
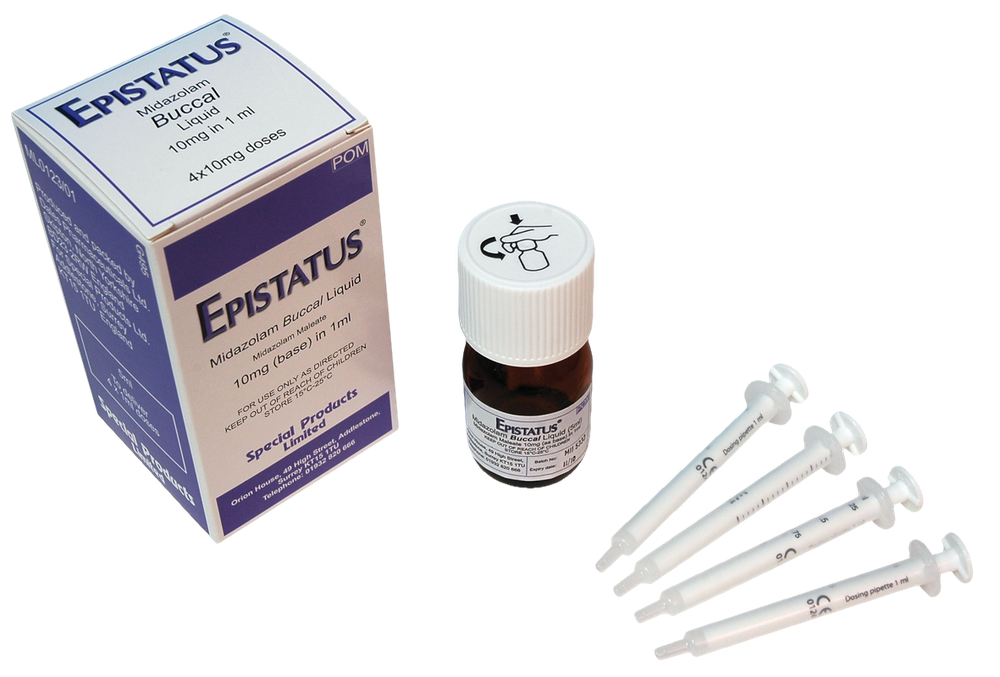
Epistatus

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Epistatus

How to use Epistatus
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Epistatus, 2.5 mg, oral solution
Epistatus, 5 mg, oral solution
Epistatus, 7.5 mg, oral solution
Epistatus, 10 mg, oral solution
Midazolam
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for a specific person. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Epistatus and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Epistatus
- 3. How to use Epistatus
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Epistatus
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Epistatus and what is it used for
Epistatus contains the active substance midazolam, which belongs to a group of medicines called benzodiazepines.
Epistatus is used to stop prolonged, acute seizure attacks in infants, young children, children, and adolescents from 3 months to less than 18 years of age.
In the case of infants from 3 to 6 months of age, this medicine should be used in a hospital setting where monitoring and access to resuscitation equipment are possible (see section Warnings and precautions).
This medicine can only be administered by parents or caregivers when the child has been diagnosed with epilepsy. The doctor treating the patient should provide the parents or caregivers with instructions on how to administer Epistatus and what to do if the seizure does not stop (see also section "How to use Epistatus").
2. Important information before using Epistatus
When not to use Epistatus
- if the patient is allergic to midazolam, other benzodiazepines (such as diazepam or nitrazepam), or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if the patient has a disease called myasthenia (which causes muscle weakness).
- if the patient has significant breathing difficulties (Epistatus may worsen breathing difficulties).
- if the patient has sleep apnea syndrome (which causes frequent pauses in breathing during sleep).
- if the patient has severe liver function disorders.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Epistatus, the patient should discuss with their doctor or pharmacist if they:
- have a lung disease that causes breathing problems, as this medicine may worsen breathing;
- have kidney, liver, or heart problems;
- are taking other sedative medicines and feel very weak, tired, and lack energy, as this medicine affects the central nervous system (CNS);
- regularly drink large amounts of alcohol or have had problems with alcohol abuse in the past (see section "Epistatus contains ethanol (alcohol)");
- regularly take non-prescription medicines or have had problems with drug abuse in the past.
