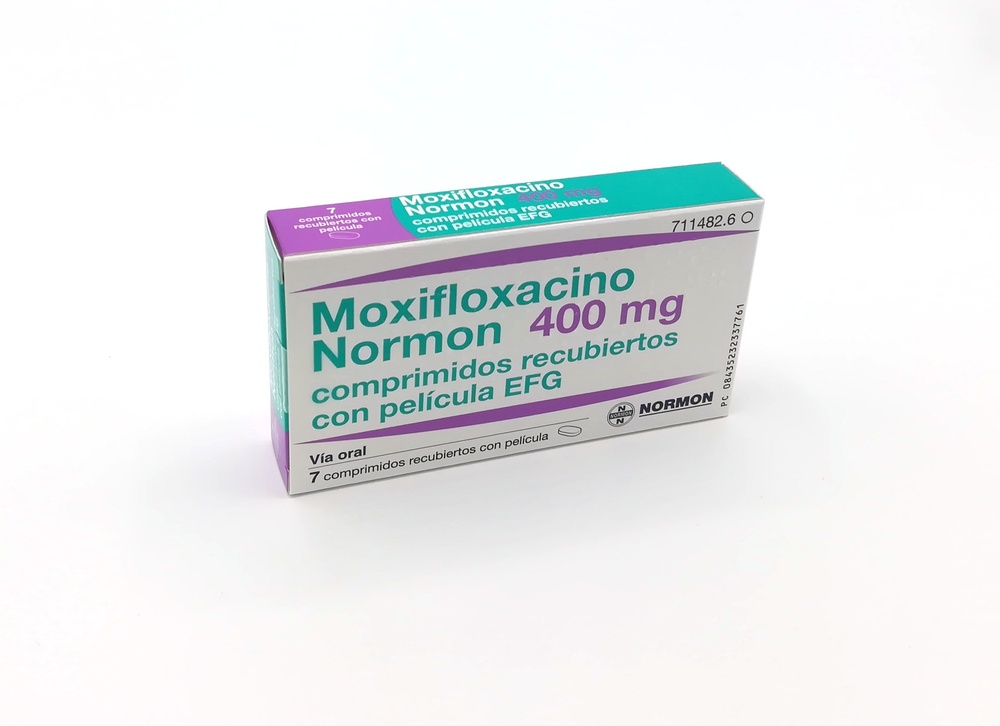
MOXIFLOXACIN NORMON 400 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS

How to use MOXIFLOXACIN NORMON 400 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Moxifloxacino Normon 400 mg Film-Coated Tablets EFG
Read the entire package leaflet carefully before starting to take this medication, as it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any questions, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medication has been prescribed to you only, and you should not give it to others, even if they have the same symptoms as you, as it may harm them.
- If you experience side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are side effects not listed in this package leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Moxifloxacino Normon and what is it used for
- What you need to know before taking Moxifloxacino Normon
- How to take Moxifloxacino Normon
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Moxifloxacino Normon
- Package Contents and Additional Information
1. What is Moxifloxacino Normon and what is it used for
Moxifloxacino Normon contains moxifloxacino as the active ingredient, which belongs to the group of antibiotics known as fluoroquinolones. Moxifloxacino acts by eliminating bacteria that cause infections.
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and are not effective against viral infections such as the flu or common cold.
It is essential to follow the instructions regarding dosage, administration interval, and treatment duration indicated by your doctor.
Do not store or reuse this medication. If you have any leftover antibiotic after completing treatment, return it to the pharmacy for proper disposal. Do not throw away medications down the drain or in the trash.
Moxifloxacino Normon is indicated in patients 18 years and older for the treatment of the following bacterial infections when caused by bacteria susceptible to moxifloxacino. Moxifloxacino should only be used to treat these infections when usual antibiotics cannot be used or have not worked.
Sinus infection, sudden worsening of long-term airway inflammation or lung infection (pneumonia) acquired outside the hospital in the community (except severe cases).
