
Midanium

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Midanium

How to use Midanium
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
MIDANIUM, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection
MIDANIUM, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Midazolam
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- The leaflet should be kept in case it needs to be read again.
- In case of any further doubts, the doctor, pharmacist, or nurse should be consulted.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for one person. It should not be passed on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if the symptoms of their illness are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Midanium and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Midanium
- 3. How to use Midanium
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Midanium
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Midanium and what is it used for
Midanium contains the active substance midazolam. Midazolam belongs to a group of medicines called benzodiazepines. It is characterized by a short, strong sedative and hypnotic effect.
Midanium is used in adults:
- -for sedation (calming, relieving anxiety and restlessness) with preserved consciousness before and during short diagnostic and therapeutic procedures;
- -in patient preparation (premedication) before various procedures, e.g. before surgery, endoscopy;
- -as a sedative component for induction of general anesthesia, before the use of another anesthetic agent;
- -for sedation in intensive care units.
Midanium is used in children:
- -for sedation (calming, relieving anxiety and restlessness) with preserved consciousness before and during short diagnostic and therapeutic procedures;
- -in patient preparation (premedication) before various procedures, e.g. before surgery, endoscopy;
- -for sedation in intensive care units.
2. Important information before using Midanium
When not to use Midanium:
- if the patient is allergic to midazolam (or other benzodiazepines) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has severe respiratory failure or acute respiratory depression (very serious breathing difficulties).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Midanium, the doctor or nurse should be consulted.
It is necessary to consult a doctor in the case of patients:
- -over 60 years old, weakened;
- -with liver function disorders, chronic liver or kidney failure;
- -with chronic respiratory failure;
- -in a serious condition, especially with heart diseases and breathing difficulties;
- -with myasthenia (a chronic disease characterized by muscle weakness). Patients with the above-mentioned diseases should inform their doctor about them.
After receiving Midanium, the patient should be discharged from the hospital or treatment room only with the doctor's consent. The patient should be accompanied after discharge.
Midanium should not be used for a long time, as this may increase the risk of dependence and the development of tolerance to the medicine. The development of tolerance means that the medicine's effect becomes weaker over time, requiring an increase in the dose.
Children
- -In infants under 6 months of age, Midanium should only be used in intensive care units.
- -During the use of Midanium in children, so-called paradoxical reactions (symptoms listed in section 4 "Possible side effects") may occur. If these symptoms occur, the use of the medicine should be stopped.
- -In children with heart diseases (especially with unstable circulation), special caution should be exercised.
Midanium and other medicines
The doctor should be informed about all medicines currently or recently used by the patient, as well as about medicines that the patient plans to use.
Midanium and other medicines used at the same time may affect each other's effects.
In particular, this applies to the following medicines listed below:
- -antifungal medicines (ketoconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole);
- -macrolide antibiotics (erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- -HIV protease inhibitors (medicines used in HIV infection - saquinavir);
- -verapamil and diltiazem (calcium channel blockers, mainly used in cardiovascular diseases);
- -atorvastatin (a medicine that lowers blood cholesterol levels);
- -aprepitant (an antiemetic medicine);
- -rifampicin (an antibiotic);
- -phenytoin (an antiepileptic medicine);
- -efavirenz (a medicine used in HIV infection);
- -strong painkillers (called opioid painkillers, e.g. morphine, buprenorphine);
- -medicines used in mental disorders (e.g. haloperidol, carbamazepine);
- -sedatives, anxiolytics, and hypnotics;
- -medicines used in the treatment of depression (fluoxetine, fluvoxamine);
- -medicines used in the treatment of allergies (with a sedative effect);
- -hydralazine (a medicine for hypertension);
- -inhaled anesthetics used for general anesthesia;
- -herbal mixtures containing St. John's Wort extract ( Hypericum perforatum).
The concurrent use of Midanium and opioids (strong painkillers, substitution therapy drugs, and some cough medicines) increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and can be life-threatening. For this reason, the concurrent use of these medicines can only be considered when other treatment methods are not possible.
If, however, the doctor has prescribed Midanium together with opioid medicines, the doctor should reduce the dose and recommend the shortest possible treatment time.
