Simbicort

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Simbicort

How to use Simbicort
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Symbicort, (80 micrograms + 2.25 micrograms)/inhalation dose, inhalation aerosol, suspension
budesonide + formoterol fumarate dihydrate
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed to you specifically. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Symbicort and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Symbicort
- 3. How to use Symbicort
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Symbicort
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Symbicort and what is it used for
What is Symbicort
Symbicort is an inhaler medicine used to treat asthma in adults and adolescents aged 12 to 17 years. Symbicort contains two different active substances: budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate.
- Budesonide belongs to a group of medicines called "corticosteroids".
- Formoterol fumarate dihydrate belongs to a group of medicines called "long-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists" or "bronchodilators".
In the treatment of which diseases is Symbicort used
Symbicort is used to treat asthma and may be prescribed as the only medicine or with a separate inhaler for emergency use:
- Some people are prescribed two inhalers to treat asthma: an inhaler with Symbicort and a separate emergency inhaler
- These patients use Symbicort daily. This helps prevent asthma symptoms.
- If these patients experience asthma symptoms, they use the emergency inhaler to make breathing easier.
- In some people, Symbicort is prescribed as the only inhaler for asthma
- These patients use Symbicort daily. This helps prevent asthma symptoms.
- Symbicort is also used by them when they feel the need to take additional inhalations of the medicine to relieve asthma symptoms and restore normal breathing, and if this has been agreed with the doctor, also to prevent asthma symptoms (e.g. during physical exercise or exposure to allergens). These patients do not need to use a separate inhaler in such situations.
How does Symbicort work
- Budesonide works by reducing and preventing swelling and inflammation in the lungs.
- Formoterol fumarate dihydrate works by relaxing the muscles in the airways, making it easier to breathe.
2. Important information before using Symbicort
When not to use Symbicort:
- if the patient is allergic to budesonide, formoterol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Symbicort, the patient should discuss with their doctor or pharmacist if they have:
- diabetes
- respiratory infection
- high blood pressure or if they have ever had heart problems (including irregular heartbeat, very fast heart rate, narrowing of the arteries or heart failure)
- thyroid or adrenal gland problems
- low potassium levels in the blood
- severe liver disease. If the patient experiences blurred vision or other vision problems while using Symbicort, they should contact their doctor.
Children
This medicine should not be used in children under 12 years of age.
Symbicort and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
- Medicines that block beta-adrenergic receptors used in high blood pressure - such as atenolol or propranolol
- Eye drops - such as timolol used to treat glaucoma
- Medicines used in the case of accelerated or irregular heart rhythm - such as quinidine
- Medicines such as digoxin - often used to treat heart failure
- Diuretics used in high blood pressure - such as furosemide
- Oral steroids - such as prednisolone
- Xanthine derivatives - such as theophylline or aminophylline. These are medicines often used to treat asthma
- Other bronchodilators - such as salbutamol.
- Antidepressants - such as amitriptyline and nefazodone
- Phenothiazine derivatives - such as chlorpromazine and prochlorperazine
- Medicines used to treat HIV infection - such as ritonavir
- Medicines used to treat infections - such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, clarithromycin and telithromycin
- Medicines used to treat Parkinson's disease - such as levodopa
- Medicines used to treat thyroid disorders - such as levothyroxine. If any of these points apply to the patient or if the patient has any doubts, they should discuss this with their doctor or pharmacist before using Symbicort.
The patient should also inform their doctor or pharmacist if they are planning to undergo general anesthesia for a surgical or dental procedure.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- If the patient is pregnant or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using Symbicort - they should not use Symbicort without consulting their doctor.
- If a patient treated with Symbicort becomes pregnant, they should not stop taking Symbicort but should contact their doctor immediately.
- If the patient is breastfeeding, they should discuss this with their doctor before using Symbicort.
Driving and using machines
Symbicort has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Symbicort
This medicine should always be used in accordance with the doctor's recommendations. If the patient has any doubts, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
- It is important to use Symbicort daily, even if the patient does not experience any asthma symptoms at the time.
- The doctor will regularly check the patient's asthma symptoms.
- The doctor may consider adding oral steroids to the usual treatment during periods of stress (e.g. during a respiratory infection or before surgery).
Symbicort may be prescribed for the treatment of asthma as the only medicine or with a separate emergency inhaler. The patient should take two puffs (inhalations) of Symbicort to receive a full dose. The amount of Symbicort to be taken and the duration of treatment depend on the doctor's prescription.