This medicine may affect the patient's memory after administration (temporary memory loss).
Parents or caregivers should closely monitor patients after administration of this medicine. See also section 4 ("Possible side effects").
As it cannot be excluded that younger children may experience delayed severe breathing problems (such as slower or weaker than expected breathing), infants from 3 months to less than 6 months of age should only be treated in a hospital setting where vital functions can be monitored and resuscitation equipment is available.
In case of doubt as to whether any of the above situations apply to the patient, the doctor or pharmacist should be consulted before administering this medicine.
Children and adolescents
This medicine must not be given to children under 3 months of age, as there is not enough information for this age group.
Epistatus and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. In case of doubt as to whether any medicine taken by the patient may have a negative impact on the use of Epistatus, the doctor or pharmacist should be consulted.
This is very important, as taking more than one medicine at the same time may enhance or weaken the effect of these medicines.
The effect of Epistatus may be enhanced by medicines such as:
- antiepileptic medicines (used to treat epilepsy), e.g., phenytoin;
- antibiotics, e.g., erythromycin, clarithromycin;
- antifungal medicines, e.g., ketoconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole;
- medicines used to treat stomach and duodenal ulcers, e.g., cimetidine, ranitidine, and omeprazole;
- medicines used to treat high blood pressure, e.g., diltiazem, verapamil;
- certain medicines used to treat HIV and AIDS, e.g., saquinavir, lopinavir + ritonavir;
- opioid painkillers (very strong painkillers), e.g., fentanyl;
- medicines used to reduce the amount of fat in the blood, e.g., atorvastatin;
- medicines used to treat nausea, e.g., nabilone;
- sleeping medicines (medicines that cause sleep);
- sedative antidepressants (medicines used to treat depression that cause sleepiness);
- sedatives (medicines that cause relaxation);
- anesthetics (used to relieve pain);
- antihistamines (used to treat allergies).
The effect of Epistatus may be weakened by medicines such as:
- rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis);
- xanthines (used to treat asthma);
- St. John's Wort (a herbal medicine). Patients taking Epistatus should avoid using it.
Epistatus may also enhance the effect of certain muscle relaxants, e.g., baclofen (causing increased sleepiness). This medicine may also inhibit the effect of certain other medicines, e.g., levodopa (a medicine used to treat Parkinson's disease).
Taking Epistatus and opioids (contained in very strong painkillers, replacement therapy medicines, and some cough medicines) at the same time increases the risk of sleepiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and may also be life-threatening.
Therefore, concurrent use should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
However, if the doctor recommends taking Epistatus with opioids, the dose of the medicines and the duration of concurrent treatment should be limited.
The patient should tell their doctor about all opioid medicines they are taking and strictly follow the doctor's instructions regarding dosage. The patient should consider informing their friends or relatives so that they are aware of the above-mentioned symptoms. The patient should contact their doctor in case of these symptoms.
Epistatus contains a small amount of alcohol and therefore should not be taken at the same time as disulfiram.
The patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist for information on which medicines to avoid during treatment with Epistatus.
Procedures
If the patient is to be given inhaled anesthesia (products that are administered during breathing) during a surgical procedure or dental treatment, it is essential to inform the doctor or dentist that the patient is taking Epistatus.
Epistatus with food, drink, and alcohol
While taking Epistatus, the patient should not drink alcohol. Alcohol may enhance the sedative effect of Epistatus and cause increased sleepiness.
While taking Epistatus, the patient should not drink grapefruit juice. Grapefruit juice may enhance the sedative effect of Epistatus and cause increased sleepiness.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Pregnancy
If the patient is pregnant, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a baby, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine.
Midazolam may be used during pregnancy if necessary. Frequent administration of Epistatus in the last 3 months of pregnancy or during childbirth may cause problems in the baby, such as: heart rhythm disorders, hypothermia (low body temperature), weak sucking reflex, breathing difficulties, and weak muscle tone.