Mild or moderate infections of the upper female genital tract (pelvic inflammatory disease), including fallopian tube infection and uterine mucous membrane infection. For this type of infection, moxifloxacino is not sufficient as the sole treatment; therefore, in addition to moxifloxacino, your doctor will prescribe another antibiotic for the treatment of mild or moderate infections of the upper female genital tract (see section 2 2. What you need to know before taking Moxifloxacino Normon, Warnings and Precautions, Consult your doctor before taking Moxifloxacino Normon).
If the following diseases have shown improvement during initial treatment with moxifloxacino solution for infusion, your doctor may prescribe Moxifloxacino Normon tablets to complete the treatment: Community-acquired pneumonia, skin and soft tissue infections.
Moxifloxacino should not be used to initiate treatment for any type of skin and soft tissue infection or severe lung infections.
2. What you need to know before taking Moxifloxacino Normon
Consult your doctor if you are not sure if you belong to one of the patient groups described below.
Do not take Moxifloxacino Normon:
- If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to the active ingredient moxifloxacino or to other quinolones or to any of the other components of this medicine (included in section 6).
- If you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- If you are under 18 years old.
- If you have a history of tendon disorders or injuries related to treatment with quinolone antibiotics (see sections Warnings and precautionsand 4. Possible adverse effects). If you suffer from any inherited disease or have suffered from any disease related to an abnormal heart rhythm (observed in ECG, heart electrical record), suffer from electrolyte imbalances in the blood (especially low potassium or magnesium levels in the blood), have a very slow heart rate (called “bradycardia”), have a weak heart (heart failure), have a history of heart rhythm disorders or are taking other medications that cause ECG disorders (see section Other medicines and Moxifloxacino Normon). This is because moxifloxacino may cause changes in the ECG, such as a prolongation of the QT interval, i.e., delayed conduction of electrical signals in the heart.
- If you suffer from severe liver disease or increased liver enzyme levels (transaminases) 5 times above the upper limit of normal.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to take this medicine
You should not take antibacterial medicines that contain fluoroquinolones or quinolones, including Moxifloxacino Normon, if you have experienced any severe adverse reaction in the past when taking a quinolone or a fluoroquinolone. If this is the case, you should inform your doctor as soon as possible.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking Moxifloxacino Normon
- Moxifloxacino may modify the heart's ECG, especially if you are a woman or an elderly patient. If you are currently taking any medication that leads to a decrease in potassium levels in the blood, consult your doctor before taking this moxifloxacino. (see also sections Do not take Moxifloxacino Normonand Other medicines and Moxifloxacino Normon)
- If you have ever developed a severe skin rash or skin peeling, blisters, and/or sores in the mouthafter taking moxifloxacino.
- If you suffer from epilepsy or any other condition that may cause seizures, consult your doctor before taking moxifloxacino.
- If you have or have ever had any mental health problems, consult your doctor before taking moxifloxacino.
- If you have myasthenia gravis, your symptoms may worsen if you take moxifloxacino. If you think this affects you, consult your doctor immediately.
- If you have been diagnosed with an enlargement or a "lump" of a large blood vessel(aortic aneurysm or large peripheral vessel aneurysm).
- If you have suffered a previous episode of aortic dissection(tear in the aorta wall).
- If you have been diagnosed with heart valve insufficiency(regurgitation of the heart valves).
- If you have a family history of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection or congenital heart valve diseaseor other risk factors or predisposing disorders (e.g., connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome, vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Turner syndrome, or Sjögren's syndrome (an autoimmune inflammatory disease), or vascular disorders such as Takayasu arteritis, giant cell arteritis, Behçet's disease, arterial hypertension, or atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis (a joint disease) or endocarditis (a heart infection)).
- If you are diabeticbecause you may experience a risk of change in blood sugar levelswith moxifloxacino.
- If you or a family member suffers from glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (a rare inherited disease), inform your doctor, who will indicate whether moxifloxacino is suitable for you.
- If you have a complicated upper female genital tract infection(associated with an abscess in the fallopian tubes and ovary or pelvis), for which your doctor considers intravenous treatment necessary, treatment with moxifloxacino tablets is not appropriate.
- For the treatment of a mild to moderate upper female genital tract infection, your doctor should prescribe another antibiotic along with moxifloxacino. If you do not notice an improvement in symptoms after three days of treatment, consult your doctor.
