
INIXA 6,000 IU (60 mg)/0.6 mL Injectable Solution

How to use INIXA 6,000 IU (60 mg)/0.6 mL Injectable Solution
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Inhixa 2,000 IU (20 mg)/0.2 ml Solution for Injection
Inhixa 4,000 IU (40 mg)/0.4 ml Solution for Injection
Inhixa 6,000 IU (60 mg)/0.6 ml Solution for Injection
Inhixa 8,000 IU (80 mg)/0.8 ml Solution for Injection
Inhixa 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml Solution for Injection
Sodium enoxaparin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Inhixa and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Inhixa
- How to use Inhixa
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Inhixa
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Inhixa and what is it used for
Inhixa contains the active substance sodium enoxaparin, which is a low molecular weight heparin (LMWH).
Inhixa works in two ways:
- Preventing existing blood clots from getting bigger. This helps your body to break them down and stop them from causing harm.
- Stopping the formation of blood clots.
Inhixa can be used to:
- treat blood clots
- prevent the formation of blood clots in the following situations:
- before and after surgery
- when you have an acute illness and are about to undergo a period of reduced mobility
- if you have had blood clots due to cancer, to prevent new clots from forming
- if you have unstable angina (a condition where not enough blood reaches the heart)
- after a heart attack
- prevent blood clots from forming in the tubes of a dialysis machine (used in people with severe kidney problems).
2. What you need to know before you use Inhixa
Do not use Inhixa
- If you are allergic to sodium enoxaparin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). Signs of an allergic reaction include: rash, problems swallowing or breathing, swelling of the lips, face, throat, or tongue.
- If you are allergic to heparin or other low molecular weight heparins such as nadroparin, tinzaparin, or dalteparin.
- If you have had a reaction to heparin that caused a severe decrease in the number of cells involved in blood clotting (platelets) – this reaction is called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia – in the last 100 days or if you have antibodies against enoxaparin in your blood.
- If you are bleeding heavily or have a high risk of bleeding (such as stomach ulcers, recent eye or brain surgery), including recent hemorrhagic stroke.
- If you are using Inhixa to treat blood clots and are going to have spinal or epidural anesthesia or a lumbar puncture within 24 hours.
Warnings and Precautions
Inhixa should not be exchanged with other medicines that belong to the group of low molecular weight heparins. This is because they are not exactly the same and do not have the same activity or instructions for use.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Inhixa if:
- you have ever had a reaction to heparin that caused a severe decrease in the number of platelets
- you are going to have spinal or lumbar anesthesia or a lumbar puncture (see "Surgical Operations and Anesthesia"): a delay should be observed between Inhixa and the use of this procedure
- you have had a heart valve implanted
- you have endocarditis (an infection of the inner lining of the heart)
- you have a history of stomach ulcers
- you have recently had a stroke
- you have high blood pressure
- you have diabetes or problems with the blood vessels in your eyes caused by diabetes (called diabetic retinopathy)
- you have recently had eye or brain surgery
- you are an elderly person (over 65 years old) and especially if you are over 75 years old
- you have kidney problems
- you have liver problems
- you are underweight or overweight
- you have high levels of potassium in your blood (which could be checked with a blood test)
- you are currently using medicines that affect bleeding (see below - Use of Inhixa with other medicines)
You may need to have a blood test before starting to use this medicine and while you are using it; this is to check the level of cells involved in blood clotting (platelets) and the levels of potassium in your blood.
Children and Adolescents
The safety and efficacy of Inhixa in children and adolescents have not been established.
Use of Inhixa with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
- Warfarin - another anticoagulant medicine used to reduce blood clotting
- Acetylsalicylic acid (also known as aspirin or AAS), clopidogrel, or other medicines used to prevent blood clots from forming (see also section 3, "Change of anticoagulant treatment")
- Dextran injection - used as a blood substitute
- Ibuprofen, diclofenac, ketorolac, and other medicines known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs used to treat pain and inflammation in arthritis and other diseases
- Prednisolone, dexamethasone, and other medicines used to treat asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and other diseases
- Medicines that increase the level of potassium in your blood, such as potassium salts, diuretics, and some medicines used to treat heart problems.
