ESTRADOT 25 micrograms/24 hours, transdermal patch


How to use ESTRADOT 25 micrograms/24 hours, transdermal patch
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Estradot 25 micrograms/24 hours transdermal patch
Estradiol (as hemihydrate)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information:
- What is Estradot and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Estradot
- How to use Estradot
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Estradot
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Estradot and what is it used for
Estradot is a Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) that contains the female hormone estrogen.
Estradot is used in postmenopausal women who have been through menopause at least 12 months since their last natural period.
Estradot comes as a patch that you apply to your skin.
Estradot is used to:
Relieve symptoms of menopause
During menopause, the amount of estrogen produced by the body decreases. This can cause symptoms such as sudden hot flashes in the face, neck, and chest. Estradot relieves these symptoms after menopause. You will only be prescribed Estradot if your symptoms seriously affect your daily life.
2. What you need to know before you use Estradot
Medical history and regular check-ups
The use of HRT involves risks that need to be considered when deciding whether to use it or to continue treatment.
Experience in treating women with premature menopause (due to ovarian failure or surgery) is limited. If you have premature menopause, the risks of using HRT may be different. Please consult your doctor.
Before starting (or restarting) HRT, your doctor will ask about your personal and family medical history. Your doctor may decide to perform a physical examination. This may include a breast examination and/or an internal examination, if necessary.
Once you start treatment with Estradot, you should see your doctor for regular check-ups (at least once a year). During these check-ups, discuss the benefits and risks of continuing Estradot with your doctor.
Have regular breast checks as recommended by your doctor.
Do not useEstradot
if any of the following applies to you. If you are not sure about any of the points below, consult your doctorbefore using Estradot.
Do not use Estradot:
- if you have or have had breast cancer, or if there is a suspicion that you may have it;
- if you have an estrogen-dependent cancer, such as cancer of the lining of the uterus (endometrium), or if there is a suspicion that you may have it;
- if you have abnormal vaginal bleeding;
- if you have an over-thickening of the lining of the uterus(endometrial hyperplasia) for which you are not receiving treatment;
- if you have or have had a blood clot in a vein(thrombosis), such as in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism);
- if you have a blood clotting disorder(such as protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency);
- if you have or have recently had a disease caused by blood clots in the arteries, such as a heart attack, stroke, or angina;
- if you have or have had a liver diseaseand your liver function tests have not returned to normal;
- if you have a rare blood disorder called porphyriathat is inherited from your parents;
- if you are allergic(hypersensitive) to estradiol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6 Contents of the pack and other information);
If you experience any of the conditions mentioned above for the first time while using Estradot, stop treatment immediately and consult your doctor right away.
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor if you suffer or have suffered from any of the following conditions before starting treatment, as they may come back or get worse during treatment with Estradot. In that case, you should see your doctor more often for regular check-ups:
- fibroids in the uterus;
- growth of the lining of the uterus outside the uterus (endometriosis) or a history of over-thickening of the lining of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia);
- increased risk of developing blood clots (see "Blood clots in a vein (thrombosis)");
- increased risk of developing an estrogen-dependent cancer (such as breast cancer, especially if your mother, sister, or grandmother has had breast cancer);
- high blood pressure;
- liver disorder, such as a benign tumor in the liver;
- diabetes;
- gallstones (cholelithiasis);
- migraine or severe headache;
- a disease that affects the immune system and various organs of the body (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE);
- epilepsy;
- asthma;
- a disease that affects the eardrum and ear (otosclerosis);
- a very high level of fat in your blood (triglycerides);
- fluid retention due to heart or kidney problems;
- hereditary and acquired angioedema.
Stop using Estradot and see a doctor immediately.
If you experience any of the following while using HRT:
- any of the conditions mentioned in the 'Do not use Estradot' section
- yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes (jaundice). This may be a sign of liver disease
- swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, and difficulty swallowing or hives accompanied by difficulty breathing, which suggest angioedema;
- a significant increase in your blood pressure (symptoms may be headache, fatigue, dizziness)
- migraine-like headaches that occur for the first time
- if you become pregnant
- if you notice signs of a blood clot, such as:
- painful swelling and redness of the legs;
- sudden chest pain;
- difficulty breathing.