During treatment with Moxifloxacino Normon
- If you notice palpitations or irregular heartbeatsduring the treatment period, you should inform your doctor immediately. He or she may perform an ECG to measure your heart rate.
- The risk of heart problemsmay increase with the increase in dose. Therefore, you should take the recommended dose.
- In rare cases, you may suffer a sudden severe allergic reaction(anaphylactic shock) even with the first dose, and develop the following symptoms: chest tightness, dizziness, nausea, or fainting, or feel dizzy when standing up. If you experience these symptoms, stop taking moxifloxacino and consult your doctor immediately.
- Moxifloxacino may cause a rapid and severe liver inflammation, which can lead to life-threatening liver failure (including fatal cases, see section 4 Possible adverse effects). Please consult your doctor before continuing treatment if you develop symptoms such as sudden discomfort and/or discomfort associated with a yellowish color of the whites of the eyes, dark urine, skin itching, tendency to bleed, or brain disease induced by liver damage (symptoms of reduced liver function or rapid and severe liver inflammation).
- Severe skin reactions
Severe skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome or drug hypersensitivity syndrome), have been reported with the use of moxifloxacino.
- SSJ/TEN may initially appear on the trunk as reddish grains in a target shape or circular spots often with central blisters. Ulcers may also appear in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes (red and swollen eyes). These severe skin rashes are often preceded by fever and/or flu-like symptoms. The rashes can progress to generalized skin peeling and life-threatening complications.
- AGEP appears at the start of treatment as a red, scaly, and generalized rash with bumps under the skin and blisters accompanied by fever. The most common location: mainly localized in skin folds, trunk, and upper limbs.
- Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) appears initially with pseudo-flu-like symptoms and a rash on the face, later, a widespread rash appears with high body temperature, increased liver enzyme levels in blood tests, and increased eosinophilia and lymph node enlargement.
If you develop a severe rash or any of these skin symptoms, stop taking moxifloxacino and contact your doctor or seek medical attention immediately.
- Quinolone antibiotics, including moxifloxacino, may cause seizures. If this occurs, treatment with moxifloxacino should be discontinued, and you should contact your doctor immediately.
- Severe, long-lasting, and potentially irreversible adverse effects. Antibacterial medicines that contain fluoroquinolones or quinolones, including Moxifloxacino Normon, have been associated with very rare but severe adverse effects, some of which were long-lasting (persistent for months or years), disabling, or potentially irreversible. This includes pain in the tendons, muscles, and joints of the upper and lower limbs, difficulty walking, abnormal sensations such as pinching, tingling, prickling, numbness, or burning (paresthesia), sensory disorders such as decreased vision, taste, smell, and hearing, depression, decreased memory, intense fatigue, and severe sleep disorders.
If you experience any of these adverse effects after taking Moxifloxacino Normon, contact your doctor immediately, before continuing treatment. You and your doctor will decide whether to continue or not the treatment, also considering the use of an antibiotic of another class.
- In rare cases, you may experience symptoms of nerve damage(neuropathy) such as pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness, especially in feet and legs or hands and arms. If this happens, stop taking Moxifloxacino Normon and inform your doctor immediately to prevent the development of a potentially irreversible disorder.
- You may experience mental health problemseven after the first administration of quinolone antibiotics, including moxifloxacino. In very rare cases, mental health problems and depression have evolved into suicidal thoughts and self-harming behaviors such as suicide attempts (see section 4). If you develop these reactions, you should discontinue treatment with moxifloxacino and inform your doctor immediately.
- You may develop diarrheaduring or after taking antibiotics, including moxifloxacino. If the diarrhea is severe or persistent, or if you notice blood or mucus in the stool, stop taking moxifloxacino immediately and consult your doctor. In these situations, you should not take medications that interrupt or slow down intestinal movement.
- In rare cases, pain and swelling in the joints and tendon inflammation or rupturemay occur (see sections Do not take Moxifloxacino Normonand 4. Possible adverse effects). The risk is higher if you are an elderly person (over 60 years old), have received an organ transplant, have kidney problems, or are being treated with corticosteroids. Tendon inflammation and rupture can occur within the first 48 hours of treatment and even several months after discontinuing treatment with Moxifloxacino Normon. At the first sign of pain or tendon inflammation (e.g., in the ankle, wrist, elbow, shoulder, or knee), stop taking Moxifloxacino Normon, contact your doctor, and rest the affected area. Avoid any unnecessary exercise, as this could increase the risk of tendon rupture.