Surgical Operations and Anesthesia
If you are going to have a lumbar puncture or are going to undergo surgery where spinal or epidural anesthesia is used, inform your doctor that you are using Inhixa. See "Use of Inhixa with other medicines". Also, inform your doctor if you have any problems with your spine or if you have had spine surgery.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
If you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
If you are pregnant and have a mechanical heart valve, you may be at higher risk of blood clots. Your doctor will discuss this with you.
If you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed, you should consult your doctor before using this medicine.
Driving and Using Machines
Inhixa does not affect your ability to drive or use machines.
Traceability
It is important to keep a record of the batch number of your Inhixa. Therefore, each time you receive a new pack of Inhixa, note the date and batch number (which is on the pack after "Batch") and keep this information in a safe place.
Inhixa contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Inhixa
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medication indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Using the medication
- Normally, your doctor or nurse will administer Inhixa to you. This is because it must be administered by injection.
- When you return home, you may need to continue using Inhixa and administer it yourself (see the instructions on how to do it).
- Inhixa is usually administered by injection under the skin (subcutaneously).
- Inhixa can be administered by injection into your veins (intravenously) after certain types of heart attacks and surgical operations.
- Inhixa can be added to the tube that comes out of the body (arterial line) at the beginning of the dialysis session.
Do not administer Inhixa into a muscle (intramuscularly).
How much will be administered to you
- Your doctor will decide the amount of Inhixa that will be administered to you. The dose will depend on the reason why it is going to be used.
- If you have any kidney problems, you may be administered a smaller amount of Inhixa.
1) Treatment of blood clot formation:
- The usual dose is 150 IU (1.5 mg) per kilogram of body weight once a day or 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight twice a day.
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Inhixa.
- Interruption of blood clot formation in the following situations:
- Surgery or periods of limited mobility due to illness
- The dose will depend on the probability that you will develop a clot. You will be administered 2,000 IU (20 mg) or 4,000 IU (40 mg) of Inhixa per day.
- If you are going to have surgery, you will usually be given the first injection 2 or 12 hours before the operation.
- If you have reduced mobility due to illness, you will usually be administered 4,000 IU (40 mg) of Inhixa per day.
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Inhixa.
- After having a heart attack
Inhixa can be used in 2 different types of heart attacks, called STEMI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction) or non-STEMI. The amount of Inhixa that will be administered to you will depend on your age and the type of heart attack you had.
Non-STEMI heart attack:
- The usual dose is 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight every 12 hours.
- Usually, your doctor will tell you to also take acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin).
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Inhixa.
STEMI heart attack if you are under 75 years old:
- You will be administered an initial intravenous injection of 3,000 IU (30 mg) of Inhixa.
- At the same time, you will be administered a subcutaneous injection of Inhixa. The usual dose is 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight, every 12 hours.
- Usually, your doctor will tell you to also take acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin).
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Inhixa.
STEMI heart attack if you are 75 years old or older:
- The usual dose is 75 IU (0.75 mg) per kilogram of body weight, every 12 hours.
- The maximum amount of Inhixa administered in the first two injections is 7,500 IU (75 mg).
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Inhixa.
For patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI):
Depending on when you received the last injection of Inhixa, your doctor may decide to administer an additional dose of Inhixa before a PCI intervention. It would be by intravenous injection.
- Interruption of blood clot formation in the dialysis machine tubes
- The usual dose is 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight.
- Inhixa is added to the tube that comes out of the body (arterial line) at the beginning of the dialysis session. This amount is usually sufficient for a 4-hour session. However, your doctor may administer a new injection of 50 IU to 100 IU/kg (0.5 to 1 mg/kg) per kilogram of body weight, if necessary.
Self-administration of an Inhixa injection with a pre-filled syringe without a needle protector
Your pre-filled syringe includes a needle protector to protect you from a needle stick injury.
If you can administer this medication to yourself, your doctor or nurse will show you how to do it. Do not attempt to inject yourself if you have not been taught how to do it. If you do not know what to do, consult your doctor or nurse immediately.
Before injecting Inhixa
- Check the expiration date of the medication. If it has expired, do not use it.
- Check if the syringe is not damaged and the liquid inside is transparent. If not, use another syringe.
- Do not use this medication if you notice any change in its appearance.
- Check the amount to be injected.
- Review if the last injection caused redness, skin color change, swelling, suppuration, or if it still hurts. If so, talk to your doctor or nurse.
- Decide on the area where you will inject the medication. Alternate, each time you inject, the right side of the abdomen (belly) with the left. This medication should be injected just under the skin of the abdomen, but not too close to the navel or any scar (at least 5 cm away from them).
- The pre-filled syringe is for single use.
Instructions for self-injecting Inhixa
- Wash your hands and the injection area with water and soap. Dry them.
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable and relaxed position. Make sure you can see the area where you will inject. The most suitable is on a couch, a reclining armchair, or in a bed with pillows for support.
- Choose an area on the right or left side of the belly. It should be more than 5 cm away from the navel and towards the sides.
Remember.Do not inject in the 5 cm around the navel or scars or hematomas that you may have. Inject in the opposite area to the one you injected the last time (alternating the right side of the belly with the left).
- Take the plastic blister pack containing the pre-filled syringe out of the box. Open the blister pack and remove the pre-filled syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe by pulling it. The syringe is pre-filled and ready for use.
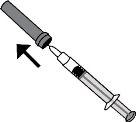
Do notpress the plunger before injecting. Once you have removed the cap, do not touch anything with the needle. This way, you will ensure that the needle remains clean (sterile).
- Hold the syringe with the hand you write with (like a pencil) and, with the other hand, gently pinch the area of the abdomen between the index finger and thumb to form a skin fold.
Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Hold the syringe so that the needle points downwards (vertically at a 90-degree angle). Insert the entire needle into the skin fold.
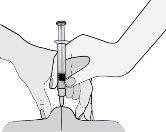
- Press the plunger with your thumb. This way, you will inject the medication into the abdominal fatty tissue. Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Remove the needle by pulling it straight out.
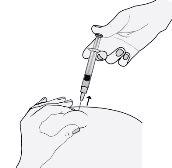
To avoid a hematoma, do not rub the injection area after injecting.
- Dispose of the used syringe in the sharps container. Close the container lid tightly and keep it out of the reach of children.
When the container is full, dispose of it as your doctor or pharmacist has indicated. Do not throw it in the trash.
Self-administration of an Inhixa injection with a pre-filled syringe with a needle protector
Your pre-filled syringe includes a needle protector to protect you from a needle stick injury.
If you can administer this medication to yourself, your doctor or nurse will show you how to do it. Do not attempt to inject yourself if you have not been taught how to do it. If you do not know what to do, consult your doctor or nurse immediately.
Before injecting Inhixa
- Check the expiration date of the medication. If it has expired, do not use it.
- Check if the syringe is not damaged and the liquid inside is transparent. If not, use another syringe.
- Do not use this medication if you notice any change in its appearance.
- Check the amount to be injected.
- Review if the last injection caused redness, skin color change, swelling, suppuration, or if it still hurts. If so, talk to your doctor or nurse.
- Decide on the area where you will inject the medication. Alternate, each time you inject, the right side of the abdomen (belly) with the left. This medication should be injected just under the skin of the abdomen, but not too close to the navel or any scar (at least 5 cm away from them).
- The pre-filled syringe is for single use.
Instructions for self-injecting Inhixa
- Wash your hands and the injection area with water and soap. Dry them.
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable and relaxed position. Make sure you can see the area where you will inject. The most suitable is on a couch, a reclining armchair, or in a bed with pillows for support.
