
Tobradex

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Tobradex

How to use Tobradex
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Warning! Keep the Leaflet! Information on the Immediate Packaging in a Foreign Language.
Tobradex
(3 mg + 1 mg)/ml, eye drops, suspension
Tobramycin + Dexamethasone
Read the Leaflet Carefully Before Using the Medication, as it Contains Important Information for the Patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medication has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not give it to others. The medication can harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet:
- 1. What is Tobradex and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Tobradex
- 3. How to use Tobradex
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Tobradex
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Tobradex and what is it used for
Tobradex is used to treat inflammatory eye diseases, which may be accompanied by
infection.Eye inflammation can result from eye surgery, infection, or be caused by the presence of a foreign body or eye injury.
Tobradex is a combination medication containing an antibacterial component and
corticosteroid. Corticosteroids (in this case, dexamethasone) are used to prevent and reduce eye inflammation. The antibacterial medication in Tobradex (tobramycin) acts on many species of pathogenic bacteria that infect the eye.
The indication for using Tobradex is to prevent and treat inflammation and prevent infections associated with cataract surgery in adults and children aged 2 years and older.
2. Important information before using Tobradex
When not to use Tobradex:
- if the patient is allergic to dexamethasone, tobramycin, or any of the other ingredients of this medication (listed in section 6); or if the patient has:
- herpetic keratitis;
- keratitis caused by the virus of smallpox, chickenpox, or other viral diseases of the cornea or conjunctiva;
- eye tuberculosis;
- fungal eye infection or untreated parasitic eye infections;
- untreated purulent eye infections;
- if the patient has had a foreign body removed from the cornea and no complications are present.
Warnings and precautions
- If the patient experiences allergic reactions after using Tobradex, they should discontinue treatment and consult their doctor immediately (see section 4). Hypersensitivity symptoms can vary in severity: from local itching or skin redness to severe allergic reactions (anaphylactic reaction) or severe skin reactions. Such allergic reactions can occur when using other topical or systemic antibiotics from the same group (aminoglycosides).
- If the patient's symptoms worsen or suddenly recur, they should consult their doctor. During Tobradex treatment, the patient may be more susceptible to eye infections.
- If the patient is using other antibiotics, including those taken orally, they should consult their doctor.
- If the patient has or suspects myasthenia or Parkinson's disease, they should consult their doctor. Antibiotics from this group can exacerbate muscle weakness.
- If the patient uses Tobradex for a longer period, they may experience:
- increased susceptibility to eye infections,
- increased eye pressure,
- development of cataracts,
- development of Cushing's syndrome due to the medication entering the bloodstream. The patient should consult their doctor if they experience swelling and weight gain, especially in the torso and face, as these are usually the first symptoms of Cushing's syndrome. Adrenal insufficiency may occur after discontinuing long-term or intensive use of Tobradex. The patient should consult their doctor before stopping treatment. This risk is particularly important in children and patients treated with ritonavir or cobicistat.
- During Tobradex treatment, the patient should regularly check their intraocular pressure; they should consult their doctor. This is especially important in children, as the risk of developing ocular hypertension caused by corticosteroids may be higher in children and may occur faster than in adults. Especially in children and adolescents, the patient should consult their doctor. The risk of ocular hypertension and cataract formation is also higher in patients with other diseases (e.g., patients with diabetes).
- Corticosteroids administered to the eye can cause delayed healing of eye injuries. Topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can slow down and delay the healing process. Concurrent topical use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids can increase the risk of eye healing problems.
- If the patient has a disease that causes thinning of the eye tissue, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences persistent corneal ulceration during Tobradex treatment, they should consult their doctor as soon as possible, as this may be a sign of fungal eye infection.
If the patient experiences blurred vision or other vision disturbances, they should contact their doctor.
Tobradex and other medications
The patient should tell their doctor about all medications they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medications they plan to take.
The patient should especially tell their doctor if they are using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Concurrent topical use of corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can cause problems with eye healing.
