

Olimel N9e

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Olimel N9e

How to use Olimel N9e
Patient Information Leaflet: User Information
OLIMEL N9E, infusion emulsion
Read the leaflet carefully before administering the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or nurse.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, inform the doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet
- 1. What OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before administering OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion
- 3. How to administer OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion is and what it is used for
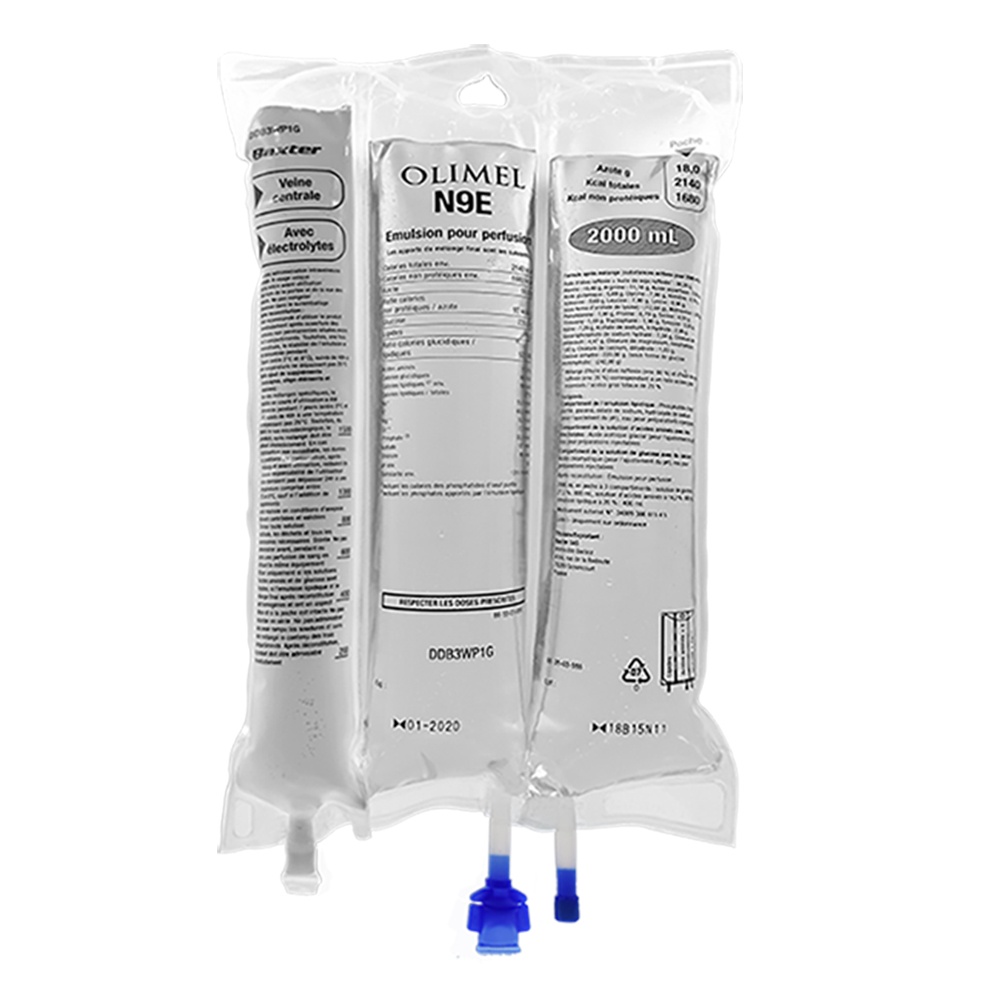
OLIMEL is an infusion emulsion. The preparation is supplied in a triple-chamber bag.
In the first chamber, there is a glucose solution with calcium, in the second - a fat emulsion, and in the third - an amino acid solution with other electrolytes.
OLIMEL is used for intravenous nutrition in adults and children over 2 years of age when oral nutrition is not appropriate.
OLIMEL should only be used under medical supervision.
