
Fentanil Kalceks

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fentanil Kalceks

How to use Fentanil Kalceks
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Fentanyl Kalceks, 0.05 mg/mL, solution for injection
Fentanyl
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Fentanyl Kalceks and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before administering Fentanyl Kalceks
- 3. How Fentanyl Kalceks is administered
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fentanyl Kalceks
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Fentanyl Kalceks and what is it used for
Fentanyl Kalceks solution for injection contains the active substance fentanyl (as fentanyl citrate). It belongs to a group of medicines called opioid analgesics. These medicines prevent pain and relieve it.
Fentanyl Kalceks is used:
- as a narcotic analgesic to supplement general or regional anesthesia;
- in combination with a neuroleptic (e.g., droperidol) in neuroleptanalgesia;
- for induction of anesthesia and as a maintenance anesthetic for general and regional anesthesia;
- as an anesthetic with oxygen in high-risk surgical patients.
2. Important information before administering Fentanyl Kalceks
When not to use Fentanyl Kalceks:
- if the patient is allergic to fentanyl or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- if the patient is allergic to medicines with a similar effect to morphine.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Fentanyl Kalceks, discuss with your doctor or nurse:
- if the patient or anyone in their family has ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription drugs, or illegal substances (addiction),
- if the patient smokes,
- if the patient has ever had mood disorders (depression, anxiety, or personality disorder) or has been treated by a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses.
As with all potent opioids, respiratory depression is dose-dependent and can be reversed by administering an opioid antagonist (naloxone), although additional doses of naloxone may be necessary as respiratory depression may last longer than the effect of opioid antagonists. Deep analgesia is accompanied by pronounced respiratory depression that may persist or recur in the postoperative period. Patients should therefore be kept under appropriate surveillance. Fentanyl should be administered in conditions where it is possible to maintain airway patency, with resuscitation equipment and opioid receptor antagonists available, as well as personnel able to maintain airway patency. Hyperventilation during anesthesia may change the patient's response to CO2, affecting breathing in the postoperative period.
Muscle stiffness may occur, including chest muscles, but can be avoided by:
- slowly administering the intravenous injection (usually sufficient when administering lower doses);
- using benzodiazepine premedication;
- using muscle relaxants.
Non-epileptic (myo)clonic movements may also occur.
If the patient has received insufficient anticholinergic medication or if fentanyl has been combined with muscle relaxants that do not have a vagolytic effect, the patient may experience bradycardia or even sudden cardiac arrest. Bradycardia can be reversed with atropine.
Opioids can cause hypotension, especially in patients with hypovolemia. Appropriate measures should be taken to maintain stable blood pressure.
In patients with impaired cerebrovascular reactivity, rapid bolus administration of opioids should be avoided, as transient hypotension may occasionally be accompanied by brief decreases in cerebral perfusion pressure in these patients. Patients who have been taking opioid analgesics for a long time or abusing opioid substances may require higher doses.
In elderly and very weak patients, a dose reduction is recommended. Opioid doses should be carefully and gradually adjusted in patients with the following conditions: untreated or inadequately treated hypothyroidism, lung disease, decreased respiratory reserve, alcoholism, impaired renal function, or impaired liver function. These patients also require longer postoperative monitoring.
If fentanyl is administered with a neuroleptic, such as droperidol, hypotension occurs more frequently. Neuroleptics can cause extrapyramidal symptoms, which can be controlled with drugs used in Parkinson's disease.
As with other opioids, fentanyl administration may lead to increased intrabiliary pressure, and in single cases, spastic contractions of the Oddi sphincter (circular muscle controlling bile flow) may occur.
In patients with muscle weakness (myasthenia gravis), the use of certain anticholinergic drugs and neuromuscular blocking agents before and during general anesthesia with intravenous fentanyl administration should be undertaken with caution.
Repeated use of opioid analgesics can lead to reduced efficacy (tolerance to the drug may develop). This can also lead to dependence and abuse, which can cause life-threatening overdose. If the patient is concerned about becoming dependent on Fentanyl Kalceks, they should consult their doctor.
If treatment is discontinued, withdrawal symptoms may occur. If the patient suspects this is happening, they should tell their doctor or nurse (see also section 4. Possible side effects).
Children and adolescents
Techniques involving analgesia in children with spontaneous breathing should only be used in the context of anesthesia or sedation combined with analgesia, in the presence of experienced personnel and in conditions that allow for the implementation of appropriate measures in case of sudden onset of chest wall stiffness requiring intubation or apnea requiring respiratory support.
Fentanyl Kalceks and other medicines
Tell your doctor or nurse about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
Using opioid premedication, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, neuroleptics, halogenated gases, some medicines used to treat neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin), and other non-selective substances with a depressant effect on the central nervous system (CNS) (e.g., alcohol) may enhance or prolong respiratory depression caused by fentanyl. When patients received these agents, the required dose of fentanyl was lower than usual.
Tell your doctor if you are taking other medicines that have a depressant effect on the CNS, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs).
When patients received these medicines, the required dose of fentanyl was lower than usual.
Fentanyl, as a rapidly eliminated drug, is rapidly and extensively metabolized, mainly through CYP3A4. Oral itraconazole (a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor) at a dose of 200 mg/day for 4 days had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered fentanyl.
Oral ritonavir (one of the most potent CYP3A4 inhibitors) reduced the clearance of intravenously administered fentanyl by two-thirds. Maximum plasma concentrations after a single dose of fentanyl administered intravenously did not change, however.
In the case of single-dose administration of fentanyl, concomitant administration of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as ritonavir, requires particularly careful patient care and monitoring.
Concomitant use of fluconazole or voriconazole with fentanyl may lead to increased exposure to the latter.
In the case of continuous administration of fentanyl, it may be necessary to reduce its dose to avoid accumulation in the body, which could increase the risk of prolonged or delayed respiratory depression.
It is usually recommended to discontinue monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) 2 weeks before any surgical procedure or anesthesia. However, there have been reports of fentanyl use during surgical procedures or anesthesia in patients taking MAOIs — without any interactions.
Effect of fentanyl on other medicines
After administering fentanyl, the doses of other medicines with a depressant effect on the CNS should be reduced.
When fentanyl is used concomitantly with etomidate, the total clearance of etomidate from plasma and its volume of distribution decrease (2- to 3-fold), without changing the half-life, resulting in a significant increase in etomidate plasma concentrations. Concomitant administration of fentanyl and midazolam intravenously leads to an increase in the elimination half-life of midazolam and a decrease in midazolam clearance from plasma. When these medicines are administered together with fentanyl, it may be necessary to reduce their doses.
Using Fentanyl Kalceks with alcohol
Alcohol may enhance or prolong respiratory depression caused by fentanyl.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, ask your doctor or nurse for advice before using this medicine.
There are insufficient data on the use of fentanyl in pregnant women. Fentanyl may cross the placenta in early pregnancy. Animal studies have shown a low toxic effect on fertility. The potential risk to humans is unknown.
Therefore, before administering this medicine to a pregnant woman, the risks and potential benefits associated with its use should be considered.
Fentanyl should not be used (intramuscularly or intravenously) during labor (including cesarean section), as it crosses the placenta and affects the fetal respiratory center, which is particularly sensitive to the effects of opioids. However, if fentanyl is administered, an antidote should be available for administration to the newborn.
Fentanyl passes into breast milk, and breastfeeding should be avoided for 24 hours after administration. The balance of risks and benefits associated with breastfeeding after fentanyl administration should be considered.
Driving and using machines
The patient should not drive or operate machinery if a sufficient amount of time has not passed since the administration of fentanyl.
Fentanyl Kalceks contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per 2 mL ampoule, i.e., the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
The medicine contains 35.41 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per 10 mL ampoule, which corresponds to 1.78% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
3. How Fentanyl Kalceks is administered
This medicine should always be used as directed by your doctor. If you are unsure, ask your doctor.
- Fentanyl Kalceks can be administered by infusion or injection into a vein or muscle.
- Fentanyl Kalceks will be injected into a vein just before surgery. This medicine will help the patient fall asleep and prevent pain during surgery.
- The patient may receive anesthetics and/or other medicines to prevent some of the side effects of fentanyl, such as slowed heart rate and muscle stiffness.
- Your doctor will provide detailed information on the dosage of the medicine. The doctor will adjust the doses of the medicine according to the patient's overall condition, age, weight, concomitant diseases, type of surgery, anesthesia, and concomitant medicines.
Use in children and adolescents
The dose of the medicine in children depends on their weight.
Using a higher dose of Fentanyl Kalceks than recommended
Since this medicine is administered by a doctor or nurse, it is unlikely that you will receive more fentanyl than you should. Overdose of Fentanyl Kalceks can cause respiratory depression (see warnings and precautions) and brain disorders (called toxic leukoencephalopathy).
If you have any further questions about using this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Possible side effects may occur in the patient, especially during surgery, and will be managed by the doctor. Some side effects may occur immediately after surgery; therefore, the patient will be monitored postoperatively.
Very commonside effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- nausea, vomiting
- muscle stiffness (including chest muscles)
Commonside effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- involuntary, repetitive body movements
- drowsiness, dizziness
- vision disturbances
- accelerated or slowed heart rate
- irregular heartbeat
- low or high blood pressure
- vein pain
- choking caused by painful (spastic) contraction of the throat muscles
- difficulty breathing or wheezing
- short-term breathing stop (apnea) (the doctor has a medicine that prevents this)
- skin rash
- postoperative disorientation
Uncommonside effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- elevated mood
- headache
- vein swelling and thrombophlebitis (vein inflammation)
- irregular changes in blood pressure
- accelerated breathing
- hiccups
- difficulty swallowing
- decreased body temperature or chills
- anesthesia-related respiratory complications
- postoperative psychomotor agitation
Side effects with unknown frequency(frequency cannot be estimated from available data):
- severe allergic reaction with sudden drop in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, or skin rash (anaphylaxis)
- urticaria
- seizures
- loss of consciousness
- minor muscle spasms
- cardiac arrest (the doctor has a medicine that prevents this)
- respiratory depression
- itching
- delirium (symptoms may include agitation, restlessness, disorientation, confusion, anxiety, seeing or hearing things that do not exist, sleep disturbances, nightmares)
- withdrawal symptoms (may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, chills, tremors, and sweating)
If Fentanyl Kalceks is used in combination with other medicines called neuroleptics, which are administered before surgery to induce sleepiness, other effects can be expected, such as body tremors and/or shivers, psychomotor agitation, and after surgery, hallucinations, tremors, severe muscle stiffness, or spastic contractions, slowed movements, and excessive salivation.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Fentanyl Kalceks
There are no special recommendations for the storage temperature of the medicinal product.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light.
Do not freeze.
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton after EXP.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
After opening the ampoule, the medicine should be used immediately.
Physical and chemical stability of the medicine has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 25°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the solution should be used immediately. If the solution is not used immediately, the responsibility for the subsequent storage period and conditions lies with the user, and this period should not exceed 24 hours at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C, unless the dilution was performed under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Fentanyl Kalceks contains
- The active substance of the medicine is fentanyl (as fentanyl citrate). 1 mL of the solution contains 0.05 mg of fentanyl in the form of 0.0785 mg of fentanyl citrate.
One 2 mL ampoule contains 0.1 mg of fentanyl in the form of 0.157 mg of fentanyl citrate.
One 10 mL ampoule contains 0.5 mg of fentanyl in the form of 0.785 mg of fentanyl citrate.
- Other ingredients are sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), and water for injections.
What Fentanyl Kalceks looks like and contents of the packaging
Solution for injection (solution).
Clear, colorless liquid. pH of the solution: 4.0-7.5.
Fentanyl Kalceks is manufactured in the form of colorless glass type I ampoules with a capacity of 2 mL or 10 mL.
Pack sizes: 5, 10, or 50 ampoules.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
AS KALCEKS
Krustpils iela 71E
1057 Riga
Latvia
tel.: +371 67083320
e-mail: [email protected]
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Portugal: Fentanilo Kalceks
Poland:
Fentanyl Kalceks
Czech Republic:
Fentanyl Kalceks
Malta:
Fentanyl Kalceks 0.05 mg/mL solution for injection
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 01/2024
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Dosage
The dose of the medicine should be determined individually, depending on the patient's age, weight, physical condition, underlying disease, concomitant medicines, and type of surgical procedure and anesthesia used.
- As an analgesic to supplement general anesthesia: In low doses for minor surgical procedures: 2 micrograms of fentanyl per kilogram of body weight. Moderate dose: 2 to 20 micrograms of fentanyl per kilogram of body weight. In high doses during major surgical procedures: 20 to 50 micrograms of fentanyl per kilogram of body weight. The duration of the effect depends on the dose administered. It has been shown that during major surgical procedures, administration of 20 to 50 micrograms of fentanyl per kilogram of body weight with a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen has a sparing effect. When these doses are used during surgery, it is necessary to ensure postoperative ventilation of the patient and monitor their condition due to prolonged respiratory depression in the postoperative period. Depending on the requirements of the individual patient and the duration of the surgical procedure, 25 to 250 micrograms (0.5 to 5 mL) of fentanyl can be administered as a supplement.
- As an anesthetic: In cases where it is particularly important to suppress the body's response to stress associated with the surgical procedure, fentanyl doses of 50 to 100 micrograms/kg can be administered with oxygen and a muscle relaxant. This allows anesthesia to be performed without the use of additional anesthetics. In some cases, it may be necessary to administer fentanyl in doses of up to 150 micrograms/kg to achieve an anesthetic effect. In this way, fentanyl is used in open-heart surgery and some other major surgical procedures in patients for whom myocardial protection is particularly indicated.
Use in elderly or very weak patients
In this group of patients, the initial dose should be reduced. When determining additional doses, the response to the initial dose should be taken into account. To prevent bradycardia, it is recommended to administer a small intravenous dose of an anticholinergic agent directly before induction of anesthesia. To prevent nausea and vomiting, droperidol can be administered.
Use in patients with impaired liver function
In patients with impaired liver function, it is recommended to carefully and gradually adjust the dose of fentanyl.
Use in patients with impaired renal function
In patients with impaired renal function, it is recommended to carefully and gradually adjust the dose of fentanyl.
Use in children and adolescents
Children aged 2 to 11 years
The usual dosing regimen in children is as follows:
Age
Initial dose
Supplemental dose
Spontaneous breathing
2-11 years
1-3 micrograms/kg
1-1.25 micrograms/kg
Assisted ventilation
2-11 years
1-3 micrograms/kg
1-1.25 micrograms/kg
Children aged 12 to 17 years
Dosing is the same as for adults.
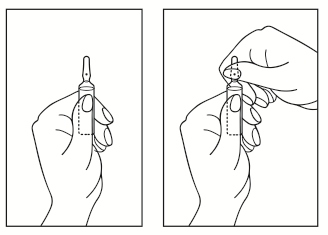
Instructions for opening the ampoule:
- 1. Turn the ampoule with the colored dot upwards. If there is a solution in the upper part of the ampoule, gently tap the ampoule wall with your finger so that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
- 2. To open the ampoule, use both hands; holding the lower part of the ampoule with one hand, break off the upper part of the ampoule with the other hand, in the direction away from the colored dot (see illustrations below).
Incompatibilities:
If necessary, fentanyl can be mixed with sodium chloride solution (0.9%) or glucose solution (5%) for intravenous infusions. Such solutions are compatible with the plastic equipment used for infusions.
Overdose
Symptoms
Symptoms of fentanyl overdose are a continuation of its pharmacological effect. Depending on individual sensitivity, the clinical picture is mainly determined by the degree of respiratory depression, which can range from slowed breathing to apnea.
Management
Slowed breathing or apnea: oxygen administration, assisted or controlled ventilation.
Respiratory depression: administration of a specific opioid antagonist (e.g., naloxone). This does not exclude the use of other immediate measures.
Respiratory depression may last longer than the effect of the antagonist, so additional doses of the antagonist may be necessary.
Muscle stiffness: administration of a neuromuscular blocking agent to facilitate assisted or controlled ventilation .
The patient should be closely monitored, maintaining adequate body temperature and fluid supply. In case of severe or persistent hypotension, consider the possibility of hypovolemia, and if confirmed, correct it with intravenous administration of an appropriate infusion solution.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAS Kalceks
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Fentanil KalceksDosage form: Solution, 5 mcg/ml (50 mcg/10 ml)Active substance: sufentanilPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 50 mcg/ml, (250 mcg/5 ml, 1 mg/20 ml)Active substance: sufentanilPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 5 mcg/mlActive substance: sufentanilManufacturer: hameln rds a.s. HBM Pharma s.r.o. Siegfried Hameln GmbHPrescription not required
Alternatives to Fentanil Kalceks in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fentanil Kalceks in Ukraine
Alternative to Fentanil Kalceks in Spain
Online doctors for Fentanil Kalceks
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fentanil Kalceks – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