- Choose an area on the right or left side of the belly. It should be more than 5 cm away from the navel and towards the sides.
Remember.Do not inject in the 5 cm around the navel or scars or hematomas that you may have. Inject in the opposite area to the one you injected the last time (alternating the right side of the belly with the left).
- Take the plastic blister pack containing the pre-filled syringe out of the box. Open the blister pack and remove the pre-filled syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe by pulling it. The syringe is pre-filled and ready for use.

Do notpress the plunger before injecting. Once you have removed the cap, do not touch anything with the needle. This way, you will ensure that the needle remains clean (sterile).
- Hold the syringe with the hand you write with (like a pencil) and, with the other hand, gently pinch the area of the abdomen between the index finger and thumb to form a skin fold.
Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Hold the syringe so that the needle points downwards (vertically at a 90-degree angle). Insert the entire needle into the skin fold.
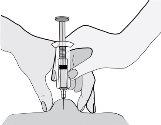
- Press the plunger with your thumb. This way, you will inject the medication into the abdominal fatty tissue. Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Remove the needle by pulling it straight out. Do not stop pressing the plunger!
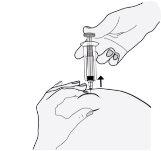
To avoid a hematoma, do not rub the injection area after injecting.
- Release the plunger and allow the syringe to move upwards until the entire needle is stored and locked in its place.

- Dispose of the used syringe in the sharps container. Close the container lid tightly and keep it out of the reach of children.
When the container is full, dispose of it as your doctor or pharmacist has indicated. Do not throw it in the trash.
Self-administration of an Inhixa injection with a pre-filled syringe with an Ultrasafe Passive needle protector
Your pre-filled syringe includes an Ultrasafe Passive needle protector to protect you from a needle stick injury.
If you can administer this medication to yourself, your doctor or nurse will show you how to do it. Do not attempt to inject yourself if you have not been taught how to do it. If you do not know what to do, consult your doctor or nurse immediately.
Before injecting Inhixa
- Check the expiration date of the medication. If it has expired, do not use it.
- Check if the syringe is not damaged and the liquid inside is transparent. If not, use another syringe.
Do not use this medication if you notice any change in its appearance.
- Check the amount to be injected.
- Review if the last injection caused redness, skin color change, swelling, suppuration, or if it still hurts. If so, talk to your doctor or nurse.
- Decide on the area where you will inject the medication. Alternate, each time you inject, the right side of the abdomen (belly) with the left. This medication should be injected just under the skin of the abdomen, but not too close to the navel or any scar (at least 5 cm away from them).
- The pre-filled syringe is for single use.
Instructions for self-injecting Inhixa
- Wash your hands and the injection area with water and soap. Dry them.
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable and relaxed position. Make sure you can see the area where you will inject. The most suitable is on a couch, a reclining armchair, or in a bed with pillows for support.
- Choose an area on the right or left side of the belly. It should be more than 5 cm away from the navel and towards the sides.
Remember.Do not inject in the 5 cm around the navel or scars or hematomas that you may have. Inject in the opposite area to the one you injected the last time (alternating the right side of the belly with the left).
- Take the plastic blister pack containing the pre-filled syringe out of the box. Open the blister pack and remove the pre-filled syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe by pulling it. The syringe is pre-filled and ready for use.

Do notpress the plunger before injecting. Once you have removed the cap, do not touch anything with the needle. This way, you will ensure that the needle remains clean (sterile).
- Hold the syringe with the hand you write with (like a pencil) and, with the other hand, gently pinch the area of the abdomen between the index finger and thumb to form a skin fold.
Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Hold the syringe so that the needle points downwards (vertically at a 90-degree angle). Insert the entire needle into the skin fold.
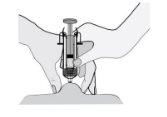
- Press the plunger with your thumb. This way, you will inject the medication into the abdominal fatty tissue. Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Remove the needle by pulling it straight out. Do not stop pressing the plunger!