2. Important information before administering OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion
When not to use OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion:
- in preterm infants, newborns, and children under 2 years of age;
- if the patient is allergic to eggs, soy, peanut proteins, corn/corn products (see also "Warnings and precautions" below) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the use of certain amino acids causes an abnormal reaction in the patient's body;
- if the patient has a particularly high level of fats in the blood;
- if the patient has hyperglycemia (too high blood sugar level);
- if the patient's blood has an abnormally high content of any of the electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, and/or phosphorus).
In each case, the doctor will decide on the administration of the medicine based on factors such as age, body weight, and the patient's health status, including the results of the tests performed.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting OLIMEL N9E administration, discuss it with your doctor or nurse.
Too rapid administration of total parenteral nutrition solutions may result in injury or death of the patient.
If unusual signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction occur (such as sweating, fever, chills, headache, skin rash, or breathing difficulties), the infusion should be stopped immediately. The medicine contains soybean oil and egg phospholipids. Soy and egg proteins may cause hypersensitivity reactions. Cross-allergic reactions have been observed between soy and peanut proteins.
OLIMEL contains glucose derived from corn, which may cause hypersensitivity reactions if the patient is allergic to corn or corn products (see "When not to use OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion" above).
Breathing difficulties may also be a sign that small particles have formed that can block blood vessels in the lungs (pulmonary embolism). If any breathing difficulties occur, inform the doctor or nurse. They will decide on the appropriate action.
The antibiotic ceftriaxone should not be mixed or administered simultaneously with any calcium-containing solutions (including OLIMEL) by intravenous drip. These medicines should not be administered simultaneously even through different infusion lines or injection sites.
However, OLIMEL and ceftriaxone can be administered sequentially, one after the other, if the infusion lines are inserted at different sites or are changed or thoroughly flushed with physiological saline solution between infusions to avoid precipitate formation.
Certain medicines and diseases may increase the risk of infection or sepsis (presence of bacteria in the blood). There is a particular risk of infection or sepsis after the insertion of a tube (central venous catheter) into the patient's vein. The doctor will closely monitor the patient to detect any signs of infection. Patients requiring parenteral nutrition (administration of nutrients through a tube inserted into a vein) are, due to their clinical condition, more prone to developing infections. Using aseptic procedures during catheter placement, handling, and preparation of the nutrition mixture (total parenteral nutrition) can reduce the risk of infection.
If the patient is severely malnourished and needs to receive food through a vein, the doctor should start treatment slowly. At the same time, the doctor should closely monitor the patient to prevent sudden changes in fluid volume, vitamin, electrolyte, and mineral levels.
Before starting the infusion, the doctor should correct any water-electrolyte and metabolic disorders in the patient. The doctor will monitor the patient during therapy and may adjust the dosage or prescribe additional nutritional supplements such as vitamins, electrolytes, and trace elements if necessary.
In patients receiving intravenous nutritional therapy, liver function disorders have been reported, including difficulty in removing bile (cholestasis), fat accumulation (fatty liver), fibrosis, possibly leading to liver failure, as well as gallbladder inflammation and gallstones. The causes of these disorders are thought to be different in different patients. If the patient experiences symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, yellowing of the skin or eyes, they should consult a doctor to identify possible causes and therapeutic measures.
The doctor should be informed about:
- severe kidney diseases. The doctor should also be informed if the patient is undergoing dialysis (artificial kidney) or other blood purification methods;
- severe liver diseases;
- blood coagulation disorders;
- adrenal gland disorders (adrenal insufficiency). The adrenal glands are triangular glands located on top of the kidneys;
- heart failure;
- lung disease;
- fluid accumulation in the body (overhydration);
- insufficient fluid in the body (dehydration);
- untreated high blood sugar levels (diabetes);
- heart attack or shock caused by sudden heart failure;
- severe metabolic acidosis (too acidic blood);
- sepsis (blood infection);
- coma.
To check the effectiveness and safety of the medicine, the patient will undergo clinical and laboratory tests ordered by the doctor during treatment. If the medicine is administered for several weeks, the patient's blood will be regularly tested.
A reduced ability of the body to remove lipids contained in the administered preparation may result in a so-called fat overload syndrome (see section 4 - "Possible side effects").
