
CLEXANE 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION


How to use CLEXANE 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
- Introduction
- What is Clexane and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Clexane
- Do not use Clexane if you are affected by any of these conditions. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using Clexane.
- If you are going to have a lumbar or spinal puncture, or are going to have surgery where spinal or epidural anesthesia will be used, tell your doctor that you are using Clexane.
- How to use Clexane
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Clexane
- Package contents and additional information
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
CLEXANE 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe
enoxaparin sodium
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet
- What is Clexane and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Clexane
- How to use Clexane
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Clexane
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Clexane and what is it used for
Clexane contains the active substance enoxaparin sodium. It belongs to a group of medicines called “low molecular weight heparin” or LMWH.
How Clexane works
Clexane works in two ways:
- Preventing existing blood clots from getting bigger. This helps your body to break them down and stop them from causing harm.
- Stopping new blood clots from forming.
What Clexane is used for
Clexane can be used to:
- Treat blood clots
- Prevent blood clots from forming in the following situations:
- before and after surgery
- when you have a short-term illness and are unable to move for a period of time
- if you have had a blood clot due to cancer, to prevent more clots from forming.
- Prevent blood clots from forming when you have unstable angina (a condition where not enough blood reaches the heart) or after a heart attack
- Prevent blood clots from forming in the tubes of a dialysis machine (used in people with severe kidney problems).
2. What you need to know before you use Clexane
Do not use Clexaneif:
- you are allergic to:
- enoxaparin sodium or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- heparin or other low molecular weight heparins such as nadroparin, tinzaparin, or dalteparin.
The signs of an allergic reaction include: rash, problems breathing or swallowing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, mouth, throat, or eyes.
- you have had a reaction to heparin that caused a severe decrease in the number of cells involved in blood clotting (platelets) in the last 100 days
- you have antibodies against enoxaparin in your blood
- you are bleeding heavily or have a high risk of bleeding, such as:
- stomach ulcer, recent brain or eye surgery, or cerebral hemorrhage.
- you are using Clexane to treat blood clots, and you are going to have:
- a lumbar or spinal puncture
- surgery with spinal or epidural anesthesia.
Do not use Clexane if you are affected by any of these conditions. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using Clexane.
Warnings and precautions
Clexane should not be exchanged with other “low molecular weight heparins” such as nadroparin, tinzaparin, or dalteparin. This is because they are not exactly the same and do not have the same activity or instructions for use.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you start using Clexane if:
- you have ever had a reaction to heparin that caused a severe decrease in the number of cells involved in blood clotting (platelets)
- you have had a heart valve implanted
- you have endocarditis (an infection of the inner lining of the heart)
- you have a history of stomach ulcers
- you have recently had a cerebral hemorrhage
- you have high blood pressure
- you have diabetes or problems with the blood vessels in your eyes caused by diabetes (called diabetic retinopathy)
- you have recently had eye or brain surgery
- you are an elderly person (over 65 years old) and especially if you are over 75 years old
- you have kidney problems
- you have liver problems
- you are underweight or overweight
- you have high levels of potassium in your blood (which could be checked with a blood test)
- you are currently using medicines that affect bleeding (see section 2, “Using Clexane with other medicines”)
- you have any problems with your spine or have had spinal surgery.
If you are affected by any of these conditions (or are not sure), talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using Clexane.
For patients who receive doses higher than 210 mg/day, this medicine contains more than 24 mg of sodium (the main component of table/cooking salt) in each dose. This is equivalent to 1.2% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
Tests and checks
You may need to have a blood test before you start using this medicine, and while you are using it; this is to check the level of cells involved in blood clotting (platelets) and the levels of potassium in your blood.
Children and adolescents
The efficacy and safety of Clexane in children and adolescents have not been established.
Using Clexane with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
- warfarin - used to reduce blood clotting
- aspirin (also known as acetylsalicylic acid or ASA), clopidogrel, or other medicines used to prevent blood clots from forming (see section 3, “Changing anticoagulant medicine”)
- dextran injection - used as a blood substitute
- ibuprofen, diclofenac, ketorolac, and other medicines known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) used to treat pain and inflammation in arthritis and other diseases
- prednisolone, dexamethasone, and other medicines used to treat asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and other diseases
- medicines that increase potassium levels in the blood, such as potassium salts, diuretics, and some medicines used to treat heart problems.