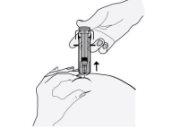
To avoid a hematoma, do not rub the injection area after injecting.
- Release the plunger and allow the syringe to move upwards until the entire needle is stored and locked in its place.

- Dispose of the used syringe in the sharps container. Close the container lid tightly and keep it out of the reach of children.
When the container is full, dispose of it as your doctor or pharmacist has indicated. Do not throw it in the trash.
Self-administration of an Inhixa injection with a pre-filled syringe with a manually activated needle protector
Your pre-filled syringe includes a manually activated needle protector to protect you from a needle stick injury.
If you can administer this medication to yourself, your doctor or nurse will show you how to do it. Do not attempt to inject yourself if you have not been taught how to do it. If you do not know what to do, consult your doctor or nurse immediately.
Before injecting Inhixa
- Check the expiration date of the medication. If it has expired, do not use it. Check if the syringe is not damaged and the liquid inside is transparent. If not, use another syringe.
- Do not use this medication if you notice any change in its appearance.
- Check the amount to be injected.
- Review if the last injection caused redness, skin color change, swelling, suppuration, or if it still hurts. If so, talk to your doctor or nurse.
- Decide on the area where you will inject the medication. Alternate, each time you inject, the right side of the abdomen (belly) with the left. This medication should be injected just under the skin of the abdomen, but not too close to the navel or any scar (at least 5 cm away from them).
- The pre-filled syringe is for single use.
Instructions for self-injecting Inhixa
- Wash your hands and the injection area with water and soap. Dry them.
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable and relaxed position. Make sure you can see the area where you will inject. The most suitable is on a couch, a reclining armchair, or in a bed with pillows for support.
- Choose an area on the right or left side of the belly. It should be more than 5 cm away from the navel and towards the sides. Remember. Do not inject in the 5 cm around the navel or scars or hematomas that you may have.
Inject in the opposite area to the one you injected the last time (alternating the right side of the belly with the left).
- Take the plastic blister pack containing the pre-filled syringe out of the box. Open the blister pack and remove the pre-filled syringe.
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe by pulling it. The syringe is pre-filled and ready for use.

Do notpress the plunger before injecting. Once you have removed the cap, do not touch anything with the needle. This way, you will ensure that the needle remains clean (sterile).
- Hold the syringe with the hand you write with (like a pencil) and, with the other hand, gently pinch the area of the abdomen between the index finger and thumb to form a skin fold.
Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Hold the syringe so that the needle points downwards (vertically at a 90-degree angle). Insert the entire needle into the skin fold.

- Press the plunger with your thumb. This way, you will inject the medication into the abdominal fatty tissue. Make sure to hold the skin fold during the entire injection.
- Remove the needle by pulling it straight out.

To avoid a hematoma, do not rub the injection area after injecting.
- Dispose of the used syringe in the sharps container. Close the container lid tightly and keep it out of the reach of children.
When the container is full, dispose of it as your doctor or pharmacist has indicated. Do not throw it in the trash.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone experiences them.
Like other anticoagulant medications (medications that reduce blood clots), Inhixa may cause bleeding, which could potentially put your life at risk. In some cases, the bleeding may not be apparent.
If you experience any episode of bleeding that does not stop on its own or if you notice signs of excessive bleeding (unusual weakness, fatigue, paleness, dizziness, headache, or unexplained swelling), consult your doctor immediately.
Your doctor may decide to keep you under close observation or change your medication.
Stop treatment with Inhixa and inform your doctor or nurse immediately if you experience any signs of a severe allergic reaction (such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the lips, mouth, throat, or eyes).
Stop treatment with Inhixa and inform your doctor or nurse immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- A widespread, red, scaly rash with bumps and blisters, accompanied by fever. These symptoms usually appear at the start of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis).
You must inform your doctor immediately
- If you experience any signs of a blood vessel blockage due to a blood clot, such as:
- cramping pain, redness, heat, or swelling in one of your legs – which are symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
- difficulty breathing, chest pain, fainting, or coughing up blood – which are symptoms of pulmonary embolism
- If you have a painful skin rash with dark red spots under the skin that do not disappear when pressed.
Your doctor may request a blood test to check your platelet count.
General list of possible side effects:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Bleeding.
- Increased liver enzymes.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- If bruises appear more frequently than usual. This could be due to a blood problem caused by a low platelet count.
- Pink patches on the skin. These appear more frequently in the area where you have been injected with Inhixa.
- Skin rash (hives, urticaria).
- Redness and itching of the skin.
- Bruising or pain at the injection site.
- Decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood.
- Increase in the number of platelets in the blood.
- Headache.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Sudden severe headache. This could be a sign of bleeding in the brain.
- Feeling of tenderness and swelling of the stomach. This could be indicative of gastric bleeding.
- Large, irregular red marks on the skin, with or without blisters.
- Skin irritation (local irritation).
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes, and darkening of urine color. These could be signs of a liver problem.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Severe allergic reaction. The signs of this reaction may include: skin rash, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of the lips, face, throat, or tongue.
- Increased potassium levels in the blood. This is more likely to occur in people with kidney problems or diabetes. Your doctor can check this with a blood test.
- Increased number of white blood cells called eosinophils in the blood. Your doctor can check this with a blood test.
- Hair loss.
- Osteoporosis (a disease in which bones can fracture more easily).
- Numbness, tingling, and weakness in the muscles (especially in the lower part of the body) when a lumbar puncture or spinal anesthesia has been performed.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (so that you cannot control your needs).
- Hardening or nodule at the injection site.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Inhixa
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date stated on the label and carton. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store below 25°C. Do not freeze.
The solution must be used within 8 hours of dilution.
Do not use this medication if you notice any visible change in the appearance of the solution.
The pre-filled syringes of Inhixa are for single use only. Discard any unused medication.
Medications should not be disposed of in wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medication. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Inhixa Composition
- The active ingredient is sodium enoxaparin.
Each milliliter contains 10,000 IU (100 mg) of sodium enoxaparin.
Each 0.2 ml pre-filled syringe contains 2,000 IU (20 mg) of sodium enoxaparin.
Each 0.4 ml pre-filled syringe contains 4,000 IU (40 mg) of sodium enoxaparin.
Each 0.6 ml pre-filled syringe contains 6,000 IU (60 mg) of sodium enoxaparin.
Each 0.8 ml pre-filled syringe contains 8,000 IU (80 mg) of sodium enoxaparin.
Each 1 ml pre-filled syringe contains 10,000 IU (100 mg) of sodium enoxaparin.
- The other components are water for injectable preparations.
Product Appearance and Container Content
Inhixa 2,000 IU (20 mg)/0.2 ml is 0.2 ml of solution contained in:
- a transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a purple polypropylene plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional needle shield or a manual needle shield; or
- a transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a white polycarbonate plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional UltraSafe Passive needle shield.
This medicinal product is presented in packs of:
- 1, 2, 6, 10, 20, and 50 pre-filled syringes
- 2, 6, 10, 20, 50, and 90 pre-filled syringes with needle shield
- 6, 10, and 20 pre-filled syringes with manual needle shield
- 2 and 6 pre-filled syringes with UltraSafe Passive needle shield
Inhixa 4,000 IU (40 mg)/0.4 ml injectable solution is 0.4 ml of solution contained in:
- a transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a yellow polypropylene plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional needle shield or a manual needle shield; or
- a transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a white polycarbonate plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional UltraSafe Passive needle shield.
This medicinal product is presented in packs of:
- 2, 5, 6, 10, 20, 30, and 50 pre-filled syringes
- 2, 5, 6, 10, 20, 30, 50, and 90 pre-filled syringes with needle shield
- 2, 6, 10, 20, and 50 pre-filled syringes with manual needle shield
- 2 and 6 pre-filled syringes with UltraSafe Passive needle shield
Inhixa 6,000 IU (60 mg)/0.6 ml injectable solution is 0.6 ml of solution contained in:
- a graduated, transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and an orange polypropylene plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional needle shield or a manual needle shield; or
- a graduated, transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a white polycarbonate plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional UltraSafe Passive needle shield.
