassium (mmol) | 32.0 | 0 | 32.0 |
Magnesium (mmol) | 2.6 | 0 | 2.6 |
Calcium (mmol) | 3.8 | 6.4 | 10.2 |
Phosphate* (mmol) | 9.4 | 0 | 9.4 |
Oligoelements and Vitamins | - | 15 ml TE2 + 1 vial V1 + 10 ml V2 | 15 ml TE2 + 1 vial V1 + 10 ml V2 |
- Organic Phosphate
The composition of the vitamin and oligoelement preparations is illustrated below in Tables 7 and 8:
Table 7: Composition of the Commercially Available Oligoelement Preparation:
Composition per 10 ml | TE1 | TE2 | TE4 |
Iron | - | 8.9 µmol or 0.5 mg | - |
Zinc | 38.2 µmol or 2.5 mg | 15.3 µmol or 1 mg | 15.3 µmol or 1 mg |
Selenium | 0.253 µmol or 0.02 mg | 0.6 µmol or 0.05 mg | 0.253 µmol or 0.02 mg |
Copper | 3.15 µmol or 0.2 mg | 4.7 µmol or 0.3 mg | 3.15 µmol or 0.2 mg |
Iodine | 0.0788 µmol or 0.01 mg | 0.4 µmol or 0.05 mg | 0.079 µmol or 0.01 mg |
Fluorine | 30 µmol or 0.57 mg | 26.3 µmol or 0.5 mg | - |
Molybdenum | - | 0.5 µmol or 0.05 mg | - |
Composition ofNumeta G19%E
The active ingredients are:
Active ingredient | B2C activated (775 ml) | B3C activated (1000 ml) |
Amino acid compartment | ||
Alanine | 1.83 g | 1.83 g |
Arginine | 1.92 g | 1.92 g |
Aspartic acid | 1.37 g | 1.37 g |
Cysteine | 0.43 g | 0.43 g |
Glutamic acid | 2.29 g | 2.29 g |
Glycine | 0.91 g | 0.91 g |
Histidine | 0.87 g | 0.87 g |
Isoleucine | 1.53 g | 1.53 g |
Leucine | 2.29 g | 2.29 g |
Lysine monohydrate (equivalent to lysine) | 2.82 g (2.51 g) | 2.82 g (2.51 g) |
Methionine | 0.55 g | 0.55 g |
Ornithine HCl (equivalent to ornithine) | 0.73 g (0.57 g) | 0.73 g (0.57 g) |
Phenylalanine | 0.96 g | 0.96 g |
Proline | 0.69 g | 0.69 g |
Serine | 0.91 g | 0.91 g |
Taurine | 0.14 g | 0.14 g |
Threonine | 0.85 g | 0.85 g |
Tryptophan | 0.46 g | 0.46 g |
Tyrosine | 0.18 g | 0.18 g |
Valine | 1.74 g | 1.74 g |
Sodium chloride | 1.79 g | 1.79 g |
Potassium acetate | 3.14 g | 3.14 g |
Calcium chloride dihydrate | 0.56 g | 0.56 g |
Magnesium acetate tetrahydrate | 0.55 g | 0.55 g |
Sodium glycerophosphate hydrate | 2.21 g | 2.21 g |
Glucose compartment | ||
Glucose monohydrate (equivalent to anhydrous glucose) | 210.65 g (191.50 g) | 210.65 g (191.50 g) |
Lipid compartment | ||
Refined olive oil (approx. 80%) + refined soybean oil (approx. 20%) | - | 7.5 g |
B2C = 2-chamber bag, B3C = 3-chamber bag
The reconstituted solution/emulsion contains the following:
Composition | ||||
B2C activated | B3C activated | |||
Per unit of volume (ml) | 775 | 100 | 1000 | 100 |
Nitrogen (g) | 3.5 | 0.45 | 3.5 | 0.35 |
Amino acids (g) | 23.0 | 3.0 | 23.0 | 2.3 |
Glucose (g) | 192 | 24.7 | 192 | 19.2 |
Lipids (g) | 0 | 0 | 28.1 | 2.8 |
Energy | ||||
Total calories (kcal) | 858 | 111 | 1139 | 114 |
Non-protein calories (kcal) | 766 | 99 | 1047 | 105 |
Glucose calories (kcal) | 766 | 99 | 766 | 77 |
Lipid calories (kcal) | 0 | 0 | 281 | 28 |
Non-protein calories/nitrogen (kcal/g N) | 220 | 220 | 301 | 301 |
Lipid calories (% non-protein calories) | NA | N/A | 27 | 27 |
Lipid calories (% total calories) | NA | N/A | 25 | 25 |
Electrolytes | ||||
Sodium (mmol) | 45.1 | 5.8 | 45.8 | 4.6 |
Potassium (mmol) | 32.0 | 4.1 | 32.0 | 3.2 |
Magnesium (mmol) | 2.6 | 0.33 | 2.6 | 0.26 |
Calcium (mmol) | 3.8 | 0.50 | 3.8 | 0.38 |
Phosphate (mmol) | 7.2 | 0.93 | 9.4 | 0.93 |
Acetate (mmol) | 37.1 | 4.8 | 37.1 | 3.71 |
Malate (mmol) | 8.8 | 1.1 | 8.8 | 0.88 |
Chloride (mmol) | 42.6 | 5.5 | 42.6 | 4.3 |
pH (approx.) | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
Osmolality (approx.) (mOsm/L) | 1835 | 1835 | 1460 | 1460 |
(a) Includes calories from egg phospholipids for infusion.
(b) Includes phosphate provided by egg phospholipids for lipid infusion.
The other components are:
L-Malic acid |
Hydrochloric acid |
Egg phospholipids for infusion |
Glycerol |
Sodium oleate |
Sodium hydroxide |
Water for injectable preparations |
for pH adjustment
Baxter and Numeta are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to NUMETA G19%E, EMULSION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 3.92 g / 1.26 g / 7.21 g / 3.36 g / 4.2 g / 5.11 g / 2.94 g / 2.8 g / 4.76 g / 5.07 g / 4.06 g / 14.49 g / 0.28 g / 8.05 g / 3.5 g / 200 gActive substance: combinationsManufacturer: Baxter S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE INFUSION, 3.5 g / 200 g / 5.22 g / 1.88 g / 3.92 g / 1.26 g / 7.21 g / 3.36 g / 4.2 g / 5.11 g / 2.94 g / 2.8 g / 662 mg / 1.02 g / 4.76 g / 5.15 g / 5.07 g / 4.06 g / 14.49 g / 0.28 g / 8.05 gActive substance: combinationsManufacturer: Baxter S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 4.25 g / 300 g / 5.22 g / 1.54 g / 4.76 g / 1.53 g / 8.76 g / 4.08 g / 5.1 g / 6.2 g / 3.57 g / 3.4 g / 662 mg / 1.02 g / 5.78 g / 5.94 g / 6.16 g / 4.93 g / 17.6 g / 0.34 g / 9.78 gActive substance: combinationsManufacturer: Baxter S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for NUMETA G19%E, EMULSION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about NUMETA G19%E, EMULSION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















