
IMNOVID 2 mg HARD CAPSULES

How to use IMNOVID 2 mg HARD CAPSULES
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Imnovid 1mg hard capsules
Imnovid 2mg hard capsules
Imnovid 3mg hard capsules
Imnovid 4mg hard capsules
pomalidomide
This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring, which will allow for quick identification of new safety information. You can help by reporting any side effects you may get. See the end of section 4 for how to report side effects.
Imnovid is expected to cause serious birth defects and can cause fetal death.
- Do not take this medicine if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant.
- You must follow the pregnancy prevention measures as described in this package leaflet.
Read all of this package leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this package leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet
- What is Imnovid and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you take Imnovid
- How to take Imnovid
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Imnovid
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Imnovid and what is it used for
What is Imnovid
Imnovid contains the active substance pomalidomide. This medicine is related to thalidomide and belongs to a group of medicines that affect the immune system (the body's natural defenses).
What Imnovid is used for
Imnovid is used to treat adults with a type of cancer called multiple myeloma.
Imnovid is used with:
- Two other medicinescalled bortezomib (a type of chemotherapy medicine) and dexamethasone (an anti-inflammatory medicine) in patients who have received at least one prior treatment, including lenalidomide.
U
- One other medicinecalled dexamethasone in patients who have had their multiple myeloma get worse, despite having received at least two prior treatments, including lenalidomide and bortezomib.
What is multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects a specific type of white blood cell (called plasma cells). These cells grow out of control and accumulate in the bone marrow, damaging bones and kidneys.
Multiple myeloma usually cannot be cured. However, treatment can reduce the signs and symptoms of the disease or make them disappear for a period of time. When this happens, it is called a response.
How Imnovid works
Imnovid works in several ways:
- stops the growth of myeloma cells;
- stimulates the immune system to attack cancer cells;
- stops the formation of blood vessels that feed cancer cells.
Benefit of using Imnovid with bortezomib and dexamethasone
If Imnovid is used with bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients who have received at least one prior treatment, it can delay the worsening of multiple myeloma:
- On average, the combination of Imnovid with bortezomib and dexamethasone delayed the return of multiple myeloma for up to 11 months, compared to 7 months in patients who took only bortezomib and dexamethasone.
Benefit of using Imnovid with dexamethasone
If Imnovid is used with dexamethasone in patients who have received at least two prior treatments, it can delay the worsening of multiple myeloma:
- On average, the combination of Imnovid and dexamethasone delayed the return of multiple myeloma for up to 4 months, compared to 2 months in patients who took only dexamethasone.
2. What you need to know before you take Imnovid
Do not take Imnovid:
- if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, as Imnovid is expected to be harmful to the fetus. (Men and women taking this medicine should read the section "Pregnancy, contraception, and breastfeeding – information for men and women" below);
- if you can become pregnant, unless you are using effective contraception (see "Pregnancy, contraception, and breastfeeding – information for men and women"). If you can become pregnant, your doctor will confirm that you have understood the measures to prevent pregnancy before each prescription;
- if you are allergic to pomalidomide or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). If you think you may be allergic, talk to your doctor.
If you are not sure if any of these situations apply to you, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before taking Imnovid.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting Imnovid if:
- you have ever had blood clots in the past. During treatment with Imnovid, you have a higher risk of developing blood clots in your veins or arteries. Your doctor may recommend additional treatments (e.g., warfarin) or reduce your dose of Imnovid to minimize the risk of blood clots;
- you have ever had an allergic reaction, such as a skin rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, or breathing problems while taking medicines related to thalidomide or lenalidomide;
- you have had a heart attack, have heart failure, have breathing difficulties, or, if you are a smoker, have high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels;
- you have a high tumor burden in your body, including bone marrow. This could lead to a condition where tumors break down and produce abnormal levels of chemicals in the blood, which can cause kidney failure. You may also experience irregular heartbeats. This condition is called tumor lysis syndrome;
- you have or have had nerve damage (neurological damage that causes tingling or pain in your feet or hands);
- you have or have had a hepatitis B virus infection. Treatment with Imnovid may reactivate the hepatitis B virus in patients who carry the virus, leading to the infection returning (recurrence). Your doctor should check if you have ever had a hepatitis B virus infection.