Surgery and anesthesia
If you are going to have a lumbar or spinal puncture, or are going to have surgery where spinal or epidural anesthesia will be used, tell your doctor that you are using Clexane.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
If you are pregnant and have a mechanical heart valve, you may be at higher risk of blood clots forming. Your doctor will discuss this with you.
If you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed, you should consult your doctor before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Clexane does not affect your ability to drive or use machines.
It is recommended that your healthcare professional records the trade name and batch number of the product you are using.
3. How to use Clexane
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medication as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Using the medication
- Normally, your doctor or nurse will administer Clexane to you. This is because it must be administered by injection.
- Clexane is usually administered by injection under the skin (subcutaneously).
- Clexane can be administered by injection into your veins (intravenously) after certain types of heart attacks or surgical operations.
- Clexane can be added to the tube that comes out of your body (arterial line) at the beginning of a dialysis session.
- Do not administer Clexane into a muscle (intramuscularly).
How much will be administered to you
- Your doctor will decide the amount of Clexane to be administered to you. The amount will depend on the reason for its use.
- If you have kidney problems, you may be administered a smaller amount of Clexane.
- Treatment of blood clot formation
- The usual dose is 150 IU (1.5 mg) per kilogram of body weight once a day or 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight twice a day.
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Clexane.
- Prevention of blood clot formation during surgical operations or periods of limited mobility due to illness
- The dose will depend on the likelihood of you developing a clot. You will be administered 2,000 IU (20 mg) or 4,000 IU (40 mg) of Clexane per day.
- If you are going to have surgery, you will usually be given the first injection 2 or 12 hours before the operation.
- If you have reduced mobility due to illness, you will usually be administered 4,000 IU (40 mg) of Clexane per day.
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Clexane.
- Prevention of blood clot formation when you have unstable angina or after having a heart attack
- Clexane can be used in 2 different types of heart attacks.
- The amount of Clexane administered to you will depend on your age and the type of heart attack you had.
Heart attack type IAMSEST (myocardial infarction without ST segment elevation):
- The usual dose is 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight every 12 hours.
- Usually, your doctor will tell you to also take aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid).
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Clexane.
Heart attack type IAMCEST (myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation) if you are under 75 years old:
- You will be administered an initial intravenous injection of 3,000 IU (30 mg) of Clexane.
- At the same time, you will be administered a subcutaneous injection of Clexane. The usual dose is 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight, every 12 hours.
- Usually, your doctor will tell you to also take aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid).
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Clexane.
Heart attack type IAMCEST if you are 75 years old or older:
- The usual dose is 75 IU (0.75 mg) per kilogram of body weight, every 12 hours.
- The maximum amount of Clexane administered in the first two injections is 7,500 IU (75 mg).
- Your doctor will decide how long you will receive Clexane.
For patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI):
- Depending on when you last received a Clexane injection, your doctor may decide to administer an additional dose of Clexane before a PCI intervention. This would be by intravenous injection.
- Prevention of blood clot formation in the tubes of the dialysis equipment
- The usual dose is 100 IU (1 mg) per kilogram of body weight.
- Clexane is added to the tube that comes out of your body (arterial line) at the beginning of a dialysis session. This amount is usually sufficient for a 4-hour session. However, your doctor may perform a new injection of 50 IU to 100 IU (0.5 to 1 mg) per kilogram of body weight if necessary.
If you are going to inject Clexane yourself
If you can administer Clexane to yourself, your doctor or nurse will show you how to do it. Do not attempt to inject yourself if you have not been taught how to do it. If you are unsure what to do, consult your doctor or nurse immediately. If the injection is performed correctly under the skin (subcutaneously), this will help reduce pain and bruising at the injection site.
Before injecting Clexane yourself
- Prepare what you will need: syringe, cotton swab with alcohol or soap and water, and container for sharp objects
- Check the expiration date of the medication. If it has expired, do not use it
- Check that the syringe is not damaged and that the medication solution is clear. If it is not, use another syringe
- Make sure you know the amount to be injected
- Check the area of your stomach where the last injection was given for redness, skin color change, swelling, suppuration, or pain that still persists. If this occurs, consult your doctor or nurse
Instructions for injecting Clexane yourself:
(Instructions for syringes without safety device)
Preparing the injection site
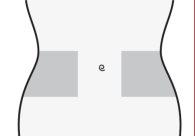
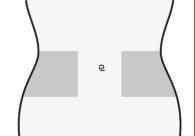
- Choose an area on the right or left side of your stomach. At least 5 cm from the navel and towards either side.