For signs of a blood clot, see "Stop using Estradot and see a doctor immediately".
Note: Estradot is not a contraceptive. If you have been through menopause less than 12 months ago or are under 50 years old, you may still need to use additional contraceptive measures to prevent pregnancy. Talk to your doctor for advice.
HRT and cancer
Thickening of the lining of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia) and cancer of the lining of the uterus (endometrial cancer)
Taking HRT with estrogen-only products will increase the risk of thickening of the lining of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia) and cancer of the lining of the uterus (endometrial cancer).
Adding a progestogen to estrogen-only HRT for at least 12 days of each 28-day cycle will protect you from this extra risk. Therefore, your doctor will prescribe a progestogen separately if you still have your uterus. If you have had a hysterectomy, ask your doctor if you can be treated safely with this medicine without the use of a progestogen.
In women between 50 and 65 years old who still have their uterus and are not taking HRT, about 5 in 1000 will be diagnosed with endometrial cancer.
In women between 50 and 65 years old who still have their uterus and are taking estrogen-only HRT, between 10 and 60 in 1000 will be diagnosed with endometrial cancer (i.e., between 5 and 55 extra cases), depending on the dose and duration of therapy.
Unexpected bleeding
You will experience monthly bleeding (called withdrawal bleeding) while using Estradot with a progestogen. However, if you experience any of the following, see your doctor as soon as possible:
- bleeding or spotting that continues for more than the first 6 months;
- bleeding or spotting that starts after you have been using Estradot for more than 6 months;
- bleeding or spotting that continues after you stop using Estradot;
Breast cancer
Evidence shows that using combined estrogen-progestogen HRT or estrogen-only HRT increases the risk of breast cancer. The extra risk depends on how long you use HRT. The extra risk becomes apparent within 3 years of use. After stopping HRT, the extra risk will decrease over time but may persist for 10 years or more if you have used HRT for more than 5 years.
Comparison
In women between 50 and 54 years old who are not using HRT, about 13 to 17 in 1000 will be diagnosed with breast cancer over a 5-year period.
In women starting estrogen-only HRT at age 50 for 5 years, there will be between 16 and 17 cases per 1000 users (i.e., between 0 and 3 extra cases).
In women starting combined estrogen-progestogen HRT at age 50 for 5 years, there will be about 21 cases per 1000 users (i.e., between 4 and 8 extra cases).
In women between 50 and 59 years old who are not taking HRT, about 27 cases of breast cancer per 1000 women will be diagnosed over a 10-year period.
In women starting estrogen-only HRT at age 50 for 10 years, there will be about 34 cases per 1000 users (i.e., 7 extra cases).
In women starting combined estrogen-progestogen HRT at age 50 for 10 years, there will be about 48 cases per 1000 users (i.e., 21 extra cases).
- Examine your breasts regularly. See your doctor if you notice any change, such as:
- grooves or dimpling of the skin;
- changes in the nipples;
- any lump that you can see or feel.
Additionally, you are advised to participate in breast screening programs. During breast screening, it is essential to inform the nurse or healthcare professional performing the X-ray that you are using HRT, as this medication may increase breast density, which can affect the result of the mammogram. When breast density increases, the mammogram may not detect all lumps.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is less common than breast cancer. Using HRT with estrogen-only or combined estrogen-progestogen therapy has been associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The risk of ovarian cancer varies with age. For example, in women between 50 and 54 years old who are not using HRT, about 2 cases of ovarian cancer per 2000 women will be diagnosed over a 5-year period. In women using HRT for 5 years, about 3 cases per 2000 users will be diagnosed (i.e., about 1 extra case).