If the patient is using other eye drops or ointments, they should wait at least 5 minutes between administering different medications. Eye ointments should be used last.
The patient should tell their doctor about taking ritonavir or cobicistat, as these medications can increase the dexamethasone content in the blood.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medication.
Tobradex is not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Tobradex eye drops, suspension have no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
For a while after administering Tobradex, vision may be blurred. The patient should not drive or operate machines until this symptom subsides.
Tobradex contains benzalkonium chloride, solution
The medication contains 0.1 mg of benzalkonium chloride, solution per milliliter (0.1 mg/ml).
Benzalkonium chloride, solution can be absorbed by soft contact lenses and change their color. The patient should remove contact lenses before administering the drops and wait at least 15 minutes before putting them back on.
Benzalkonium chloride, solution can also cause eye irritation, especially in people with dry eye syndrome or corneal disorders (the transparent layer on the front of the eye).
If the patient experiences abnormal sensations in the eye, stinging, or eye pain after using the medication, they should contact their doctor.
3. How to use Tobradex
This medication should always be used as directed by the doctor. If the patient has any doubts, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
The dosage of Tobradex is determined individually by the doctor for each patient. The doctor will decide how long the medication should be used. If the doctor does not recommend otherwise, the patient should administer one to two drops of the medication into the conjunctival sac (sacs) of the infected eye (eyes) every 4-6 hours.
Use in children
The medication can be used in children aged 2 years and older in the same doses as in adults.
The safety and efficacy of Tobradex in children under 2 years of age have not been established, and no data are available for this age group.
Use in patients with liver or kidney impairment
The effect of Tobradex has not been studied in these patient populations. However, due to the low systemic absorption of tobramycin and dexamethasone after local administration, it is considered that there is no need to modify the dosage.
Tobradex is intended exclusivelyfor eye drops.
1
2
3
4
- 1. Prepare the Tobradex bottle and a mirror.
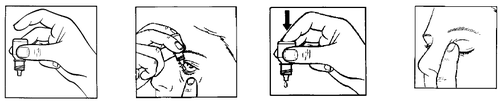
- 2. Wash your hands.
- 3. Shake the bottle.
- 4. Remove the cap. If the protective collar is loose after removing the cap, it should be discarded before using the medication.
- 5. Hold the bottle in your hand and direct it upwards with the bottom, holding it with your thumb and middle finger (figure 1).
- 6. Tilt your head back. Pull the lower eyelid down with a clean finger to form a "pocket" between the eyelid and the eye; the drop should fall into this pocket (figure 2).
- 7. Bring the dropper tip close to the eye. You can use a mirror to help.
8. Do not touch the dropper tip to the eye, eyelid, or surrounding areas.
Failing to follow this instruction can lead to infection of the drops. Using infected drops can cause serious complications, even vision loss.
- 9. Gently squeeze the bottom of the bottle to release a single drop of Tobradex (figure 3). If the drop does not fall into the eye,try again.
- 10. After administering Tobradex, release the lower eyelid. Gently close your eye and press the corner of your eye near your nose with your finger (figure 4). This helps prevent the medication from entering the entire body.
- 11. If it is necessary to administer the medication to both eyes, repeat the above steps for the second eye.
- 12. Immediately after using the medication, tighten the bottle cap.
- 13. Use only one bottle of Tobradex at a time.
Using more than the recommended dose of Tobradex
In case of overdose, excess medication can be rinsed from the eye with lukewarm water. Do not administer additional drops. The next dose should be administered at the usual time.
Missing a dose of Tobradex
If the patient forgets to use Tobradex, eye drops, they should continue treatment by administering the next dose according to the dosage schedule. If it is almost time for the next dose, the patient should skip the missed dose and continue treatment according to the recommended dosage schedule. Do not use a double doseto make up for the missed dose.
If you have any further doubts about using this medication, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, Tobradex can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If the patient experiences allergic reactions, including rash, face, lip, tongue, and (or)
throat swelling, which can cause difficulty breathing or swallowing, or other severe
side effects, they should discontinue using Tobradex and contact their doctor or the Emergency Department of the nearest hospital immediately.
During Tobradex treatment, the following side effects have been observed:
Uncommon( may occur in less than 1 in 100 patients): high intraocular pressure, eye pain, eye itching, eye discomfort, eye irritation.
Rare( may occur in less than 1 in 1000 patients): keratitis, eye allergy, blurred vision, dry eye syndrome, redness, taste disorders.
Frequency not known( frequency cannot be estimated from the available data): eyelid swelling, eyelid redness, pupil dilation, increased tearing, blurred vision, severe allergic reactions (hypersensitivity), dizziness, headache, nausea, abdominal discomfort, severe skin reactions (erythema multiforme), itching, face swelling, increased body hair growth (especially in women), muscle weakness, and muscle mass loss, purple striae on the skin, high blood pressure, irregular menstrual periods or amenorrhea, changes in protein and calcium levels in the body, growth retardation in children and adolescents, and swelling and weight gain, especially in the torso and face (a condition known as Cushing's syndrome) (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions").
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
Reporting side effects can help gather more information on the safety of the medication.
5. How to store Tobradex
To avoid infecting the medication, the bottle should be discarded 4 weeks after first opening. The patient should write the date of opening the bottle in the space provided below.
Date of first opening:…………….
The medication should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze.
Store the bottle upright.
Store the bottle tightly closed.
Do not use this medication after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
Medications should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste containers. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of unused medications. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Tobradex contains
- The active substances of Tobradex are tobramycin 3 mg/ml and dexamethasone 1 mg/ml.
- The other ingredients are: benzalkonium chloride, solution, disodium edetate, sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, tyloxapol, hydroxyethylcellulose, purified water. The medication may contain minimal amounts of sulfuric acid and/or sodium hydroxide (to adjust the pH).
What Tobradex looks like and what the package contains
Tobradex is a liquid (suspension, white to off-white) available in DROPTAINER bottles with a LDPE dropper and a PP cap, with a capacity of 5 ml, in a cardboard box.
For more detailed information, the patient should contact the marketing authorization holder or parallel importer.
Marketing authorization holder in the Czech Republic, the country of export:
Novartis s.r.o.
Na Pankráci 1724/129
140 00 Prague 4
Czech Republic
Manufacturer:
Alcon-Couvreur N.V.
Rijksweg 14
B-2870 Puurs, Belgium
Siegfried El Masnou, S.A.
Camil Fabra 58
08320 El Masnou, Barcelona
Spain
Novartis Farmacéutica, S.A.
Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes 764
08013 Barcelona
Spain
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25 und Obere
Turnstrasse 8-10
90429 Nuremberg
Germany
Parallel importer:
InPharm Sp. z o.o.
ul. Strumykowa 28/11
03-138 Warsaw
Repackaged by:
InPharm Sp. z o.o. Services sp. k.
ul. Chełmżyńska 249
04-458 Warsaw
Marketing authorization number in the Czech Republic, the country of export:64/706/99-C
Parallel import authorization number:384/19
Date of leaflet approval: 16.10.2024
[Information about the trademark]
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Marketing authorisation holder (MAH)Novartis s.r.o.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to TobradexDosage form: Drops, (3 mg + 1 mg)/mlActive substance: dexamethasone and antiinfectivesManufacturer: Rafarm S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Drops, (5 mg + 1 mg)/mlActive substance: dexamethasone and antiinfectivesManufacturer: Dr. Gerhard Mann Chem. - Pharm. Fabrik GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Ointment, (5 mg + 0.3 mg)/gActive substance: dexamethasone and antiinfectivesManufacturer: Dr. Gerhard Mann Chem. - Pharm. Fabrik GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Tobradex in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Tobradex in Ukraine
Alternative to Tobradex in Spain
Online doctors for Tobradex
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Tobradex – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