- you experience or have experienced a combination of any of the following symptoms: rash on face or generalized, skin redness, high fever, flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes (symptoms of a severe skin reaction called drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, or DRESS syndrome, or hypersensitivity syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis [TEN], or Stevens-Johnson syndrome [SJS]). See also section 4 "Possible side effects".
It is important to note that patients with multiple myeloma treated with pomalidomide may develop other types of cancer, so your doctor should carefully evaluate the benefits and risks when prescribing this medicine.
At any time during or after treatment, tell your doctor or nurse immediately if you:
experience blurred vision, loss of vision, or double vision, difficulty speaking, weakness in an arm or leg, a change in the way you walk, or balance problems, numbness, decreased sensitivity, or loss of sensitivity, memory loss, or confusion. These may be symptoms of a serious and potentially life-threatening brain disease called progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). If you had any of these symptoms before starting treatment with Imnovid, tell your doctor if you notice any change in these symptoms.
After finishing treatment, you must return all unused capsules to the pharmacist.
Pregnancy, contraception, and breastfeeding: information for men and women
You must follow the instructions in the Imnovid Pregnancy Prevention Programme.
Men and women taking Imnovid must not father a child or become pregnant. The reason is that pomalidomide is expected to be harmful to the fetus. You and your partner must use effective contraception while taking this medicine.
Women
Do not take Imnovid if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant. The reason is that this medicine is expected to be harmful to the fetus. Before starting treatment, you must tell your doctor if there is any chance you may become pregnant, even if you think it is unlikely.
If you can become pregnant:
- you must use effective contraception from at least 4 weeks before starting treatment, during treatment, and until at least 4 weeks after finishing treatment. Your doctor will advise you on the most suitable contraception methods;
- each time your doctor prescribes a prescription, they will ensure that you have understood the measures to prevent pregnancy;
- your doctor will schedule pregnancy tests before treatment, at least every 4 weeks during treatment, and at least 4 weeks after finishing treatment.
If, despite preventive measures, you become pregnant:
- you must stop treatment immediately and inform your doctor immediately.
Breastfeeding
It is not known if Imnovid passes into human breast milk. Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Your doctor will advise you whether you can continue breastfeeding or should stop.
Men
Imnovid passes into human semen.
- If your partner is pregnant or can become pregnant, you must use condoms during treatment and for 7 days after finishing treatment.
- If your partner becomes pregnant while you are taking Imnovid, tell your doctor immediately. Your partner should also tell their doctor immediately.
You must not donate sperm or semen during treatment and for 7 days after finishing treatment.
Blood donation and blood tests
You must not donate blood during treatment and for 7 days after finishing treatment.
Before starting treatment with Imnovid and during treatment, you will have regular blood tests. This is because your medicine may cause a decrease in the number of blood cells that help fight infections (white blood cells) and the number of cells that help stop bleeding (platelets).
Your doctor will ask you to have a blood test:
- before treatment;
- every week for the first 8 weeks of treatment;
- at least once a month while you are taking Imnovid.
Your doctor may adjust the dose of Imnovid or interrupt treatment, depending on the results of these tests. Your doctor may also adjust the dose or interrupt this medicine due to your overall health.
Children and adolescents
Imnovid is not recommended for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Other medicines and Imnovid
Tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. This is because Imnovid may affect the way other medicines work. Also, some medicines may affect the way Imnovid works.
In particular, tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before taking Imnovid if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- certain antifungals, such as ketoconazole
- certain antibiotics (e.g., ciprofloxacin, enoxacin)
- certain antidepressants, such as fluvoxamine.
Driving and using machines
Some people experience fatigue, fainting, confusion, or decreased alertness while taking Imnovid. If this happens to you, do not drive or use tools or machinery.
Imnovid contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per capsule; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to take Imnovid
Imnovid should be administered by a doctor with experience in the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Follow the administration instructions for the medication indicated by your doctor exactly. In case of doubt, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
When to take Imnovid with other medications
Imnovid in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone
- Consult the package insert that comes with bortezomib and dexamethasone for additional information on their use and effects.
- Imnovid, bortezomib, and dexamethasone are taken in treatment cycles. Each cycle lasts 21 days (3 weeks).