Using Symbicort with a separate emergency inhaler
The patient should use Symbicort daily. This helps prevent asthma symptoms.
- Adults (18 years and older) should usually use 2-4 inhalations, twice a day.
- The doctor may increase the dose to 8 inhalations, twice a day.
- If the asthma symptoms are well controlled, the doctor may recommend that the patient take the medicine once a day.
Adolescents (12-17 years) should usually use 2-4 inhalations, twice a day.
- If the asthma symptoms are well controlled, the doctor may recommend that the patient take the medicine once a day.
The doctor (or nurse) will help the patient control their asthma symptoms. They will adjust the dose of the medicine to the smallest amount that controls the asthma symptoms. However, the patient should not adjust the dose or stop treatment without consulting their doctor (or nurse) first.
- If asthma symptoms occur, the patient should use a separate emergency inhaler to treat them.
- The patient should always carry the emergency inhaler with them so that they can use it whenever necessary.
- The patient should not use Symbicort to treat asthma symptoms - they should use the emergency inhaler.
Using Symbicort as the only inhaler for asthma
Symbicort should be used in this way if the doctor has recommended it and if the patient is 12 years or older.
The patient should use Symbicort daily. This helps prevent asthma symptoms. The patient can use the medicine by choosing one of the following dosing schedules:
- 2 inhalations in the morning and 2 inhalations in the evening or
- 4 inhalations in the morning or
- 4 inhalations in the evening
The doctor may increase the dose to 4 inhalations twice a day.
Symbicort should also be used as a rescue medicine to treat asthma symptoms after they occur and to prevent asthma symptoms (e.g. during physical exercise or exposure to allergens).
- If the patient experiences asthma symptoms, they should take 2 inhalations and wait a few minutes.
- If the patient does not feel better, they should take another 2 inhalations.
- The patient should not take more than 12 inhalations of the medicine at a time.
The patient should always carry the Symbicort inhaler with them so that they can use it whenever necessary.
Usually, there is no need to use a total daily dose greater than 16 inhalations. However, the doctor may allow the patient to take up to 24 inhalations of the medicine per day for a limited time.
If the patient needs to regularly use 16 or more inhalations, they should make an appointment with their doctor or nurse. The treatment may need to be changed.
The patient should not use more than 24 inhalations of the medicine per day.
If the patient experiences asthma symptoms during physical exercise, they should use Symbicort as described here. It is essential to discuss the use of Symbicort with the doctor to prevent asthma symptoms; the frequency of physical exercise and exposure to allergens may affect the treatment prescribed to the patient.
Symbicort and oral steroids
If the patient is taking oral steroids for asthma, when introducing Symbicort, the doctor may reduce the number of oral steroid tablets taken. If the patient has been taking oral steroids for a long time, the doctor may occasionally recommend blood tests.
After reducing the dose of oral steroids, the patient's general well-being may worsen, even if the respiratory symptoms are less severe. The following symptoms may occur:
- stuffy nose or runny nose
- weakness
- joint or muscle pain
- rash (hives)
The patient should talk to their doctor immediately if they experience any of these symptoms, such as:
- headache
- fatigue
- nausea
- vomiting
If the patient experiences any of these symptoms, they should contact their doctor immediately - other medicines may need to be used. If the patient has any doubts about continuing to use Symbicort, they should consult their doctor.
Using Symbicort in children
Other forms of this medicine are suitable for use in children; the patient should ask their doctor or pharmacist about this.
Important information about asthma symptoms
If the patient experiences shortness of breath or wheezing while using Symbicort, they should continue to use Symbicort but should contact their doctor as soon as possible, as additional treatment may be necessary.
- The patient should contact their doctor immediately if:
- breathing difficulties worsen or the patient wakes up at night due to asthma.
- The patient has a feeling of chest tightness in the morning after waking up or the feeling of chest tightness lasts longer than usual.
- These symptoms may indicate inadequate control of asthma and may require immediate use of other or additional treatment.
Information about Symbicort
- Before starting to use Symbicort, the patient should take it out of the foil packaging. Dispose of the foil packaging and the desiccant contained in it. If the desiccant has come out of the bag, do not use the inhaler.
- After removing the inhaler from the foil, it can be used for 3 months. Write the expiration date (3 months after opening the foil packaging) on the inhaler label to help remember when to stop using the inhaler.