Breastfeeding
The patient should tell their doctor if they are breastfeeding. Although small amounts of Epistatus may pass into breast milk, breastfeeding may not need to be discontinued. The doctor will decide whether the patient should temporarily stop breastfeeding after administration of Epistatus.
Driving and using machines
Epistatus has a significant impact on the ability to drive and use machines.
Epistatus may cause sleepiness, forgetfulness, or impaired concentration and coordination in the patient. Such effects may interfere with the performance of learned tasks, such as driving, cycling, or operating machinery. After administration of this medicine, the patient should not drive, cycle, or operate machinery until they have fully recovered.
The patient should consult their doctor if they need further information.
Epistatus contains maltitol
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should consult their doctor before taking this medicine.
Epistatus contains ethanol (alcohol)
Epistatus 2.5 mg, oral solution
This medicine contains 49 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per dose. The amount of alcohol in the dose of this medicine is equivalent to less than 1 mL of beer or 1 mL of wine.
Epistatus 5 mg, oral solution
This medicine contains 99 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per dose. The amount of alcohol in the dose of this medicine is equivalent to less than 3 mL of beer or 1 mL of wine.
Epistatus 7.5 mg, oral solution
This medicine contains 148 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per dose. The amount of alcohol in the dose of this medicine is equivalent to less than 4 mL of beer or 2 mL of wine.
Epistatus 10 mg, oral solution
This medicine contains 197 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per dose. The amount of alcohol in the dose of this medicine is equivalent to less than 5 mL of beer or 2 mL of wine.
A small amount of alcohol in this medicine will not have noticeable effects.
Epistatus contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per dose, which means that the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to use Epistatus
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. In case of doubt, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist. The doctor treating the patient should provide the parents or caregivers with instructions on how to administer Epistatus and what to do if the seizure does not stop.
Epistatus is intended for use in the mouth only, which means it can only be used in the oral cavity.
When administering the medicine, care should be taken to avoid the risk of the patient choking.
Depending on the age of the child, they will receive the following doses from the packaging labeled with a specific color:
| Age | Dose | Color of packaging |
| From 3 to 6 months in a hospital setting | 2.5 mg (0.25 mL) | yellow |
| from 6 months to less than 1 year | 2.5 mg (0.25 mL) | yellow |
| from 1 year to less than 5 years | 5 mg (0.5 mL) | blue |
| from 5 years to less than 10 years | 7.5 mg (0.75 mL) | purple |
| from 10 years to less than 18 years | 10 mg (1 mL) | orange |
The dose is the full contents of one oral syringe. Do not give more than one dose without the prior advice of a doctor.
In the case of infants from 3 to 6 months of age, treatment should only be carried out in a hospital setting where monitoring and access to resuscitation equipment are possible.
After administration of Epistatus, patients should remain under the supervision of a caregiver who should stay with the patient.
Epistatus should not be injected intravenously or intramuscularly. The needle should not be attached to the syringe.
Preparing the medicine for administration
If the patient has a seizure, they should be allowed to move their body freely and should not be restrained. The patient should only be moved if they are in danger due to surrounding objects or obstacles, for example, if they are near a road, an open water tank, hot kitchen appliances, fire, or sharp objects.
The patient's head should be secured with something soft, such as a pillow or the caregiver's knee.
How to administer the medicine
The patient should ask their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse to show them how to take or administer this medicine. In case of doubt, the patient should consult their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
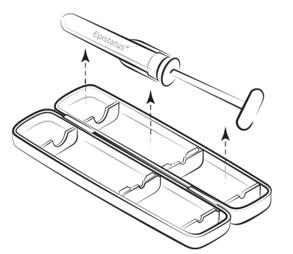
Step 1
Remove the plastic tamper-evident device from the side of the packaging, open the packaging, and remove the syringe.
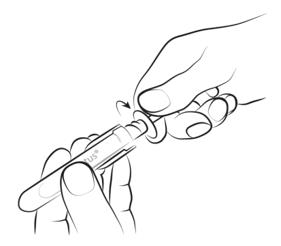
Step 2
Holding the transparent handles of the syringe, unscrew the amber cap in the opposite direction to the arrow and remove it.
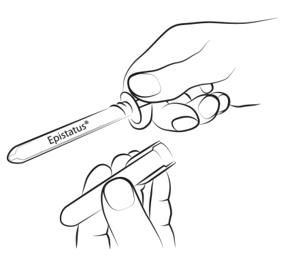
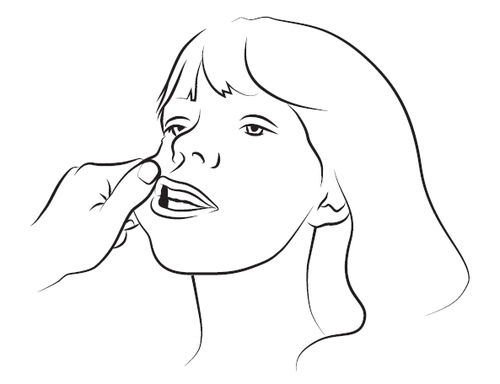
Step 3
Gently squeeze and pull the patient's cheek with the index finger and thumb. Place the tip of the syringe in the back of the space between the inner surface of the cheek and the lower gum (buccal cavity).
Step 4
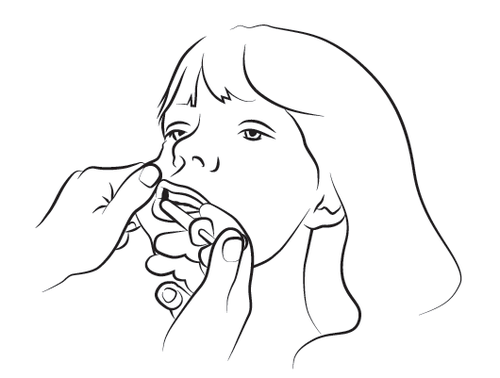
Slowly administer about half of the solution volume into the buccal cavity on one side of the mouth, and then slowly administer the rest on the other side, pressing the syringe plunger until it stops. If it is particularly difficult to introduce the syringe into the mouth on one side, the entire dose should be administered on one side of the mouth within 4-5 seconds. Safely dispose of the syringe and cap.
What to do if the patient's condition does not improve
Emergency medical help should be sought immediately - the patient or their caregiver should call an ambulance immediately if the seizures do not stop shortly after administration of Epistatus.
The patient or their caregiver should follow the doctor's instructions.
A second dose of Epistatus should not be administered without the explicit advice of a doctor.
What to do if the patient's condition improves but the seizure recurs
Emergency medical help should be sought immediately - the patient or their caregiver should call an ambulance immediately.
A second dose of Epistatus should not be administered without the explicit advice of a doctor.
The empty syringe of the administered medicine should be given to the ambulance crew or doctor so that they know what medicine and dose were administered.
What to do if too much Epistatus is used
Emergency medical help should be sought immediately - the patient or their caregiver should call an ambulance immediately.
Symptoms that may occur after taking too much Epistatus include:
- Sleepiness, fatigue, feeling of exhaustion,
- Confusion or feeling of disorientation,
- Lack of coordination,
- Muscle weakness,
- Low blood pressure - this may cause dizziness and fainting,
- Breathing difficulties.
The empty syringe of the administered medicine should be kept to show to the ambulance crew or doctor.
In case of further doubts about the use of this medicine, the patient or their caregiver should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Epistatus can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects
The patient or their caregiver should seek medical advice immediately or call an ambulance immediately if they experience any of the following side effects:
- Significantly increased breathing difficulties, e.g., slow or shallow breathing or blue discoloration of the lips or fingers. In very rare cases, breathing may stop completely.
- Cardiac arrest (the heart stops beating) occurs very rarely. Symptoms include loss of consciousness associated with lack of pulse.