The patient should inform the doctor about all opioid medicines being taken and strictly follow the doctor's dosage instructions. It may be helpful to inform friends or relatives about the risk, so they are aware of the above-mentioned symptoms. If such symptoms occur, the doctor should be contacted.
Midanium and alcohol
Alcohol (ethanol) significantly enhances the sedative effect of midazolam. Consuming alcohol during the use of Midanium is contraindicated.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, suspects she may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, she should consult her doctor before using this medicine.
Midazolam may be used during pregnancy only when absolutely necessary.
Midazolam is not recommended during cesarean section.
Midazolam passes into breast milk in small amounts. If the medicine needs to be used, the patient should stop breastfeeding and resume after 24 hours from the administration of midazolam.
Driving and operating machinery
After using the medicine, the following may occur: sedation, amnesia, concentration disorders, muscle weakness, which may adversely affect the performance of tasks that require increased attention.
The patient should not drive vehicles or operate machinery until fully recovered.
The doctor will decide when the patient can resume these activities.
Midanium contains sodium
The medicine contains 3.16 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) per 1 ml. This corresponds to 0.16% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake in the diet for adults.
The medicine may be diluted - see below, section "Method of preparation of Midanium for administration and method of administration". When calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine, the sodium from the diluent should be taken into account. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, the patient information leaflet of the diluent should be consulted.
3. How to use Midanium
This medicine should always be used in accordance with the doctor's recommendations. In case of doubts, the doctor should be consulted.
- -Midanium is administered by medical personnel.
- -The medicine is used intramuscularly, intravenously, and rectally.
- -The doctor will determine the dosage of the medicine and the duration of treatment individually for each patient.
Detailed information on dosing is contained in the section "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals".
Use of a higher dose of Midanium than recommended
The medicine is administered by medical personnel, so it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should. In case of an overdose of midazolam, the following may occur: drowsiness, clumsiness, speech disorders or slurred speech, and nystagmus. In severe cases, loss of reflexes, apnea, hypotension, severe breathing difficulties, and in rare cases - coma.
If the patient feels that they have received a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, they should immediately consult their doctor, who will provide appropriate treatment.
In case of missed dose of Midanium
A double dose should not be used to make up for a missed dose.
Discontinuation of Midanium
In the case of long-term use of midazolam in intensive care units, after sudden discontinuation of the medicine, symptoms of withdrawal syndrome may occur. These symptoms include: headaches, muscle pain, anxiety, tension, restlessness, confusion, irritability, insomnia, mood changes, hallucinations, and seizures.
The doctor will choose the dose and duration of treatment to minimize the risk of these symptoms.
In case of any further doubts related to the use of this medicine, the doctor, pharmacist, or nurse should be consulted.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects may occur during the use of this medicine. Their frequency is unknown and cannot be determined based on available data.
The use of Midanium should be discontinued and the doctor should be consulted immediately if the patient experiences any of the following side effects. They may be life-threatening and may require immediate treatment:
- anaphylactic shock (a life-threatening allergic reaction). Symptoms may include sudden rash, itching or hives, and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or other parts of the body. The patient may also experience shortness of breath, wheezing, or breathing difficulties, or pallor, weak and rapid pulse, or a feeling of loss of consciousness. Additionally, chest pain may occur, which may be a symptom of a serious allergic reaction called Kounis syndrome.
- shortness of breath and breathing difficulties (sometimes leading to respiratory arrest), apnea;
- laryngospasm causing choking;
- heart disorders, such as bradycardia, vasodilation, cardiac arrest.
Other side effects, the frequency of which is unknown (the frequency cannot be determined based on available data):
- confusion, euphoria, hallucinations;
- excitement, feelings of hostility and anger, aggression, outbursts of excitement, involuntary movements (including clonic-tonic seizures and muscle tremors), excessive activity, violent acts (so-called paradoxical reactions, especially in children and the elderly); physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms, abuse of the medicine, seizures (in preterm and newborn infants, also as withdrawal symptoms);
- sedation (excessive calming) lasting longer and postoperative, decreased level of consciousness, drowsiness, dizziness; ataxia; anterograde amnesia (the patient does not remember events that occurred shortly after administration of the medicine) - the duration of these side effects depends on the dose used.
