
EPREX 1000 IU/0.5 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION

How to use EPREX 1000 IU/0.5 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
EPREX 1,000 UI/0.5 ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
EPREX 2,000 UI/0.5 ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
EPREX 3,000 UI/0.3 ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
EPREX 4,000 UI/0.4 ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
EPREX 10,000 UI/ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
EPREX 40,000 UI/ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
(epoetin alfa)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What EPREX is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use EPREX
- How to use EPREX
- Possible side effects
- Storage of EPREX
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What EPREX is and what it is used for
EPREX contains the active substance epoetin alfa, a protein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells, which carry haemoglobin (a substance that carries oxygen). Epoetin alfa is a copy of human erythropoietin and works in the same way.
- EPREX is used to treat symptomatic anaemia due to kidney disease
- in children on haemodialysis,
- in adults on haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis,
- in adults with severe anaemia who have not yet undergone dialysis.
If you have kidney disease and your kidney does not produce enough erythropoietin (necessary for the production of red blood cells), you may have anaemia. EPREX is prescribed to stimulate your bone marrow to produce more red blood cells.
- EPREX is used to treat anaemia in adults receiving chemotherapy for solid tumours, malignant lymphoma, or multiple myeloma (bone marrow cancer) that requires a blood transfusion. EPREX may reduce the need for blood transfusions in these patients.
- EPREX is used in adults with moderate anaemia who are donating their own blood before surgeryso that it can be transfused back to them during or after surgery. As EPREX stimulates the production of red blood cells, doctors can take more blood from these patients.
- EPREX is used in adults with moderate anaemia who are about to undergo major elective orthopaedic surgery(e.g. knee or hip replacement operations),to reduce the possible need for blood transfusions.
EPREX is used to treat anaemia in adults with a bone marrow disorder that causes a severe disruption in the production of blood cells (myelodysplastic syndromes).EPREX may reduce the need for blood transfusions.
2. What you need to know before you use EPREX
Do not use EPREX
- If you are allergicto epoetin alfa or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have been diagnosed with Pure Red Cell Aplasia(the bone marrow cannot produce enough red blood cells) after previous treatment with any product that stimulates the production of red blood cells (including EPREX). See section 4, Possible side effects.
- If you have high blood pressurethat is not adequately controlled with medication.
- To stimulate the production of red blood cells (so that your doctor can take more blood from you) if you cannot receive transfusions of your own bloodduring or after surgery.
- If you are about to undergomajor elective orthopaedic surgery(such as a knee or hip replacement) and:
- you have severe heart disease
- you have severe problems with your veins and arteries
- you have recently had a heart attack or stroke
- you cannot take medicines to thin your blood.
You may not be suitable for EPREX. Consult your doctor. While receiving EPREX, some patients may need to take medicines to reduce the risk of blood clotting. If you cannot take medicines that prevent blood clotting, you should not use EPREX.
Warnings and precautions
Be careful with EPREX
EPREX and other products that stimulate the production of red blood cells may increase the risk of blood clots in all patients.This risk may be higher if you have other risk factors (e.g. if you have had a blood clot in the past or if you are overweight, if you have diabetes, if you have heart disease, or if you are immobile for a long time due to surgery or illness).Please discuss this with your doctor. Your doctor will help you decide if EPREX is suitable for you.
It is important that you inform your doctorif you have any of the following. You may still be able to use EPREX, but consult your doctor first.
- If you know that you haveor have had:
- high blood pressure;
- seizuresor epileptic fits
- a liver disease
- anaemia due to other causes
- porphyria (a rare blood disorder)
- a latex allergy. The needle cap of this medicine contains latex, which may cause severe allergic reactions in people sensitive to latex. See section 4 for signs of an allergic reaction.
- If you are a patient with chronic kidney disease, and especially if you do not respond adequately to treatment with EPREX, your doctor will review your EPREX dose, as repeated increases in the EPREX dose when there is no response to treatment may increase the risk of heart or blood vessel problems and may increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death.
- If you are a cancer patient, you should know that products that stimulate the production of red blood cells (such as EPREX) may act as a growth factor and may, in theory, affect the progression of your cancer. Depending on your personal situation, a blood transfusion may be preferable.Discuss this with your doctor.
