
Midazolam Kalceks
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Midazolam Kalceks

How to use Midazolam Kalceks
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: Information for the user
Midazolam Kalceks, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection/infusion
Midazolam Kalceks, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection/infusion
Midazolam
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or nurse.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Midazolam Kalceks and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before receiving Midazolam Kalceks
- 3. How to use Midazolam Kalceks
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Midazolam Kalceks
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Midazolam Kalceks and what is it used for
Midazolam belongs to a group of medicines called benzodiazepines (sedatives). It is a short-acting medicine used to induce sedation (a state of calm, drowsiness, or sleep) and to relieve anxiety symptoms and reduce muscle tension. This medicine is used for:
- Inducing shallow sedation (a state of calm or drowsiness while maintaining consciousness) in adults and children.
- Inducing sedation in adults and children in intensive care units.
- Anesthesia in adults (used before induction, during induction of anesthesia, as the sole agent or in combination with other anesthetics).
- Used before anesthesia in children.
2. Important information before receiving Midazolam Kalceks
When not to use Midazolam Kalceks:
Warnings and precautions
Before receiving Midazolam Kalceks, the patient should discuss with their doctor or nurse if:
- the patient is over 60 years old,
- the patient has a chronic illness or is debilitated (e.g., chronic respiratory, kidney, liver, or heart disease),
- the patient has muscle weakness (a neuromuscular disease characterized by muscle weakness),
- the patient has a history of alcohol or drug abuse,
- the patient is taking other medicines, including those not prescribed by the attending doctor (see "Midazolam Kalceks and other medicines"),
- the patient is pregnant or thinks she may be pregnant.
Midazolam Kalceks should only be used in facilities equipped with resuscitation equipment suitable for the patient's age and weight. Administering midazolam may decrease cardiac muscle contractility (the ability of the heart muscle to contract) and cause apnea (pauses in breathing). Rarely, serious side effects related to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems have been observed, such as respiratory disorders (slow or shallow breathing), apnea, respiratory arrest, and/or cardiac arrest. To avoid these events, the medicine should be injected slowly and in the smallest possible dose.
Special caution should be exercised when administering midazolam to infants and children. The doctor should be informed if the child has cardiovascular or respiratory diseases. The child will then be monitored, and the dose will be adjusted accordingly.
Patients under 6 months of age undergoing sedation in intensive care units are more prone to respiratory disorders, and therefore, dosing will be increased very slowly, and respiratory rate and oxygen saturation will be monitored.
When midazolam is used for premedication (to induce relaxation, calmness, and drowsiness before administering an anesthetic), the patient's reactions will be carefully checked to ensure the correct dose is administered, as sensitivity to the medicine varies among patients. It is not recommended to use midazolam in newborns and children under 6 months of age.
Paradoxical reactions and anterograde amnesia (loss of memory of recent events) have been reported after using midazolam (see section 4).
Long-term treatment
If midazolam is used for a long time, the patient may develop tolerance (midazolam becomes less effective) or dependence on the medicine.
After long-term treatment (e.g., in intensive care units), the following withdrawal symptoms may occur: headaches, diarrhea, muscle pain, anxiety, tension, restlessness, disorientation, irritability, sleep disturbances, mood changes, hallucinations, and seizures. In severe cases, depersonalization, numbness, and tingling of limbs, hypersensitivity to light, noise, and physical contact may occur. To prevent these side effects, the doctor will gradually reduce the dose of the medicine.
Midazolam Kalceks and other medicines
The patient should inform their doctor or nurse about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
This is very important because taking more than one medicine at a time can enhance or weaken the effect of the medicines being taken.
In particular, the doctor or nurse should be informed if the patient is taking any of the following medicines:
- anxiolytics (used in cases of anxiety or to help fall asleep),
- sedatives (inducing a state of calm or drowsiness),
- sleeping pills,
- antidepressants (used to treat depression, e.g., nefazodone),
- narcotic analgesics (very strong painkillers, e.g., fentanyl),
- anesthetics (e.g., propofol),
- certain antihistamines (used to treat allergies),
- antifungal medicines (ketoconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole),
- antibiotics (erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin, roxithromycin),
- medicines that affect blood pressure, calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem, verapamil,
- medicines used to treat HIV infection (efavirenz or saquinavir, lopinavir, and other protease inhibitors),
- medicines used to treat hepatitis C virus infection (simeprevir, boceprevir, and telaprevir),
- antiepileptic medicines (carbamazepine, phenytoin, or valproic acid),
- atorvastatin (used to treat high cholesterol levels),
- rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis),
- tikagrelor (used to prevent heart attack),
- aprepitant, netupitant, casoprepitant (used to prevent nausea and vomiting),
- certain medicines used to treat cancer (e.g., imatinib, lapatinib, idelalisib, vemurafenib),
- everolimus, cyclosporine (used to prevent organ rejection),
- propiverine (used to treat urinary incontinence),
- herbal medicines (e.g., St. John's Wort, Ginkgo biloba, or ginseng).
Concomitant use of midazolam and opioid medicines (strong painkillers, medicines used for substitution therapy, and some cough medicines) increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and can be life-threatening. Therefore, concomitant use should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
If the doctor has prescribed midazolam concomitantly with opioid medicines, they should limit the dose and duration of concomitant treatment.
The patient should inform their doctor about all opioid medicines they are taking and strictly follow the doctor's instructions regarding dosing. It may be helpful to inform friends or relatives so that they are aware of the above symptoms. If such symptoms occur, the patient should contact their doctor.
Surgical procedures
If the patient is to receive an inhaled anesthetic (one that is inhaled) during surgery or dental treatment, it is essential to inform the doctor or dentist that they have taken Midazolam Kalceks.
Midazolam Kalceks with alcohol
Alcohol may enhance the sedative effect of midazolam, so the patient should avoid consuming alcohol.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks she may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, she should consult her doctor before taking this medicine. The doctor will decide whether the patient should receive the medicine.
If the patient has been given Midazolam Kalceks, she should not breastfeed for the next 24 hours. This is because midazolam may pass into breast milk.
Driving and operating machinery
Midazolam has a significant impact on the ability to drive and operate machinery.
This medicine can cause drowsiness, memory disturbances, affect concentration, and coordination, which can affect the performance of tasks that require precision, such as driving and operating machinery. After receiving midazolam, the patient should not drive or operate machinery until the effects of the medicine have completely worn off. The doctor will decide when the patient can resume these activities.
After the procedure, the patient should go home accompanied by a responsible adult.
Inadequate sleep or consuming alcohol increases the likelihood of impaired alertness and attention.
Midazolam Kalceks contains sodium
Midazolam Kalceks, 1 mg/ml
In a daily dose of up to 6.5 ml, this medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium, i.e., the medicine is considered "sodium-free". If the daily dose exceeds 6.6 ml (corresponding to more than 1 mmol of sodium), the following should be considered: The medicine contains 3.5 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) per ml of solution. This corresponds to 0.18% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
Midazolam Kalceks, 5 mg/ml
In a daily dose of up to 7.3 ml, this medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg of sodium), i.e., the medicine is considered "sodium-free". If the daily dose exceeds 7.4 ml (corresponding to more than 1 mmol of sodium), the following should be considered: The medicine contains 3.15 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) per ml of solution. This corresponds to 0.16% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
3. How to use Midazolam Kalceks
This medicine should only be administered by experienced doctors in a facility equipped with equipment for monitoring and supporting respiratory and cardiovascular systems or by persons trained to recognize and treat possible adverse events.
Dosing and administration route
The suitable dose for a given patient is determined by the doctor. Doses vary and depend on the planned treatment and the desired level of sedation. The dose size depends on the patient's weight, age, overall health, concomitantly used medicines, reaction to the medicine, and whether the patient will require administration of other medicines at the same time.
If the patient is to receive strong painkillers, they will be administered first, and then Midazolam Kalceks will be administered in an appropriately adjusted dose.
