

Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal

How to use Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
MORPHINI SULFAS WZF 0.1% SPINAL 1 mg/ml, solution for injection
Morphine hemisulfate 2.5-hydrate
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
- 3. How to use Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal and what is it used for
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal contains morphine, which is a very potent pain reliever. Morphine belongs to a group of pain relievers called opioids. Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is intended for intravenous, epidural, and subarachnoid (injection of the drug into the so-called epidural or spinal canal at a suitable level of the spine) administration. Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is used for acute and chronic pain of varying intensity, from moderate to severe. Morphine is used for postoperative and chronic pain, most often of cancer origin. Epidural or subarachnoid administration of the drug provides long-lasting pain relief. Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal does not contain preservatives.
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is always administered by medical personnel.
2. Important information before using Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
When not to use Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal:
- if the patient is allergic to the active substance, other opioid pain relievers, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has breathing difficulties or a disease that causes breathing difficulties or shortness of breath (called obstructive disease of the upper airways);
- if the patient has general contraindications to the use of the drug subarachnoid and epidural, e.g. inflammatory condition at the injection site, use of anticoagulant drugs by the patient, bleeding disorder.
Tolerance, dependence, and addictive use This medicine contains morphine, which is an opioid. Repeated use of opioids can lead to reduced efficacy of the medicine (the patient gets used to it, which is known as tolerance to the medicine). Repeated use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal may also lead to dependence, abuse, and addictive use, which can result in life-threatening overdose. The risk of these side effects may increase with increasing dose and duration of use. Dependence or addictive use can cause the patient to feel a loss of control over how much medicine to take or how often to take it. The risk of dependence on Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal or its addictive use varies from person to person. The risk of dependence on Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal or its addictive use may be higher if:
- the patient or any of their relatives have ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription drugs, or narcotics ("dependence");
- the patient smokes;
- the patient has ever had mood disorders (depression, anxiety disorders, or personality disorders) or has been treated by a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses.
If any of the following symptoms occur while taking Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal, it may indicate dependence or addictive use:
- the patient must take the medicine for a longer period than prescribed by the doctor;
- the patient must take a higher dose than recommended;
- the patient uses the medicine for reasons other than those for which the doctor prescribed it, e.g. "to calm down" or "to be able to sleep";
- the patient has repeatedly made unsuccessful attempts to stop or control the use of the medicine;
- after stopping the medicine, the patient feels unwell, and their condition improves when they take the medicine again ("withdrawal effect"). If any of these symptoms are noticed, the patient should discuss with their doctor the best treatment strategy, including when it is appropriate to stop the treatment and how it can be safely terminated (see section 3 "Stopping the use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal").
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal, consult a doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. During treatment with Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) has been reported. Symptoms usually occur within the first 10 days of treatment. Tell your doctor if you have ever had a severe skin rash or skin peeling after taking Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal or other opioids, or if you have had blisters and (or) ulcers in the mouth. Stop using Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal and consult a doctor immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms: blisters, widespread skin peeling, or pustular eruptions with fever. Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal may cause sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep) and hypoxemia (low oxygen level in the blood). Symptoms may include pauses in breathing during sleep, nighttime awakenings due to shortness of breath, difficulty maintaining sleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness. If the patient or another person notices these symptoms, they should contact a doctor. The doctor may consider reducing the dose. Consult a doctor if the patient experiences severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, nausea, vomiting, or fever, as these may be symptoms related to pancreatitis and bile ducts. If any of the following symptoms occur during treatment with Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal, consult a doctor:
- Increased sensitivity to pain, despite increased dose of the medicine (hyperalgesia). The doctor will decide whether a change in dosage or the use of a strong pain reliever is necessary (see section 2).
- Weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, or low blood pressure. These may be symptoms that the adrenal glands are not producing enough cortisol and hormone supplements may be necessary.
- Loss of sexual desire, impotence, amenorrhea. This may be due to decreased production of sex hormones.
- If the patient has a history of drug or alcohol dependence. The patient should also tell their doctor if they notice that they are becoming dependent on Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal during its use. For example, when they start thinking about taking the next dose frequently, even if they don't need it to relieve pain.
- Withdrawal symptoms or dependence. The most common withdrawal symptoms are listed in section 3. In such a case, the doctor may change the medicine or the time between doses.