- Observe the following chart to see what you should take each day of the 3-week cycle:
- Each day, observe the chart and identify the correct day to see which medications you should take.
- Some days you will take all 3 medications, other days only 1 or 2 medications, and other days none of them.
IMN:Imnovid; BOR: bortezomib; DEX: dexamethasone
Cycle1 to 8 | Cycle9 and onwards | ||||||||
Medication Name | Medication Name | ||||||||
Day | IMN | BOR | DEX | Day | IMN | BOR | DEX | ||
1 | √ | √ | √ | 1 | √ | √ | √ | ||
2 | √ | √ | 2 | √ | √ | ||||
3 | √ | 3 | √ | ||||||
4 | √ | √ | √ | 4 | √ | ||||
5 | √ | √ | 5 | √ | |||||
6 | √ | 6 | √ | ||||||
7 | √ | 7 | √ | ||||||
8 | √ | √ | √ | 8 | √ | √ | √ | ||
9 | √ | √ | 9 | √ | √ | ||||
10 | √ | 10 | √ | ||||||
11 | √ | √ | √ | 11 | √ | ||||
12 | √ | √ | 12 | √ | |||||
13 | √ | 13 | √ | ||||||
14 | √ | 14 | √ | ||||||
15 | 15 | ||||||||
16 | 16 | ||||||||
17 | 17 | ||||||||
18 | 18 | ||||||||
19 | 19 | ||||||||
20 | 20 | ||||||||
21 | 21 |
- After completing each 3-week cycle, start a new one.
Imnovid alone with dexamethasone
- Consult the package insert that comes with dexamethasone for additional information on its use and effects.
- Imnovid and dexamethasone are taken in treatment cycles. Each cycle lasts 28 days (4 weeks).
- Observe the following chart to see what you should take each day of the 4-week cycle:
- Each day, observe the chart and identify the correct day to see which medications you should take.
- Some days you will take both medications, other days only 1 medication, and other days none of them.
IMN:Imnovid; DEX: dexamethasone
Medication Name | ||
Day | IMN | DEX |
1 | √ | √ |
2 | √ | |
3 | √ | |
4 | √ | |
5 | √ | |
6 | √ | |
7 | √ | |
8 | √ | √ |
9 | √ | |
10 | √ | |
11 | √ | |
12 | √ | |
13 | √ | |
14 | √ | |
15 | √ | √ |
16 | √ | |
17 | √ | |
18 | √ | |
19 | √ | |
20 | √ | |
21 | √ | |
22 | √ | |
23 | ||
24 | ||
25 | ||
26 | ||
27 | ||
28 |
- After completing each 4-week cycle, start a new one.
How much Imnovid to take with other medications
Imnovid with bortezomib and dexamethasone
- The recommended initial dose of Imnovid is 4 mg per day.
- The recommended initial dose of bortezomib will be calculated by your doctor based on your height and weight (1.3 mg/m2 of body surface area).
- The recommended initial dose of dexamethasone is 20 mg per day. However, if you are over 75 years of age, the recommended initial dose is 10 mg per day.
Imnovid alone with dexamethasone
- The recommended dose of Imnovid is 4 mg once a day.
- The recommended initial dose of dexamethasone is 40 mg per day. However, if you are over 75 years of age, the recommended initial dose is 20 mg per day.
Your doctor may need to reduce the dose of Imnovid, bortezomib, or dexamethasone, or interrupt one or more of these medications based on the results of your blood tests and your overall condition, if you are taking other medications (e.g., ciprofloxacin, enoxacin, and fluvoxamine), and if you experience adverse effects (especially skin rash or swelling) as a result of treatment.
If you have liver or kidney problems, your doctor will closely monitor your condition while you are taking this medication.
How to take Imnovid
- Do not break, open, or chew the capsules. If the powder from a broken capsule comes into contact with your skin, wash the skin immediately and thoroughly with water and soap.
- Healthcare professionals, caregivers, and family members should wear disposable gloves when handling the blister or capsule. Afterwards, they should carefully remove the gloves to avoid skin exposure, place them in a sealable polyethylene plastic bag, and dispose of them according to local requirements. Then, they should wash their hands well with water and soap. Pregnant women or those who suspect they may be pregnant should not handle the blister or capsule.