If pain, burning, or swelling occurs at the infusion site or if the infused fluid leaks during infusion, inform the doctor or nurse.
The administration of the preparation will be stopped immediately and then resumed in a different vein.
If the blood sugar level increases excessively, the doctor should adjust the rate of administration of OLIMEL or administer a medicine that regulates blood sugar levels (insulin).
OLIMEL can be administered through a tube (catheter) inserted into a large vein in the patient's chest (central vein).
Children and adolescents
When used in children under 18 years of age, particular caution should be exercised to administer the correct dose of the preparation. Due to the increased susceptibility of children to infection risk, increased precautions should also be taken. Vitamin and trace element supplementation is always required. For children, pediatric compositions and quantities must be used.
OLIMEL and other medicines
Inform the doctor about all medicines the patient is currently taking or using, as well as any medicines the patient plans to take or use.
Concomitant use of other medicines is usually not contraindicated. However, the doctor should be informed about all medicines taken recently, including those available without a prescription, to check their compatibility.
Inform the doctor about taking or receiving:
- insulin,
- heparin.
Do not administer OLIMEL simultaneously with blood through the same infusion set.
OLIMEL contains calcium. It should not be administered together with the antibiotic ceftriaxone or through the same tube, as particles may form. If these medicines are administered sequentially using the same device, it should be thoroughly flushed.
Due to the risk of precipitate formation, OLIMEL should not be administered through the same infusion line or added to ampicillin (an antibiotic) or fosphenytoin (an antiepileptic drug).
The olive and soybean oil present in OLIMEL contain vitamin K. This usually has no effect on the action of blood-thinning medicines (anticoagulants) such as coumarin. However, if the patient is taking anticoagulant medicines, they should inform their doctor.
The fats in the emulsion may interfere with the results of certain laboratory tests if the blood sample for testing is taken before the fats are removed from the patient's bloodstream (they are removed from the blood after 5 to 6 hours after fat administration).
OLIMEL contains potassium. Particular caution should be exercised in patients taking diuretic medicines, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (medicines used in hypertension), or immunosuppressive medicines. These types of medicines may cause an increase in potassium levels in the blood.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before administering this medicine.
There is limited experience with the use of OLIMEL N9E in pregnant or breastfeeding women. If necessary, OLIMEL N9E may be considered during pregnancy and breastfeeding. OLIMEL N9E should be administered to pregnant or breastfeeding women only after careful consideration.
Driving and using machines
Not applicable.
3. How to administer OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion
Dosage
OLIMEL should only be used in adults and children over 2 years of age.
The medicine is an infusion emulsion administered through a tube (catheter) into a large vein in the patient's chest.
Before use, OLIMEL should be at room temperature.
OLIMEL is for single use only.
The infusion of one bag usually lasts from 12 to 24 hours.
Dosage - adults
The rate of administration, according to the patient's needs and clinical condition, will be determined by the doctor.
The medicine can be used for as long as necessary, depending on the patient's clinical condition.
Dosage - children over 2 years of age and adolescents
The dose of the medicine and the duration of administration are determined by the doctor, depending on the patient's age, body weight, height, health status, and the body's ability to break down and utilize the components of OLIMEL N9E.
Administration of a higher dose of OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion than recommended
If the patient is administered too high a dose of the medicine or too rapid an infusion, the contained amino acids may contribute to an increase in blood acidity and the occurrence of symptoms of hypervolemia (increased blood volume). The blood sugar level may increase, and hyperosmolar syndrome (excessive blood viscosity) may occur, and the fats contained in the emulsion may increase the level of triglycerides in the blood. Administration of an infusion that is too rapid or of too large a volume of OLIMEL may cause nausea, vomiting, chills, headache, flushing, excessive sweating, and electrolyte disturbances. In such a situation, the infusion should be stopped immediately.
In severe cases, the doctor may be forced to temporarily subject the patient to kidney dialysis to support the kidneys in removing the excess medicine.
To prevent such situations, the doctor regularly monitors the patient's condition and checks blood parameters.