- hiccups;
- vasodilation;
- hypotension;
- dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation;
- skin rash, urticaria, itching;
- severe venous diseases (thrombophlebitis and venous thrombosis);
- pain and redness at the injection site;
- fatigue;
- an increased risk of falls and fractures has been reported in elderly patients and patients taking sedatives.
Prolonged intravenous administration of midazolam, even in therapeutic doses, may lead to the development of physical dependence, and sudden discontinuation of the medicine may be accompanied by withdrawal symptoms, including seizures - see the section "Discontinuation of Midanium".
In elderly patients and weakened or critically ill patients, especially those with heart diseases and breathing difficulties, more severe side effects may occur, especially after rapid injection or administration of large doses.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, the doctor, pharmacist, or nurse should be informed. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181 C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Midanium
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The medicine should not be used after the expiry date stated on the packaging and ampoule. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP indicates the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot indicates the batch number.
Store at a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The pharmacist should be asked how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Midanium contains
- The active substance of the medicine is midazolam. 1 ml of the solution contains 1 mg or 5 mg of midazolam.
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, disodium edetate, hydrochloric acid 10%, sodium hydroxide 10% or hydrochloric acid 10% (to adjust pH), water for injections.
What Midanium looks like and what the packaging contains
Midanium, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection is a colorless, clear liquid.
The cardboard box contains 10 ampoules of colorless glass, each containing 5 ml.
Midanium, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection is a colorless or light yellow, clear liquid.
The cardboard box contains 10 ampoules of colorless glass, each containing 1 ml or 5 ampoules of colorless glass, each containing 3 ml or 5 ampoules of colorless glass, each containing 10 ml.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:December 2024
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals
MIDANIUM, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection
MIDANIUM, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Midazolam
Method of preparation of Midanium for administration and method of administration
- -Midanium is used intramuscularly, intravenously, and rectally.
- -Midazolam should only be administered by experienced doctors in a facility fully equipped with equipment for monitoring and supporting respiratory and cardiovascular functions, and by persons properly trained in recognizing and treating expected adverse reactions, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- -Midanium can be mixed with 500 ml of the following infusion solutions:
- 5% glucose solution;
- 0.9% NaCl solution;
- 4% glucose solution with 0.18% NaCl solution. The prepared solution maintains physicochemical stability during storage at room temperature for 24 hours. From a microbiological point of view, the solution should be used immediately after preparation. If it is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the time and conditions of storage before use. It has not been confirmed that midazolam is adsorbed on plastic elements of infusion equipment or syringes.
- Midanium 5 mg/ml can be mixed with morphine sulfate (Morphini sulfas WZF 20 mg/ml) (see also "Warnings and precautions" below) within the following ranges of active substances: 10 mg of morphine sulfate with midazolam in a dose of 1.66 mg to 10 mg. To obtain a mixture of 10 mg of morphine sulfate: 1.66 mg of midazolam, 2.1 ml of Morphini sulfas WZF 20 mg/ml should be mixed with 1.4 ml of Midanium 5 mg/ml. To obtain a mixture of 10 mg of morphine sulfate: 10 mg of midazolam, 1.0 ml of Morphini sulfas WZF 20 mg/ml should be mixed with 4.0 ml of Midanium 5 mg/ml. The shelf life of the mixture of Morphini sulfas WZF 20 mg/ml with Midanium 5 mg/ml is 24 hours. Chemical and physical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 25°C. The mixture should be prepared immediately before administration. From a microbiological point of view, the prepared mixture should be used immediately. If it is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the conditions and time of storage. If necessary, the prepared mixture can be stored for up to 24 hours at 25°C, provided that the mixture is prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. Unused mixture should be discarded after 24 hours. The prepared mixture does not require protection from light.
