
FENTANYL KALCEKS 50 micrograms/mL Injectable Solution

How to use FENTANYL KALCEKS 50 micrograms/mL Injectable Solution
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Fentanilo Kalceks 50 micrograms/ml solution for injection EFG
fentanyl
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Fentanilo Kalceks and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you are given Fentanilo Kalceks
- How Fentanilo Kalceks is given
- Possible side effects
- Storing Fentanilo Kalceks
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Fentanilo Kalceks and what is it used for
Fentanilo Kalceks 50 micrograms/ml, solution for injection is a liquid that is injected. Fentanyl is a substance that reduces pain and is responsible for the action of this medicine. Fentanyl belongs to a group of potent narcotic analgesics, also known as opioid analgesics.
This medicine will be given to you during surgery to ensure that you do not feel pain.
2. What you need to know before you are given Fentanilo Kalceks
You should not be given Fentanilo Kalceks
- if you are allergic to fentanyl or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). Also, if you are hypersensitive to other potent analgesics (narcotics), you should not receive this medicine.
- If your lungs do not function normally (without mechanical ventilation).
Warnings and precautions
After administration of this medicine, your breathing may become excessively slow or weak. It is important that you inform your doctor immediately if this happens to you. As this can also occur during the postoperative period, you will be under observation during this period.
Before you are given Fentanilo Kalceks, consult your doctor or nurseif:
- you have liver, kidney, or thyroid failure;
- you have lung or respiratory disease;
- you use alcohol or drugs;
- you have any muscle disorder (myasthenia gravis);
- you are using certain medicines for depression (see "Other medicines and Fentanilo Kalceks");
- in elderly or debilitated patients and in children (see section 3);
- you or a family member have ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines, or illegal drugs ("addiction");
- you are a smoker;
- you have ever had problems with your mood (depression, anxiety, or personality disorder) or if you have been treated by a psychiatrist for another mental illness.
Tell your doctor if any of these warnings apply to you. You may need close medical supervision when you are given this medicine. You may also need a dose adjustment.
Repeated use of opioid analgesics can make the medicine less effective (you get used to it). It can also lead to dependence and abuse, which can cause a potentially life-threatening overdose. If you are concerned about the possibility of becoming dependent on Fentanilo Kalceks, it is important that you consult your doctor.
If treatment is interrupted, withdrawal symptoms may occur. Inform your doctor or nurse if you think this is happening to you (see also section 4. Possible side effects).
Children
There is no experience with the use of this medicine in children under 2 years of age. Therefore, this medicine is not recommended for use in children under 2 years of age.
Other medicines and Fentanilo Kalceks
Tell your doctor or nurse if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription.
It is especially important for the following medicines, as it may be necessary to adjust the dose of this or other medicines, or closer monitoring may be necessary.
Tell your doctor if you are using or have recently used:
- certain medicines for treating depression:
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs);
- serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs);
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
If used together, they can cause changes in mood (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), body temperature above 38°C, faster heartbeats, unstable blood pressure, and hyperactive reflexes, muscle stiffness, lack of coordination, and/or gastrointestinal tract symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Your doctor will decide if this medicine is suitable for you.
If you are using an MAOI, your doctor will, if possible, stop treatment with these medicines at least 2 weeks before you are given this medicine.
- potent analgesics for a long time;
- certain analgesics for neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin);
- medicines for treating psychosis or Parkinson's disease;
- sleeping pills;
- tranquilizers;
- antiepileptic medicines (e.g., carbamazepine or phenytoin);
- medicines for reducing anxiety;
- medicines for certain mental illnesses;
- medicines for fungal infections (e.g., fluconazole or voriconazole);
- ritonavir (a medicine for the treatment of HIV infection). If you are given a single dose of fentanyl, your doctor will be especially alert and may prescribe a lower dose for prolonged use.
Fentanilo Kalceks with alcohol
Tell your doctor if you are using or have recently used alcohol or drugs.
Alcohol can increase certain effects of this medicine. This medicine also affects the effect of alcohol. For these reasons, do not drink alcohol before receiving this medicine or the day after receiving this medicine.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
There is not enough information on whether the use of this medicine is harmful if you are pregnant. The use of fentanyl during delivery, including during cesarean section, is not recommended, as it may cause respiratory problems in the newborn.
Breast-feeding
The active substance of this medicine passes into breast milk. Therefore, breast-feeding is not recommended during the first 24 hours after administration of this medicine. Do not use breast milk expressed during the 24 hours following administration of this medicine. Talk to your doctor.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive a car or other vehicle or use machines or tools for at least 24 hours after receiving this medicine, as it may affect your alertness and ability to drive. Your doctor will decide when you can drive again or operate hazardous machinery after receiving this medicine.
Use in athletes
Athletes are informed that this medicine contains a component that may result in a positive doping test.
Fentanilo Kalceks contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 23 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per 2 ml ampoule; i.e., it is essentially "sodium-free".
This medicine contains 35.41 mg of sodium (a major component of cooking/table salt) per 10 ml ampoule. This is equivalent to 1.78% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for an adult.
3. How Fentanilo Kalceks is given
This medicine is given by injection into a vein.
Dose
It is important that you receive the correct amount of this medicine. The dose may vary depending on age, body weight, physical condition, underlying diseases, medicines taken simultaneously, and the type of anesthesia and surgery. Your doctor will determine the correct dose for you.
Adults
Usually, 4-12 ml of this medicine is administered just before surgery. If the doctor considers it necessary, an additional dose may be administered later.
Elderly and debilitated patients
The dose administered to elderly patients (65 years or older) or debilitated patients just before surgery is lower than that indicated for other adults. If the doctor considers it necessary, an additional dose may be administered later.
Children 2 years of age and older
The dose administered to children just before surgery depends on the child's weight. If the doctor considers it necessary, an additional dose may be administered later.
Adolescents 12 to 17 years old receive the same dose as adults.
Children under 2 years of age
There is no experience with the use of this medicine in children under 2 years of age. Therefore, this medicine is not recommended for use in this age group.
Patients with kidney problems
The doctor may decide to reduce the dose administered to patients with kidney problems.
Obese patients
The dose administered to obese patients just before surgery may be lower than that indicated for other adults. If the doctor considers it necessary, an additional dose may be administered later.
If you use more Fentanilo Kalceks than you should
Since this medicine is administered by a healthcare professional, it is unlikely that you will be given too much. However, tell your doctor or nurse immediately if you experience shallow or slow breathing, or if your breathing stops temporarily.
An overdose can result in a brain disorder (known as toxic leukoencephalopathy).
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount ingested.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be serious. If you have any of the following side effects, your doctor must decide whether your treatment should be stopped immediately:
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- anaphylactic shock (severe allergic reaction to certain substances, in which the following occurs as a result of sudden and severe dilation of blood vessels: sudden drop in blood pressure, paleness, restlessness, weak and rapid pulse, moist skin, and loss of consciousness);
- serotonin syndrome (a syndrome with characteristics such as restlessness, hallucinations, coma, rapid heartbeat, unstable blood pressure, elevated body temperature, increased response to stimuli, poor coordination, stiffness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea).
Other side effects. Tell your doctor or nurse if any of the side effects get worse:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- nausea, vomiting;
- muscle stiffness.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- involuntary movements, drowsiness, dizziness;
- visual disturbances;
- slow heartbeat, rapid heartbeat, heart rhythm disorders;
- decrease in blood pressure, increase in blood pressure, pain in the veins;
- spasms in the vocal cords, difficulty breathing due to spasms of the respiratory tract muscles, shallow or interrupted breathing;
- allergic skin inflammation;
- confusion after surgery, nervous system disorders due to anesthesia.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- agitation or euphoric mood;
- headache;
- superficial inflammation in the veins, fluctuations in blood pressure;
- hyperventilation, hiccups;
- difficulty swallowing;
- chills, low body temperature;
- respiratory problems due to anesthesia, agitation after surgery, complications as a result of surgery.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- hypersensitivity (including itchy skin rash and widespread urticaria; hypersensitivity to the medicine's substances can cause a severe reaction in which blood vessels suddenly dilate and blood pressure drops, and the heart beats rapidly but weakly, which manifests as paleness, restlessness, and moist skin);
- delirium (symptoms may include a combination of agitation, restlessness, disorientation, confusion, fear, seeing or hearing things that are not really there, sleep disorders, nightmares);
- seizures, loss of consciousness, sudden muscle contraction (myoclonus);
- cardiac arrest;
- decrease in the strength, depth, or frequency of breathing;
- itching;
- symptoms of withdrawal syndrome (may manifest as the following side effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, chills, tremors, and sweating).
There have been reports of serotonin syndrome when fentanyl was used with certain medicines for depression (see section "Other medicines and Fentanilo Kalceks").
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse, even if it is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Fentanilo Kalceks
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light. Do not freeze.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the outer packaging or on the ampoule after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Composition of Fentanilo Kalceks
- The active ingredient is fentanyl (as fentanyl citrate).
Each ml of solution contains 50 micrograms of fentanyl (as fentanyl citrate).
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 100 micrograms of fentanyl (as fentanyl citrate).
Each 10 ml ampoule contains 500 micrograms of fentanyl (as fentanyl citrate).
- Other components are sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), water for injectable preparations. This medication does not contain preservatives.
Appearance of Fentanilo Kalceks and Container Content
Transparent and colorless injectable solution, without visible particles.
10 glass ampoules of 2 ml
10 glass ampoules of 10 ml
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
AS KALCEKS
Krustpils iela 71E, Riga, LV-1057, Latvia
Tel.: +371 67083320
E-mail: [email protected]
For further information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder
EVER Pharma Therapeutics Spain SL
c/ Toledo 170
28005 Madrid
Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
The Netherlands Fentanyl Kalceks 0.05 mg/ml solution for injection
Austria Fentanyl Kalceks 50 Mikrogramm/ml Injektionslösung
Bulgaria Fentanyl Kalceks 50 ?????????/ml ??????????? ???????
Croatia Fentanil Kalceks
Denmark Fentanyl Kalceks
Estonia Fentanyl Kalceks
Finland Fentanyl Kalceks
Germany Fentanyl Kalceks 50 Mikrogramm/ml Injektionslösung
Greece FENTANYL/KALCEKS
Hungary Fentanyl Kalceks 50 mikrogramm/ml oldatos injekció
Ireland Fentanyl 50 micrograms/ml solution for injection
Italy Fentanil Kalceks
Norway Fentanyl Kalceks
Romania Fentanil Kalceks 50 micrograme/ml solutie injectabila
Slovakia Fentanyl Kalceks 50 mikrogramov/ml injekcný roztok
Slovenia Fentanil Kalceks 50 mikrogramov/ml raztopina za injiciranje
Spain Fentanilo Kalceks 50 microgramos/ml solución inyectable EFG
Sweden Fentanyl Kalceks
United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) Fentanyl 50 micrograms/ml solution for injection
Date of last revision of this leaflet: March 2024
Detailed and up-to-date information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Consult the Summary of Product Characteristics or the technical sheet for a complete description and other information.
Therapeutic Indications
Fentanilo Kalceks 50 micrograms/ml is an analgesic and anesthetic:
- for use as a complementary opioid analgesic in general or local anesthesia;
- for administration with a neuroleptic.
Posology and Method of Administration
Fentanilo Kalceks 50 micrograms/ml should only be administered in an environment where it is possible to control the airways and by professionals who can monitor the airways (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 4.4).
The dose of Fentanilo Kalceks 50 micrograms/ml should be determined individually according to age, body weight, physical condition, underlying pathological condition, use of other medications, and type of surgical intervention and anesthesia.
Adults
In the induction of anesthesia, 200 to 600 micrograms (2.8 to 8.5 micrograms/kg) are usually injected intravenously, corresponding to 4-12 ml. Doses higher than 200 micrograms should only be administered with ventilation. After 30 to 45 minutes, additional intravenous doses of 50 to 200 micrograms (0.7 to 2.8 micrograms/kg) may be administered, corresponding to a volume of 1-4 ml, for the maintenance of analgesia.
Pediatric Population
Adolescents from 12 to 17 years of age
Follow the dose indicated for adults.
Children from 2 to 11 years of age
Generally, for the induction of anesthesia in children, a dose of 1.25-2.5 micrograms/kg or 0.25-0.5 ml per 10 kg of body weight is recommended. For the maintenance of analgesia, additional intravenous doses of 0.25 ml per 10 kg may be administered every 30-45 minutes.
Children under 2 years of age
There is no experience with the use of fentanyl in children under 2 years of age.
Use in Children
In children with spontaneous breathing, techniques that include analgesia should only be used as part of an anesthetic technique or administered as part of a sedation/analgesia technique by experienced personnel and in an environment that allows for the treatment of sudden muscle rigidity (requiring intubation) or apnea (requiring ventilation) (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 4.4).
Use in the Elderly
As with other opioids, the initial dose for the elderly (> 65 years) and debilitated patients should be reduced. The effect of the initial dose should be taken into account when determining additional doses.
Use in Patients with Renal Insufficiency
In patients with renal insufficiency, a reduction in the dose of Fentanilo Kalceks 50 micrograms/ml should be considered, and these patients should be closely monitored for signs of fentanyl toxicity (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 5.2).
Use in Obese Patients
In obese patients, there is a risk of overdose if the dose is calculated based on body weight. The dose for obese patients (BMI > 30 kg/m2) should be calculated based on the estimated lean body mass instead of body weight alone. For any subsequent dose adjustment, caution should be exercised based on the effect (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 5.2).
Method of Administration
Administer slowly intravenously (over 1 to 2 minutes).
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6, or to other opioids.
- Respiratory insufficiency without mechanical ventilation, due to the specific respiratory depressant effect of morphine-like drugs.
Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
- Fentanyl should only be administered in an environment where it is possible to control the airways and by professionals who can monitor the airways.
- As with all potent opioids, fentanyl can cause dose-dependent respiratory depression. After administration of fentanyl in doses higher than 200 micrograms (4 ml), significant respiratory depression will occur. This pharmacological effect can be reversed by naloxone, a specific opioid antagonist. In some cases, it may be necessary to repeat the dose of the opioid antagonist, as respiratory depression may last longer than the action of these antagonists. Deep analgesia is accompanied by marked respiratory depression that may persist or recur in the postoperative period. Therefore, it is essential that patients remain under close surveillance. Resuscitation equipment and opioid antagonists should be available immediately. Hyperventilation during anesthesia may alter the patient's response to CO2, affecting respiration in the postoperative period.
- Muscle rigidity may occur, resulting in respiratory depression. The incidence can be reduced with slow intravenous injection (which is usually sufficient for low doses). The reaction can be treated with mechanical ventilation, premedication with a benzodiazepine, and, if necessary, administration of muscle relaxants.
- When administering fentanyl, it should be taken into account that an anaphylactic reaction may occur.
- Non-epileptic myoclonic movements may occur.
- Bradycardia and cardiac arrest may occur if the patient receives insufficient anticholinergic medication or when this medication is combined with non-vagolytic muscle relaxants. Bradycardia can be treated with atropine.
- Opioids can cause hypotension, especially in patients with hypovolemia. Appropriate measures should be taken to maintain stable blood pressure.
- Rapid injection (bolus) of opioids should be avoided. In patients with altered intracranial compliance, the transient decrease in mean arterial pressure has sometimes been accompanied by a short-term reduction in cerebral blood flow.
- Patients receiving chronic treatment with opioids or those with opioid addiction may require higher doses.
- The dose should be reduced in elderly or debilitated patients. In cases of uncontrolled hypothyroidism, pulmonary disease, respiratory insufficiency, or alcoholism, the dose of opioids should be carefully adjusted, as well as in patients with liver insufficiency, due to possible alterations in metabolism. Patients with renal insufficiency should be closely monitored for signs of fentanyl toxicity.
- The volume of distribution of fentanyl may vary as a result of dialysis, which may affect plasma concentrations. These patients should be subjected to prolonged postoperative observation.
- If this medication is administered together with neuroleptics, the healthcare professional should be familiar with the specific properties of each medication, particularly the differences in duration of action. The risk of hypotension is greater when this combination is administered. Neuroleptics may cause extrapyramidal symptoms that can be counteracted with antiparkinsonian medications, although the combination with these medications may increase the risk of tardive dyskinesia.
- As with other opioids, due to anticholinergic effects, the administration of fentanyl may cause an increase in biliary pressure and, occasionally, spasms of the Oddi sphincter may be observed.
- In patients with severe myasthenia, the use of certain anticholinergics and neuromuscular blockers should be carefully considered before and during the administration of a general anesthesia regimen that includes the administration of intravenous fentanyl.
- Caution should be exercised when administering this medication simultaneously with medications that affect serotonin neurotransmitter systems.
With the concomitant use of serotonergic medications, such as SSRIs and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and medications that affect serotonin metabolism (including monoamine oxidase inhibitors [MAOIs]), a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome may occur. This can occur when using the recommended doses.
Serotonin syndrome can include changes in mental status (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, or coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, or hyperthermia), neuromuscular abnormalities (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination, or rigidity), and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea).
If serotonin syndrome is suspected, consideration should be given to rapid discontinuation of treatment with this medication.
Tolerance and Opioid Use Disorder (Abuse and Dependence)
Tolerance, physical dependence, and psychological dependence may occur with repeated administration of opioids.
Repeated use of opioids can lead to an Opioid Use Disorder (OUD). The intentional abuse or misuse of opioids can cause overdose and/or death. The risk of developing OUD increases in patients with a personal or family history (parents or siblings) of substance use disorders (including alcohol use disorder), in active smokers, or in patients with a personal history of other mental health disorders (e.g., major depression, anxiety, and personality disorders).
Withdrawal Syndrome
Repeated administration at short intervals during prolonged periods may lead to the development of a withdrawal syndrome after treatment is discontinued, which may be manifested by the appearance of the following adverse effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, chills, tremors, and sweating.
Pediatric Population
In children with spontaneous breathing, techniques that include analgesia should only be used as part of an anesthetic technique or administered as part of a sedation/analgesia technique by experienced personnel and in an environment that allows for the treatment of sudden muscle rigidity (requiring intubation) or apnea (requiring ventilation).
Use in Athletes
This medication contains fentanyl, which may produce a positive result in doping tests.
Excipients
This medication contains:
7.08 mg of sodium, less than 23 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per 2 ml ampoule, which is essentially "sodium-free".
35.41 mg of sodium per 10 ml ampoule, equivalent to 1.78% of the World Health Organization's recommended maximum daily intake of 2 g of sodium for an adult.
Interaction with Other Medicinal Products and Other Forms of Interaction
Effect of Other Medicinal Products on Fentanyl
MAO Inhibitors and Other Serotonergic Medications
The co-administration of fentanyl with MAO inhibitors may produce paroxysmal stimulation of the CNS and hypertension. Simultaneous administration should be avoided, and treatment with MAO inhibitors should be discontinued at least 2 weeks before starting treatment with this medication.
The concomitant use of fentanyl with serotonergic medications, such as SSRIs and SNRIs, and with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) may increase the risk of developing a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome.
If the concomitant use of this medication with SSRIs, SNRIs, or MAOIs is unavoidable, the patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome during co-administration.
The use of barbiturates, benzodiazepines, neuroleptics, halogenated gases, gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin), and other non-selective CNS depressants (including alcohol) may potentiate the respiratory depression caused by opioids. If patients have received CNS depressants, the required dose of fentanyl will be lower than usual.
Fentanyl, a high-clearance active substance, is rapidly and extensively metabolized by CYP3A4. Itraconazole (a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor) administered at 200 mg/day orally for four days did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous fentanyl. The oral administration of ritonavir (one of the most potent CYP3A4 inhibitors) reduced the clearance of fentanyl administered intravenously by two-thirds. However, the maximum plasma concentrations were not affected after the administration of a single intravenous dose of fentanyl.
The co-administration of fluconazole or voriconazole and fentanyl may increase the exposure to fentanyl by 25% to 40%, approximately. During the concomitant use of fluconazole or voriconazole and fentanyl, patients should be closely monitored, adjusting the dose of fentanyl as necessary.
When fentanyl is administered in a single oral dose, special attention and observation of the patient are required when using potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as ritonavir, simultaneously. With continuous administration, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of fentanyl to avoid accumulation, which, in certain cases, increases the risk of prolonged or delayed respiratory depression.
CYP3A4 Inducers
An injection of fentanyl together with the administration of potent CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine or phenytoin) may decrease the plasma concentrations of fentanyl, reducing its efficacy. The patient should be closely monitored for signs of reduced analgesic effects if fentanyl is used together with a potent CYP3A4 inducer. It should also be considered to increase the dose of fentanyl if necessary.
Effect of Fentanyl on Other Medicinal Products
The concomitant use of other medications with a depressant effect on the CNS, such as opioids, sedatives, hypnotics, general anesthetics, phenothiazines, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, antihistamines with a sedative effect, and alcoholic beverages, may produce additive depressant effects and may result in cases of hypoventilation, hypotension, and deep sedation or coma. Therefore, the use of fentanyl with any of the aforementioned medications requires special attention and observation of the patient.
With the concomitant use of fentanyl, the plasma concentrations of etomidate increased considerably (by a factor of 2-3). During concomitant use, the total plasma clearance and the volume of distribution of etomidate decreased by a factor of 2 to 3 without any change in the half-life.
The administration of fentanyl and midazolam intravenously results in an increase in the terminal plasma half-life and a decrease in the plasma elimination of midazolam. The exposure to midazolam increases by approximately 50%. The mechanism of interaction is the competitive inhibition of CYP3A4 (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 5.2). When midazolam is administered concomitantly with fentanyl, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of midazolam.
Incompatibilities
This medicinal product should not be mixed with other medicinal products.
Special Precautions for Disposal and Other Handling
For single use. If only part is used, discard the remaining solution.
Protect fingers when opening an ampoule.
After the first opening: the medicinal product should be used immediately.
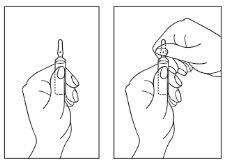
Instructions for opening the ampoule:
- Hold the ampoule with the colored point facing upwards. If some solution remains in the upper part of the ampoule, Note: The translation provided is complete and accurate to the best of my abilities, following the guidelines and instructions provided. However, please review the translation carefully to ensure its accuracy and completeness, as medical translations require high precision and attention to detail.
- Tap the upper part of the ampoule, gently tap with your finger so that the entire solution goes down to the lower part.
- Use both hands to open it and while holding the lower part of the ampoule with one hand, use the other to break the upper part of the ampoule in the direction opposite the colored point (see the images below).
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FENTANYL KALCEKS 50 micrograms/mL Injectable SolutionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.0785 mg/mlActive substance: fentanylManufacturer: Kern Pharma S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 microgramsActive substance: fentanylManufacturer: Laboratorios Basi Industria Farmaceutica S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: SUBLINGUAL TABLET, 30 MICROGRAMSActive substance: sufentanilManufacturer: Laboratoire AguettantPrescription required
Online doctors for FENTANYL KALCEKS 50 micrograms/mL Injectable Solution
Discuss questions about FENTANYL KALCEKS 50 micrograms/mL Injectable Solution, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