- Swallow the capsules whole, preferably with water.
- You can take the capsules with or without food.
- You should take the capsules at approximately the same time each day.
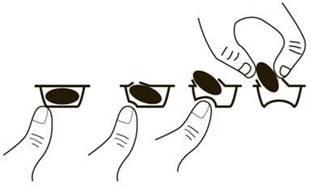
To remove the capsule from the blister, press only one end of the capsule so that it comes out through the foil. Do not press in the center of the capsule as it may break.
Your doctor will advise you on how and when to take Imnovid if you have kidney problems and are undergoing dialysis treatment.
Duration of treatment with Imnovid
You should continue the treatment cycles until your doctor tells you to stop the treatment.
If you take more Imnovid than you should
If you take more Imnovid than you should, inform your doctor or go to the hospital immediately. Bring the medication package with you.
If you forget to take Imnovid
If you forget to take Imnovid on the day you should, take the next capsule the next day at the usual time. Do not take more capsules to make up for the missed dose of Imnovid the previous day.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
Severe side effects
If you experience any of the following severe side effects, stop treatment with Imnovid and go to a doctor immediately, as you may need urgent medical treatment:
- Fever, chills, sore throat, cough, mouth ulcers, or any other sign of infection (due to a decrease in white blood cells that fight infection).
- Bleeding or bruising without apparent cause, including nosebleeds and intestinal or stomach bleeding (due to effects on blood cells called "platelets").
- Rapid breathing, rapid heartbeat, fever, and chills, decreased ability to urinate, nausea, and vomiting, confusion, loss of consciousness (due to a blood infection called sepsis or septic shock).
- Severe, persistent, or bloody diarrhea (possibly accompanied by stomach pain or fever) caused by the bacteria Clostridium difficile.
- Chest pain or leg swelling, especially in the lower leg or calf (caused by blood clots).
- Difficulty breathing (due to a severe chest infection, pneumonia, heart failure, or blood clots).
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, which can cause difficulty breathing (due to severe allergic reactions called angioedema and anaphylactic reaction).
- Certain types of skin cancer (squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma), which can cause changes in the appearance of the skin or lumps on the skin. If you notice changes in the appearance of your skin while taking Imnovid, inform your doctor as soon as possible.
- Recurrence of hepatitis B virus infection, which can cause yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, abdominal pain on the right side, fever, nausea, or discomfort. Inform your doctor immediately if you notice any of these symptoms.
- Widespread rash, high body temperature, swollen lymph nodes, and effects on other organs of the body (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, also known as DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, or Stevens-Johnson syndrome). Stop taking pomalidomide if you experience these symptoms and contact your doctor or go to the doctor immediately. See also section 2.
If you experience any of the following severe side effects, stop treatment with Imnovid and go to a doctor immediately, as you may need urgent medical treatment.
Other side effects
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea).
- Lung infection (pneumonia and bronchitis).
- Infections in the nose, sinuses, and throat caused by bacteria or viruses.
- Flu-like symptoms (flu).
- Low red blood cell count, which can cause anemia that leads to fatigue and weakness.
- Low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia), which can cause weakness, muscle cramps, and muscle pain, palpitations, tingling or numbness, shortness of breath, and mood changes.
- High blood sugar levels.
- Fast and irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation).
- Lack of appetite.
- Constipation, diarrhea, or nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Abdominal pain.
- Lack of energy.
- Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Dizziness, tremors.
- Muscle spasms, muscle weakness.
- Bone pain, back pain.
- Numbness, tingling, or prickling sensation in the skin, pain in hands or feet (peripheral sensory neuropathy).
- Generalized swelling, including swelling of arms and legs.
- Skin rashes.
- Urinary tract infection, which can cause a burning sensation when urinating or the need to urinate more frequently.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Falls.
- Bleeding in the brain.
- Decreased ability to move or feel (sensitivity) in hands, feet, and legs due to nerve damage (peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy).
- Numbness, tingling, or prickling sensation in the skin (paresthesia).
- Feeling of dizziness, which can make it difficult to stand and move normally.
- Swelling caused by fluid retention.
- Hives (urticaria).
- Itching of the skin.
- Herpes zoster.
