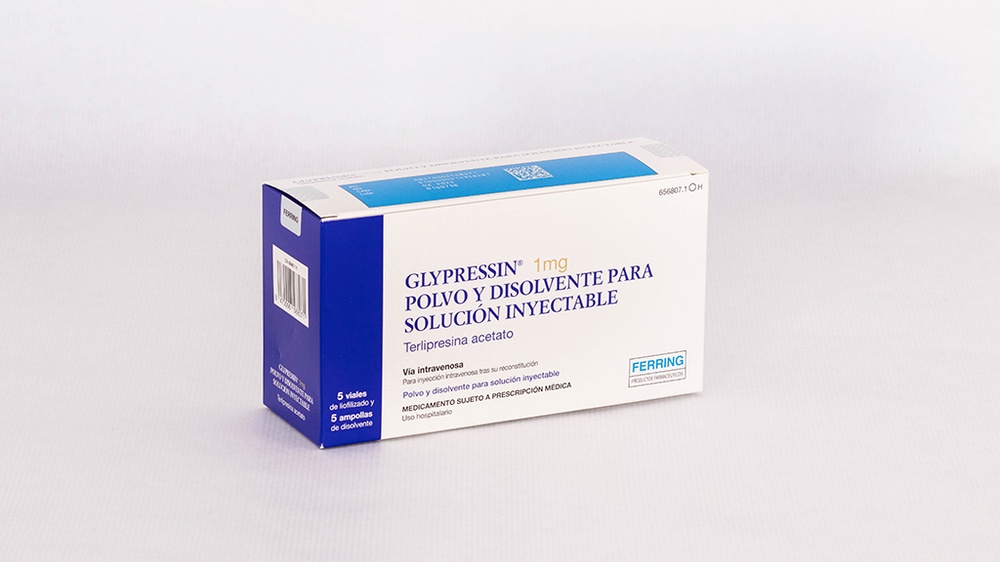
GLYPRESSIN 1mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use GLYPRESSIN 1mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
GLYPRESSIN 1mg powder and solvent for solution for injection
Terlipressin acetate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What Glypressin is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Glypressin
- How to use Glypressin
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Glypressin
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Glypressin is and what it is used for
Glypressin is presented as a powder and solvent for solution for injection, containing terlipressin acetate, which belongs to a group of medicines that decrease the pressure in the liver veins (portal venous pressure) in patients with high blood pressure in the vein that carries blood to the liver (portal hypertension). Terlipressin acts by constricting the blood vessels (vasoconstriction) in this area, helping to control bleeding from esophageal and stomach varices (esophagogastric) when it occurs.
Glypressin also contributes to improving blood circulation in the kidney, helping to recover renal function in patients with Hepatorenal Syndrome (a type of kidney failure in patients with severe liver dysfunction).
Glypressin is indicated for the treatment of:
- Gastrointestinal bleeding due to rupture of esophagogastric varices.
- Emergency treatment of hepatorenal syndrome type 1, defined according to the criteria of the CIA (International Ascites Club).
2. What you need to know before you use Glypressin
Do not use Glypressin:
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to terlipressin acetate or any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you are pregnant
Warnings and precautions:
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Glypressin:
- if you have high blood pressure (hypertension).
- if you have heart problems, such as irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias), coronary artery disease, or your heart pumps less blood than it should (heart failure), as you are at greater risk of suffering from heart-related side effects.
- if you have cerebral vascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, or vascular disease of the intestine, as you are at greater risk of suffering from side effects related to lack of blood flow in these locations.
- if you have swelling of the legs due to poor circulation in the veins or are overweight (obese), as you are at greater risk of suffering from decreased blood flow to the skin (ischemia) and even, in isolated cases, death of skin cells (necrosis).
- if you have a severe generalized infection with a drop in blood pressure (septic shock).
- if you have impaired renal function (renal insufficiency).
- if you have asthma or respiratory problems (respiratory insufficiency).
- in patients over 70 years of age with current or past cardiovascular disease.
- in children because experience is limited in this age group.
Glypressin should be used under the supervision of a specialist in units with the availability to regularly monitor blood pressure, cardiac function, blood parameters, and fluid balance.
The injection should be administered exclusively by the intravenous routeto avoid local skin necrosis due to leakage of the product onto the skin.
Glypressin may increase the risk of developing respiratory failure, which can be fatal. If you experience difficulty breathing or symptoms of fluid overload, before or during treatment with Glypressin, inform your doctor immediately.
If you are being treated for severe liver and kidney disease (hepatorenal syndrome type 1), your doctor should ensure that your cardiac function and fluid and electrolyte balance are monitored during treatment. Special care is required if you have pre-existing heart or lung disease, as Glypressin may induce cardiac ischemia (decreased blood flow to the heart) and respiratory failure (severe breathing difficulties). Treatment with Glypressin should be avoided if you have liver failure with multiple organ failures and/or renal insufficiency with very high levels of creatinine (a waste product) in the blood, as it increases the risk of adverse outcomes.
If you are being treated for severe liver and kidney disease, Glypressin may increase the risk of developing sepsis (bacteria in the blood and extreme response of the body to an infection) and septic shock (a serious condition that occurs when a major infection causes low blood pressure and reduced blood flow). Your doctor will take additional precautions in your case.
Using Glypressin with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
It is very important to inform your doctor if you are being treated with:
- Beta-blockers (medicines to slow down the heart rate), as their effects may be increased if used at the same time as Glypressin.
- Anti-arrhythmics (used to treat irregular heartbeats), such as quinidine or amiodarone.
- Diuretics (used to increase urine production, such as furosemide).
Tell your doctor if you have previously had a sudden slowing of the heart rate with certain anesthetics (propofol, sufentanil). Glypressin may increase the effect of these medicines if they are administered again.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Glypressin should not be administered if you are pregnant, as it may harm your baby.
Glypressin should not be administered during breastfeeding, as it is not known whether Glypressin can pass into breast milk.
Driving and using machines
No studies have been conducted on the effects on the ability to drive or use machines.
Use in children and over 65 years of age
Glypressin should be used with caution in patients over 70 years of age with current or past cardiovascular disease.
Special caution should be exercised when treating children, as experience is limited in this age group.
Use in patients with liver problems
In patients with liver problems, it is not necessary to adjust the dose of terlipressin.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Glypressin
Once reconstituted with the supplied solvent, this medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per 5 ml, so the product is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Glypressin
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as indicated by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Method of use and route of administration
Administration of Glypressin should be performed by qualified healthcare personnel following these recommendations:
Reconstitute Glypressin lyophilized powder by introducing the sterile solvent into the vial. The clear solution obtained should only be injected by the intravenous route. The medicine, once reconstituted, should be used immediately.
Glypressin is injected or infused by the intravenous route.
The normal dose in adults is:
Gastrointestinal bleeding due to rupture of esophagogastric varices
This will be determined by your doctor, depending on the patient's weight.
Generally, if the patient's weight is less than 50 kilograms, 1 milligram will be administered every four hours. In patients with a body weight between 50 and 70 kilograms, 1.5 milligrams will be administered every four hours. In patients with a body weight of more than 70 kilograms, 2 milligrams will be administered every 4 hours.
Treatment should continue for 24 consecutive hours until bleeding has been controlled. Treatment should be limited to 2-3 days, depending on the patient's condition. After the initial injection, subsequent doses may be reduced to 1 milligram of Glypressin if necessary, such as in the case of adverse reactions.
Hepatorenal syndrome
It is recommended to start treatment with 1 mg of terlipressin every 6 hours for at least 3 days. If after 3 days of treatment, the decrease in serum creatinine is less than 30% compared to the baseline value, it should be considered to double the dose to 2 mg every 6 hours.
Treatment with terlipressin should be discontinued if there is no response to treatment (defined as a decrease in serum creatinine of less than 30% on day 7 compared to the baseline value) or in patients with complete response (serum creatinine values below 1.5 mg/dl for at least two consecutive days).
In patients who present an incomplete response (decrease in serum creatinine of at least 30% compared to the baseline value but without reaching a value below 1.5 mg/dl on day 7), treatment with terlipressin may be continued for up to a maximum of 14 days.
In the event of a relapse of hepatorenal syndrome after a complete response, treatment with terlipressin may be restarted according to medical judgment.
The usual duration of treatment for hepatorenal syndrome is 7 days, and the maximum recommended duration is 14 days.
Hepatorenal syndrome type 1
Glypressin may also be administered as a drip (continuous intravenous infusion), usually starting with 2 mg of terlipressin acetate per day and increasing stepwise up to a maximum of 12 mg of terlipressin acetate per day.
If you use more Glypressin than you should:
If you are administered more Glypressin than recommended, there is an increased risk of serious circulatory effects, including a hypertensive crisis.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 915 620 420, indicating the medicine and the amount ingested.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Tell your doctor or another healthcare professional immediately:
- If you develop breathing difficulties or experience a worsening of respiratory capacity (signs or symptoms of respiratory failure). This side effect is very common if you are being treated for hepatorenal syndrome type 1: it may affect more than 1 in 10 people.
- If you develop signs or symptoms of infection in the blood (sepsis/septic shock), which may include fever and chills or very low body temperature, pale or blue-tinged skin, severe shortness of breath, decreased urine production, rapid heart rate, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue and weakness, and dizziness. This side effect is common if you are being treated for hepatorenal syndrome type 1: it may affect up to 1 in 10 people.
Other side effects that may occur with different frequencies depending on the disease being treated.
Very common:may affect more than 1 in 10 people.
If you have hepatorenal syndrome type 1:
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
Common:may affect up to 1 in 10 people.
- Headache
- Bradycardia (very slow heart rate)
- Increased blood pressure (hypertension)
- Peripheral vasoconstriction (inadequate blood flow to tissues) resulting in pallor
- Transient stomach pain
- Transient diarrhea
If you have hepatorenal syndrome type 1:
- Fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
- Breathing difficulties (respiratory difficulty)
Uncommon:may affect up to 1 in 100 people.
- Decreased sodium in the blood if fluid balance is not controlled
- Irrregular heart rhythm
- Increased heart rate
- Chest pain
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Pulmonary edema
- Torsade de pointes (serious cardiac event)
- Heart failure. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling of the ankles
- Inadequate blood flow to the intestines
- Peripheral cyanosis (blue-tinged skin due to lack of oxygen)
- Hot flashes
- Breathing difficulties and respiratory failure (severe breathing difficulties)
- Transient nausea
- Transient vomiting
- Skin necrosis (tissue damage)
- Uterine contraction (contraction of the uterus)
- Decreased uterine blood flow
- Necrosis at the injection site (tissue damage)
If you have gastrointestinal bleeding due to rupture of esophagogastric varices
- Fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
- Breathing difficulties (respiratory difficulty)
Rare:may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people.
If you have gastrointestinal bleeding due to rupture of esophagogastric varices:
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
The antidiuretic effect of the medicine (decreased urine production) may cause decreased sodium in the blood (hyponatremia) unless fluid balance is controlled.
Patient with Hepatorenal Syndrome treated with Glypressin presented during clinical trials a higher risk of suffering from cardiovascular side effects, such as decreased blood flow to the heart (myocardial ischemia), irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia), decreased blood flow to the intestine (intestinal ischemia), or circulatory overload (which may manifest as increased blood pressure, headache, difficulty breathing, or increased size of the neck veins).
During clinical trials and post-marketing experience, several cases of serious cardiac arrhythmias have been reported.
During post-marketing experience, several cases of skin ischemia (decreased blood flow to the skin) and skin necrosis (death of skin cells) in areas of the skin other than the injection site of Glypressin have been reported.
Reporting of side effects:
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines and Healthcare Products Agency (AEMPS) website: http://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Glypressin
Keep out of the sight and reach of children
Do not use Glypressin after the expiry date stated on the pack, after "EXP". The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Store in the original package to protect from light.
The reconstituted solution should be used immediately after reconstitution.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Glypressin:
The active substance is terlipressin acetate. Each vial contains 1 milligram of terlipressin acetate, corresponding to 0.86 milligrams of terlipressin. The concentration of the reconstituted solution is 0.2 milligrams/milliliter of terlipressin acetate.
The other ingredients are:
Powder: mannitol (E421) and hydrochloric acid.
Solvent: sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, and water for injection.
Appearance of the product and pack contents
The product is a powder and solvent for solution for injection.
The powder is white. When dissolved in the supplied solvent, a clear and colorless solution should be obtained.
It is marketed in packs of 1 vial and 1 ampoule of solvent and packs of 5 vials and 5 ampoules of solvent.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
FERRING S.A.U.
C/ del Arquitecto Sánchez Arcas nº3, 1º
28040 Madrid
Spain
Manufacturer:
FERRING GmbH
Wittland 11, 24109 Kiel,
Germany
Date of last revision of this leaflet January 2023
Detailed and up-to-date information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Medicines and Healthcare Products Agency (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to GLYPRESSIN 1mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.1 mg/mlActive substance: terlipressinManufacturer: Ferring S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.2 mg/mlActive substance: terlipressinManufacturer: Ever Valinject GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1 mgActive substance: terlipressinManufacturer: Altan Pharmaceuticals SaPrescription required
Online doctors for GLYPRESSIN 1mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about GLYPRESSIN 1mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions