
Optirai 350

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Optirai 350

How to use Optirai 350
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Enclosed leaflet: information for the user
Optiray 350 solution for injection and infusion, 741 mg/ml
(Ioversol)
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any further questions.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in the leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Optiray and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Optiray
- 3. How to use Optiray
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Optiray
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Optiray and what is it used for
Optiray is used in adults for various radiological examinations, including:
- vascular imaging, both arterial and venous
- kidneys
- computed tomography
Optiray is a contrast agent containing iodine. Iodine blocks X-rays, allowing blood vessels and internal organs to be visualized as the blood flows through them.
2. Important information before using Optiray
When not to use Optiray:
- if the patient is allergicto iodine-containing contrast agentsor any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if the patient has hyperthyroidism
Warnings and precautions
Before using Optiray, tell your doctor if you have:
- asthma or a history of allergic reactions, such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, skin symptoms
- heart failure, high blood pressure, circulatory disorders, or stroke, and if you are elderly
- diabetes
- kidney or liver disease
- brain disorders
- bone marrow disorders, such as certain blood cancers, called paraproteinemia, multiple myeloma
- certain red blood cell disorders, called sickle cell anemia
- an adrenal gland tumor that affects blood pressure, called pheochromocytoma
- increased homocysteine levels due to abnormal metabolism
- recent gallbladder examination using a contrast agent
- planned thyroid examination using an iodine-containing substance. It should be postponed, as Optiray may affect the results for up to 16 days.
Severe skin reactions have been reported in patients who received Optiray, such as eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), which can be life-threatening. During or shortly after the imaging procedure, a temporary brain disorder called encephalopathy may occur. Tell your doctor immediately if you notice any symptoms related to this condition described in section 4.
Children and adolescents under 18 years of age
Optiray 350 is not recommended for use in this age group. If a child is exposed to Optiray (direct exposure or newborns whose mothers received an iodine-containing contrast agent during pregnancy), thyroid function should be evaluated after birth and in all children under 3 years of age within one month after exposure.
Optiray and other medicines
Tell your doctor or radiologist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take. The following medicinesmay affect Optirayor Optiray may affect them:
- metformin:a medicine used to treat diabetes. Your doctor will check your kidney function before and after using Optiray. Depending on your kidney function, your doctor may consider stopping metformin 48 hours before the examination and not restarting it for at least 48 hours after the examination, unless your kidney function returns to normal.
- interleukins:medicines used to treat certain cancers
- certain blood pressure-lowering medicinesthat constrict blood vessels. To prevent the risk of neurological disorders, Optiray should never be used while taking these medicines.
- general anesthetics. Increased frequency of side effects has been reported.
- diuretics:medicines that increase urine production and lower blood pressure. In cases of dehydration caused by diuretic use, the use of iodine-containing contrast agents may increase the risk of acute kidney failure.
Optiray with food and drink
Ask your doctor. In patients with existing kidney disease, do not restrict fluid intake, as this may further impair kidney function.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Pregnancy. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant. Your doctor will only give you Optiray if it is absolutely necessary, as the medicine may harm the unborn child.
- Breastfeeding. Stop breastfeeding for one day after injection, as there is not enough data on the safety of use. Consult your doctor or radiologist.
Driving and using machines
Driving or operating machinery is not recommended for 1 hour afterinjection. Additionally, symptoms such as dizziness, drowsiness, weakness, and vision disturbances have been observed. If you experience these symptoms, do not attempt to perform any activities that require concentration and reaction.
Optiray contains sodium.
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per dose, which means it is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to use Optiray
Examinations using Optiray will be performed only by a doctor or radiologistwho will also decide on the dose. Optiray is injected into a blood vesseland distributed in the body through the bloodstream. Before use, the medicine is heated to body temperature, then injected once or several times during the radiological examination. The dose depends on the type of examination and other factors, such as the patient's condition and age. The smallest dose that allows for images of sufficient quality to be obtained is used.
Using more than the recommended dose of Optiray
Overdose is potentially dangerous and may affect breathing, heart, and circulation. Tell your doctor or radiologist immediately if you notice any of these symptoms after receiving Optiray. If you have any further questions about using this medicine, ask your doctor or radiologist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Optiray can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Side effects related to Optiray are generally dose-independent. In most cases, they are mild or moderate and very rarely severe or life-threatening. You should contact your doctor immediatelyif you experience any of the following severe side effects:
- cardiac arrest or respiratory arrest
- constriction of coronary arteries or blood clots
- stroke, cyanosis, fainting
- memory loss
- speech disorders
- sudden movements
- temporary blindness
- acute kidney failure
- skin rash, redness, or blisters that can develop into life-threatening skin reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) or drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
- allergic reaction symptoms, such as anaphylactic shock, constricted airways, swelling of the larynx, throat, tongue, difficulty breathing, coughing, sneezing, redness, and (or) swelling of the face and eyes, itching, rash, and hives
Side effects may occur with the following frequency:
very common, occurring in more than 1 in 10 users
- feeling of heat
common, occurring in 1 to 10 in 100 users
- pain
- nausea
uncommon, occurring in 1 to 10 in 1,000 users
- hives
- redness of the skin, itching
- dizziness
- headache
- taste disturbance
- sensory disturbances, such as tingling, numbness
- vomiting
- sneezing
- high blood pressure
rare, occurring in 1 to 10 in 10,000 users
- fainting
- dizziness
- blurred vision
- pulsating heartbeat
- low blood pressure
- sudden flushing of the face
- laryngospasm
- swelling and constriction of airways, including throat tightness, wheezing
- breathing difficulties
- nasal inflammation, causing sneezing and runny nose
- cough, throat irritation
- dry mouth
- rash
- urinary urgency
- swelling of the face, including eyes
- chills
- uncontrolled shaking
- feeling of cold
very rare, occurring in less than 1 in 10,000 users
- severe allergic reaction
- disorientation, anxiety, nervousness
- loss of consciousness, numbness
- paralysis
- drowsiness
- stupor
- speech disorders
- hearing disturbances
- allergic eye inflammation, causing redness, tearing, and itching of the eyes
- ringing or buzzing in the ears
- irregular heartbeat, slow pulse
- chest pain
- changes in heart activity measured by ECG
- disease affecting blood flow to the brain
- high blood pressure
- phlebitis, vasodilation
- fluid accumulation in the lungs
- sore throat
- low oxygen levels in the blood
- abdominal pain
- salivary gland inflammation, tongue swelling
- difficulty swallowing, increased saliva production
- most often painful, severe swelling of deep skin layers, mainly on the face
- increased sweating
- muscle cramps
- acute kidney failure or abnormal kidney function
- urinary incontinence, blood in urine, impaired urination
- swelling of tissues due to excess fluid
- reactions at the injection site, including pain, redness, bleeding, or tissue degeneration
- feeling unwell or abnormal, fatigue, lethargy
unknown: frequency cannot be estimated from available data
- severe allergic reaction with anaphylactic shock
- transient hypothyroidism
- seizures
- temporary brain disorder (encephalopathy), which can cause disorientation, hallucinations, vision disturbances, blindness, seizures, loss of coordination, loss of movement on one side of the body, speech problems, and loss of consciousness
- movement disorder
- memory loss
- temporary blindness
- cardiac arrest, life-threatening irregular heartbeat
- extra heartbeats
- constriction of coronary arteries, rapid heartbeat
- blue discoloration of the skin (cyanosis) due to low oxygen levels in the blood
- shock
- blood clot or constriction in a blood vessel
- pallor
- respiratory arrest, asthma, constricted airways
- reduced ability to produce voice using vocal organs
- diarrhea
- severe reaction involving skin, blood, and internal organs (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, also known as DRESS)
- red, peeling, widespread rash with bumps under the skin and blisters, accompanied by fever at the beginning of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis)
- red bumps (papules or nodules)
- life-threatening reaction with flu-like symptoms and painful rash/blisters on the skin, mouth, eyes, and genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis)
- absence of or painful urination
- hypothyroidism in newborns
- fever
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in the leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Optiray
Keep the medicine out of sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month. Store the containers in the outer packaging to protect from light. Protect from X-rays. Do not store above 30°C. Optiray 350 can be stored for one month at 37°C in a contrast agent storage warmer with air circulation. Do not use this medicine if you notice discoloration or solid particles.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Optiray contains:
- The active substance is ioversol. One milliliter of Optiray 350 contains 741 mg of ioversol, which corresponds to 350 mg of organically bound iodine.
- The other ingredients are: sodium calcium edetate (stabilizer), trometamol, and trometamol hydrochloride (buffer) and water for injections. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid may be used to adjust the pH to 6.0-7.4.
What Optiray looks like and contents of the pack
Optiray 350 is packaged in:
- colorless bottles of 30, 50, 100, or 200 ml, equipped with bromobutyl rubber closures and aluminum caps. The box contains the following number of bottles: 30 ml - 10 bottles, 50 ml - 10 or 25 bottles, 100 ml - 10 or 12 bottles, 200 ml - 10 or 12 bottles.
- colorless bottles of 500 ml, equipped with bromobutyl rubber closures and aluminum caps. The box contains 5, 6, or 10 bottles.
Optiray 350 is also supplied in prefilled syringes and syringes with a pressure injector, made of polypropylene. The syringe tip and plunger are made of natural rubber. Prefilled syringes of 30 or 50 ml are packaged in a box containing 10 syringes. Syringes with a pressure injector of 50, 100, or 125 ml are packaged in a box containing 10 or 20 syringes. 75 ml size. The box contains 10 syringes. Not all pack sizes and boxes may be marketed in all countries.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer:
- Address of the marketing authorization holderGuerbet BP 57400 95943 Roissy CDG Cedex France For more information about this medicine, contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder: Guerbet Poland Sp. z o.o., tel. (22) 6684110.
- Manufacturer
Guerbet
BP 57400
95943 Roissy CDG Cedex
France
manufacturing site: 16-24 rue Jean Chaptal, 93600 Aulnay sous Bois, France
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Instructions for use of prefilled syringes
Prefilled syringe
Assembly and inspection
Warning: The outer surface of the syringe is not sterile.
The contents of the syringe and the surface under the blue cap and the plunger ribs aresterileand should be handled with care during assembly.
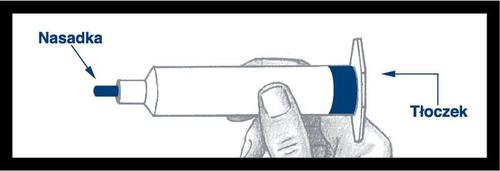
Remove the syringe from the base and check for leaks around the blue capand on the outside of the plunger. Do not use the syringe if you notice a leak. After screwing the plunger into the syringe, it is essential to turn the plunger an additional ½ turn so that the blue plunger can rotate freely.
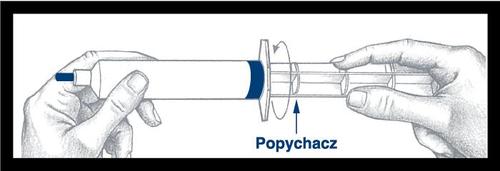
Before using the syringe, remove the blue cap and discard it. The surface under the cap is sterile; be careful not to touch it during further handling. The syringe is now ready for needle or infusion tube attachment. After use, discard the syringe and any unused portion of the medicine.
Instructions for use of syringes with a pressure injector
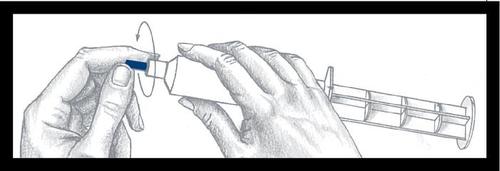
Prefilled syringe
Assembly and inspection
Warning: The outer surface of the syringe is not sterile.
The contents of the syringe and the surface under the blue cap and the plunger ribs aresterileand should be handled with care during assembly.
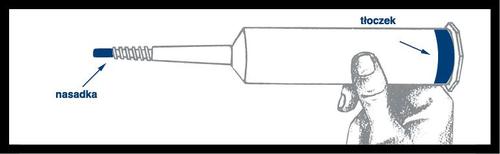
Remove the syringe from the base and check for leaks around the blue capand on the outside of the plunger. Do not use the syringe if you notice a leak. Place the syringe in the pressure injector shield.
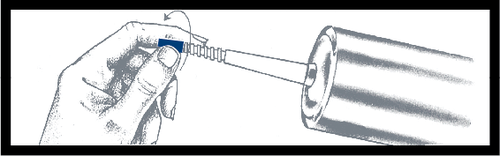
To remove the blue cap, press and twist it, then discard it. The surface under the cap is sterile; be careful during further handling.
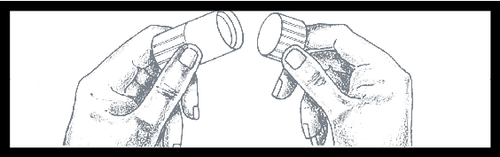
Then, remove the protective cap from the Luer connector by twisting it to break the visible seal. Discard the cap.

Screw the Luer connector onto the syringe, holding the protective cap and tightening it until it stops. Remove and discard the protective cap immediately before attaching a sterile infusion tube. After use, discard the syringe and any unused portion of the medicine.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterGuerbet
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Optirai 350Dosage form: Solution, 636 mg/ml (300 mg I/ml)Active substance: ioversolPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 678 mg/ml (320 mg iodine/ml)Active substance: ioversolPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 250 mg iodine/mlActive substance: iomeprolManufacturer: BIPSO GmbH Bracco Imaging S.p.A. Patheon Italia S.p.A.Prescription not required
Alternatives to Optirai 350 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Optirai 350 in Spain
Online doctors for Optirai 350
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Optirai 350 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