and precautions, see below) within the following ranges of active substances: 10 mg of morphine sulfate with midazolam in a dose of 1.66 mg to 10 mg. To obtain a mixture of 10 mg of morphine sulfate: 1.66 mg of midazolam, 2.1 ml of Morphini sulfas WZF 20 mg/ml should be mixed with 1.4 ml of Midanium 5 mg/ml. To obtain a mixture of 10 mg of morphine sulfate: 10 mg of midazolam, 1.0 ml of Morphini sulfas WZF 20 mg/ml should be mixed with 4.0 ml of Midanium 5 mg/ml. The shelf life of the mixture of Morphini sulfas WZF 20 mg/ml with Midanium 5 mg/ml is 24 hours. Chemical and physical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 25°C. The mixture should be prepared immediately before administration. From a microbiological point of view, the prepared mixture should be used immediately. If it is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the conditions and time of storage. If necessary, the prepared mixture can be stored for up to 24 hours at 25°C, provided that the mixture is prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. Unused mixture should be discarded after 24 hours. The prepared mixture does not require protection from light.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down.
A colored dot (see Figure 1) is placed on each ampoule as a mark indicating the location of the break.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically in both hands, with the colored dot facing each other - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
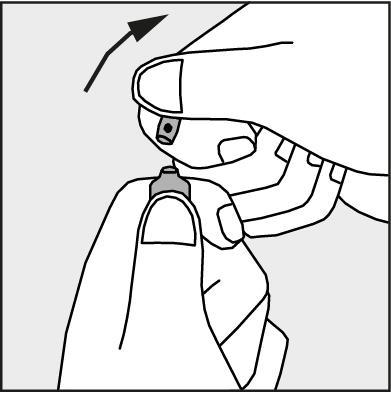
- Press according to the arrow on Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused medicine should be discarded in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1.
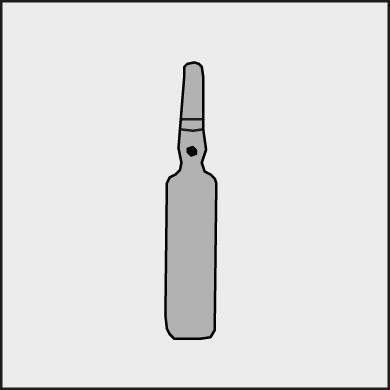
Figure 2.
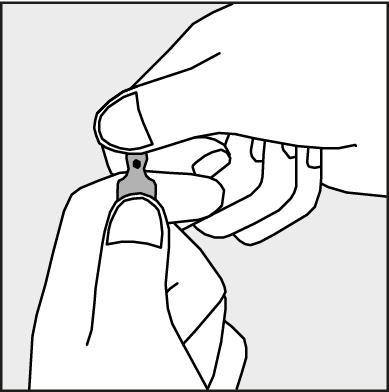
Figure 3.
Warnings and precautions
Special caution should be exercised when using the medicine in the following patients:
- with respiratory disorders;
- children under 6 months and children with unstable circulation;
- over 60 years old;
- chronically ill or weakened, e.g. with chronic respiratory failure, chronic kidney or liver failure, heart disease;
- with kidney function disorders (creatinine clearance <10 ml min). the pharmacokinetics of unbound midazolam after intravenous administration is similar to that observed in healthy volunteers. however, prolonged infusion, mean sedative effect duration was significantly longer patients with renal failure, probably due accumulation α-hydroxymidazolam glucuronide. there are no data on severe failure (creatinine clearance below 30 min) receiving for induction anesthesia.< li>
- with impaired liver function - the clearance of midazolam after intravenous administration decreases with increasing terminal half-life. Therefore, the clinical effect may be stronger and longer. In such cases, the dose of midazolam should be reduced and the patient's condition monitored. Patients at high risk should receive smaller doses of the medicine and be monitored for early signs of changes in vital functions.
Severe adverse reactions from the cardiovascular and respiratory systems have been reported: respiratory depression, apnea, cardiac arrest. The occurrence of these symptoms is more likely in the case of too rapid injection or administration of a large dose of the medicine.
When midazolam is used for premedication, the patient should be monitored after administration of the medicine, as individual sensitivity may vary and symptoms of overdose may occur.
Similarly, as with the use of other central nervous system depressants and/or muscle relaxants, special caution should be exercised in patients with myasthenia ( myasthenia gravis).
In the case of concurrent use of midazolam and opioids, the risk of respiratory depression increases, so such cases require monitoring.