- If you feel a strong and sudden pain in the chest, abdomen, or back, which can be symptoms of aortic dissection or aneurysm, go to the emergency room immediately. The risk may increase if you are receiving systemic corticosteroid treatment.
- If you start experiencing sudden shortness of breath, especially when lying down, or if you notice swelling of the ankles, feet, or abdomen, or the appearance of heart palpitations (feeling of rapid or irregular heartbeat), you should inform your doctor immediately.
- If you are elderly and have kidney problems, be careful to drink enough fluids, as dehydration can increase the risk of kidney failure.
- If your vision worsens or if your eyes seem to be affected, consult an ophthalmologist immediately (see sections 2 Driving and using machinesand 4 Possible adverse effects).
- Fluoroquinolones may cause an increase in blood sugar levelsabove normal levels (hyperglycemia) or a decrease in blood sugar levels below normal levels (hypoglycemia), which in severe cases can cause loss of consciousness (hypoglycemic coma) (see section 4. Possible adverse effects). If you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels should be carefully monitored.
- Quinolone antibiotics may increase sensitivity of the skin to sunlight or UV. You should avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight or direct sunlight and not use sunbeds or any type of UV lamp during treatment with moxifloxacino (see section 4. Possible adverse effects).
- The efficacy of moxifloxacino has not been established in the treatment of severe burns, deep tissue infections, and diabetic foot infections with osteomyelitis (bone marrow infections).
Children and adolescents
Do not give this medicine to children and adolescents under 18 years old because the efficacy and safety have not been established for this age group (see section Do not take Moxifloxacino Normon)
Other medicines and Moxifloxacino Normon
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take other medicines in addition to Moxifloxacino Normon.
With moxifloxacino, you should consider the following:
- If you are taking moxifloxacino and other medicines that affect the heart, there is a greater risk of heart rhythm disorders. Therefore, you should not take moxifloxacino at the same time as the following drugs: medicines that belong to the class of antiarrhythmics (e.g., quinidine, hydroquinidine, disopyramide, amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide), antipsychotics (e.g., phenothiazines, pimozide, sertindole, haloperidol, sultoprid), tricyclic antidepressants, some antimicrobials (e.g., saquinavir, sparfloxacin, erythromycin administered intravenously, pentamidine, antimalarials, particularly halofantrine), some antihistamines (e.g., terfenadine, astemizole, mizolastine), and other drugs (e.g., cisapride, intravenous vincamine, bepridil, and difemanil).
- While taking moxifloxacino, you should inform your doctor if you are taking other medicines that may decrease potassium levels in the blood (e.g., loop and thiazide diuretics, laxatives, and enemas (high doses), corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory medicines) or cause a decrease in heart rate, as these may also increase the risk of severe heart rhythm disorders.
- Any other medicine that contains magnesium or aluminum, such as antacids for indigestion, or any medicine that contains iron or zinc, medicines that contain didanosine, or medicines that contain sucralfate for gastrointestinal disorders may reduce the effect of moxifloxacino tablets. Therefore, take your moxifloxacino tablets 6 hours before or after taking other medicines.
- Taking oral activated charcoal at the same time as moxifloxacino tablets reduces the effect of these tablets. Therefore, it is recommended not to use these medicines simultaneously.
- If you are currently taking oral anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), your doctor may need to monitor your blood coagulation time.
Moxifloxacino Normon with food and drinks
The effect of moxifloxacino is not altered by food, including dairy products.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Do not use moxifloxacino during pregnancy or breastfeeding. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Animal studies do not indicate that fertility may be altered by taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Moxifloxacino may cause dizziness or vertigo or a brief fainting spell; you may experience a sudden transient loss of vision. If you experience these symptoms, do not drive vehicles or operate machinery.
Moxifloxacino Normon contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per tablet; this is essentially “sodium-free”.