- Do not inject within 5 cm of the navel or around it if there are scars or bruises.
- To inject, alternate the left and right sides of your stomach, depending on where the last injection was given.
- Wash your hands. Clean (do not rub) the area where you will perform the injection with a cotton swab with alcohol or with soap and water.
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable position so that you are relaxed. Check that you can see the area where you will inject. The most suitable position is on a couch, reclining chair, or in a bed with pillows.
Selecting the dose
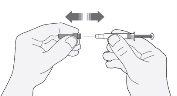
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe by pulling it. Discard the cap.
- Before injecting, do not press the plunger to eliminate air bubbles. This can cause a loss of medication.
- Once you have removed the cap, do not touch anything with the needle. This will ensure that the needle remains clean (sterile).
- When the amount of medication in the syringe matches the prescribed dose, there is no need to adjust the dose. You are now ready to administer the injection.
- When the dose depends on your body weight, you may need to adjust the dose in the syringe to match the prescribed dose. In this case, you can get rid of the excess medication by keeping the syringe pointing downwards (to keep the air bubble in the syringe) and expelling the excess into a container.
- A drop may appear at the tip of the needle. If this happens, you must eliminate the drop before administering the injection by gently tapping the syringe with the needle pointing downwards. You are now ready to administer the injection.
Administering the injection
- Hold the syringe with the hand you write with (as if it were a pencil). With the other hand, gently pinch the area you cleaned on your stomach, between your index finger and thumb to form a fold in the skin.
- Make sure to hold this skin fold while the injection lasts.
- Hold the syringe so that the needle points straight down (vertically at a 90-degree angle). Insert the entire needle into the skin fold.
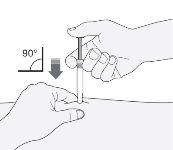
- Press the plunger with your thumb. This will administer the medication into the fatty tissue of your stomach. Complete the injection using all the medication in the syringe.
- Remove the needle from the injection site by pulling it straight out. Now you can release the skin fold.
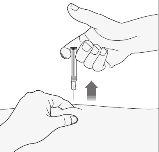
When you have finished
- To avoid bruising, do not rub the injection site after it has been injected.
- Deposit the used syringe in the container for sharp objects. Close the container lid well and place the container out of the reach of children. When the container is full, dispose of it as your doctor or pharmacist has indicated.
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Instructions for syringes with automatic safety device type ERIS TM:
Preparing the injection site
- Choose an area on the right or left side of your stomach. At least 5 cm from the navel and towards either side.
- Do not inject within 5 cm of the navel or around it if there are scars or bruises.
- To inject, alternate the left and right sides of your stomach, depending on where the last injection was given.
- Wash your hands. Clean (do not rub) the area where you will perform the injection with a cotton swab with alcohol or with soap and water.
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable position so that you are relaxed. Check that you can see the area where you will inject. The most suitable position is on a couch, reclining chair, or in a bed with pillows.
Selecting the dose
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe by pulling it. Discard the cap.
- Before injecting, do not press the plunger to eliminate air bubbles. This can cause a loss of medication.
- Once you have removed the cap, do not touch anything with the needle. This will ensure that the needle remains clean (sterile).
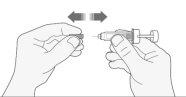
- When the amount of medication in the syringe matches the prescribed dose, there is no need to adjust the dose. You are now ready to administer the injection.
- When the dose depends on your body weight, you may need to adjust the dose in the syringe to match the prescribed dose. In this case, you can get rid of the excess medication by keeping the syringe pointing downwards (to keep the air bubble in the syringe) and expelling the excess into a container.
- A drop may appear at the tip of the needle. If this happens, you must eliminate the drop before administering the injection by gently tapping the syringe with the needle pointing downwards. You are now ready to administer the injection.
Administering the injection
- Hold the syringe with the hand you write with (as if it were a pencil). With the other hand, gently pinch the area you cleaned on your stomach, between your index finger and thumb to form a fold in the skin.
- Make sure to hold this skin fold while the injection lasts.
- Hold the syringe so that the needle points straight down (vertically at a 90-degree angle). Insert the entire needle into the skin fold.
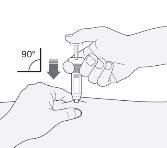
- Press the plunger with your thumb. This will administer the medication into the fatty tissue of your stomach. Complete the injection using all the medication in the syringe.