This medicine can be injected directly into the patient's vein (intravenously), into a muscle (intramuscularly), or administered rectally.
Children and infants
In infants and newborns under 6 months of age, midazolam is indicated only for sedation in intensive care units. The dose of the medicine should be administered gradually into a vein.
Children over 12 years of age usually receive midazolam intravenously. If this medicine is used for premedication, it may be administered rectally.
Receiving a higher than recommended dose of Midazolam Kalceks
The medicine is administered by a doctor or nurse.
If the patient accidentally receives too much midazolam, it may lead to drowsiness, clumsiness (coordination disorders), dysarthria (speech disorders), and oculogyric crisis (involuntary eye movements), loss of reflexes, apnea (respiratory arrest), hypotension (low blood pressure), respiratory and cardiovascular depression, and coma. In case of overdose, close monitoring of vital signs, symptomatic treatment of respiratory and cardiovascular disorders, and administration of a benzodiazepine antagonist may be required.
Stopping the use of Midazolam Kalceks
Sudden discontinuation of treatment may cause withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, muscle pain, anxiety, tension, restlessness, disorientation, mood swings, hallucinations, and seizures, insomnia with rebound, irritability. The risk of withdrawal symptoms is higher in case of sudden discontinuation of treatment, so it is recommended to gradually reduce the dose in this case.
In case of any further doubts regarding the use of this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If the patient experiences any of the following side effects, they should tell their doctor. These may be life-threatening and may require urgent treatment:
- Anaphylactic shock (a life-threatening allergic reaction). Symptoms may include sudden rash, itching, or urticaria and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or other parts of the body. It may also cause difficulty breathing, wheezing, or rapid heartbeat or feeling of loss of consciousness. Additionally, it may cause chest pain, which can be a sign of a serious allergic reaction called Kounis syndrome.
- Heart attack (cardiac arrest). Symptoms may include chest pain radiating to the neck and arms and down to the left arm.
- Breathing difficulties or complications (sometimes causing respiratory arrest).
- Choking and sudden airway obstruction (laryngospasm).
Life-threatening side effects occur more frequently in adults over 60 years of age and in patients with breathing difficulties and heart disease, especially if the medicine is injected too quickly or in too high a dose.
Other side effects:
The following side effects have been reported, the frequency of which is unknown and cannot be estimated from the available data:
Immune system disorders:generalized allergic reactions (skin reactions, cardiovascular reactions, wheezing).
Psychiatric disorders:confusion, disorientation, emotional and mood disturbances, changes in libido.
Paradoxical reactions such as restlessness, psychomotor agitation, irritability, nervousness, muscle spasms and tremors, hostility, delusions, anger, aggression, anxiety, nightmares, unusual dreams, hallucinations, psychosis, inappropriate behavior, and other adverse behavioral effects, seizures, and violent outbursts. These reactions were mainly observed in cases of too rapid injection or too high a dose of the medicine. The risk of these symptoms is higher in children and the elderly.
Dependence:midazolam may cause physical dependence, even when used in therapeutic doses. To avoid withdrawal symptoms, including seizures, which may occur after long-term use of midazolam, the dose of the medicine should be gradually reduced (see section 2).
Nervous system disorders:drowsiness and prolonged sedation, decreased alertness, drowsiness, headache, dizziness, coordination disorders. Temporary memory loss has also been reported. Its duration depends on the dose used and may occur even after the treatment has ended. In individual cases, memory loss persisted for a longer period. In preterm infants and newborns, seizures have been observed.
Cardiovascular disorders:severe side effects such as low blood pressure, slow heart rate, vasodilation (e.g., flushing of the face and neck, fainting, and headache).
Gastrointestinal disorders:nausea, vomiting, constipation, dry mouth.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:skin rash, allergic reaction, itching.
General disorders and administration site conditions:fatigue, flushing, swelling, and pain at the injection site (flushing, thrombophlebitis, and thrombosis).