Dosage
Standard dosing
Midazolam is a potent sedative that should be administered slowly and gradually. Gradual administration of midazolam will facilitate safe achievement of the desired level of sedation, depending on the patient's clinical needs, health status, and age, as well as other concomitantly administered medicines. The dose of the medicine in patients over 60 years old, weakened, or chronically ill, as well as in children, should be determined cautiously, taking into account specific risk factors for each patient. Standard dosing is shown in the table. Additional data are provided below the table.
| Indication | Adults under 60 years | Adults 60 years and older, weakened or chronically ill | Children |
| Sedation with preserved consciousness | Intravenously: Initial dose: 2-2.5 mg. Additional doses: 1 mg. Total dose: 3.5-7.5 mg | Intravenously: Initial dose: 0.5-1 mg. Additional doses: 0.5-1 mg. Total dose: <3.5 mg | Intravenously, from 6 months to 5 years: Initial dose: 0.05-0.1 mg/kg. Total dose: <6 mg. intravenously, 6-12 years: initial dose: 0.025-0.05 mg kg. total <10 rectally, over 6 months: 0.3-0.5 kg< td> |
| Premedication before induction of anesthesia | Intramuscularly: 0.07-0.1 mg/kg. Intravenously: 1-2 mg; the dose can be repeated | Intramuscularly: 0.025-0.05 mg/kg. Intravenously: Initial dose: 0.5 mg; if necessary, the dose can be slowly increased | Rectally, over 6 months: 0.3-0.5 mg/kg. Intramuscularly, 1-15 years: 0.08-0.2 mg/kg |
| Induction of anesthesia | Intravenously: 0.15-0.2 mg/kg (0.3-0.35 without premedication) | Intravenously: 0.05-0.15 mg/kg (0.15-0.3 without premedication) | |
| Sedation as part of combined anesthesia | Intravenously: Repeated doses: 0.03-0.1 mg/kg or continuous infusion: 0.03-0.1 mg/kg/h | Intravenously: Doses smaller than those recommended for adults under 60 years | |
| Sedation in intensive care units | Intravenously: Loading dose: 0.03-0.3 mg/kg, administered in 1-2.5 mg doses. Maintenance dose: 0.03-0.2 mg/kg/h | Intravenously: Loading dose: 0.03-0.3 mg/kg, administered in 1-2.5 mg doses. Maintenance dose: 0.03-0.2 mg/kg/h | Intravenously, newborns under 32 weeks of gestational age: 0.03 mg/kg/h. Intravenously, newborns over 32 weeks of gestational age and children up to 6 months: 0.06 mg/kg/h. Intravenously, over 6 months: Loading dose: 0.05-0.2 mg/kg. Maintenance dose: 0.06-0.12 mg/kg/h |
| 0.06 mg/kg/h |
- SEDATION WITH PRESERVED CONSCIOUSNESS
Before diagnostic or therapeutic procedures, midazolam should be administered intravenously. The dose should be adjusted to the individual patient's condition and administered gradually. The medicine should not be injected rapidly or administered in a single dose (bolus). The onset of the sedative effect may occur at different times in individual patients, depending on the patient's condition and the method of administration (e.g. speed of administration, dose size). If deeper sedation is required, small doses should be continued until the desired level of sedation is achieved.
Infants and young children under 5 years may require significantly higher doses (in mg/kg) than older children and adolescents.
Children under 6 months - are particularly prone to airway obstruction and hypoventilation. Therefore, midazolam is not recommended for sedation in children under 6 months.
Children from 6 months to 5 years: Initial dose: 0.05 mg/kg to 0.1 mg/kg. To achieve the desired effect, up to 0.6 mg/kg may be required, but the total dose should not exceed 6 mg. After administration of higher doses of midazolam, the risk of hypoventilation and prolonged sedation increases.
Children from 6 to 12 years: Initial dose: 0.025 mg/kg to 0.05 mg/kg. Up to 0.4 mg/kg may be required; maximum 10 mg. After administration of higher doses of midazolam, the risk of hypoventilation and prolonged sedation increases.
Children from 12 to 16 years: Dosing as in adults.
Rectally: The total dose of midazolam is usually 0.3 mg/kg to 0.5 mg/kg, administered once. Rectal administration should be performed using a syringe with a plastic applicator. If the volume of the solution to be administered is small, water can be added to a maximum volume of 10 ml. The rectal dose should not be repeated. Midazolam is not recommended for rectal administration in children under 6 months, as data for these patients are limited.
Intramuscularly: The doses range from 0.05 mg/kg to 0.15 mg/kg. The total dose is usually not higher than 10 mg. Intramuscular administration of the medicine should be limited to exceptional situations, as it is painful. Rectal administration is preferred. Children with a body weight below 15 kg should not be administered a midazolam solution with a concentration higher than 1 mg/ml. Higher concentrations should be diluted to 1 mg/ml.
- ANESTHESIA
Adults:Midazolam can be administered as a sedative before induction of anesthesia. Premedication with midazolam before procedures induces sedation (causes drowsiness or sleep and reduces anxiety) and amnesia during the preoperative period. Midazolam can also be administered with anticholinergic medicines. In such cases, midazolam should be administered intravenously or deeply intramuscularly in large muscle groups, 20 to 60 minutes before induction of anesthesia, while in children, the preferred route of administration is rectal (see below). After administration of the medicine, the patient's condition should be constantly and closely monitored, as individual sensitivity to the medicine may vary and symptoms of overdose may occur.
- Premedication before induction of anesthesia
- Adults:For preoperative sedation and amnesia, patients classified as I and II according to the ASA classification and patients under 60 years old are recommended to receive an intravenous dose of 1-2 mg, which can be repeated as needed, or intramuscularly 0.07 mg/kg to 0.1 mg/kg of midazolam. In patients over 60 years old, weakened, or chronically ill, the dose should be reduced and adjusted to the individual patient's condition.
Children
Newborns and children under 6 months
Midazolam is not recommended for use in children under 6 months, as the data on its use are limited.
Children over 6 months
Rectally: The total dose of midazolam is usually 0.3 mg/kg to 0.5 mg/kg, administered 15 to 30 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Rectal administration should be performed using a syringe with a plastic applicator. If the volume of the solution to be administered is small, water can be added to a maximum volume of 10 ml.
Intramuscularly: Because intramuscular administration is painful, it should be limited to exceptional situations. Rectal administration is preferred. Effective and safe doses administered intramuscularly range from 0.08 mg/kg to 0.2 mg/kg.
Children from 1 to 15 years require proportionally higher doses compared to adults, per kilogram of body weight.
Children with a body weight below 15 kg should not be administered a midazolam solution with a concentration higher than 1 mg/ml. Higher concentrations should be diluted to 1 mg/ml.
- INDUCTION OF ANESTHESIA
Adults:When midazolam is used for induction of anesthesia, before the administration of other anesthetic agents, individual patient reactions to the medicine may vary. The dose should be administered gradually to achieve the desired effect, taking into account the patient's age and condition. If midazolam is administered before other intravenous or inhalation anesthetics used for induction of anesthesia, or concurrently with these medicines, the usual initial dose of each of these medicines should be significantly reduced, sometimes to 25% of the usual initial dose. The desired anesthetic effect is achieved by gradual administration of the medicine. The intravenous dose of midazolam for induction of anesthesia should be administered slowly, in a fractionated manner. Each dose, not exceeding 5 mg, should be administered over 20-30 seconds, with a 2-minute interval between consecutive doses.
Patients under 60 years old who have received premedication: The usual intravenous dose is 0.15 mg/kg to 0.2 mg/kg.
Patients under 60 years old without premedication - the dose should be higher (intravenously 0.3 mg/kg to 0.35 mg/kg). If necessary, additional injections of up to 25% of the initial dose can be administered. The induction of anesthesia can also be completed using inhalation anesthetics. In resistant cases, up to 0.6 mg/kg of midazolam can be administered, but after such high doses, recovery may be prolonged.
Patients over 60 years old who have received premedication, weakened, or chronically ill: The dose should be significantly reduced, e.g. to 0.05-0.15 mg/kg, administered intravenously over 20-30 seconds, and wait 2 minutes for the effect.