- The parts of the inhaler are shown in the picture. The inhaler is already assembled in the packaging. If the container is loose, secure it back into the inhaler and continue to use the inhaler.
Preparing the Symbicort inhaler for use
The inhaler should be prepared for use in the following situations:
- when using a new Symbicort inhaler for the first time.
- if the inhaler has not been used for more than 7 days.
- if the inhaler has been dropped.
To prepare the inhaler for use, the patient should follow the instructions below:
- 1. Shake the inhaler vigorously for at least 5 seconds to mix the contents of the canister with the aerosol.
- 2. Remove the protective cap from the mouthpiece by gently pressing the tabs on the side. The strap on the cap will remain attached to the inhaler.
- 3. Hold the inhaler upright. Then press the counter (at the top of the inhaler) to release one puff into the air. The patient can use one or both hands, as shown in the pictures.
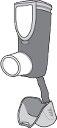
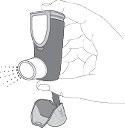
- 4. Release the pressure on the finger or fingers on the counter.
- 5. Wait 10 seconds, shake the device vigorously, and repeat steps 3 and 4.
- 6. The inhaler is now ready for use.
Using the inhaler
To perform an inhalation, the patient should follow the instructions below each time:
- 1. Shake the inhaler vigorously for at least 5 seconds to mix the contents of the canister with the aerosol.
- 2. Remove the protective cap from the mouthpiece, gently pressing the tabs on the side. Check that the mouthpiece is not blocked.
- 3. Hold the inhaler upright (with one or both hands). Perform a slow exhalation.
- 4. Place the mouthpiece of the inhaler gently between the teeth. Close the mouth (enclose the mouthpiece with the lips).
- 5. Start to breathe in slowly and deeply through the mouth. Press the counter (at the top of the inhaler) firmly to release the inhalation. Continue to breathe in for a while after pressing the counter. Breathing in at the same time as pressing the counter ensures that the medicine reaches the lungs.
- 6. Hold the breath for 10 seconds or as long as possible without feeling uncomfortable.
- 7. Before exhaling, release the pressure on the finger on the counter and remove the inhaler from the mouth. Hold the inhaler upright.
- 8. Then perform a slow exhalation. To perform another inhalation, shake the inhaler vigorously for at least 5 seconds and repeat steps 3 to 7.
- 9. Put the protective cap back on the mouthpiece.
- 10. Rinse the mouth with water after taking the morning and evening inhalations of Symbicort. Do not swallow the water.
Using the inhalation chamber
The doctor, nurse, or pharmacist may suggest using an inhalation chamber (e.g. AeroChamber Plus
Flow Vu or AeroChamber Plus). The patient should follow the instructions in the leaflet accompanying the packaging of the inhalation chamber.
Cleaning the Symbicort inhaler
- The patient should wipe the inner and outer surface of the mouthpiece with a dry cloth at least once a week.
- The patient should not use water or other liquids.
- The patient should not detach the container from the inhaler.
How to know when to replace Symbicort with a new one
- The counter at the top of the inhaler shows how many inhalations are left in the Symbicort inhaler. At the beginning, it shows 60 or 120 inhalations when the container is full.

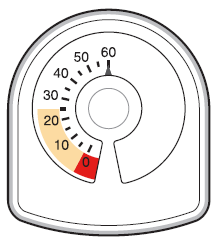
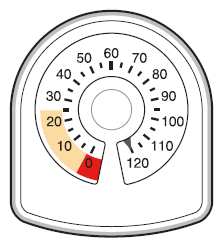
- Each time the patient takes an inhalation or performs a puff into the air, the arrow moves, counting down to zero ("0").
- When the arrow is in the yellow marked area, it means that there are about 20 inhalations left.
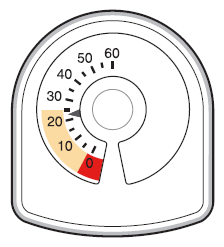
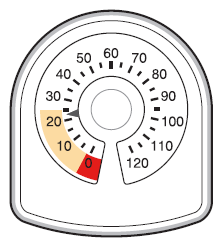
- When the arrow reaches "0", the patient should stop using the Symbicort inhaler. It may seem that the inhaler is not empty and that it still works. However, if the patient continues to use it, they will not receive the correct dose of the medicine.
Using more than the recommended dose of Symbicort
It is essential to take the medicine as prescribed or as recommended by the doctor. The patient should not exceed the prescribed dose without consulting their doctor.
If the patient uses more than the recommended dose of Symbicort, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist. The following symptoms may occur: tremors, headaches, or rapid heart rate.
Missing a dose of Symbicort
- If the patient misses an inhalation, they should take it as soon as they remember. However, if it is almost time for the next inhalation, they should skip the missed inhalation.
- The patient should notuse a double inhalation to make up for a missed inhalation.
Stopping the use of Symbicort
Before stopping the use of Symbicort, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Stopping the use of Symbicort may worsen asthma symptoms.
If the patient has any further doubts about using this medicine, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Symbicort can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The patient should stop using Symbicort and contact their doctor immediately if they experience the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the face, especially around the mouth (tongue and/or throat) and/or difficulty swallowing, rash or hives occurring at the same time as difficulty breathing (angioedema) and/or sudden feeling of weakness (fainting). This may indicate an allergic reaction. This occurs rarely, less often than in 1 in 1000 patients.
- Sudden worsening of wheezing or shortness of breath occurring immediately after inhalation of Symbicort. If any of these symptoms occur, the patient should stop using Symbicort and use an emergency inhaler if available. The patient should contact their doctor immediately, as a change in treatment may be necessary. These symptoms occur very rarely, less often than in 1 in 10,000 patients.
Other possible side effects:
Common (may occur in less than 1 in 10 patients)
- Pounding heart (feeling of heart beating), tremors. If these symptoms occur, they are usually mild and usually disappear during continued use of Symbicort.
- Thrush (fungal infection) in the mouth. The occurrence of thrush is less likely if the patient rinses their mouth with water after morning and evening use of Symbicort.
- Mild sore throat, cough, and hoarseness.
- Headache.
Uncommon (may occur in less than 1 in 100 patients)
- Anxiety, nervousness, or restlessness.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea (vomiting).
- Rapid heart rate.
- Bruises on the skin.
- Muscle cramps.
- Blurred vision.
Rare (may occur in less than 1 in 1000 patients)
- Rash, itching.
- Bronchospasm (constriction of the airway muscles, manifested by wheezing). If wheezing occurs immediately after using Symbicort, the patient should stop using Symbicort and contact their doctor immediately.
- Low potassium levels in the blood.
- Irregular heartbeat.
Very rare (may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 patients)
- Depression.
- Changes in behavior, especially in children.
- Chest pain or feeling of chest tightness (symptoms of angina pectoris).
- Increased blood sugar (glucose) levels.
- Taste disturbances, such as unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Changes in blood pressure.
Inhaled corticosteroids may affect the production of steroid hormones in the body, especially if they are used for a long time in high doses. The symptoms include:
- changes in bone mineral density (thinning of the bones)
- cataract (clouding of the lens in the eye)
- glaucoma (increased pressure in the eye)
- slowing of growth in children and adolescents
- effects on the adrenal glands (small glands located near the kidneys).
The likelihood of these symptoms is much lower when using inhaled corticosteroids than when taking corticosteroid tablets.
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Symbicort
- The medicine should be stored out of the sight and reach of children.
- The patient should not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the label of the container, carton, and foil packaging after "EXP". The expiration date refers to the last day of the month stated.
- After removing the inhaler from the foil, it can be used for 3 months. The patient should write the expiration date (3 months after opening the foil packaging) on the inhaler label to help remember when to stop using the inhaler.
- As with most pressurized inhalers, the effectiveness of this medicine may decrease if the container is cold. To get the best results, this medicine should be stored at room temperature before use.
- The patient should not store it in the refrigerator or freeze it. The patient should protect it from frost and direct sunlight.
- After using the inhaler, the patient should always put the protective cap back on the mouthpiece and snap it into place.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment. Warning:The container contains a pressurized liquid. Do not expose to temperatures above 50°C. Do not pierce the container. Even if the container appears to be empty, the patient should not crush, puncture, or burn it.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Symbicort contains
The active substances of Symbicort are budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. Each inhalation of Symbicort contains 80 micrograms of budesonide and 2.25 micrograms of formoterol fumarate dihydrate.
The other ingredients are: HFA 227, povidone K 25, and macrogol 1000. The inhaler does not contain chlorofluorocarbons.
What Symbicort looks like and contents of the packaging
Symbicort is an inhaler medicine. The pressurized container with a built-in counter contains a white suspension for inhalation. The container is equipped with a red plastic actuator with a white plastic mouthpiece and an integrated gray plastic cap. Each inhaler contains 60 or 120 inhalations after preparation for use. Each inhaler is packaged individually in a foil pouch containing a desiccant.