The doctor will exercise particular caution when using morphine and will take appropriate action in patients:
- with reduced thyroid function (hypothyroidism);
- with asthma or other breathing problems, e.g. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- with prostate enlargement or difficulty urinating;
- with low blood pressure and heart function disorders;
- with reduced blood flow to the body's tissues;
- in the elderly, frail, or debilitated by disease;
- with bile duct disorders (morphine may exacerbate painful conditions);
- with liver function disorders;
- with kidney function disorders;
- after head injuries, in case of increased intracranial pressure and in the eyes;
- with spinal curvature (kyphoscoliosis);
- with significant obesity;
- with epilepsy or a history of seizures;
- with metabolic disorders.
Children and adolescents
There are no data on the use of the medicine in patients under 18 years of age. The safety of using morphine epidurally and subarachnoidally in children has not been established. In case of any doubts, consult a doctor.
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, and about medicines you plan to take, if possible and your condition allows. This is especially important when using the following medicines:
- Rifampicin, used to treat e.g. tuberculosis.
- Concomitant use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal and sedative medicines, e.g. benzodiazepines or derivatives, increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), or coma, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, combination therapy should only be considered when other treatment options are not available. If Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is used with sedative medicines, the doctor should limit the dose and duration of concomitant use. The patient should tell their doctor about all sedative medicines they are taking and strictly follow the dose prescribed by the doctor. It may be helpful to inform a relative or close friend of the patient about the possibility of these symptoms. If these symptoms occur, consult a doctor.
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal interacts with:
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (antidepressants), e.g. moclobemide, especially if the patient has taken these medicines in the last 2 weeks;
- tricyclic antidepressants, e.g. amitriptyline;
- sleeping pills, e.g. phenobarbital;
- sedative and anxiolytic medicines, e.g. diazepam;
- phenothiazine derivatives, e.g. promazine, chlorpromazine;
- butyrophenone derivatives, e.g. haloperidol, droperidol;
- neuroleptics used to sedate the patient before surgery (premedication) and administered during surgery, which can exacerbate breathing difficulties.
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal with alcohol
Alcohol should be avoided during treatment with morphine.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult a doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
- The use of morphine during pregnancy and breastfeeding will be decided by the doctor.
- If Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal was used during pregnancy for a longer period, there is a risk of withdrawal symptoms in the newborn, which should be treated by a doctor.
- Intravenous use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is not recommended during childbirth. Newborns born to mothers who have taken morphine for a long time may experience withdrawal symptoms - see section 3, subsection: "Stopping the use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal".
Driving and using machines
Morphine can cause drowsiness and impair psychophysical performance. During treatment with the medicine, do not drive vehicles or operate machines.
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal contains sodium
The medicine contains 7.08 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in each ampoule (2 ml). This corresponds to 0.354% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
3. How to use Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is administered by medical personnel. Before starting and regularly during treatment, the doctor will discuss with the patient what to expect from using Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal, when and how long to take it, when to consult a doctor, and when to stop using the medicine (see also "Stopping the use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal" in this section).
- The dose of morphine is determined individually by the doctor for each patient.
- Adult patients are given Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal intravenously, epidurally, or subarachnoidally.
- Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal should not be given to children and adolescents (see above, subsection "Children and adolescents").
Using a higher dose of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal than recommended
Morphine is administered by medical personnel, so it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should. If a higher dose of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is taken than recommended, aspiration pneumonia may occur. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, and fever. After using a higher dose of the medicine, the following symptoms may occur: very narrow pupils ("pinpoint pupils"), coma, shallow breathing, cyanosis, cold skin, and limb weakness. There may be breathing difficulties (which can occur up to 24 hours after subarachnoid administration), significant decrease in blood pressure with heart failure, decrease in body temperature, seizures, or severe muscle pain. Additionally, overdose symptoms may include breathing difficulties leading to loss of consciousness, and even death. If such symptoms occur, immediately inform medical personnel, who will take appropriate action.