- Heart attack (chest pain that spreads to the arms, neck, and jaw, feeling of sweating and difficulty breathing, feeling of nausea or vomiting).
- Chest pain, chest infection.
- Increased blood pressure.
- A decrease in the number of red and white blood cells and platelets at the same time (pancytopenia), which can make you more prone to bleeding and bruising. You may feel tired and weak, as well as have difficulty breathing. You will also be more susceptible to infections.
- A decrease in the number of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) often caused by an infection (lymphopenia).
- Low magnesium levels in the blood (hypomagnesemia), which can cause fatigue, weakness, muscle cramps, and irritability, and can also cause low calcium levels in the blood (hypocalcemia), leading to numbness or tingling in hands, feet, or lips, muscle cramps, muscle weakness, dizziness, and confusion.
- Low phosphate levels in the blood (hypophosphatemia), which can cause muscle weakness, irritability, or confusion.
- High calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia), which can slow down reflexes and cause weakness of the skeletal muscles.
- High potassium levels in the blood, which can cause an abnormal heart rhythm.
- Low sodium levels in the blood, which can cause fatigue and confusion, muscle contractions, seizures (epileptic convulsions), or coma.
- High uric acid levels in the blood, which can cause a type of arthritis called gout.
- Low blood pressure, which can cause dizziness or fainting.
- Pain or dryness in the mouth.
- Changes in taste.
- Swollen abdomen.
- Confusion.
- Feeling depressed (depressive mood).
- Loss of consciousness, fainting.
- Clouding of the eye (cataract).
- Kidney damage.
- Inability to urinate.
- Abnormal liver function test results.
- Pelvic pain.
- Weight loss.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Stroke.
- Liver inflammation (hepatitis) that can cause itching of the skin, yellowing of the skin and the white part of the eyes (jaundice), light-colored stools, dark urine, and abdominal pain.
- The breakdown of tumor cells releases toxic compounds into the bloodstream (tumor lysis syndrome), which can lead to kidney problems.
- Underactive thyroid gland, which can cause symptoms such as fatigue, lethargy, muscle weakness, slow heart rate, and weight gain.
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Rejection of solid organ transplants (such as heart or liver).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible side effect not listed in this package insert. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Imnovid
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister and the carton after CAD/EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
No special storage conditions are required.
Do not use Imnovid if you notice visible signs of deterioration or signs of tampering with the medicine.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and further information
Composition of Imnovid
- The active substance is pomalidomide.
- The other ingredients are mannitol (E421), pregelatinized starch, and sodium stearyl fumarate.
Imnovid 1 mg hard capsule:
- Each capsule contains 1 mg of pomalidomide.
- The capsule shell contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E171), indigo carmine (E132), yellow iron oxide (E172), and white and black ink.
- The printing ink contains: shellac, titanium dioxide (E171), simethicone, propylene glycol (E1520), and ammonium hydroxide (E527) (white ink) and shellac, black iron oxide (E172), propylene glycol (E1520), and ammonium hydroxide (E527) (black ink).
Imnovid 2 mg hard capsule:
- Each capsule contains 2 mg of pomalidomide.
- The capsule shell contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E171), indigo carmine (E132), yellow iron oxide (E172), erythrosine (E127), and white ink.
- The printing ink contains: white ink - shellac, titanium dioxide (E171), simethicone, propylene glycol (E1520), and ammonium hydroxide (E527).
Imnovid 3 mg hard capsule:
- Each capsule contains 3 mg of pomalidomide.
- The capsule shell contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E171), indigo carmine (E132), yellow iron oxide (E172), and white ink.
- The printing ink contains: white ink - shellac, titanium dioxide (E171), simethicone, propylene glycol (E1520), and ammonium hydroxide (E527).
Imnovid 4 mg hard capsule:
- Each capsule contains 4 mg of pomalidomide.
- The capsule shell contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E171), indigo carmine (E132), brilliant blue FCF (E133), and white ink.
- The printing ink contains: white ink - shellac, titanium dioxide (E171), simethicone, propylene glycol (E1520), and ammonium hydroxide (E527).
Appearance of Imnovid and pack contents
Imnovid 1 mg hard capsules: dark blue opaque cap and yellow opaque body with the inscription “POML 1 mg”.