- Remove the needle from the injection site by pulling it straight out. A protective sheath will automatically cover the needle. Now you can release the skin fold. The safety device will only release the protective sheath when the syringe is empty by pressing the plunger deeply.
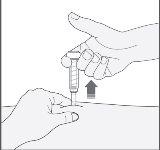
When you have finished
- To avoid bruising, do not rub the injection site after it has been injected.
- Deposit the used syringe in the container for sharp objects. Close the container lid well and place the container out of the reach of children. When the container is full, dispose of it as your doctor or pharmacist has indicated.
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Instructions for syringes with automatic safety device type PREVENTIS TM:
Preparing the injection site
- Choose an area on the right or left side of your stomach. At least 5 cm from the navel and towards either side.
- Do not inject within 5 cm of the navel or around it if there are scars or bruises.
- To inject, alternate the left and right sides of your stomach, depending on where the last injection was given.
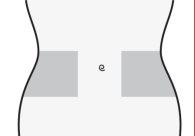
- Wash your hands. Clean (do not rub) the area where you will perform the injection with a cotton swab with alcohol or with soap and water.
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable position so that you are relaxed. Check that you can see the area where you will inject. The most suitable position is on a couch, reclining chair, or in a bed with pillows.
Selecting the dose
- Carefully remove the needle cap from the syringe by pulling it. Discard the cap.
- Before injecting, do not press the plunger to eliminate air bubbles. This can cause a loss of medication.
- Once you have removed the cap, do not touch anything with the needle. This will ensure that the needle remains clean (sterile).
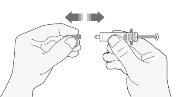
- When the amount of medication in the syringe matches the prescribed dose, there is no need to adjust the dose. You are now ready to administer the injection.
- When the dose depends on your body weight, you may need to adjust the dose in the syringe to match the prescribed dose. In this case, you can get rid of the excess medication by keeping the syringe pointing downwards (to keep the air bubble in the syringe) and expelling the excess into a container.
- A drop may appear at the tip of the needle. If this happens, you must eliminate the drop before administering the injection by gently tapping the syringe with the needle pointing downwards. You are now ready to administer the injection.
Administering the injection
- Hold the syringe with the hand you write with (as if it were a pencil). With the other hand, gently pinch the area you cleaned on your stomach, between your index finger and thumb to form a fold in the skin.
- Make sure to hold this skin fold while the injection lasts.
- Hold the syringe so that the needle points straight down (vertically at a 90-degree angle). Insert the entire needle into the skin fold.
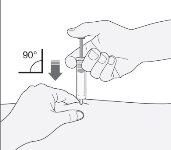
- Press the plunger with your thumb. This will administer the medication into the fatty tissue of your stomach. Complete the injection using all the medication in the syringe.
- Remove the needle from the injection site by pulling it straight out, keeping your finger on the plunger. Orient the needle away from yourself and others, and press the plunger firmly to activate the safety system. The protective sheath will automatically cover the needle. You will hear a "click" that confirms the activation of the safety system. Now you can release the skin fold.
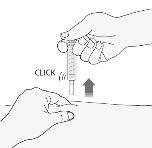
When you have finished
- To avoid bruising, do not rub the injection site after it has been injected.
- Deposit the used syringe in the container for sharp objects. Close the container lid well and place the container out of the reach of children. When the container is full, dispose of it as your doctor or pharmacist has indicated.
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Changing medication
- Changing from Clexane to anticoagulant medications called vitamin K antagonists (such as warfarin)
Your doctor will request that you have a blood test to determine a parameter called INR and will tell you when to stop treatment with Clexane.
- Changing from vitamin K antagonist medications (such as warfarin) to Clexane
Stop using the vitamin K antagonist. Your doctor will request that you have a blood test to determine a parameter called INR and will tell you when to start using Clexane.
- Changing from Clexane to treatment with direct oral anticoagulants
Stop using Clexane. Start taking the direct oral anticoagulant.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
Severe side effects
Stop treatment with Clexaneand inform your doctor or nurse immediatelyif you experience any signs of a severe allergic reaction (such as a rash, breathing or swallowing problems, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, mouth, throat, or eyes).
Stop treatment with enoxaparin and inform your doctor or nurse immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- a widespread, red, scaly rash with bumps and blisters, accompanied by fever. Symptoms usually appear at the start of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis).
Like other medications to reduce blood clots, Clexane may cause bleeding. This could put your life at risk. In some cases, the bleeding may not be apparent.