3. How to take Moxifloxacino Normon
Follow the administration instructions for moxifloxacino indicated by your doctor or pharmacist exactly. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
The recommended dose in adults is one 400 mg film-coated tablet, once a day.
Moxifloxacino tablets are for oral administration. Take the tablet whole without chewing (to mask the bitter taste) and with plenty of liquid. Moxifloxacino can be taken with or without food. It is recommended that you take the tablet at approximately the same time every day.
No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients, in patients with low body weight, or in patients with kidney problems.
The duration of treatment depends on the type of infection. Unless your doctor has indicated otherwise, the duration of treatment with moxifloxacino is as follows:
- Sudden worsening of chronic bronchitis (acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, including bronchitis): 5-10 days.
- Community-acquired lung infections (pneumonia), except in severe cases: 10 days.
- Acute infections of the paranasal sinuses (bacterial sinusitis): 7 days.
- Mild or moderate infections of the upper female genital tract (pelvic inflammatory disease), including fallopian tube infection and uterine mucous membrane infection: 14 days.
When Moxifloxacino 400 mg tablets are used to complete treatment initiated with Moxifloxacino solution for infusion (intravenous treatment), the recommended durations are:
- Community-acquired lung infections (pneumonia): 7-14 days.
Most patients with pneumonia switched from intravenous to oral treatment after 4 days
- Skin and soft tissue infections: 7-21 days.
Most patients with skin and soft tissue infections switched from intravenous to oral treatment after 6 days.
It is essential to take the complete treatment, even if you start to feel better after a few days. If you interrupt treatment too early, the infection may not be completely cured, the infection may return, or your condition may worsen, and you may also develop bacterial resistance to the antibiotic.
Do not exceed the recommended dose and treatment duration (see section 2. What you need to know before taking Moxifloxacino Normon, Warnings and precautions).
If you take more Moxifloxacino Normon than you should
If you take more than one of the recommended tablets per day, consult your doctor immediately, and if possible, bring the remaining medication, packaging, or this leaflet to show the doctor or pharmacist what you have taken.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service. Phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount used.
If you forget to take Moxifloxacino Normon
In case of forgetting a dose, take it as soon as you remember on the same day. If you do not take your tablet one day, take the normal dose (one tablet) the next day. Do not take two tablets to make up for the forgotten dose.
If you are unsure what to do, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
If you interrupt treatment with Moxifloxacino Normon
If you interrupt treatment too early, your infection may not be completely cured. Consult your doctor if you intend to stop taking the tablets before completing the full treatment.
If you have any other questions about using this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, moxifloxacino can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
The most serious side effectsobserved during treatment with moxifloxacino are listed below:
If you notice:
- An abnormally fast heart rate (rare side effect).
- A sudden feeling of discomfort or notice a yellowish color of the whites of the eyes, dark urine, skin itching, tendency to bleed, or alterations in thought or wakefulness (these may be signs and symptoms of a fulminant liver inflammation that can potentially lead to potentially fatal liver failure (very rare side effect, with reported fatal cases)).
- Severe skin rashes, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. These can appear on the trunk as reddish spots in a target shape or circular patches, often with blisters in the center, skin peeling, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes, and may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (very rare side effects, with possible life-threatening potential).
- A red, scaly, and generalized rash with bumps under the skin and blisters, accompanied by fever at the start of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis) (the frequency of this side effect is "unknown").
- A generalized rash, high body temperature, elevated liver enzymes, blood abnormalities (eosinophilia), enlarged lymph nodes, and involvement of other body organs (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, also known as DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome) (the frequency of this side effect is "unknown").
- Syndrome associated with alterations in water elimination and low sodium levels (SIADH) (very rare side effect).
- Loss of consciousness due to a severe decrease in blood sugar levels (hypoglycemic coma) (very rare side effect).
- Inflammation of blood vessels (signs may be red spots on the skin, usually on the legs, or effects such as joint pain) (very rare side effect).
- Severe allergic reaction, sudden and generalized, including very rarely life-threatening shock (e.g., difficulty breathing, decreased blood pressure, rapid pulse) (rare side effect).
- Swelling, including swelling of the airways (rare side effect, potentially fatal).
- Seizures (rare side effect).
- Nervous system problems, such as pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness in the limbs (rare side effect).