Missing a dose of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping the use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
In case of sudden cessation of morphine use, especially in dependent individuals, withdrawal symptoms occur. Do not stop using Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal unless the doctor advises otherwise. To stop using Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal, consult a doctor, who will decide how to gradually reduce the dose to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal symptoms may include body aches, seizures, diarrhea, stomach pain, nausea, flu-like symptoms, rapid heartbeat, and dilated pupils. Psychological symptoms include intense dissatisfaction, anxiety, and irritability. Dependence is rare in patients receiving morphine for medical reasons. If you have any further doubts about using this medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Stop using the medicine and consult a doctor immediately if you experience:
- severe allergic reactions causing breathing difficulties or dizziness;
- symptoms of allergy, e.g. hives, itching, or skin irritation - such symptoms occur frequently (less often than 1 in 10 people) after epidural or subarachnoid administration of morphine;
- severe skin reaction with blisters, widespread skin peeling, or pustular eruptions with fever. This may be a condition called acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP);
- breathing difficulties leading to loss of consciousness, usually after using a higher dose of the medicine than recommended (see above, subsection "Using a higher dose of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal than recommended");
- withdrawal symptoms or dependence (symptoms are described in section 3, subsection: "Stopping the use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal").
Consult a doctor if you experience frequent side effects (less often than 1 in 10 people):
- itching - occurs after epidural or subarachnoid administration of a single dose of morphine, not only at the injection site;
- urinary retention - may persist for 10 to 20 hours after a single epidural and subarachnoid administration of the medicine and is a side effect that can be expected, especially in men (in women it occurs less frequently).
Consult a doctor if you experience side effects with unknown frequency (frequency cannot be estimated from available data):
- increased sensitivity to pain;
- sweating;
- dry mouth;
- nausea, vomiting;
- constipation;
- development of tolerance to the medicine (which means that the medicine becomes less effective over time, requiring an increase in dose);
- urination difficulties, decreased urine output;
- dizziness;
- rapid or slow heart rate, palpitations, increased or sudden drops in blood pressure when changing position from lying down to standing;
- decreased or increased body temperature;
- anxiety, anxiety disorders, mood disorders, euphoria, psychosis;
- pupil constriction;
- headache;
- hives;
- urticaria and (or) local tissue irritation (a type of allergy);
- suppressed cough reflex, breathing difficulties up to respiratory arrest;
- sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep);
- symptoms related to pancreatitis and bile ducts, e.g. severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, nausea, vomiting, or fever.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products Al. Jerozolimskie 181C 02-222 Warsaw Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301 Fax: +48 22 49 21 309 Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
Store the ampoules in the original packaging to protect them from light. Do not freeze. The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the box and ampoule. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated. The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal contains
- The active substance of the medicine is morphine sulfate 2.5-hydrate. Each ml of the solution contains 1 mg of morphine sulfate 2.5-hydrate.
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, water for injections.
What Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal looks like and contents of the packaging
Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal is a colorless or almost colorless transparent liquid. Packaging: cardboard boxes containing 10 ampoules of 2 ml each.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A. ul. Pelplińska 19 83-200 Starogard Gdański tel. +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet
INFORMATION INTENDED EXCLUSIVELY FOR MEDICAL PROFESSIONALS
MORPHINI SULFAS WZF 0.1% SPINAL 1 mg/ml, solution for injection
Morphine hemisulfate 2.5-hydrate
Read the current Summary of Product Characteristics of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
Administration of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
- Dosage is determined individually for each patient. The medicine is administered subarachnoidally, epidurally, or intravenously (see "Dosage").
- The medicine is intended for adult patients.
- Morphine forms insoluble compounds with heparin. Do not mix morphine and heparin solutions in the same syringe.
- A physicochemical incompatibility (precipitate formation) has been demonstrated between morphine sulfate solutions and 5-fluorouracil.
- Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal should not be heat-sterilized.
- The medicine does not contain preservatives.
- Do not use if there is a visible change in color.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule. You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down. Each ampoule has a colored dot (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing each other - see Figure 2. Hold the upper part of the ampoule in such a way that your thumb is above the colored dot.
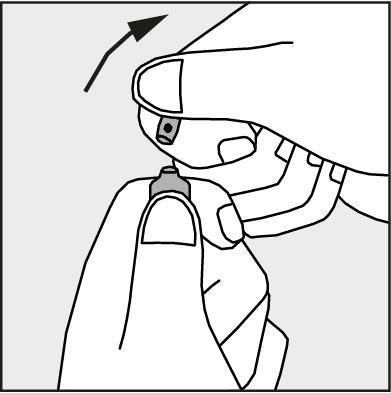
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. Any remaining contents of the unused product should be disposed of in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
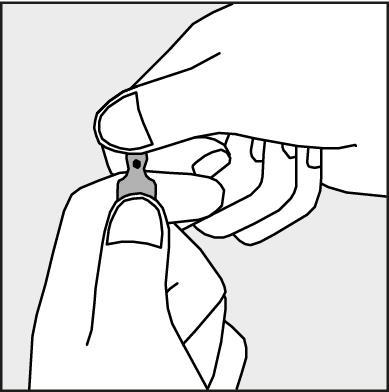
Figure 3.