In case of doubts related to the use of the medicine, consult a doctor.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, OLIMEL can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any changes in the patient's condition are observed during or after treatment, the doctor or nurse should be informed immediately.
Tests performed by the doctor during treatment should minimize the risk of side effects.
If any unusual signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction occur, such as excessive sweating, fever, chills, headache, skin rash, or breathing difficulties, the infusion should be stopped immediately.
The following side effects have been reported during the use of OLIMEL:
- increased heart rate (tachycardia);
- decreased appetite;
- increased blood fat levels (hypertriglyceridemia);
- abdominal pain;
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- increased blood pressure (hypertension).
Frequency - Unknown: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including sweating, fever, chills, headache, skin rash (erythematous, papular, pustular, maculopapular, generalized rash), itching, flushing, and breathing difficulties;
- Infusion site reactions, which may lead to pain, irritation, swelling, redness (erythema)/warmth, tissue necrosis, or blistering/bullae, inflammation, thickening, or tightening of the skin at the infusion site;
- Vomiting.
The following side effects have been reported with the use of similar parenteral nutrition products:
- Fat overload syndrome associated with a sudden worsening of the patient's condition. The symptoms of fat overload syndrome usually resolve after stopping the fat emulsion infusion. These include:
· Fever
· Decreased red blood cell count, which can cause paleness and weakness or shortness of breath (anemia)
· Low white blood cell count, which can increase the risk of infection (leukopenia)
· Low platelet count, which can increase the risk of bruising and/or bleeding (thrombocytopenia)
· Coagulation disorders affecting the blood's ability to clot
· High blood fat levels (hyperlipidemia)
· Fatty liver deposits (hepatomegaly)
· Impaired liver function
· Central nervous system symptoms (e.g., coma).
Frequency - Unknown: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- Allergic reactions;
- Abnormal liver function test results;
- Bile excretion disorders (cholestasis);
- Liver enlargement (hepatomegaly);
- Liver diseases related to parenteral nutrition (see "Warnings and precautions" in section 2);
- Jaundice;
- Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia);
- High blood nitrogen levels (azotemia);
- Increased liver enzyme activity;
- Formation of small particles that can block blood vessels in the lungs, leading to pulmonary embolism and breathing difficulties (respiratory failure).
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any not listed in the leaflet, inform the doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion
Store the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the container and outer packaging (MM/RRRR). The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not freeze.
Store in protective packaging.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion contains
The active substances in each bag of the ready-to-use emulsion are: 14.2% (corresponding to 14.2 g/100 ml) L-amino acid solution (alanine, arginine, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine (as lysine acetate), methionine, phenylalanine, proline, serine, threonine, tryptophan, tyrosine, valine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid) with electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium, phosphates, acetates, chlorides), 20% (corresponding to 20 g/100 ml) fat emulsion (purified olive oil and purified soybean oil) and 27.5% (corresponding to 27.5 g/100 ml) glucose solution (as glucose monohydrate) with calcium.
Other ingredients of the medicine are:
| Chamber containing fat emulsion | Chamber containing amino acid solution with electrolytes | Chamber containing glucose solution with calcium |
| Purified egg phospholipids, glycerol, sodium oleate, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), water for injections | Acetic acid (for pH adjustment), water for injections | Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), water for injections |
How OLIMEL N9E infusion emulsion looks and what the package contains
OLIMEL is an infusion emulsion supplied in a triple-chamber bag. The first chamber contains the fat emulsion, the second chamber contains the amino acid solution with electrolytes, and the third chamber contains the glucose solution with calcium. The chambers are separated from each other by non-permeable welds.
Before administration, the contents of the individual chambers should be mixed by rolling the bag towards each other, starting from the top of the bag, until the welds open.
After mixing, a homogeneous mixture with a milky appearance is obtained.
Appearance before mixing:
- Amino acid and glucose solutions are clear, colorless, or slightly yellow.
- The fat emulsion is homogeneous with a milky appearance.
Appearance after mixing: homogeneous emulsion with a milky appearance.
The triple-chamber bag is a multi-layer plastic bag. The inner (contact) layer of the bag is compatible with the ingredients and permitted additives.