Patients over 60 years old without premedication: They usually require a higher dose of midazolam for induction of anesthesia - the recommended initial dose is 0.15 mg/kg to 0.3 mg/kg. Patients with severe systemic diseases or weakened, in whom premedication was not used, usually require a smaller dose of midazolam - usually 0.15 mg/kg to 0.25 mg/kg is sufficient.
- COMBINED ANESTHESIA (MIDAZOLAM AS A SEDATIVE COMPONENT)
Adults:Midazolam can be administered as a sedative component in combined anesthesia in the form of repeated small intravenous doses (0.03 mg/kg to 0.1 mg/kg) or continuous infusion (0.03 mg/kg/h to 0.1 mg/kg/h), usually in combination with analgesics. The doses and intervals between administration of consecutive doses depend on the individual patient's reaction. In patients over 60 years old, weakened, or chronically ill, smaller maintenance doses should be used.
- SEDATION IN INTENSIVE CARE UNITS
The desired level of sedation is achieved by gradually increasing the dose of midazolam, and then continuous intravenous infusion or repeated injections, depending on clinical needs, the patient's condition, and age, as well as any other medicines being used.
Adults:
Intravenous loading dose: 0.03 mg/kg to 0.3 mg/kg of midazolam, administered slowly, in consecutive injections. Each single injection of 1 mg to 2.5 mg should be administered over 20-30 seconds, with a 2-minute interval between consecutive injections. In patients with hypovolemia, vasoconstriction, or hypothermia, the loading dose should be reduced or omitted.
If midazolam is administered with potent analgesics, these medicines should be administered first, to safely adjust the sedative effect of midazolam according to the level of sedation caused by the analgesic.
Intravenous maintenance dose: 0.03 mg/kg/h to 0.2 mg/kg/h.
In patients with hypovolemia, vasoconstriction, or hypothermia, the maintenance dose should be reduced. The level of sedation should be regularly assessed. During prolonged sedation, tolerance may develop - in such cases, there is a need to increase the dose.
Children
Neonates and infants up to 6 months
Midazolam should be administered as a continuous intravenous infusion, starting at 0.03 mg/kg/h (0.5 μg/kg/min) in neonates with a gestational age below 32 weeks or 0.06 mg/kg/h (1 μg/kg/min) in neonates with a gestational age above 32 weeks and infants up to 6 months.
It is not recommended to use loading doses in preterm infants, neonates, and infants below 6 months. The drug should be administered by infusion, at a higher rate over the first few hours, in order to achieve therapeutic serum concentrations. The infusion rate should be carefully and frequently controlled, especially after the first day, to administer the smallest effective dose and prevent potential accumulation of the drug. Close monitoring of respiratory function and oxygen saturation is recommended.
Children over 6 months
In children over 6 months, intubated and mechanically ventilated, a loading dose of 0.05 mg/kg to 0.2 mg/kg should be administered intravenously, slowly over 2 to 3 minutes, to achieve the desired clinical effect.
Midazolam should not be administered by rapid intravenous injection. After the loading dose, a continuous intravenous infusion of 0.06 mg/kg/h to 0.12 mg/kg/h (1 to 2 μg/kg/min) is administered. The infusion rate can be increased or decreased as needed (usually by 25% of the initial or subsequent rate) or additional intravenous doses of midazolam can be administered to increase or maintain the effect of the drug at the desired level.
When initiating midazolam in patients with impaired cardiovascular function, the drug should be administered in small, consecutive injections and these patients should be monitored for signs of hemodynamic instability, such as hypotension.
These patients are also prone to the depressive effect of midazolam on the respiratory system and require particularly close monitoring of respiratory function and oxygen saturation.
The use of a midazolam solution with a concentration greater than 1 mg/ml is not recommended in preterm infants, neonates, and children with a body weight below 15 kg. Higher concentrations should be diluted to 1 mg/ml.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to MidaniumDosage form: Tablets, 15 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Recipharm Leganes S.L.U. Roche Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 7.5 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Recipharm Leganes S.L.U. Roche Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 10 mgActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: MoNo chem-pharm. Produkte GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Midanium in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Midanium in Spain
Alternative to Midanium in Ukraine
Online doctors for Midanium
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Midanium – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