In elderly patients using benzodiazepines, an increased risk of falls and fractures has been observed, especially in elderly patients taking other sedative medicines (including alcoholic beverages).
The likelihood of side effects is higher in patients with severe renal impairment.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including those not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their anesthesiologist or another doctor. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Midazolam Kalceks
There are no special recommendations for the storage temperature of the medicine.
Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect them from light.
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
After opening the ampoule, the medicinal product should be used immediately.
Chemical and physical stability of diluted solutions has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 25°C and for 3 days at 2°C - 8°C with the following infusion solutions: 0.9% sodium chloride, 5% and 10% glucose, Ringer's solution, and Hartmann's solution.
From a microbiological point of view, the medicine should be used immediately after dilution. If not used immediately, the responsibility for the storage time and conditions before use lies with the user, but this time should not exceed 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C, unless dilution was performed under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Do not use the medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoule after "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Midazolam Kalceks contains
- The active substance of the medicine is midazolam.
Midazolam Kalceks, 1 mg/ml
1 ml of solution contains 1 mg of midazolam.
One ampoule with 5 ml of solution contains 5 mg of midazolam.
Midazolam Kalceks, 5 mg/ml
1 ml of solution contains 5 mg of midazolam.
One ampoule with 1 ml of solution contains 5 mg of midazolam.
One ampoule with 3 ml of solution contains 15 mg of midazolam.
One ampoule with 10 ml of solution contains 50 mg of midazolam.
- Excipients are: hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), water for injections.
What Midazolam Kalceks looks like and contents of the pack
A clear, colorless solution for injection/infusion in ampoules made of colorless glass type I with one break point, containing 1 ml, 3 ml, or 10 ml of solution (for 5 mg/ml) and 5 ml of solution (for 1 mg/ml).
Package size: 5 or 10 ampoules.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer/importer
AS KALCEKS
Krustpils iela 71E
1057 Rīga
Latvia
Tel.: +371 67083320
Email: [email protected]
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 08/2023
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Instructions for use
Midazolam Kalceks is compatible with the following infusion solutions:
- 0.9% sodium chloride solution
- 5% glucose solution
- 10% glucose solution
- Ringer's solution
- Hartmann's solution
To administer an intravenous infusion, the contents of the Midazolam Kalceks ampoules should be diluted with one of the above-mentioned solutions in a ratio of 15 mg of midazolam per 100 to 1,000 ml of infusion solution.
Midazolam Kalceks solution for injection/infusion should not be diluted in 6% Macrodex in glucose.
Midazolam Kalceks solution for injection/infusion should not be mixed with alkaline solutions for injection. Midazolam precipitates in solutions containing bicarbonates.
To avoid potential incompatibility, Midazolam Kalceks solution for injection/infusion should not be mixed with other solutions, except those listed above.
Midazolam Kalceks solution for injection/infusion is intended for single use only.
Before administration, the solution should be inspected. Only solutions without visible particles should be used.
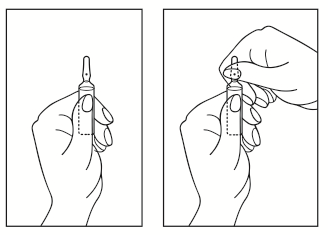
Instructions for opening the ampoule:
- 1) Position the ampoule so that the colored dot is at the top. If there is a part of the solution in the upper part of the ampoule, gently tap with your finger to ensure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
- 2) Use both hands to open; holding the lower part of the ampoule in one hand, break the upper part of the ampoule in the direction opposite to the colored dot (see pictures below).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAS Kalceks
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Midazolam KalceksDosage form: Tablets, 15 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Recipharm Leganes S.L.U. Roche Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 7.5 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Recipharm Leganes S.L.U. Roche Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 10 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: MoNo chem-pharm. Produkte GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Midazolam Kalceks in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Midazolam Kalceks in Spain
Alternative to Midazolam Kalceks in Ukraine
Online doctors for Midazolam Kalceks
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Midazolam Kalceks – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









