
ADVATE 250 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use ADVATE 250 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for theuser
ADVATE 250 UI powder and solvent for solutionfor injectionADVATE 500 UI powder and solvent for solutionfor injectionADVATE 1000 UI powder and solvent for solutionfor injectionADVATE 1500 UI powder and solvent for solutionfor injectionADVATE 2000 UI powder and solvent for solutionfor injectionADVATE 3000 UI powder and solvent for solutionfor injection
Octocog alfa (human coagulation factor VIII recombinant)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again. If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others, even if their symptoms are the same as yours, as it may harm them.
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, even if you think they are not serious. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What is ADVATE and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use ADVATE
- How to use ADVATE
- Possible side effects
- Storage of ADVATE
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is ADVATE and what is it used for
ADVATE contains the active substance octocog alfa, human coagulation factor VIII produced by recombinant DNA technology. Factor VIII is necessary for blood to clot and stop bleeding. In patients with hemophilia A, factor VIII is missing or does not work properly (hereditary absence of factor VIII).
ADVATE is used for the treatment and prevention of bleeding in patients of all age groups with hemophilia A (a hereditary bleeding disorder caused by the absence of factor VIII).
ADVATE is prepared without adding any human or animal-derived protein during the entire manufacturing process.
2. What you need to know before you use ADVATE Do not use ADVATE
if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to octocog alfa or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
if you are allergic to mouse or hamster proteins
If you are not sure if you are allergic, consult your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before you start using ADVATE. Inform your doctor if you have been previously treated with medicines that contain factor VIII, especially if you developed inhibitors, as there may be a high risk that this will happen again. Inhibitors are antibodies that block factor VIII and reduce the effectiveness of ADVATE for bleeding control. The development of inhibitors is a known complication in the treatment of hemophilia A. If your bleeding is not controlled with ADVATE, consult your doctor immediately.
There is a small risk that you may experience a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to ADVATE. You should be aware that the first symptoms of an allergic reaction are rash, itching, hives, generalized itching, swelling of the lips and tongue, difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest tightness, feeling of general discomfort, and dizziness. These symptoms can be a warning of anaphylactic shock, which can also cause severe dizziness, loss of consciousness, and severe breathing difficulties.
If you experience any of these symptoms, stop the administration of the medicine immediately and consult a doctor. Severe symptoms, including difficulty breathing and (near) fainting, require rapid emergency treatment.
Patients who develop factor VIII inhibitors
The formation of inhibitors (antibodies) is a known complication that can occur during treatment with all factor VIII medicines. These inhibitors, especially in large quantities, prevent the treatment from working properly, so you and your child will be carefully monitored for the development of such inhibitors. If your bleeding or your child's bleeding is not controlled with ADVATE, consult your doctor immediately.
Children and adolescents
The warnings and precautions mentioned apply to adults and children (from 0 to 18 years of age).
Using ADVATE with other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Treatment with ADVATE does not affect the ability to drive and use machines.
ADVATE contains sodium
This medicine contains 0.45 mmol of sodium (10 mg) per vial, which should be taken into account in patients on a low-sodium diet.
3. How to use ADVATE
Treatment with ADVATE will be started by a doctor who is experienced in the treatment of patients with hemophilia A.
Your doctor will calculate your dose of ADVATE (in international units or IU) based on your condition, body weight, and whether it is to be used for prevention or treatment of bleeding.
The frequency of administration will depend on how ADVATE works. Replacement therapy with ADVATE is usually a lifelong treatment.
Follow your doctor's instructions for administering this medicine exactly. If you are unsure, consult your doctor again.
Prevention of bleeding
The usual dose of octocog alfa is 20 to 40 IU per kilogram of body weight, administered every 2 or 3 days. However, in some cases, especially in younger patients, more frequent administration of injections or higher doses may be required.
Treatment of bleeding
The dose of octocog alfa is calculated based on your body weight and the desired factor VIII levels. The factor VIII levels to be achieved will depend on the severity and location of the bleeding.
Dose (IU) = body weight (kg) x desired increase in factor VIII (% of normal) x 0.5
If you think the effect of ADVATE is insufficient, consult your doctor.
Your doctor will perform the necessary laboratory tests to ensure you have adequate factor VIII levels. This is especially important if you are going to undergo major surgery.
Use in children and adolescents(from 0 to 18 years of age)
For the treatment of bleeding, the dose in children does not differ from that in adult patients. To prevent bleeding in children under 6 years of age, doses of 20 to 50 IU per kilogram of body weight are recommended 3 to 4 times a week. The administration of ADVATE in children (intravenously) does not differ from administration in adults. A central venous access device (CVAD) may be necessary to allow frequent infusions of factor VIII products.
How ADVATE is administered
ADVATE is usually injected into a vein (intravenously) by your doctor or nurse. You or another person can also administer the injection of ADVATE, but only after receiving proper training. Detailed instructions for administration are described at the end of this leaflet.