This medicinal product is presented in packs of:
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, and 50 pre-filled syringes
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, and 50 pre-filled syringes with needle shield
- 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, and 50 pre-filled syringes with manual needle shield
- 2 and 10 pre-filled syringes with UltraSafe Passive needle shield
Inhixa 8,000 IU (80 mg)/0.8 ml injectable solution is 0.8 ml of solution contained in:
- a graduated, transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a red polypropylene plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional needle shield or a manual needle shield; or
- a graduated, transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a white polycarbonate plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional UltraSafe Passive needle shield.
This medicinal product is presented in packs of:
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, and 50 pre-filled syringes
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, and 50 pre-filled syringes with needle shield
- 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, and 50 pre-filled syringes with manual needle shield
- 2 and 10 pre-filled syringes with UltraSafe Passive needle shield
Inhixa 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml injectable solution is 1 ml of solution contained in:
- a graduated, transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a black polypropylene plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional needle shield or a manual needle shield; or
- a graduated, transparent, colorless, neutral glass syringe of type I, with a fixed needle and needle shield closed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and a white polycarbonate plunger. The syringe can be equipped with an additional UltraSafe Passive needle shield.
This medicinal product is presented in packs of:
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, 50, and 90 pre-filled syringes
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, and 50 pre-filled syringes with needle shield
- 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, and 50 pre-filled syringes with manual needle shield
- 2 and 10 pre-filled syringes with UltraSafe Passive needle shield
Only some pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V.
Strawinskylaan 1143, Toren C-11
1077XX Amsterdam
Netherlands
Manufacturer
SciencePharma spólka z ograniczona odpowiedzialnoscia
Chelmska 30/34
00-725 Warsaw
Poland
For further information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Belgium Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +31 (0)76 531 5388 | Lithuania Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +37125892152 |
| Luxembourg Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 |
Czech Republic Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +420255790502 | Hungary Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +3618001930 |
Denmark Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +4578774377 | Malta Mint Health Ltd +441483928995 |
Germany Co-marketing: Techdow Pharma Germany GmbH Potsdamer Platz 1, 10785 Berlin +49 (0)30 98 321 31 00 | Netherlands Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +31208081112 |
Estonia Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +37125892152 | Norway Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +4721569855 |
Greece Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 | Austria Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +43720230772 |
Spain TECHDOW PHARMA SPAIN, S.L. Tel: +34 91 123 21 16 | Poland Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 |
France Viatris Santé +33 4 37 25 75 00 | Portugal Laboratórios Atral, S.A. +351308801067 |
Croatia Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +385 17776255 Ireland Techdow Pharma England Ltd +441483928995 | Romania Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 Slovenia Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 |
Iceland Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 | Slovakia Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +421233331071 |
Italy Techdow Pharma Italy S.R.L. Tel: +39 0256569157 | Finland Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +358942733040 |
Cyprus MA Pharmaceuticals Trading Ltd +357 25 587112 | Sweden Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +46184445720 |
Latvia Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +37125892152 | United Kingdom(Northern Ireland) Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V + 44 28 9279 2030 |
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price54.34 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to INIXA 6,000 IU (60 mg)/0.6 mL Injectable SolutionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 mg (10000 IU) enoxaparin sodium/mlActive substance: enoxaparinManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 120 mg (12000 IU) /0.8 mlActive substance: enoxaparinManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 150 mg (15000 IU) /1 mlActive substance: enoxaparinManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for INIXA 6,000 IU (60 mg)/0.6 mL Injectable Solution
Discuss questions about INIXA 6,000 IU (60 mg)/0.6 mL Injectable Solution, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
