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, which makes swallowing or breathing difficult, or pale skin, weak and rapid pulse, or feeling of loss of consciousness. This may indicate a severe allergic reaction.
Other side effects
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Sleepiness or loss of consciousness, muscle spasms, and tremors (involuntary muscle contractions), reduced alertness, headache, dizziness;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Fatigue.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Agitation, hallucinations (seeing and sometimes hearing things that are not there);
- Transient memory loss;
- Rash, urticaria (uneven rash), itching.
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- Aggression, difficulty in coordinating muscle movements, physical assault;
- Seizures (convulsions), restlessness;
- Low blood pressure, slow heart rate, or flushing of the face and neck (flushing);
- Shortness of breath;
- Constipation;
- Dry mouth;
- Hiccups.
Side effects with unknown frequency (frequency cannot be estimated from available data):
- Irritability, confusion, hostility, euphoria (excessive feeling of happiness or excitement);
- Thrombosis (blood clotting or formation of clots in certain parts of the circulatory system), laryngospasm (constriction of the vocal cords causing difficulty breathing and loud breathing).
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, the patient or their caregiver should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel: +48 22 492 13 01, fax: +48 22 492 13 09, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl .
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Epistatus
The medicine should be stored out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton after: EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not store above 25°C.
Do not store in the refrigerator or freeze.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light.
Do not use this medicine if the syringe is damaged or the solution is not clear (e.g., cloudy or white particles are visible).
Medicines should not be disposed of via household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Epistatus contains
- The active substance of Epistatus is midazolam (as midazolam maleate). Each 0.25 mL oral syringe contains 2.5 mg of midazolam. Each 0.5 mL oral syringe contains 5 mg of midazolam. Each 0.75 mL oral syringe contains 7.5 mg of midazolam. Each 1 mL oral syringe contains 10 mg of midazolam.
- The other ingredients are: anhydrous ethanol, sodium saccharin, glycerol, purified water, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), and liquid maltitol.
What Epistatus looks like and contents of the pack
Epistatus is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution. Epistatus is available in a 1 mL transparent, colorless, plastic, single-dose (needle-free) oral syringe filled (without the need for a needle) with a transparent, amber, plastic cap with different fill volumes. Each syringe contains a single dose of 0.25 mL, 0.5 mL, 0.75 mL, or 1 mL of the medicine.
Each oral syringe is provided in an individual packaging with a tamper-evident seal in a polypropylene container.
Epistatus 2.5 mg, oral solution: yellow label on the syringe, yellow container.
Epistatus 5 mg, oral solution: blue label on the syringe, blue container.
Epistatus 7.5 mg, oral solution: purple label on the syringe, purple container.
Epistatus 10 mg, oral solution: orange label on the syringe, orange container.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
SERB SA
Avenue Louise 480
1050 Brussels
Belgium
Tel. +48 22 307 03 61
Manufacturer/Importer
MoNo chem-pharm Produkte GmbH, Leystraße 129, 1-1200 Vienna, Austria
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Denmark
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
Mundhulevæske, opløsning
Finland
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
Liuos suuonteloon
Sweden
Epistatus
Slovenia
Epistatus 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg
oralna raztopina
Norway
Epistatus
Germany
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
Lösung zur Anwendung in der Mundhöhle
Greece
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
Στοματικό διάλυμα
Ireland
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
Oromucosal Solution
Italy
Epistatus
Poland
Epistatus
Hungary
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
szájnyálkahártyán alkalmazott oldat
Portugal
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
solução bucal
Austria
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
Lösung zur Anwendung in der Mundhöhle
United Kingdom (Northern Ireland)
Epistatus 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg
oromucosal solution
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 07/2023
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterMoNo chem-pharm. Produkte GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to EpistatusDosage form: Tablets, 15 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Recipharm Leganes S.L.U. Roche Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 7.5 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Recipharm Leganes S.L.U. Roche Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription required
Alternatives to Epistatus in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Epistatus in Spain
Alternative to Epistatus in Ukraine
Online doctors for Epistatus
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Epistatus – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