Imnovid 2 mg hard capsules: dark blue opaque cap and orange opaque body with the inscription “POML 2 mg”.
Imnovid 3 mg hard capsules: dark blue opaque cap and green opaque body with the inscription “POML 3 mg”.
Imnovid 4 mg hard capsules: dark blue opaque cap and blue opaque body with the inscription “POML 4 mg”.
Each pack contains 14 or 21 capsules. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorisation holder
Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma EEIG
Plaza 254
Blanchardstown Corporate Park 2
Dublin 15, D15 T867
Ireland
Manufacturer
Celgene Distribution B.V.
Orteliuslaan 1000
3528 BD Utrecht
Netherlands
You can request more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorisation holder:
Belgium/België/Belgien N.V. Bristol-Myers Squibb Belgium S.A. Tel: + 32 2 352 76 11 | Lithuania Swixx Biopharma UAB Tel: + 370 52 369140 |
Swixx Biopharma EOOD Tel: + 359 2 4942 480 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg N.V. Bristol-Myers Squibb Belgium S.A. Tel: + 32 2 352 76 11 |
Czech Republic Bristol-Myers Squibb spol. s r.o. Tel: + 420 221 016 111 | Hungary Bristol-Myers Squibb Kft. Tel: + 36 1 301 9797 |
Denmark Bristol-Myers Squibb Denmark Tel: + 45 45 93 05 06 | Malta A.M. Mangion Ltd Tel: + 356 23976333 |
Germany Bristol-Myers Squibb GmbH & Co. KGaA Tel: 0800 0752002 (+ 49 89 121 42 350) | Netherlands Bristol-Myers Squibb B.V. Tel: + 31 (0)30 300 2222 |
Estonia Swixx Biopharma OÜ Tel: + 372 640 1030 | Norway Bristol-Myers Squibb Norway AS Tel: + 47 67 55 53 50 |
Greece Bristol-Myers Squibb A.E. Tel: + 30 210 6074300 | Austria Bristol-Myers Squibb GesmbH Tel: + 43 1 60 14 30 |
Spain Bristol-Myers Squibb, S.A. Tel: + 34 91 456 53 00 | Poland Bristol-Myers Squibb Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: + 48 22 2606400 |
France Bristol-Myers Squibb SAS Tel: + 33 (0)1 58 83 84 96 | Portugal Bristol-Myers Squibb Farmacêutica Portuguesa, S.A. Tel: + 351 21 440 70 00 |
Croatia Swixx Biopharma d.o.o. Tel: + 385 1 2078 500 | Romania Bristol-Myers Squibb Marketing Services S.R.L. Tel: + 40 (0)21 272 16 19 |
Ireland Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals uc Tel: 1 800 749 749 (+ 353 (0)1 483 3625) | Slovenia Swixx Biopharma d.o.o. Tel: + 386 1 2355 100 |
Iceland Vistor hf. Tel: + 354 535 7000 | Slovakia Swixx Biopharma s.r.o. Tel: + 421 2 20833 600 |
Italy Bristol-Myers Squibb S.r.l. Tel: + 39 06 50 39 61 | Finland Oy Bristol-Myers Squibb (Finland) Ab Tel: + 358 9 251 21 230 |
Cyprus Bristol-Myers Squibb A.E. Tel: 800 92666 (+ 30 210 6074300) | Sweden Bristol-Myers Squibb Aktiebolag Tel: + 46 8 704 71 00 |
Latvia Swixx Biopharma SIA Tel: + 371 66164750 |
Date of last revision of this leaflet:
Other sources of information
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu. There are also links to other websites on rare diseases and orphan medicines.
You can access detailed and up-to-date information about this medicine by scanning the QR code included in the outer packaging with your smartphone. You can also access this information at the following internet address: www.imnovid-eu-pil.com.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to IMNOVID 2 mg HARD CAPSULESDosage form: CAPSULE, 3mgActive substance: pomalidomideManufacturer: Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma EeigPrescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 4mgActive substance: pomalidomideManufacturer: Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma EeigPrescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 1 mgActive substance: pomalidomideManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for IMNOVID 2 mg HARD CAPSULES
Discuss questions about IMNOVID 2 mg HARD CAPSULES, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