Precautions for the use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal
- Due to the increased risk of early and late side effects after subarachnoid administration of morphine, epidural administration should be used whenever possible. Epidural and subarachnoid injections should be performed in the lumbar segment of the spine.
- The medicine can only be used epidurally and subarachnoidally by an experienced doctor who is well aware of the technique and side effects associated with this route of administration. After epidural or subarachnoid administration, the patient should be monitored for 24 hours after the last dose of the medicine, due to the risk of respiratory center inhibition (both early and late).
- Opioids can cause sleep disorders, including central sleep apnea (CSA) and hypoxemia. The use of opioids increases the risk of CSA in a dose-dependent manner. In patients with CSA, the total dose of opioids should be reduced.
- Ensure access to resuscitation equipment, oxygen, and a specific antidote - naloxone hydrochloride. Respiratory center inhibition or other side effects may also occur after unintentional subarachnoid or intravenous administration of too high a dose (subarachnoid administration uses 1/10 of the epidural dose).
- Before epidural administration of morphine, it is necessary to check the correct position of the needle or catheter. To rule out the presence of the needle or catheter in a vessel or subarachnoid space, aspiration should be performed and checked for the presence of blood or cerebrospinal fluid.
- In patients with chronic pain treated with morphine administered epidurally or subarachnoidally, after starting therapy in a hospital setting, treatment can be continued on an outpatient basis or at home. Supervision of morphine use can be carried out by a doctor or nurse. In patients treated in palliative and hospice care centers and at home, documentation should be kept, including the occurrence of side effects and the procedure in case of their occurrence.
- Morphine can cause liver function disorders and spasm of the Oddi sphincter, leading to increased pressure in the bile ducts.
- Repeated use of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal may lead to the occurrence of opioid use disorders (OUD). A higher dose and longer treatment with opioids may increase the risk of OUD. Abuse or intentional misuse of Morphini sulfas WZF 0.1% Spinal can lead to overdose and (or) death. The risk of OUD is increased in patients with a history of substance abuse (including alcohol), current tobacco use, or other mental disorders (e.g. severe depression, anxiety disorders, or personality disorders).
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) has been reported during treatment with morphine, which can be life-threatening or fatal. Most of these reactions occurred within the first 10 days of treatment.
Dosage
Adults The dosage is determined individually, taking into account clinical indications, the type of pain (acute or chronic), previously used pain relievers, and the patient's condition. Intravenous administration - the initial dose for adults is 2 mg to 10 mg/70 kg body weight. Epidural administration - the initial dose for adults is 5 mg, administered in an injection in the lumbar segment of the spine, which can provide pain relief for 24 hours. If pain relief is not achieved within 1 hour, a supplementary dose of 1 mg to 2 mg can be administered with caution. Do not use a dose higher than 10 mg per day. Continuous infusion - the initial dose is 2 mg to 4 mg per day. If the initial dose is insufficient, a supplementary dose of 1 mg to 2 mg can be administered. Subarachnoid administration - the single dose for adults is 0.2 mg to 1 mg, administered in an injection, which can provide pain relief for 24 hours. Do not use more than 1 ml of the solution subarachnoidally. Repeated subarachnoid injections are not recommended. Continuous intravenous infusion of naloxone hydrochloride at a dose of 0.6 mg/h for 24 hours after subarachnoid administration reduces the possibility of side effects. Elderly patients In elderly and debilitated patients, the medicine should be used with caution. Usually, a dose reduction is sufficient. Children and adolescents There are no data on the use of the medicine in patients under 18 years of age. The safety of using morphine epidurally and subarachnoidally in children has not been established.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% SpinalDosage form: Solution, 20 mg/2 mlActive substance: morphinePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 20 mg/mlActive substance: morphineManufacturer: AS KalceksPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 10 mg/mlActive substance: morphinePrescription required
Alternatives to Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal in Ukraine
Alternative to Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal in Spain
Online doctors for Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Morphini sulfas Vzf 0,1% Spinal – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