If you use more ADVATE than you should
Follow your doctor's instructions for administering this medicine exactly. Consult your doctor if you have any doubts. If you inject a higher dose of ADVATE than recommended, consult your doctor as soon as possible.
If you forget to use ADVATE
Do not inject a double dose to make up for forgotten doses. Administer the next injection as scheduled and continue as your doctor has instructed.
If you stop using ADVATE
Do not stop using ADVATE without consulting your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you experience sudden and severe allergic reactions(anaphylaxis), stop the injection immediately. Contact your doctor immediately if you have any of the following initial symptoms of allergic reactions:
rash, hives, and generalized itching,
swelling of the lips and tongue,
difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest tightness, feeling of general discomfort,
dizziness and loss of consciousness.
Severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing and (near) fainting, require rapid emergency treatment.
In children who have not received previous treatment with factor VIII medicines, inhibitor antibodies may occur very frequently (more than 1 in 10 patients); however, in patients who have received previous treatment with factor VIII (more than 150 days of treatment), the risk is infrequent (less than 1 in 100 patients). If this happens, the medicines you or your child are taking may stop working properly, and you or your child may experience persistent bleeding. In this case, contact your doctor immediately.
Very common side effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 patients)
Factor VIII inhibitors (in children who have not received previous treatment with factor VIII medicines).
Common side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 patients) Headache and fever
Uncommon side effects(may affect up to 1 in 100 patients)
Factor VIII inhibitors (in patients who have received previous treatment with factor VIII [more than 150 days of treatment]), dizziness, flu-like symptoms, fainting, abnormal heartbeats, red spots associated with itching, chest discomfort, injection site reaction, itching, increased sweating, unusual taste in the mouth, hot flashes, migraines, memory loss, chills, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing, sore throat, infection of the lymphatic vessels, paleness, eye inflammation, rash, excessive sweating, inflammation of feet and legs, decrease in red blood cell count, increase in a type of white blood cell (monocytes), and pain in the upper abdomen or lower chest.
Related to surgery
catheter-related infection, decrease in red blood cell count, swelling of the limbs and joints, prolonged bleeding after drain removal, decrease in factor VIII levels, and postoperative hematoma
Related to central venous access devices (CVADs)
Catheter-related infection, systemic infection, and local blood clot at the catheter site.
Side effects with unknown frequency(cannot be estimated from the available data)
Potentially life-threatening reactions (anaphylaxis) and other allergic reactions (hypersensitivity), general disorders (fatigue, lack of energy).
Additional side effects in children
In addition to the development of inhibitors in pediatric patients without prior treatment and complications associated with the catheter, no age-specific differences in side effects were observed in clinical trials.
Reporting of side effects
 If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, even if you think they are not serious. You can also report side effects directly through the national reporting system listed in Annex V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, even if you think they are not serious. You can also report side effects directly through the national reporting system listed in Annex V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of ADVATE
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2 °C and 8 °C). Do not freeze.
Until the expiry date, the powder vial can be stored at room temperature (up to 25 °C) for a single period not exceeding 6 months. In this case, this medicine expires at the end of this 6-month period or on the expiry date printed on the vial, whichever is earlier. Please note on the carton the date of completion of the 6-month storage period at room temperature. The medicine cannot be refrigerated again after storage at room temperature.
Store the vial in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
This medicine is for single use only. Dispose of the unused solution properly. Use the medicine immediately after complete dissolution of the powder.
Do not refrigerate the medicine after preparation.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of ADVATE
The active ingredient is octocog alfa (human coagulation factor VIII produced by recombinant DNA technology). Each vial of powder nominally contains 250, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, or 3000 IU of octocog alfa.
The other components are mannitol, sodium chloride, histidine, trehalose, calcium chloride, tromethamine, polysorbate 80, and glutathione (reduced)
Vial of solvent: 5 ml of sterile water for injectable preparations
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
ADVATE is a white to off-white powdery substance.
After reconstitution, the solution is transparent, colorless, and free of foreign particles. Each container also includes a reconstitution device (BAXJECT II).
Marketing Authorization Holder
Baxter AG Industriestrasse 67
A-1221 Vienna
Tel: +44(0)1256 894 959
E-mail: [email protected]
ManufacturersBaxalta Belgium Manufacturing SA Boulevard René Branquart 80
B-7860 Lessines
Belgium
Baxter SA
Boulevard René Branquart 80
B-7860 Lessines
Belgium
Date of Last Revision of this Prospectus
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu/.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Instructions for Preparation and Administration
Aseptic technique is required for the preparation of the solution and its administration.
Use only the sterile water for injectable preparations and the reconstitution device included in each ADVATE container. ADVATE should not be mixed with other medications or solvents.
It is strongly recommended to record the name and batch number of the product each time ADVATE is administered.
Reconstitution Instructions
? Do not use after the expiration date shown on the labels and on the container.