- If you are a cancer patient,you should know that the use of EPREX may be associated with lower survival and higher mortality rates in patients with head and neck cancer, metastatic breast cancer, who receive chemotherapy.
- Severe skin reactions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been observed with the administration of epoetins.
SJS/TEN can initially appear as red, circular patches on the skin, often with central blisters, on the trunk. Ulcers on the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes (eye irritation and swelling) may also appear. These severe skin reactions are often preceded by fever or flu-like symptoms. The skin rash may progress to widespread skin peeling and potentially life-threatening complications.
If you experience a severe skin rash or any of these other skin symptoms, stop taking EPREX and contact your doctor or seek medical attention immediately.
Be careful with other products that stimulate the production of red blood cells:
EPREX belongs to a group of products that stimulate the production of red blood cells, like the human protein erythropoietin. Your doctor will always record the exact name of the product you are using.
If you are given a different product from this group during your treatment, inform your doctor or pharmacist before using it.
Other medicines and EPREX
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
If you are taking a medicine called ciclosporin(which is used, for example, after kidney transplants), your doctor may ask for blood tests to check your ciclosporin levels while you are taking EPREX.
Iron supplements and other blood stimulantsmay increase the effectiveness of EPREX. Your doctor will decide if it is suitable for you to take them.
If you go to hospital, a clinic, or your general practitioner, inform them that you are being treated with EPREX. It may affect other treatments or the results of some tests.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
It is important that you inform your doctorif any of the following apply to you. You will probably be able to continue using EPREX, but discuss it with your doctor first.
- If you are pregnantor think you may be pregnant.
- If you are breast-feeding.
EPREX contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose; this is essentially “sodium-free”.
EPREX contains polysorbate 80
This medicine contains a maximum of 0.30 mg of polysorbate 80 per syringe, equivalent to a concentration of 0.30 mg/ml. Polysorbates may cause allergic reactions. Inform your doctor if you or your child have any known allergies.
3. How to use EPREX
Follow your doctor's administration instructions for this medication exactly. If in doubt, consult your doctor again.
Your doctor has done blood testsand has decided that you need EPREX.
EPREX can be administered by injection:
- Eitherin a vein or a tube inserted into a vein (intravenously)
- Orunder the skin (subcutaneously).
Your doctor will decide how EPREX should be administered. Usually, injections are given by a doctor, nurse, or other healthcare professional. Some people, depending on the reason they need EPREX, may later learn to self-administer the injection under the skin: see Instructions for self-administering EPREX.
EPREX should not be used:
- after the expiration date on the label and outer packaging
The dose of EPREX you receive is based on your body weight in kilograms. The cause of your anemia is also a factor that your doctor will consider when deciding the correct dose.
Your doctor will monitor your blood pressureregularly while you are using EPREX.
People with kidney disease
- Your doctor will keep your hemoglobin levels between 10 and 12 grams/deciliter since high hemoglobin levels can increase the risk of blood clots and death. In children, hemoglobin levels should be kept between 9.5 and 11 grams/deciliter.
- The usual initial doseof EPREX in adults and children is 50 International Units (IU) per kilogram (/kg) of body weight three times a week.
- In patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis, EPREX can be administered twice a week.
- In adults and children, EPREX is administered as an injection into a vein or into a tube inserted into a vein. When this access (vein or tube) is not readily available, your doctor may decide that EPREX should be injected under the skin (subcutaneous injection). This also applies to patients on dialysis and patients who are not yet on dialysis.
- Your doctor will request regular blood tests to monitor your response to anemia treatment and adjust the dose, usually no more frequently than every four weeks. An increase in hemoglobin of more than 2 grams/deciliter in a four-week period should be avoided.
- After correcting anemia, your doctor will continue to monitor your blood regularly. They may make new adjustments to the dose and frequency of EPREX administration to maintain your response to treatment. Your doctor will use the lowest effective dose to control the symptoms of your anemia.
- If you do not respond adequately to EPREX, your doctor will review your dose and inform you if it is necessary to change your EPREX doses.
- If you are on a wider EPREX dosing interval (more than once a week), you may not maintain adequate hemoglobin levels and may need an increase in the dose or frequency of EPREX administration.
- It is possible that you will receive iron supplements before and during treatment with EPREX to make it more effective.
- If you are undergoing dialysis at the time of starting treatment with EPREX, it may be necessary to adjust your dialysis regimen. Your doctor will decide this.
Adults receiving chemotherapy
- Your doctor may start treatment with EPREX if your hemoglobin is 10 grams/deciliter or less.
- Your doctor will keep your hemoglobin levels between 10 and 12 grams/deciliter since high hemoglobin levels can increase the risk of blood clots and death.
- The initial dose is either150 IU per kilogram of body weight three times a week or450 IU per kilogram of body weight once a week.
- EPREX is administered subcutaneously.
- Your doctor will request blood tests and may adjust the dose, depending on your response to anemia treatment with EPREX.
- It is possible that you will receive iron supplements before and during treatment with EPREX to make it more effective.
- You will usually continue treatment with EPREX for a month after chemotherapy ends.
Adults donating blood for autotransfusion
- The usual doseis 600 IU per kilogram of body weight twice a week.
- EPREX is administered as an intravenous injection immediately after you have donated blood during the 3 weeks prior to surgery.
- It is possible that you will receive iron supplements before and during treatment with EPREX to make it more effective.
Patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery
- The recommended doseis 600 IU per kilogram of body weight once a week.
- EPREX is administered subcutaneously once a week for the 3 weeks prior to surgery and on the day of the operation.
- If for medical reasons it is necessary to reduce the interval until the operation, you will receive a daily dose of 300 IU/kg for a period of up to 10 days before the operation, on the day of the operation, and in the 4 days immediately after.
- Treatment will be discontinued if blood tests indicate that hemoglobin values are too high before the operation.
- It is possible that you will receive iron supplements before and during treatment with EPREX to make it more effective.
Adults with myelodysplastic syndrome
- Your doctor may start treatment with EPREX if your hemoglobin is less than or equal to 10 grams/deciliter. The goal of treatment is to keep your hemoglobin levels between 10 and 12 grams/deciliter since higher hemoglobin levels can increase the risk of blood clots and death.
- EPREX is administered subcutaneously.
- The initial dose is 450 IU per kilogram of body weight once a week.
- Your doctor will request blood tests and may adjust the dose, depending on your response to anemia treatment with EPREX.
Instructions for self-injecting EPREX
When starting treatment, EPREX is usually administered by medical or nursing staff. Later, your doctor may suggest that you or a caregiver learn to inject EPREX under the skin (subcutaneously).
- Do not attempt to inject the medication unless a doctor or nurse has taught you.
- Always use EPREX following your doctor's or nurse's exact instructions.
- Use EPREX only if it has been stored correctly – See section 5, Storage of EPREX.
- Before use, wait for the EPREX syringe to reach room temperature.This usually takes 15-30 minutes.
Draw only one dose of EPREX from each syringe.
If you inject EPREX under the skin (subcutaneously), the amount administered in each injection is usually not more than one milliliter (1 ml).
EPREX is administered alone and not mixed with other injectable liquids.
Do not shake EPREX syringes.Prolonged vigorous shaking can damage the product. Do not use the product if it has been shaken vigorously.
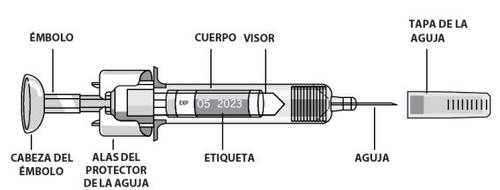
How to self-inject subcutaneously using a pre-filled syringe:
Pre-filled syringes have a needle protection device called PROTECS™ that helps prevent needle sticks after use. This is indicated on the box.
- Remove a syringe from the refrigerator.It is necessary for the liquid to reach room temperature. Do not remove the needle cap from the syringe while it is reaching room temperature.
- Check the syringeto ensure that the dose is correct, the expiration date has not been exceeded, it is not damaged, and the liquid is transparent and has not been frozen.
- Remove the detachable part of the syringe label.If you cannot see the graduation marks through the viewing window, hold the syringe body and gently turn the syringe by the needle cap to align the graduation marks with the viewing window.
- Choose the injection site.The most suitable places are the top of the thigh and around the abdomen (but away from the navel). Change the injection site from day to day.
- Wash your hands.Apply an antiseptic swab to the injection siteto disinfect it.
- Hold the pre-filled syringe by the syringe body with the needle cap pointing upwards.
- Do not hold it by the plunger head, plunger, needle protector wings, or needle cap.
- Do not pull the plunger at any time.
- Do not remove the needle cap from the pre-filled syringe until you are ready to inject EPREX.
- Remove the syringe capby holding the body and carefully pulling the needle cap without twisting. Do not touch the needle or shake the syringe.
- Eliminate the air bubble by holding the syringe with the needle pointing upwards and gently pressing the plunger until a drop of liquid comes out of the needle tip.
- If you only need a partial dose from the syringe as indicated by your doctor, press the plunger until the desired numbered graduation mark to eliminate the liquid you do not need before injection.
- Do not touch the needle protector wings to avoid premature activation of the needle protector.
- Hold a skin foldbetween your thumb and index finger. Do not squeeze it.
- Insert the entire needle.Your doctor or nurse will have shown you how to do this.
- Push the plunger with your thumb to the end to inject the total amount of liquid. Do this slowly and evenly, keeping the skin fold pinched. The PROTECS™ needle protector will not activate unless the entire dose is administered. You should hear a clickwhen the PROTECS™ needle protector is activated.
- When you have pressed the plunger to the end, remove the needle and release the skin fold.
- Slowly remove your thumb from the plungerto allow the syringe to move until the entire needle is covered by the PROTECS™ needle protector.
- When you remove the needle from your skin, you may bleed a little at the injection site. This is normal. You can pressthe injection site for several seconds with an antiseptic swabafter the injection.
- Dispose of the used syringein a safe container; see section 5, Storage of EPREX.
If you use more EPREX than you should
Inform your doctor or nurse immediately if you think you have injected too much EPREX. It is unlikely that adverse effects will occur as a result of an overdose of EPREX.
If you miss a dose of EPREX
Take the next injection as soon as possible. If it is less than 24 hours until the next injection, forget the missed one and continue with your normal schedule. Do not double the injections to make up for missed doses.
If you are a patient with Hepatitis C and are receiving interferon and ribavirin
You should consult your doctor, as the combination of epoetin alfa with interferon and ribavirin has led to rare cases of loss of efficacy and the development of a disorder called pure red cell aplasia (PRCA), a severe form of anemia. EPREX is not authorized for the management of anemia associated with hepatitis C.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Tell your doctor or nurse immediatelyif you notice any of the effects listed in this list.
Severe skin rashes, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been observed with the administration of epoetins. These reactions can appear as red, circular patches, often with central blisters on the trunk, skin peeling, and ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes, and may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms. Stop using EPREX if you experience these symptoms and contact your doctor or seek immediate medical attention. See also section 2.
Very common side effects
These may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- Diarrhea
- Stomach discomfort
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Respiratory tract congestion, such as a stuffy nose and sore throat, has been reported in patients with kidney disease not yet on dialysis.
Common side effects
These may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Increased blood pressure. Headaches, especially if they are migrainous, stabbing, and sudden, feeling of confusion or convulsionscan be signs of a sudden increase in blood pressure. This requires urgent treatment. High blood pressure may require treatment with medications (or adjustment of some medications you are already taking for hypertension).
- Blood clots(including deep vein thrombosis and embolism) that may require urgent treatment. Symptoms you may experience include chest pain, difficulty breathing, and painful swelling and redness, usually of a leg.
- Cough
- Skin rashes, which can be manifestations of an allergic reaction.
- Bone or muscle pain
- Flu-like symptoms, such as headache, pricking, and pain in the joints, feeling of weakness, chills, fatigue, and dizziness. These may be more frequent at the start of treatment. If you experience these symptoms during intravenous injection, a slower administration of the injection may help prevent them from occurring.
- Redness, burning, and pain at the injection site
- Swelling of the ankles, feet, or fingers
- Pain in the arm or leg
Uncommon side effects
These may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- High levels of potassium in the bloodthat can cause heart rhythm abnormalities (this is a very common side effect in patients on dialysis).
- Seizures
- Nasal or respiratory tract congestion
- Allergic reaction
- Hives
Rare side effects
These may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Symptoms of pure red cell aplasia (PRCA).
PRCA is the inability to produce enough red blood cells in the bone marrow. PRCA can cause sudden and severe anemia. Symptoms are:
- unusual tiredness,
- feeling of dizziness,
- difficulty breathing.
Very rare cases of PRCA have been reported, mainly in patients with kidney disease after months or years of treatment with EPREX and other products that stimulate red blood cell production.
- There may be an increase in the number of small blood cells (called platelets) that normally participate in the formation of blood clots, especially when treatment is started. Your doctor will check this.
- Severe allergic reactions that can include:
- swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat
- difficulty swallowing or breathing
- itchy rash (hives)
- A blood disorder that can cause pain, dark-colored urine, or increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight (porphyria).
If you are on hemodialysis:
- Blood clots(thrombosis) can form in the dialysis fistula (shunt). This is more common if you have low blood pressure or if your fistula has complications.
- Blood clotscan also form in your hemodialysis system. Your doctor may decide to increase your heparin dose during dialysis.
If you experience any of these effects or notice any other effects while being treated with EPREX, tell your doctor or nurse immediately.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any type of side effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible side effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of EPREX
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after the letters EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2 °C and 8 °C). You can take EPREX out of the refrigerator and store it at room temperature (up to 25°C) for 3 days. Once the syringe has been taken out of the refrigerator and has reached room temperature (up to 25°C), it must be used within 3 days or else it should be discarded.
Do not freeze or shake.
Store in the original package to protect it from light.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that the seal is broken or if the liquid has a coloration or particles can be seen in suspension. If you notice any of these things, discard the medicine.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and additional information
Composition of EPREX:
The active substance is:epoetin alfa (see quantities in the table).
The other ingredients are:polysorbate 80 (E 433), sodium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, disodium phosphate dihydrate, glycine, and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of EPREX and package contents
EPREX is presented as an injectable solution in a pre-filled syringe. The pre-filled syringes have a needle protection device PROTECS™ attached (see table below). EPREX is a clear and colorless solution.
Presentation | Equivalent presentations in quantity/volume for each concentration | Quantity of epoetin alfa |
Package with 6 pre-filled syringes with a needle protection device PROTECS™ | 1,000 IU/0.5 milliliters 2,000 IU/0.5 milliliters 3,000 IU/0.3 milliliters 4,000 IU/0.4 milliliters 5,000 IU/0.5 milliliters 6,000 IU/0.6 milliliters 8,000 IU/0.8 milliliters 10,000 IU/1 milliliter | 8.4 micrograms 16.8 micrograms 25.2 micrograms 33.6 micrograms 42.0 micrograms 50.4 micrograms 67.2 micrograms 84.0 micrograms |
Package with 1 pre-filled syringe with a needle protection device PROTECS™ | 20,000 IU/0.5 milliliters 30,000 IU/0.75 milliliters 40,000 IU/1 milliliter | 168 micrograms 252 micrograms 336 micrograms |
Package with 4 pre-filled syringes with a needle protection device PROTECS™ | 20,000 IU/0.5 milliliters 30,000 IU/0.75 milliliters 40,000 IU/1 milliliter | 168 micrograms 252 micrograms 336 micrograms |
Package with 6 pre-filled syringes with a needle protection device PROTECS™ | 20,000 IU/0.5 milliliters 30,000 IU/0.75 milliliters 40,000 IU/1 milliliter | 168 micrograms 252 micrograms 336 micrograms |
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder:
Janssen-Cilag, S.A.
Paseo del Club Deportivo 1, Edificio 16
28223 Pozuelo de Alarcón (Madrid)
Spain
Manufacturer:
Janssen Biologics BV
Einsteinweg 101
2333 CB
Leiden
Netherlands
This medicine is authorized in the EEA member states and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Austria: ERYPO
Belgium: EPREX
Germany: ERYPO
Greece: EPREX
France: EPREX
Italy: EPREX
Luxembourg: EPREX
Netherlands: EPREX
Portugal: EPREX
Spain: EPREX
United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): EPREX
This leaflet was approved in:January 2025.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to EPREX 1000 IU/0.5 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20000 IUActive substance: erythropoietinManufacturer: Sandoz GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20,000 IUActive substance: erythropoietinManufacturer: Sandoz GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 40,000 IU/ml of epoetin alfaActive substance: erythropoietinManufacturer: Sandoz GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for EPREX 1000 IU/0.5 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
Discuss questions about EPREX 1000 IU/0.5 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