To prevent contact with oxygen in the air, the bag is packaged in a protective packaging that protects against oxygen, along with an oxygen absorber sachet.
Package sizes
1000 ml bag: 1 cardboard box with 6 bags
1500 ml bag: 1 cardboard box with 4 bags; 1 cardboard box with 5 bags
2000 ml bag: 1 cardboard box with 4 bags; 1 cardboard box with 5 bags
1 bag with a capacity of 1000 ml, 1500 ml, and 2000 ml.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Baxter Polska Sp. z o.o.
Ul. Kruczkowskiego 8
00-380 Warsaw
Manufacturer
BAXTER S.A.
Boulevard Rene Branquart 80
7860 Lessines, Belgium
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
France, Portugal, Estonia, Poland, Lithuania, Bulgaria, Romania, Latvia, Czech Republic, Belgium, Spain, Slovakia, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Slovenia, Italy, Greece, Cyprus, Hungary: OLIMEL N9E
In some countries, it is registered under a different trade name, as described below:
Austria: ZentroOLIMEL 5.7% mit Elektrolyten
Germany: Olimel 5.7% E
Denmark, Iceland, Sweden, Norway, Finland: Olimel N9E
United Kingdom, Ireland, Malta: Triomel 9g/l nitrogen 1070 kcal/l with electrolytes
Date of last revision of the leaflet: April 2025
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Pharmacotherapeutic group: parenteral nutrition solutions/mixtures
ATC code: B05 BA10.
A. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
OLIMEL is a triple-chamber bag.
Each bag contains a glucose solution with calcium, a fat emulsion, and an amino acid solution with other electrolytes:
| Contents per bag | |||
| 1000 ml | 1500 ml | 2000 ml | |
| 27.5% glucose solution (corresponding to 27.5 g/100 ml) | 400 ml | 600 ml | 800 ml |
| 14.2% amino acid solution (corresponding to 14.2 g/100 ml) | 400 ml | 600 ml | 800 ml |
| 20% fat emulsion (corresponding to 20 g/100 ml) | 200 ml | 300 ml | 400 ml |
The composition of the ready-to-use emulsion after mixing the contents of the three chambers:
| Active substances | 1000 ml | 1500 ml | 2000 ml |
| Purified olive oil + purified soybean oil | 40.00 g | 60.00 g | 80.00 g |
| Alanine | 8.24 g | 12.36 g | 16.48 g |
| Arginine | 5.58 g | 8.37 g | 11.16 g |
| Aspartic acid | 1.65 g | 2.47 g | 3.30 g |
| Glutamic acid | 2.84 g | 4.27 g | 5.69 g |
| Glycine | 3.95 g | 5.92 g | 7.90 g |
| Histidine | 3.40 g | 5.09 g | 6.79 g |
| Isoleucine | 2.84 g | 4.27 g | 5.69 g |
| Leucine | 3.95 g | 5.92 g | 7.90 g |
| Lysine (corresponding to lysine acetate) | 4.48 g (6.32 g) | 6.72 g (9.48 g) | 8.96 g (12.64 g) |
| Methionine | 2.84 g | 4.27 g | 5.69 g |
| Phenylalanine | 3.95 g | 5.92 g | 7.9 g |
| Proline | 3.40 g | 5.09 g | 6.79 g |
| Serine | 2.25 g | 3.37 g | 4.50 g |
| Threonine | 2.84 g | 4.27 g | 5.69 g |
| Tryptophan | 0.95 g | 1.42 g | 1.90 g |
| Tyrosine | 0.15 g | 0.22 g | 0.30 g |
| Valine | 3.64 g | 5.47 g | 7.29 g |
| Sodium acetate trihydrate | 1.50 g | 2.24 g | 2.99 g |
| Sodium glycerophosphate hydrate | 3.67 g | 5.51 g | 7.34 g |
| Magnesium chloride hexahydrate | 0.81 g | 1.22 g | 1.62 g |
| Calcium chloride dihydrate | 0.52 g | 0.77 g | 1.03 g |
| Glucose (corresponding to glucose monohydrate) | 110.00 g (121.00 g) | 165.00 g (181.50 g) | 220.00 g (242.00 g) |
Excipients are:
| Chamber containing fat emulsion | Chamber containing amino acid solution with electrolytes | Chamber containing glucose solution with calcium |