Symbicort (80 micrograms + 2.25 micrograms)/inhalation dose, inhalation aerosol, suspension (budesonide + formoterol fumarate dihydrate) is available in packages containing one inhaler.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder:
AstraZeneca AB
151 85 Södertälje
Sweden
Manufacturer:
AstraZeneca Dunkerque Production
224 Avenue de la Dordogne
59640 Dunkerque
France
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria: Symbicort 80 Mikrogramm/2,25 Mikrogramm/Inhalation Druckgasinhalation, Suspension; Belgium:
Symbicort 80 microgram/2,25 microgram/inhalation, aerosol, suspension; Symbicort 80 micrograms/2,25 micrograms/inhalation, suspension for inhalation in a pressurized container; Symbicort 80 Mikrogramm/2,25 Mikrogramm/Inhalation, Druckgasinhalation, Suspension; Bulgaria: Симбикорт 80 микрограма/2,25 микрограма/впръскване Суспензия под налягане за инхалация; Croatia: Symbicort 80 mikrograma/2,25 mikrograma po potisku, stlačeni inhalat, suspenzija; Cyprus: Symbicort 80 μικρογραμμάρια/2,25 μικρογραμμάρια/ψεκασμό; Czech Republic: Symbicort 80 micrograms/2,25 micrograms/inhalation, suspension in pMDI; Denmark: Symbicort 80 mikrogram/2.25 mikrogram/inhalation; Estonia: Symbicort; Finland: Symbicort 80 mikrog/2.25 mikrog/inhalaatio; France: Symbicort 100/3 microgrammes par inhalation, suspension pour inhalation en flacon préssurisé; Greece: Symbicort 80 μικρογραμμάρια/2,25 μικρογραμμάρια/ψεκασμό; Hungary: Symbicort 2,25 mikrogramm/80 mikrogramm/adag túlnyomásos inhalációs szuszpenzió; Iceland: Symbicort 80 míkrógrömm/2,25 míkrógrömm/inhalation; Ireland: Symbicort; Italy: Symbicort; Latvia: Symbicort 80 mikrogrami/2.25 mikrogrami/ inhalācijā, izsmidzinājumā, aerosols inhalācijām zem spiediena; Lithuania: Symbicort 80 mikrogramų/2,25 mikrogramo/išpurškime suslėgtoji įkvepiamoji suspensija; Luxembourg: Symbicort 80 microgrammes/2,25 microgrammes/inhalation, suspension pour inhalation en flacon pressurisé; Malta: Symbicort 100 micrograms/3 micrograms/inhalation, pressurised inhalation, suspension; Netherlands: Symbicort aërosol 100/3, 100 microgram/3 microgram per dosis, aërosol, suspensie; Norway: Symbicort 80 mikrogram/2.25 mikrogram/inhalasjon; Poland: Symbicort; Portugal: Symbicort 80 microgramas/2,25 microgramas/inalação Suspensão pressurizada para inalação; Romania: Symbicort 80 micrograme/2,25 micrograme/inhalație, suspensie de inhalat presurizată; Slovakia: Symbicort 80 mikrogramov/2,25 mikrogramov/inhalačná dávka, inhalačná suspenzia v tlakovom obale; Slovenia: Symbicort 80 mikrogramov/2,25 mikrograma na vdih, inhalacijska suspenzija pod tlakom; Spain: Symbicort 80 microgramos/2,25 microgramos/inhalación suspensión para inhalación en envase a presión; Sweden: Symbicort 80 mikrogram/2.25 mikrogram/inhalation; United Kingdom: Symbicort 100 micrograms/3 micrograms actuation pressurised inhalation, suspension
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterASTRAZENECA DUNKERQUE PRODUCTION
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SimbicortDosage form: Powder, (160 mcg + 4.5 mcg)/inh. doseActive substance: formoterol and budesonidePrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, (320 mcg + 9 mcg)/inh. doseActive substance: formoterol and budesonideManufacturer: Aeropharm GmbH Lek farmacevtska družba d.d. (Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d.) Salutas Pharma GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, (160 mcg + 4.5 mcg)/inh. doseActive substance: formoterol and budesonideManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription required
Alternatives to Simbicort in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Simbicort in Україна
Alternative to Simbicort in Іспанія
Online doctors for Simbicort
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Simbicort – subject to medical assessment and local rules.