? Do not use if the BAXJECT II device, the sterile protective system, or its container is damaged or shows signs of deterioration, as indicated by the symbol: .
? Do not refrigerate the preparation after reconstitution.
- If the medication is in the refrigerator, remove the ADVATE powder and solvent vials from the refrigerator and let them reach room temperature (between 15 °C and 25 °C).
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water.
- Remove the protectors from the powder and solvent vials.
- Clean the stoppers with alcohol-impregnated wipes. Place the vials on a flat and clean surface.
- Open the BAXJECT II device wrapper by removing the paper cover without touching the inside
(Fig. a). Do not remove the device from the wrapper. Do not use if the BAXJECT II device, its sterile barrier system, or its packaging is damaged or shows signs of deterioration.
- Turn the wrapper over and insert the plastic tip through the solvent stopper. Hold the wrapper by its end and pull out the BAXJECT II device from its wrapper (Fig. b). Do not remove the blue protector from the BAXJECT II device.
- For reconstitution, use only the sterile water for injectable preparations and the reconstitution device included in the container.
With the BAXJECT II device attached to the solvent vial, invert the system so that the solvent vial is on top of the device. Insert the white plastic tip into the stopper of the ADVATE powder vial. The vacuum will cause the solvent to penetrate the ADVATE powder vial (Fig. c).
- Gently shake until all the material is dissolved. Ensure that the ADVATE powder is completely dissolved; if not, the reconstituted solution will not pass through the device filter. The medication dissolves quickly (usually in less than 1 minute). After reconstitution, the solution should be transparent, colorless, and free of foreign particles.

Fig. a Fig. b Fig. c
Injection Instructions
A luer-lock syringe is required for administration.
Important Note:
? Do not attempt to administer the injection unless you have received special training from your doctor or nurse.
? Inspect the prepared solution for particles or discoloration before administration (the solution should be transparent, colorless, and free of foreign particles). Do not use ADVATE if the solution is not completely transparent or not fully dissolved.
- Remove the blue protector from the BAXJECT II device. Do not introduce air into the syringe. Connect the syringe to the BAXJECT II device (Fig. d).
- Invert the system (the vial with the reconstituted solution on top). Introduce the reconstituted solution into the syringe by slowly pulling the plunger back (Fig. e).
- Disconnect the syringe.
- Connect a winged infusion needle to the syringe. Administer intravenously. The solution should be administered slowly, at a rate determined by the patient's level of comfort, not exceeding 10 ml per minute. The pulse should be taken before and during the administration of ADVATE. If a significant increase in pulse is observed, the administration rate should be reduced or temporarily interrupted, which usually allows the symptoms to disappear immediately (see section 4 "Possible Adverse Effects").
- Dispose of the unused solution properly.
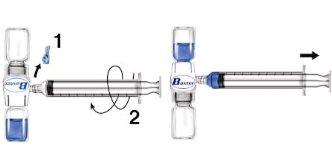
Fig. d Fig. e
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
On-Demand Treatment
In the case of subsequent hemorrhagic episodes, the factor VIII activity should not be lower than the given plasma activity level (in % of normal or IU/dl) during the corresponding period. The following table can be used as a dosage guide for hemorrhagic episodes and surgery.
The dose and frequency of administration should be adapted to the individual clinical response. In certain circumstances (e.g., presence of a low inhibitor titre), higher doses than those calculated using the formula may be necessary.
Severity of Hemorrhage / Type of Surgical Procedure | Required Factor VIII Level (% or IU/dl) | Dose Frequency (hours) / Duration of Therapy (days) |
Hemorrhage Initial hemarthrosis or muscle or oral hemorrhage. More extensive hemarthrosis, muscle hemorrhage, or hematoma. Life-threatening hemorrhage. | 20 – 40 30 – 60 60 – 100 | Repeat the injection every 12 to 24 hours (every 8 to 24 hours in patients under 6 years) for at least 1 day until the hemorrhagic episode, as indicated by pain, is resolved or healing is achieved. Repeat the injection every 12-24 hours (every 8 to 24 hours in patients under 6 years) for 3 to 4 days or more, until pain and acute disability cease. Repeat the injection every 8 to 24 hours (every 6 to 12 hours in patients under 6 years) until the danger has passed. |
Surgery Minor Including dental extraction. Major | 30 – 60 80 – 100 (pre- and postoperative) | Every 24 hours (every 12 to 24 hours in patients under 6 years), at least 1 day, until healing is achieved. Repeat the injection every 8-24 hours (every 6 to 24 hours in patients under 6 years) until adequate wound healing is achieved, and then for at least another 7 days of therapy to maintain a factor VIII activity of 30% to 60% (IU/dl). |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ADVATE 250 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1,000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1500 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1000 IU - after reconstitution in 2 ml of water for injections, the dose is 500 IU/mlActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription required
Online doctors for ADVATE 250 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about ADVATE 250 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