| Purified egg phospholipids, glycerol, sodium oleate, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), water for injections | Acetic acid (for pH adjustment), water for injections | Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), water for injections |
Nutritional values of the ready-to-use emulsion, depending on the bag size:
| 1000 ml | 1500 ml | 2000 ml | |
| Fats | 40 g | 60 g | 80 g |
| Amino acids | 56.9 g | 85.4 g | 113.9 g |
| Nitrogen | 9.0 g | 13.5 g | 18.0 g |
| Glucose | 110.0 g | 165.0 g | 220.0 g |
| Energy value: Total energy value (approximate) Non-protein energy value Glucose energy value Fat energy value Non-protein energy value/nitrogen ratio Glucose/fat energy value ratio Fat/total calories ratio | 1070 kcal 840 kcal 440 kcal 400 kcal 93 kcal/g 52/48 37% | 1600 kcal 1260 kcal 660 kcal 600 kcal 93 kcal/g 52/48 37% | 2140 kcal 1680 kcal 880 kcal 800 kcal 93 kcal/g 52/48 37% |
| Electrolytes: Sodium Potassium Magnesium Calcium Phosphates Acetates Chlorides | 35.0 mmol 30.0 mmol 4.0 mmol 3.5 mmol 15.0 mmol 54 mmol 45 mmol | 52.5 mmol 45.0 mmol 6.0 mmol 5.3 mmol 22.5 mmol 80 mmol 68 mmol | 70.0 mmol 60.0 mmol 8.0 mmol 7.0 mmol 30.0 mmol 107 mmol 90 mmol |
| pH | 6.4 | 6.4 | 6.4 |
| Osmolality | 1310 mOsm/l | 1310 mOsm/l | 1310 mOsm/l |
B. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage
OLIMEL is not recommended for use in children under 2 years of age due to the inappropriate composition and volume (see sections 4.4; 5.1 and 5.2 of the SmPC).
Do not exceed the recommended maximum daily dose. Due to the fixed composition of the multi-chamber bag, it may not be possible to meet all the nutritional needs of the patient at the same time. There may be clinical situations where patients require different amounts of nutrients than those contained in the bag with a fixed composition. In such a situation, any change in volume (dose) should take into account the impact on the dosing of all other nutrients in the OLIMEL medicinal product.
Adults
Dosage depends on the patient's energy expenditure, clinical condition, body weight, and ability to metabolize the components of OLIMEL, as well as the energy and protein components additionally administered orally/enterally; therefore, the bag size should be appropriately selected.
Average daily requirements are:
- 0.16 to 0.35 g of nitrogen/kg body weight (1 - 2 g of amino acids/kg), depending on the patient's nutritional status and degree of catabolism,
- 20 to 40 kcal/kg,
- 20 to 40 ml of fluid/kg or 1 to 1.5 ml per kcal consumed. For OLIMEL, the maximum daily dose is determined based on amino acid intake, 35 ml/kg corresponding to 2.0 g of amino acids/kg, 3.9 g of glucose/kg, 1.4 g of fat/kg, 1.2 mmol of sodium/kg, and 1.1 mmol of potassium/kg. For a 70 kg patient, this would correspond to 2450 ml of OLIMEL per day, which is equivalent to 140 g of amino acids, 270 g of glucose, and 98 g of fat (i.e., 2058 non-protein kcal and a total of 2622 kcal).
Usually, the infusion rate should be gradually increased during the first hour, and then the infusion rate should be adjusted according to the dose, daily volume of the administered medicinal product, and infusion duration.
The maximum infusion rate for OLIMEL is 1.8 ml/kg/h, which corresponds to 0.10 g of amino acids/kg/h, 0.19 g of glucose/kg/h, and 0.07 g of fat/kg/h.
Children over 2 years of age and adolescents
No studies have been conducted in the pediatric population.