- Depression (in very rare cases, it has evolved into self-harm, suicidal ideas/thoughts, or suicide attempts) (rare side effect).
- Madness that can lead to self-harming behaviors, such as suicidal ideas/thoughts or suicide attempts) (very rare side effect).
- Severe diarrhea with blood and/or mucus (antibiotic-associated colitis, including pseudomembranous colitis) that, in very rare circumstances, can generate life-threatening complications (rare side effect).
- Pain and inflammation of the tendons (tendinitis) (rare side effect) or tendon rupture (very rare side effect).
- Muscle weakness, sensitivity, or pain, particularly if you also feel discomfort, have a fever, or your urine is dark. These symptoms can be caused by abnormal muscle breakdown that can be life-threatening and cause kidney problems (a condition called rhabdomyolysis) (the frequency of this side effect is "unknown").
Stop taking moxifloxacino and contact your doctor immediatelyas you may need urgent medical attention.
Additionally, if you notice:
- Transient loss of vision (very rare side effect).
- Discomfort or pain in the eyes, especially due to light exposure (very rare to rare side effect).
Contact an ophthalmologist immediately.
If you have experienced potentially life-threatening irregular heartbeats (Torsade de Pointes) or cardiac arrest while taking moxifloxacino (very rare side effects), tell your doctor immediately that you have been taking moxifloxacino and do not restart treatment.
In very rare cases, it has been observed that myasthenia gravis symptoms can worsen. If this occurs, consult your doctor immediately.
If you have diabetes and notice that your blood sugar level increases or decreases (rare or very rare side effect), tell your doctor immediately.
If you are elderly with kidney problems and notice a decrease in urine production, swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet, fatigue, nausea, drowsiness, shortness of breath, or confusion (these may be signs and symptoms of kidney failure, a rare side effect), consult your doctor immediately.
The following are other side effectsthat have been observed during treatment with moxifloxacino, according to their probability:
Frequent(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Nausea.
- Diarrhea.
- Dizziness.
- Abdominal and stomach pain.
- Vomiting.
- Headache.
- Increased liver enzyme in the blood (transaminases).
- Infections caused by resistant bacteria or fungi, e.g., oral and vaginal infections caused by Candida.
- Change in heart rhythm (ECG), in patients with low potassium levels in the blood.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Rash.
- Gastric discomfort (indigestion/acid reflux).
- Alteration of taste (in very rare cases, loss of taste).
- Sleep disorders (predominantly insomnia).
- Increased liver enzyme in blood (gamma-glutamyl-transferase and/or alkaline phosphatase).
- Low levels of certain white blood cells (leukocytes, neutrophils).
- Constipation.
- Itching.
- Feeling of vertigo (that everything is spinning and you are going to fall).
- Drowsiness.
- Flatulence.
- Change in heart rhythm (ECG).
- Alteration of liver function (including increased liver enzyme in blood, LDH).
- Decreased appetite and food intake.
- Low white blood cell count.
- Pain and discomfort, such as back pain, limb pain, pelvic pain, and chest pain.
- Increased levels of certain blood cells necessary for blood coagulation.
- Sweating.
- Increased levels of certain white blood cells (eosinophils).
- Anxiety.
- Discomfort (mainly weakness or fatigue).
- Tremors.
- Joint pain.
- Palpitations.
- Irregular and rapid heartbeat.
- Breathing difficulties, including asthmatic conditions.
- Increased levels of a certain digestive enzyme in the blood (amylase).
- Restlessness/agitation.
- Feeling of tingling (pins and needles) and/or numbness.
- Hives on the skin.
- Dilation of blood vessels.
- Confusion and disorientation.
- Decrease in blood cells necessary for blood coagulation.
- Visual disturbances, including double vision and blurred vision.
- Decreased blood coagulation.
- Increased blood lipid levels (fats).
- Low red blood cell count.
- Muscle pain.
- Allergic reactions.
- Increased bilirubin in the blood.
- Stomach inflammation (gastritis).
- Dehydration.
- Severe heart rhythm disorders.
- Dry skin.
- Chest pain.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Muscle cramps.
- Muscle spasms.