Inform your doctor immediately if:
- you have any bleeding that does not stop by itself
- you have signs of excessive bleeding (such as feeling very weak, tired, pale, or dizzy with a headache or unexplained swelling).
Your doctor may decide to keep you under close observation or change your medication.
You must inform your doctor immediately:
- if you present any signs of a blood vessel blockage due to a blood clot, such as:
- cramp-like pain, redness, heat, or swelling in one of your legs – which are symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
- difficulty breathing, chest pain, fainting, or coughing up blood – which are symptoms of pulmonary embolism
- if you have a painful skin rash with dark red spots under the skin that do not disappear when pressed.
Your doctor may request a blood test to check the platelet count.
Other side effects:
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- bleeding
- increased liver enzymes.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- if bruises appear more frequently than usual - this could be due to a blood problem caused by a low platelet count
- pink patches on the skin - appear more frequently in the area where Clexane was injected
- skin rash (hives, urticaria)
- redness and itching of the skin
- bruising or pain at the injection site
- decrease in the number of red blood cells
- increase in the number of platelets in the blood
- headache.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- sudden severe headache - this could be a sign of bleeding in the brain
- feeling of tenderness and swelling of the stomach - could be indicative of gastric bleeding
- large, irregular red lesions on the skin, with or without blisters
- skin irritation (local irritation)
- yellowing of the skin or eyes, and darkening of urine color - this could be due to a liver problem.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- severe allergic reaction - signs of this reaction may include: skin rash, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of the lips, face, throat, or tongue
- increased potassium in the blood - this is more likely to occur in people with kidney problems or diabetes. Your doctor can check this with a blood test
- increased number of eosinophils in the blood - your doctor can check this with a blood test
- hair loss
- osteoporosis (a disease in which bones can fracture more easily)
- tingling, numbness, and weakness in the muscles (especially in the lower body) when a lumbar puncture or spinal anesthesia has been performed
- loss of bladder or bowel control (so that you cannot control your needs)
- hardening or nodule at the injection site.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are possible side effects that do not appear in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Clexane
Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze.
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date stated on the packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not use this medication if you notice a crack in the syringe, particles in suspension in the solution, or an abnormal color of the solution (see "Appearance of the product and package contents").
Medications should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packaging and medications you no longer need at the SIGRE point in the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and additional information
Composition of Clexane
- The active ingredient is enoxaparin sodium
Each ml contains 100 mg of enoxaparin sodium, equivalent to 10,000 IU of anti-Xa activity
- Each pre-filled syringe with 1.0 ml contains 10,000 IU (100 mg) of enoxaparin sodium
- The other component is water for injectable preparations
Appearance of the product and package contents
Clexane is a clear, colorless to yellowish injectable solution in a pre-filled glass syringe (with or without an automatic safety device).
It is available in packs of 2, 5, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, 50, 100 pre-filled syringes, and in multi-packs of 3 x 10, 9 x 10, 100 x 10, and 200 x 10 pre-filled syringes.
Only some pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
sanofi-aventis, S.A.
C/ Roselló i Porcel, 21
08016 Barcelona
Spain
Manufacturer
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
Boulevard Industriel
76580 Le Trait,
France
Or
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
180 rue Jean Jaurès
94700 Maisons-Alfort
France
Or
Chinoin Pharmaceutical and Chemical Works Private Co. Ltd
Csanyikvölgy site
Miskolc, Csanyikvölgy
H-3510
Hungary
Or
Sanofi-Aventis GmbH
Turm A, 29. OG, Wienerbergstraße 11
1100 Vienna
Austria
Or
Sanofi-Aventis Private Co. Ltd
Budapest Logistics and Distribution Platform
Bdg. DC5, Campona utca 1.
Budapest, 1225
Hungary
Or
Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH
Industriepark Höchst-Brüningstraße 50
65926 Frankfurt am Main
Germany
This medication is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria, France, Portugal: Lovenox.
Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Luxembourg, Malta, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, United Kingdom: Clexane.
Italy: Clexane T.
Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden: Klexane.
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:February 2022
Other sources of information
Detailed information about this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price71.7 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to CLEXANE 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 120 mg (12000 IU) /0.8 mlActive substance: enoxaparinManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 150 mg (15000 IU) /1 mlActive substance: enoxaparinManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20 mg (2000 IU) sodium enoxaparin/0.2 mlActive substance: enoxaparinManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for CLEXANE 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
Discuss questions about CLEXANE 10,000 IU (100 mg)/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