Dosage is dependent on the patient's energy expenditure, clinical condition, body weight, and ability to metabolize the components of OLIMEL, as well as the energy and protein components additionally administered orally/enterally; therefore, the bag size should be appropriately selected.
Additionally, daily requirements for fluids, nitrogen, and energy decrease with age. Two age groups are considered: 2 to 11 years and 12 to 18 years.
For OLIMEL N9E, in the 2 to 11-year-old age group, the limiting factor for the daily dose is the magnesium content. In this age group, the limiting factor for the hourly infusion rate is the glucose content. In the 12 to 18-year-old age group, the limiting factors for the daily dose are the amino acid and magnesium contents. In this age group, the limiting factor for the hourly infusion rate is the amino acid content. The resulting intakes are presented below:
| Component | 2 to 11 years | 12 to 18 years | ||
| Recommended | Maximum volume of OLIMEL N9E | Recommended | Maximum volume of OLIMEL N9E | |
| Maximum daily dose | ||||
| Fluids (ml/kg/day) |
| 25 |
| 35 |
| Amino acids (g/kg/day) |
| 1.4 |
| 2.0 |
| Glucose (g/kg/day) | 1.4 – 8.6 | 2.8 | 0.7 – 5.8 | 3.9 |
| Fats (g/kg/day) | 0.5 - 3 | 1.0 | 0.5 - 2 (up to 3) | 1.4 |
| Total energy value (kcal/kg/day) |
| 26.8 |
| 37.5 |
| Maximum hourly infusion rate | ||||
| OLIMEL N9E (ml/kg/h) | 3.3 | 2.1 | ||
| Amino acids (g/kg/h) | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| Glucose (g/kg/h) | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.23 |
| Fats (g/kg/h) | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
Usually, the infusion rate should be gradually increased during the first hour, and then the infusion rate should be adjusted according to the dose, daily volume of the administered medicinal product, and infusion duration.
Generally, in small children, it is recommended to start the infusion with a small daily dose and gradually increase it to the maximum dose (see above).
Administration method and duration
For single use only.
It is recommended to use the contents of the bag immediately after opening and not to store it for the next infusion.
After mixing, a homogeneous mixture with a milky appearance is obtained.
Instructions for preparing and administering the infusion emulsion can be found in section 6.6 of the SmPC.
Due to the high osmolality of OLIMEL, it can only be administered into a central vein.
The recommended infusion duration for a parenteral nutrition bag is from 12 to 24 hours.
Treatment with parenteral nutrition can be continued for as long as the patient's clinical condition requires.
C. PHARMACEUTICAL INCOMPATIBILITIES
Do not add any medicinal products or substances to any of the bag's components or to the ready-to-use emulsion without prior confirmation of their compatibility and stability of the resulting product (especially the stability of the fat emulsion).
Incompatibilities may arise, for example, due to excessive acidity (low pH) or inappropriate content of divalent cations (Ca and Mg), which may destabilize the fat emulsion.
As with the preparation of other parenteral nutrition mixtures, the ratio of calcium and phosphate content should be considered. Excessive addition of calcium and phosphate, especially in the form of inorganic salts, may cause the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates.
OLIMEL contains calcium ions, which pose an additional risk of clot formation in blood or blood component preparations containing citrate as an anticoagulant/preservative.
Do not mix or administer ceftriaxone simultaneously with calcium-containing intravenous solutions, including OLIMEL, through the same infusion line (e.g., through a Y-connector) due to the risk of precipitation of calcium ceftriaxone (see sections 4.4 and 4.5 of the SmPC). Ceftriaxone and calcium-containing solutions can be administered sequentially, one after the other, if the infusion lines are inserted at different sites or are changed or thoroughly flushed with physiological saline solution between infusions to avoid precipitate formation.
Due to the risk of precipitate formation, OLIMEL should not be administered through the same infusion line or added to ampicillin (an antibiotic) or fosphenytoin (an antiepileptic drug).
Check the compatibility with solutions administered simultaneously through the same infusion set, catheter, or cannula.
Due to the risk of pseudoagglutination, this product should not be administered before, during, or after blood transfusion through the same infusion set.
D. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL AND PREPARATION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT FOR ADMINISTRATION
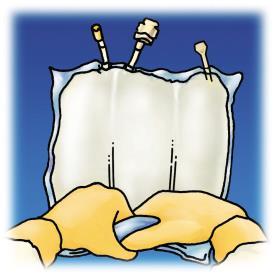
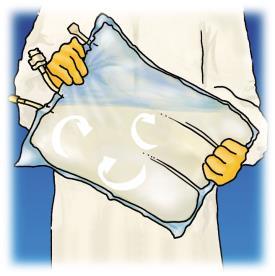
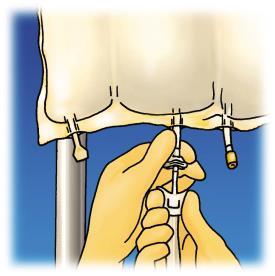
A review of the preparation stages of OLIMEL before administration is presented in Figure 1.
Opening
Remove the protective bag.
Discard the oxygen absorber sachet.
Make sure the bag or welds are not damaged. Only use if the bag is undamaged and the welds are intact (i.e., the contents of the 3 chambers have not been mixed), the amino acid and glucose solutions are clear, colorless, or slightly yellow, and practically free of visible particles, and the fat emulsion is homogeneous with a milky appearance.
Mixing of solutions and emulsions
Before breaking the welds, ensure the product is at room temperature.
Starting from the top of the bag (at the handle), roll the bag with both hands. The welds will disappear from the port side. Continue rolling the bag until the welds are broken halfway through their length.
Mix by turning the bag at least 3 times.
After mixing, the product has a homogeneous milky appearance.
Additional components
The bag volume is sufficient to allow the addition of vitamins, electrolytes, and trace elements.
Any additives (including vitamins) should be introduced into the ready-to-use emulsion (after breaking the welds and mixing the contents of the 3 chambers).
Vitamins can also be added to the glucose chamber before preparing the ready-to-use emulsion (before breaking the welds and mixing the contents of the three chambers).
When introducing additional components into products containing electrolytes, consider the amount of electrolytes already present in the bag.
Additional components must be introduced by qualified personnel under aseptic conditions.
Electrolytes can be added to OLIMEL according to the following table:
- check aseptic conditions,
- prepare the injection site on the bag,
- puncture the injection site and inject the additives using a syringe needle or a device for preparing the medicinal product,
- mix the bag contents with the additives.
2. 3.



5. 6.
Administration
For single use only.
Administer the product only after breaking the welds separating the 3 chambers and mixing their contents.
Ensure that the ready-to-use infusion emulsion does not separate phases.
After opening the bag, the contents must be used immediately. Do not store
the opened bag for the next infusion. Do not reconnect partially used bags.
To avoid the possibility of air embolism caused by the presence of gas
contained in the first bag, do not connect bags in series.
Any unused product or its waste and the entire infusion set should be
destroyed.
Extravasation
The site of catheter insertion should be regularly monitored for signs of extravasation.
In case of extravasation, the administration of the preparation should be immediately stopped, leaving the inserted catheter or cannula in place for immediate implementation of therapeutic measures. If
possible, before removing the inserted catheter/cannula, aspiration of fluid through the
catheter/cannula should be performed to reduce the amount of fluid in the tissues.
Depending on the type of extravasated product (including products mixed with OLIMEL, if applicable) and the degree/extent of potential injury, appropriate specific measures should be taken. Treatment options may include non-pharmacological, pharmacological, and (or) surgical intervention. In case of large extravasation, a plastic surgeon should be consulted within 72 hours.
The extravasation site should be monitored at least every four hours during the first
24 hours, and then once a day.
The infusion should not be resumed in the same central vein.
Baxter and Olimel are trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterBaxter S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Olimel N9eDosage form: Solution, -Active substance: combinationsPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, -Active substance: combinationsPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, -Active substance: combinationsPrescription not required
Alternatives to Olimel N9e in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Olimel N9e in Hiszpania
Alternative to Olimel N9e in Ukraina
Online doctors for Olimel N9e
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Olimel N9e – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