- Hallucinations.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Swelling (of hands, feet, ankles, lips, mouth, and throat).
- Decreased blood pressure.
- Kidney problems (including increased kidney function tests, such as urea and creatinine).
- Liver inflammation.
- Mouth inflammation.
- Ringing/ noises in the ears.
- Jaundice (yellowish color of the whites of the eyes or skin).
- Alterations in skin sensitivity.
- Abnormal dreams.
- Concentration disorders.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Alterations in smell (including loss of smell).
- Balance and coordination disorders (due to dizziness).
- Total or partial memory loss.
- Hearing impairments, including deafness (usually reversible).
- Increased uric acid levels in the blood.
- Emotional instability.
- Speech disorders.
- Fainting.
- Muscle weakness.
Very rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Decrease in the number of red and white blood cells and platelets (pancytopenia).
- Joint inflammation.
- Irregular heartbeat.
- Increased skin sensitivity.
- Depersonalization disorder (feeling that one is not oneself).
- Increased blood coagulation.
- Muscle stiffness.
- Significant decrease in certain white blood cells (agranulocytosis).
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from available data)
- Increased skin sensitivity to sunlight or UV radiation (see also section 2, Warnings and precautions).
- Clearly defined erythematous patches with/without blisters that appear in the hours following moxifloxacino administration and disappear with residual post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation; they usually reappear in the same place on the skin or mucous membrane with subsequent exposure to moxifloxacino.
The administration of antibiotics containing quinolones and fluoroquinolones has been associated with very rare cases of long-lasting (even months or years) or permanent adverse reactions, such as tendon inflammation, tendon rupture, joint pain, limb pain, difficulty walking, abnormal sensations such as pins and needles, tingling, burning, numbness, or pain (neuropathy), fatigue, decreased memory and concentration, mental health problems (such as sleep disorders, anxiety, panic attacks, depression, and suicidal ideas), and decreased hearing, vision, taste, and smell, in some cases regardless of the presence of pre-existing risk factors.
There have been reports of increased size and weakening or tearing of the aortic wall (aneurysms and dissections), which could lead to rupture and be fatal, and cardiac valve insufficiency in patients who have received fluoroquinolones. See also section 2.
Additionally, very rare cases of the following side effects have been reported after treatment with other quinolone antibiotics and may also occur during treatment with moxifloxacino: increased sodium and calcium levels in the blood, reduced count of a certain type of red blood cell (hemolytic anemia),
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible side effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Moxifloxacino Normon
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date shown on the packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
No special storage conditions are required.
Medications should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packaging and unused medication at the SIGRE collection point in the pharmacy. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and unused medication. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and additional information
Composition of Moxifloxacino Normon
The active ingredient is moxifloxacino. Each film-coated tablet contains 400 mg of moxifloxacino (in the form of moxifloxacino hydrochloride).
The other ingredients are: Tablet core: Sodium croscarmellose, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal anhydrous silica, talc, and magnesium stearate. Film coating: Hypromellose (E-464), titanium dioxide (E-171), macrogol 6000, talc, and red iron oxide (E-172).
Appearance of the product and package contents
Moxifloxacino Normon 400 mg film-coated tablets are available in packages of 5 and 7 tablets.
Film-coated tablets are pale red, elongated, biconvex, and marked with "M400" on one face.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
LABORATORIOS NORMON, S.A.
Ronda de Valdecarrizo, 6
28760 Tres Cantos, Madrid
Spain
This leaflet was approved in:January 2022
Detailed information about this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
You can access detailed and updated information about this medication by scanning the QR code included in the leaflet and packaging with your smartphone. You can also access this information at the following internet address:
https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/p/81027/P_81027.html
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price13.58 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to MOXIFLOXACIN NORMON 400 mg FILM-COATED TABLETSDosage form: INJECTABLE INFUSION, 400 mg/250 mlActive substance: moxifloxacinManufacturer: Bayer Hispania S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 400 mgActive substance: moxifloxacinManufacturer: Medochemie LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 400 mgActive substance: moxifloxacinManufacturer: Aurovitas Spain, S.A.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for MOXIFLOXACIN NORMON 400 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS
Discuss questions about MOXIFLOXACIN NORMON 400 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions