
CUTAQUIG 165 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION

How to use CUTAQUIG 165 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Cutaquig 165mg/mlsolution for subcutaneous injection
Human normal immunoglobulin (IgSC)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Cutaquig and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Cutaquig
- How to use Cutaquig
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Cutaquig
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Cutaquig and what is it used for
What is Cutaquig
Cutaquig belongs to a group of medicines called ‘human normal immunoglobulins’. Immunoglobulins are also known as antibodies and are proteins that are found in the blood of healthy people. Antibodies are part of the immune system (the body’s natural defence) and help your body to fight infections.
How Cutaquig works
Cutaquig contains immunoglobulins that have been prepared from the blood of healthy people. The medicine works in exactly the same way as the immunoglobulins that are found naturally in your blood.
What Cutaquig is used for
Cutaquig is used in patients who do not have enough antibodies to fight infections and therefore tend to get frequent infections. Regular administration of sufficient doses of Cutaquig can increase abnormally low immunoglobulin levels in your blood to normal levels (replacement therapy).
Cutaquig is prescribed to adults and children (aged 0 to 18 years) in the following situations:
Treatment of patients who are born with a reduced ability or inability to produce antibodies (primary immunodeficiency).
Patients with acquired antibody deficiency (secondary immunodeficiency) due to specific diseases and/or treatments and who experience severe or recurrent infections.
2. What you need to know before you use Cutaquig
Do not use Cutaquig:
- if you are allergic to human normal immunoglobulin or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
DO NOT inject Cutaquig into a blood vessel.
Warnings and precautions:
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Cutaquig.
You may be unknowingly allergic (hypersensitive) to immunoglobulins.
True allergic reactions, such as a sudden drop in blood pressure or anaphylactic shock (a sudden drop in blood pressure with other symptoms such as swelling of the throat, difficulty breathing and skin rash) are rare but can occur occasionally, even if you have received human immunoglobulins before and tolerated them well. They can occur especially if you do not have enough immunoglobulin A (IgA) in your blood (IgA deficiency) and have antibodies against IgA.
- Tell your doctor or healthcare professional before treatment to find out if you have an immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency. Cutaquig contains residual amounts of IgA that could cause an allergic reaction.
In these rare cases, allergic reactions can occur, such as a sudden drop in blood pressure or shock (see also section 4).
The signs and symptoms of these rare allergic reactions include
- Feeling of fainting, dizziness or weakness
- Skin rash and itching, swelling of the mouth or throat, difficulty breathing, wheezing
- Abnormal heart rhythm, chest pain, bluish discoloration of the lips or fingers
- Blurred vision
If you notice these signs during the infusion of Cutaquig, tell your doctor immediately.
He or she will decide whether to reduce the infusion rate or stop it altogether.
- Tell your doctor if you have a history of heart disease or blood vessel disease, or blood clots, thick blood or if you have been immobile for some time. These things can increase your risk of getting a blood clot after using Cutaquig. Also, tell your doctor what medicines you are using, as some medicines, such as those containing oestrogens (e.g. birth control pills), can increase your risk of developing a blood clot. Contact your doctor immediately if after receiving Cutaquig you experience signs and symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, pain and swelling of a limb, weakness or numbness on one side of the body.
- Contact your doctor if after receiving Cutaquig you experience the following signs and symptoms: severe headache, stiff neck, drowsiness, fever, photophobia, nausea and vomiting. These could be signs of aseptic meningitis. Your doctor will decide whether further tests are needed and whether to continue with Cutaquig.
- Cutaquig contains antibodies from the blood group that can cause the destruction of red blood cells and therefore anaemia (low red blood cell count).
Your healthcare professional will avoid possible complications by ensuring:
- that you are not sensitive to human normal immunoglobulin
The medicine should be infused slowly at first. The recommended infusion rate should be followed closely as indicated in section 3.
- that you are closely monitored for any symptoms during the infusion period, especially if:
- You are receiving human normal immunoglobulin for the first time
- You have changed from a different medicine to Cutaquig
- A long interval of time (more than eight weeks) has passed since the last infusion
In these cases, it is recommended that you are monitored during the first infusion and for one hour after. If the above points do not apply to you, it is recommended that you are observed for at least 20 minutes after administration.
Children and adolescents
The warnings and precautions listed apply to both adults and children.
Using Cutaquig with other medicines
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines.
- Do not mix Cutaquig with any other medicine.
- Before vaccination, tell the doctor who is going to vaccinate you about your treatment with Cutaquig. Cutaquig (like all human normal immunoglobulin solutions) may interfere with the effect of some live virus vaccines such as measles, rubella, mumps or chickenpox. Therefore, after receiving Cutaquig, you may need to wait up to 3 months before getting a live vaccine. In the case of measles vaccination, this may last for a year.
- Blood glucose test
Some types of blood glucose analysis systems (so-called glucose meters) misinterpret the maltose contained in Cutaquig as glucose. This can lead to falsely elevated glucose readings during an infusion or for a period of up to 15 hours after the end of the infusion and, as a consequence, the inappropriate administration of insulin, resulting in hypoglycaemia (i.e. a drop in blood sugar levels) that could be fatal. Similarly, actual cases of hypoglycaemia may not be treated if the hypoglycaemic state is masked by falsely elevated glucose readings.
As a result, when administering Cutaquig or other products containing maltose, blood glucose measurement should be performed with a system that uses a glucose-specific method. Systems based on glucose dehydrogenase pyrroloquinolinequinone (GDH PQQ) or glucose-colorimetric-oxidoreductase methods should not be used.
The product information of the blood glucose analysis system, including that of the test strips, should be carefully reviewed to determine if the system is suitable for use with parenteral products containing maltose. In case of doubt, consult your treating doctor to determine if the glucose analysis system you are using is suitable for use with parenteral products containing maltose.
Using Cutaquig with food, drinks and alcohol
No effects have been observed.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine. This product should only be used during pregnancy or breast-feeding after consulting your doctor or pharmacist.
No clinical studies have been conducted with Cutaquig in pregnant women. However, medicines containing immunoglobulins have been used in pregnant and breast-feeding women for years, and no adverse effects on the development of the pregnancy or the baby have been observed.
If you are breast-feeding and receive Cutaquig, the immunoglobulins in the medicine may also be found in breast milk. Therefore, your baby may be protected against certain infections.
Experience with immunoglobulins suggests that no adverse effects on fertility are to be expected.
Driving and using machines
The ability to drive and use machines may be affected by some side effects associated with Cutaquig. Patients who experience side effects during treatment should wait until they have resolved before driving or using machines.
Cutaquig contains sodium
This medicine contains 33.1 mg of sodium (a major component of table salt/cooking salt) per 48 ml vial and 13.8 mg per 20 ml vial. This is equivalent to 1.7% and 0.7% respectively of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
Information on the composition of Cutaquig
Cutaquig is made from human blood plasma (the liquid part of the blood). When medicines are made from blood or plasma, certain measures are taken to prevent infections from being transmitted to patients. These include:
- careful selection of blood and plasma donors to exclude those who may be at risk of carrying infections,
- testing of each donation and plasma pools for signs of virus/infections,
- the inclusion of steps in the processing of blood or plasma that can inactivate or remove viruses.
Despite these measures, when medicines prepared from human blood or plasma are administered, the possibility of transmitting an infection cannot be totally excluded. This also applies to any unknown or emerging virus or other types of infections.
The measures taken are considered effective against enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV, the virus that causes AIDS), hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus.
The measures taken may have a limited effect against non-enveloped viruses, such as hepatitis A virus and parvovirus B19.
Immunoglobulins have not been associated with hepatitis A or parvovirus B19 infections, possibly because the antibodies against these infections, which are contained in the product, are protective.
It is strongly recommended that every time you receive a dose of Cutaquig, the name and batch number of the medicine are recorded to keep a record of the batches used (see also Annex I: Instructions for administration).
3. How to use Cutaquig
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as told by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist again.
Cutaquig should be administered under the skin (subcutaneous administration or s.c.).
Treatment will be started by your doctor or nurse with experience in treating patients with a weak immune system.
Once your doctor/nurse has found the right dose and infusion rate for you and once you have received the first infusions under supervision, you may be allowed to administer the treatment at home or your caregiver (trained) may administer it to you. Your doctor or nurse with experience in guiding patients in their home treatment will ensure that you or your caregiver receive accurate training and information on
- the aseptic (sterile) infusion technique
- the use of the infusion device (if necessary)
- keeping a treatment diary
- what measures to take in case of serious side effects (see also section 4).
As soon as you can treat yourself, and if no side effects have occurred during treatment, your doctor may allow you to continue treatment at home.
Dosage
Your doctor will determine your individual dose and infusion rate, and adjust the dose especially for you, taking into account your weight, any previous treatment you have received and your response to treatment. Always follow the instructions of your doctor.
Replacement therapy in primary immunodeficiency syndromes:
Your doctor will determine if you need a loading dose (for adults and children) of at least 1.2 to 3.0 ml/kg body weight divided over several days. After that, you will receive Cutaquig regularly, from daily to every two weeks. The monthly cumulative dose will be approximately 2.4 to 4.8 ml/kg body weight. Your healthcare professional may adjust your dose depending on your response to treatment.
Replacement therapy in secondary immunodeficiencies:
The recommended dose of Cutaquig is a monthly cumulative dose of 1.2 – 2.4 ml/kg administered at repeated intervals (approximately once a week). It may be necessary to inject each individual dose at different anatomical sites. Your healthcare professional may adjust the dose based on your response to treatment.
Do not change the dose or infusion interval without consulting your doctor. If you think you should receive Cutaquig more or less frequently, talk to your doctor. If you think you have missed a dose, talk to your doctor as soon as possible.
Form and route of administration
Selection of the infusion site(s):
The recommended areas for subcutaneous infusion of Cutaquig are the abdomen, thighs, upper arms or upper leg/hip area. Multiple sites can be used for subcutaneous infusions at the same time. The number of infusion sites is unlimited, but they should be at least 5 cm apart. Rotate the sites with each administration as recommended by your doctor or nurse.
The amount infused per site is variable, but it is recommended to divide large infusion volumes (>30 ml) and perform the infusion at several sites. In infants and children, the infusion sites may be changed every 5 to 15 ml.
Infusion rate:
Your doctor will determine the appropriate infusion rate for you, taking into account your individual dose, dosing frequency and product tolerability.
The recommended initial infusion rate is 15 ml/h/site if you have not received IGSC treatment before. If you are already being treated with IGSC and are switching to Cutaquig, it is recommended to use the infusion rates used previously for the initial infusions. For subsequent infusions, if you tolerate it well, the infusion rate can be gradually increased by approximately 10 ml/h/site every 2-4 weeks in adults (≥ 40 kg) and up to 10 ml/h/site every 4 weeks in paediatric patients (<40 kg).< p>
After that, if you tolerate the initial infusions at the full dose per site and at the maximum rate, it may be considered to increase the infusion rate for subsequent infusions up to a maximum flow rate of 67.5 ml/h/site for adults (≥ 40 kg) and 25 ml/h/site for paediatric patients (<40 kg).< p>
Detailed instructions for use are provided below.
Cutaquig is intended for subcutaneous administration (under the skin) only. Do not inject into a blood vessel.
Use Cutaquig at home only when your healthcare professional has taught and trained you adequately.
Follow the administration instructions step by step as they appear at the end of the leaflet (Annex I) and use an aseptic/sterile technique when administering Cutaquig.
When preparing the infusion, wear gloves if you have been instructed to do so.
Use in children and adolescents
For children and adolescents (0 to 18 years), the same indications, dose and infusion frequency as for adults apply.
If you use more Cutaquig than you should
If you think you have infused too much Cutaquig, contact your healthcare professional as soon as possible.
If you miss a dose of Cutaquig
If you miss a dose, inform your doctor or healthcare professional as soon as possible. Do not infuse a double dose of Cutaquig to make up for the missed dose.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine may cause adverse effects, such as chills, headache, dizziness, fever, vomiting, allergic reactions, nausea, joint pain, low blood pressure, and moderate back pain, although not all people suffer from them.
Certain adverse effects, such as headache, chills, or body aches, may be reduced by decreasing the infusion rate.
No serious adverse reactions related to the medication were observed in subjects treated with Cutaquig during clinical trials that evaluated its safety.
You may be allergic (hypersensitive) to immunoglobulins, and allergic reactions, such as a sudden drop in blood pressure and, in isolated cases, shock, may occur. Doctors are aware of these possible adverse effects and will monitor you during and after initial infusions.
Inform your doctor immediately if you observe any of the following symptoms:
- Feeling of fainting, dizziness, or weakness
- Skin rash and itching, swelling of the mouth or throat, difficulty breathing, wheezing
- Abnormal heart rhythm, chest pain, bluish discoloration of the lips or fingers and toes
- Blurred vision
When using Cutaquig at home, you can perform the infusion in the presence of your caregiver, who will help you observe the signs of an allergic reaction. In case of any symptoms of an allergic reaction, stop the infusion and seek help if necessary.
Also, consult section 2 of this prospectus regarding the risk of allergic reactions.
The following adverse effects are very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 infusions):
- Reactions at the injection site, such as redness, swelling, itching, and discomfort.
The following adverse effects are uncommon (may affect between more than 1 in 1,000 and less than 1 in 100 infusions):
- Headache
- Nausea
- Fatigue
The following adverse effects are rare (may affect more than 1 in 10,000 infusions):
- Dizziness
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal distension
- Vomiting
- Retching
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Fever
- Chills
- Chest discomfort
- Flu-like illness
- Pain
- Feeling of general discomfort
- Positive blood test results for antibodies
- Abnormal blood test results showing destruction of red blood cells
- Increased hemoglobin
- Increased creatinine in blood
- Rash
- Skin reactions
- High levels of certain liver enzymes called transaminases
Other adverse effects that did not occur in clinical trials but have also been reported are:
- Hypersensitivity (e.g., erythema, urticaria)
- Increased blood pressure
- Problems due to the formation of blood clots in blood vessels (e.g., deep vein thrombosis, stroke)
- Blood clots in blood vessels (see also section 2 "Warnings and precautions")
- Itching
- Back pain
Adverse effects observed with similar medicines
The following additional adverse effects have been observed with the infusion of normal human immunoglobulin subcutaneously. It is possible that someone using this medicine may experience them.
- Pallor
- Chills
- Diarrhea
- Pain at the injection site
- Rapid redness of the neck/face
- Feeling of heat
- Feeling of cold
- Weakness
- Throat tightness
- Difficulty breathing
- Symptoms similar to asthma
- Cough
- Facial swelling
- A syndrome called aseptic meningitis (see also section 2 "Warnings and precautions")
Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms. They could be signs of a serious problem.
- Severe headache with nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, fever, and sensitivity to light. These could be signs of a non-infectious, temporary, and reversible inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meningitis).
- Pain, swelling, heat, redness, or a lump in the legs or arms, unexplained difficult breathing, chest pain, or discomfort that worsens with deep breathing, rapid pulse without explanation, numbness or weakness on one side of the body, sudden confusion, or speech problems. These could be signs of a blood clot.
Such adverse effects can occur even if you have received human immunoglobulin before and tolerated it well.
Also, consult section 2 for additional information on circumstances that increase the risk of adverse effects.
Reporting Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es
By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Cutaquig
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the label and packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the vial in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Within its validity period, the product can be stored at room temperature (do not store above 25°C) for up to 9 months without refrigeration during this period, and it must be discarded if not used after this period.
After the first opening, the product must be used immediately.
Do not use Cutaquig if the solution is cloudy or contains particles.
Medicines should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Cutaquig
The active ingredient is normal human immunoglobulin 165 mg/ml (at least 95% is immunoglobulin G)
- IgG1 ……….. 71%
- IgG2 ……….. 25%
- IgG3 ……….. 3%
- IgG4 ……….. 2%
The other excipients are maltose, polysorbate 80, and water for injectable preparations.
The maximum content of IgA is 300 micrograms/ml
Cutaquig contains ≤30 mmol/l of sodium
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
Cutaquig is an injectable solution.
The solution is clear and colorless.
During storage, the liquid may become slightly opalescent and pale yellow.
Cutaquig is available as:
6, 10, 12, 20, 24, or 48 ml of solution in a vial (type I glass) with a bromobutyl rubber stopper: package size of 1, 10, or 20 vials
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Octapharma, S.A.
Av. Castilla, 2 (P.E. San Fernando)
Ed. Dublín - 2ª Planta
28830 San Fernando de Henares
Madrid
Spain
Manufacturers:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
1100 Vienna
Austria
Octapharma AB Lars Forssells gata 23 112 75 Stockholm Sweden
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Estonia, Finland, France, Hungary, Ireland, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Norway, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland), Czech Republic, Romania, Sweden: | Cutaquig® |
Date of the last revision of this prospectus: 11/2023.
Annex I: Administration Guidelines
- Prepare the necessary number of Cutaquig vials
- If stored in the refrigerator, place the vials at room temperature at least 90 minutes before infusion.
- Do not heat the vials or put them in the microwave.
- Do not shake the vials to avoid foam formation.
- Prepare for infusion
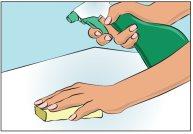 Choose and prepare a clean work area with antisepsis wipes or disinfectant solution (Figure 1).
Choose and prepare a clean work area with antisepsis wipes or disinfectant solution (Figure 1).

- Gather your infusion equipment:
- Infusion pump (optional) and compatible syringe(s)
- Needle (to extract the product from the vial)
- Infusion set
- Infusion tube and Y-connector (if necessary)
- Alcohol and alcohol wipes/antisepsis wipes
- Gauze or transparent dressing and adhesive tape
- Sharps container
- Treatment diary and pen
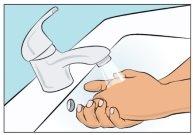
- Wash your hands well and let them dry (Figure 2). Use disinfectant gel as shown during training.
- If necessary, program the infusion pump according to the user manual and as your healthcare professional has shown you during training.
- Check and open the vials
- Inspect each vial carefully for:
- Correct dose label according to your prescription.
- Appearance of the solution (should be clear and colorless to pale yellow or light brown).
- Ensure the protective cap is not broken or missing.
- Check the expiration date and batch number.
- Do not use the solution if it is cloudy or contains particles.
- Remove the protective cap.
- Disinfect the rubber stopper with an antisepsis wipe and let it dry (Figure 3).


- Prepare and fill the syringe
- Open the sterile syringe and needle.
- Connect the needle to the syringe by screwing it on.
- Retract the plunger to fill the syringe with air, which should be approximately equal to the amount of solution needed from the vial.
- Insert the needle into the vial and place the vial upside down. Inject air: ensure the needle tip is not inside the solution to avoid foam formation.
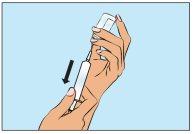 Then, ensuring the needle remains in the solution, slowly extract the Cutaquig (Figure 4).
Then, ensuring the needle remains in the solution, slowly extract the Cutaquig (Figure 4).

- Remove the needle from the vial.
- This procedure may need to be repeated if you need multiple vials for the calculated dose.
- When finished, remove the needle and place it immediately in the sharps container.
- Continue immediately with the next step, as the IgG solution must be used immediately.
- Prepare the infusion pump and tube (optional)
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions to prepare the infusion pump.
- To prime the administration tube, place the filled syringe in the infusion tube and gently press the plunger to fill the tube with Cutaquig and to eliminate all air (Figure 5).
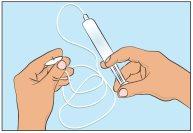

- Decide on the infusion sites and insert the infusion needle(s)
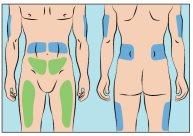 Cutaquig can be infused in the following areas: abdomen, thigh, upper arm, and/or upper leg/hip area (Figure 6).
Cutaquig can be infused in the following areas: abdomen, thigh, upper arm, and/or upper leg/hip area (Figure 6).

- The infusion sites should be at least 5 cm apart.
- Use different infusion sites than those used for the previous administration.
- Avoid inserting the needle into scars, tattoos, stretch marks, or areas where the skin is damaged/inflamed/red.
- Clean the skin of the selected infusion site(s) with an antisepsis wipe and let the skin dry.
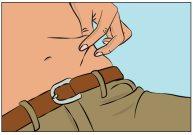
- Pinch the skin between your thumb and index finger around the injection site (Figure 7), carefully remove the needle cover, and insert the needle into the skin (Figure 8). The needle angle will depend on the type of infusion equipment used.
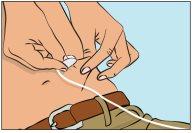


- Check the infusion
- The solution should not be infused into a blood vessel.
- Secure the needle in place by applying a sterile gauze and adhesive tape or a transparent dressing (Figure 9).
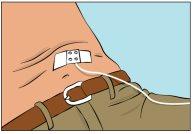

- Start the infusion
- Start the infusion. If an infusion pump is used for administration, follow the manufacturer's instructions.
- Record the infusion
- On each Cutaquig vial, you will find a removable label with batch number details. Stick this label in the patient's treatment diary or infusion logbook. Record the dose details, date, time, infusion site location, and any infection, side effects, or other comments related to this infusion.
- After completing the infusion
- Gently remove the needle(s) and place it/them immediately in the sharps container.
- If necessary, press with a small piece of gauze on the needle insertion site and apply a dressing.
- Discard all used disposable supplies, as well as any unused product and empty vial(s), as recommended by your healthcare professional and in accordance with local requirements.
Organize and store all reusable equipment (e.g., pump) safely until the next infusion.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to CUTAQUIG 165 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 200 mg/mlActive substance: immunoglobulins, normal human, for extravascular adm.Manufacturer: Baxalta Innovations GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 200 mg/mlActive substance: immunoglobulins, normal human, for extravascular adm.Manufacturer: Csl Behring GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 200 mg human plasma protein/ mlActive substance: immunoglobulins, normal human, for extravascular adm.Manufacturer: Csl Behring GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for CUTAQUIG 165 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
Discuss questions about CUTAQUIG 165 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