Effect of HRT on the heart and circulation
Blood clots in a vein (thrombosis)
The risk of blood clots in the veins is about 1.3 to 3 times higher for HRT users than for non-users, especially during the first year of treatment.
Blood clots can be serious and, if one travels to the lungs, can cause chest pain, difficulty breathing, fainting, or even death.
You are more likely to develop a blood clot in your veins with age and if you experience any of the following. Inform your doctor if any of the following apply to you:
- you are unable to walk for a long time due to major surgery, injury, or illness (see also section 3, If you need to have surgery);
- you are significantly overweight (BMI >30 kg/m2);
- you have a blood clotting disorder that requires long-term treatment with a medicine used to prevent blood clots;
- any of your close relatives have had a blood clot in a leg, lung, or other organ;
- you have systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE);
- you have cancer.
For signs of a blood clot, see "Stop using Estradot and see a doctor immediately".
Comparison
In women in their 50s who are not taking HRT, about 4 to 7 in 1000 will have a blood clot in a vein over a 5-year period.
In women in their 50s who take combined estrogen-progestogen HRT for 5 years, about 9 to 12 cases per 1000 users will occur (i.e., 5 extra cases).
In women in their 50s who have had a hysterectomy and are treated with estrogen-only HRT for 5 years, about 5 to 8 cases per 1000 users will occur (i.e., 1 extra case).
Heart disease (heart attack)
There is no evidence that HRT prevents heart attacks.
Women over 60 years old using combined estrogen-progestogen HRT have a slightly higher risk of developing heart disease than non-users.
In women who have had a hysterectomy and are using estrogen-only HRT, there is no increased risk of developing heart disease.
Stroke
The risk of having a stroke is about 1.5 times higher for women using HRT than for non-users. The number of extra stroke cases will increase with age.
Comparison
In women in their 50s who are not taking HRT, about 8 in 1000 will have a stroke over a 5-year period. In women in their 50s who are using HRT, about 11 in 1000 will have a stroke over a 5-year period (i.e., 3 extra cases).
Other conditions
- HRT does not prevent memory loss. There is some evidence of an increased risk of memory loss in women who start HRT after the age of 65. Talk to your doctor for advice.
Other medicines and Estradot
Some medicines may interfere with the effect of Estradot. This may cause irregular bleeding. This occurs with the following medicines:
- Medicines for epilepsy (such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine);
- Medicines for tuberculosis (such as rifampicin, rifabutin);
- Medicines for HIV infection (such as nevirapine, efavirenz, ritonavir, nelfinavir);
- Preparations containing the herbal remedy St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum);
HRT may affect the performance of other medicines:
- A medicine for epilepsy (lamotrigine), as it may increase the frequency of seizures.
- Other anti-infective medicines (such as ketoconazol, erythromycin).
- The combined hepatitis C virus (HCV) regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir with or without ribavirin; glecaprevir/pibrentasvir or sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (see section 4.4) may cause elevations in liver function blood test results (increase in liver enzyme ALT) in women using CHC containing ethinylestradiol. Estradot contains estradiol instead of ethinylestradiol. It is not known whether an increase in liver enzyme ALT can occur when using Estradot with this combined HCV regimen. Your doctor will inform you about this.
Please inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription, herbal medicines, or other natural products. Your doctor will inform you about this.
Lab tests
If you need a blood test, tell your doctor or the laboratory staff that you are using Estradot, as this medicine may affect the results of some tests.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Estradot is a medicine for postmenopausal women only. If you become pregnant, stop treatment with Estradot and contact your doctor.
Do not use Estradot if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Estradot has no known effects on the ability to drive or use machines.
3. How to use Estradot
Follow the administration instructions for this medication exactly as indicated by your doctor. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have any doubts.
Your doctor will try to prescribe the lowest dose to treat your symptom for the shortest possible time. Talk to your doctor if you think this dose is too strong or insufficient.
How long should you use Estradot
It is essential to use the lowest effective dose and only for as long as necessary.
Periodically, you should discuss the potential risks and benefits associated with using Estradot with your doctor and determine if you still need this treatment.
When to start treatment
- If you are not currently using any hormone replacement therapy (patches or tablets), or if you have been using a continuous combined hormone replacement therapy product (in which estrogen and progestogen are administered every day without interruption), you can start using Estradot on any day.
- If you are switching from a cyclic or sequential hormone replacement therapy (in which progestogen is added for 12-14 days of the cycle), you should start using Estradot the day after completing your previous regimen.
When to apply Estradot
- Each Estradot patch should be changed twice a week (every 3 to 4 days). It is best to always change it on the same two days of the week (e.g., Monday and Thursday). The Estradot package contains a calendar-control on the back that will help you remember your schedule. Mark the two-day-a-week schedule you want to follow. Always change the patch on the two days of the week you have marked.
- You should wear the Estradot patch continuously until it is time to change it for a new patch.
Any adhesive that remains on the skin can be easily removed by friction. If this happens, place a new Estradot patch in another area of the skin.
Women who have had a hysterectomy
The Estradot patch should be applied continuously without interruption. There is no need to add another type of hormone called progestogen, unless there is growth of the endometrium outside the uterus (endometriosis). Check the risks to consider with hormone replacement therapy in section 2, Warnings and precautions.
Women who still have their uterus
Your doctor will prescribe another hormone for you to take with Estradot, called progesterone, to reduce the risk of uterine cancer. If you apply Estradot continuously without interruption, the progesterone tablet should be taken for at least 12-14 days each month/28-day cycle. Check the risks to consider with hormone replacement therapy in section 2, Warnings and precautions.
You may experience irregular bleeding or spotting during the first few months of treatment. If you have heavy bleeding or the bleeding or spotting continues after a few months of treatment, talk to your doctor so that they can reevaluate your treatment if necessary (see section 2, Unexpected bleeding).
Where to apply Estradot
Apply the patch to the lower abdomen, below the waistline. Avoid the waistline, as clothing may cause the patch to peel off. Do not apply the patch to the breasts or near the breasts.
When changing the patch, according to your twice-a-week schedule, apply the new patch to a different area. Do not apply a new patch to the same area for at least one week.
Before applying Estradot, make sure your skin is:
- clean, dry, and cool,
- free of any dust, oil, cream, or lotion,
- free of cuts and/or irritations.
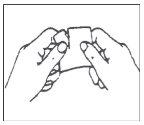
How to apply Estradot
Each patch is individually sealed in a protective pouch. Open the pouch at the slit and remove the patch (do not use scissors to open the pouch as they may damage the patch).
| |
A protective film covers the adhesive face of the patch. This film should be removed before applying the patch to the skin. Apply the patch immediately after opening the pouch and removing the protective film. Take the patch with the protective film facing you. Peel off half of the protective layer and discard it. Try to avoid touching the adhesive face of the patch with your fingers.
| |
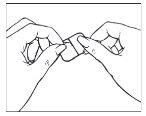
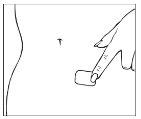
Take the other half of the protective film, apply the adhesive part of the patch to a dry area of the lower abdomen. Press the adhesive part against the skin to ensure it adheres properly, especially at the edges. Remove the other part of the protective film.
| |
Hold the straight edge of the protective film and peel it off the patch.
| |
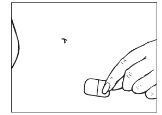
Press the adhesive part against the skin to ensure it adheres properly. Press the patch firmly onto the skin with the palm of your hand for at least 10 seconds.
| |
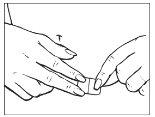
Make sure the patch has been placed correctly on the skin and run your fingers over the edges to check for good contact between the patch and the skin.
| |
When changing the patch, peel it off, and fold it in half with the adhesive side inward. See section 5, "Storage of Estradot" for instructions on how to safely dispose of the patch. Do not throw used patches down the toilet.
Additional practical information
If the patch has been applied correctly, it should not affect bathing, swimming, showering, or exercising. If a patch comes off, for example during bathing or showering, move it to eliminate water. After drying and letting the skin cool, you can apply the same patch to a different area of the skin on the lower abdomen (see "Where to apply Estradot").
If the patch does not adhere completely to the skin, use a new patch. Regardless of the day it happens, change this patch on the same day according to the initial schedule.
When sunbathing or using a sunbed, you should cover the patch. When bathing, you can wear the patch under your swimsuit.
If you need surgery
If you are going to undergo surgery, tell your surgeon that you are using Estradot. You may need to stop using Estradot 4 to 6 weeks before the operation to reduce the risk of blood clots (see section 2, Blood clots in a vein). Ask your doctor when you can start Estradot treatment again.
If you use more Estradot than you should
If you have taken too much Estradot, you should remove the patch. The symptoms of overdose are usually breast pain and/or vaginal bleeding. An acute overdose is unlikely due to the route of administration of Estradot (the patch releases the drug gradually). If the symptoms persist, you should contact your doctor.
If you forget to use Estradot
If you forgot to change the patch, apply another patch as soon as you remember. Regardless of the day it happens, change the patch on the same days as in the initial schedule.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed application.
If you stop using Estradot
Stopping treatment with Estradot may increase the risk of irregular bleeding or spotting. Inform your doctor if this happens. After a prolonged period without treatment, you should consult your doctor before starting to use the patch again.
If you have any other questions about using this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following diseases are observed more frequently in women treated with HRT compared to women not treated with HRT:
- breast cancer;
- abnormal growth of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia) or cancer of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrial cancer);
- ovarian cancer;
- blood clots in the veins of the legs or lungs (venous thromboembolism);
- heart disease;
- stroke;
- memory loss likely if HRT is started from the age of 65.
For more information on these side effects, see section 2.
Some side effects can be serious
The following symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- Sudden chest pain;
- Chest pain that spreads to the arm or neck;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Painful swelling and redness of the legs;
- Yellowing of the eyes and face, darkening of urine, itching of the skin (jaundice);
- Unexpected bleeding or spotting after using Estradot for some time or if it continues after stopping treatment;
- Changes in the breasts, such as alteration of breast skin, changes in the nipples, lumps that you can see or feel (breast cancer);
- Heavy menstrual periods;
- Unexplained migraine-type headaches.
Stop using Estradot and contact your doctor immediatelyif you experience any of the above side effects.
Check the risks to consider with hormone replacement therapy in section 2, Warnings and precautions.
Other side effects
Estradot can also cause the following side effects. If you think any of the side effects you are experiencing is serious, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Very common side effects,may affect more than 1 in 10 people:
Headache, skin reactions at the patch application site (including irritation, burning, rash, dryness, bleeding, bruising, inflammation, swelling, skin discoloration, hives, and blisters), breast tension and pain, menstrual pain, menstrual changes.
Common,may affect up to 1 in 10 people:
Depression, nervousness, mood changes, insomnia, nausea, indigestion, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, acne, rash, dry skin, itching, breast growth, heavy menstrual periods, discharge of a thick white or yellowish liquid from the vagina, irregular bleeding, severe uterine contractions, vaginal inflammation, abnormal growth of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia), pain (e.g., back, arm, leg, wrist, ankle pain), weakness, fluid retention (edema) in the limbs (arms and legs), weight changes.
Uncommon,may affect up to 1 in 100 people:
Migraine, dizziness, increased blood pressure, vomiting, skin discoloration, altered liver function.
Rare,may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people:
Numbness or tingling of hands and feet, blood clots, gallstones, hair loss, muscle weakness, benign growth of the uterus, cysts near the uterine tubes, polyps (small lumps) on the cervix of the uterus (cervix), changes in sexual desire, allergic reactions such as rashes.
Very rare,may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people:
Hives, signs of severe allergic reaction (including difficulty breathing; swelling of the face, tongue, throat, or skin; dizziness and hives), decreased glucose tolerance, involuntary movements that can affect the eyes, head, and neck, discomfort with contact lens use, severe skin reactions, excessive hair growth.
Side effects of unknown frequency(cannot be estimated from the available data):
Breast cancer, abnormal liver function test, allergic skin inflammation, breast lumps (non-cancerous).
The following side effects have been reported in association with other hormone replacement therapies:
- gallbladder disease
- various skin disorders:
- skin discoloration, especially on the face or neck, known as "pregnancy spots" (chloasma);
- painful and inflamed nodules on the skin (erythema nodosum);
- skin rash with redness in a target shape or blisters (erythema multiforme);
- decreased memory or mental ability (possible dementia)
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible side effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines and Healthcare Products Agency (AEMPS) https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Estradot
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Store Estradot in its original pouch, in a cool and dry place. Once opened or once the protective film has been removed, apply the patch to the skin immediately.
- Do not refrigerate or freeze Estradot.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the pouch after CAD/EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Do not use this medicine if you notice that the packaging is damaged or shows signs of tampering.
- After removing the patch, fold it in half with the adhesive side inward and keep it in a safe place out of the reach of children. Used or unused transdermal patches should be disposed of according to local regulations or returned to the pharmacy, preferably in their original packaging.
- Medicines should not be thrown down the drain or into the trash. Deposit the packaging and medicines you no longer need at the SIGRE collection point in the pharmacy. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and additional information
Composition of Estradot
Each 25 microgram/24 hour transdermal patch contains 0.39 mg of estradiol (as hemihydrate) and releases approximately 25 micrograms of estradiol every 24 hours.
- The active ingredient is estradiol (as hemihydrate).
- The other components of the patch adhesive layer are: acrylic adhesive, silicone adhesive, oleic acid, dipropylene glycol, povidone (E1201).
- The backing layer is an ethylene/vinyl acetate copolymer and a laminated vinylidene chloride/methyl acrylate copolymer.
- The protective film (which is removed before applying the patch) is a polyester film coated with fluoropolymer.
Appearance and packaging of the product
Estradot 25 is a rectangular patch of 2.5 cm2 with rounded edges, consisting of a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer containing estradiol, a translucent backing layer on one side, and a protective film on the other.
Estradot is available in four different concentrations: 25, 37.5, 50, and 75 micrograms/24 hours. Not all concentrations may be available.
Estradot is available in packs of 2, 8, 24, and 26 patches. Not all pack sizes may be available.
Marketing Authorization Holder
BEXAL FARMACÉUTICA, S.A.
Centro Empresarial Parque Norte
Edificio Roble
C/ Serrano Galvache, 56
28033 Madrid
Spain
Manufacturer
Novartis Farmacéutica, S.A.
Gran Vía de les Corts Catalanes, 764
08013 Barcelona
Spain
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
D-90429 Nürnberg
Germany
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Austria: Estradot
Denmark: Vivelle dot
Finland: Estradot
France: Vivelledot
Croatia: Estradot
Iceland: Vivelle dot
Ireland: Estradot
Norway: Estradot
Portugal: Estradot
Spain: Estradot
Sweden: Estradot
United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): Estradot
Date of last revision of this leaflet:May 2025
Other sources of information
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Healthcare Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Availability in pharmacies
Supply issue reported
Data from the Spanish Agency of Medicines (AEMPS) indicates a supply issue affecting this medicine.<br><br>Availability may be limited in some pharmacies.<br><br>For updates or alternatives, consult your pharmacist. - Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ESTRADOT 25 micrograms/24 hours, transdermal patchDosage form: GEL, 0.5 mgActive substance: estradiolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: GEL, 1 mgActive substance: estradiolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 3 mgActive substance: estradiolManufacturer: Merus Labs Luxco Ii S.À.R.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for ESTRADOT 25 micrograms/24 hours, transdermal patch
Discuss questions about ESTRADOT 25 micrograms/24 hours, transdermal patch, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions