

Hipnomidate

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Hipnomidate

How to use Hipnomidate
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
HYPNOMIDATE, 2 mg/ml, solution for injection
Etomidate
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Hypnomidate and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Hypnomidate
- 3. How to use Hypnomidate
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Hypnomidate
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Hypnomidate and what is it used for
The active substance of Hypnomidate is etomidate.
Hypnomidate is indicated for the induction of general anesthesia, as well as for supplementary anesthesia in local anesthesia.
Hypnomidate is indicated for short diagnostic procedures or procedures performed on an outpatient basis, where rapid recovery of the patient is necessary.
Hypnomidate is particularly indicated in cardio surgery and in patients with heart disease.
2. Important information before using Hypnomidate
When not to use Hypnomidate
If the patient is allergic to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
In case of any doubts whether the above information applies to the patient, they should consult a doctor or nurse before using Hypnomidate.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Hypnomidate, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or nurse if:
- they have liver disease;
- they have low blood pressure, e.g. due to weakness;
- they have adrenal insufficiency.
Hypnomidate should be used with caution in patients:
- with adrenal insufficiency, such as patients with sepsis (severe blood infection);
- with liver cirrhosis or those taking medications for certain mental illnesses (neuroleptics), strong painkillers (opioids), or sedatives. The dose of etomidate should be reduced.
- of advanced age.
Single inducing doses of etomidate may lead to transient adrenal insufficiency and decreased cortisol levels in the serum.
Etomidate should be used with caution in critically ill patients, including those with sepsis, as it has been associated with an increased risk of death in some studies.
Hypnomidate should only be administered by a doctor trained in endotracheal intubation. Resuscitation equipment should be available in case of respiratory depression or apnea.
Induction of general anesthesia with Hypnomidate may be accompanied by a slight, transient decrease in blood pressure. In weak patients, the doctor will take appropriate measures to prevent this.
The use of Hypnomidate may cause spontaneous muscle movements, especially if no premedication (administration of a sedative before administration of the anesthetic) has been used.
Hypnomidate does not have analgesic properties, so an appropriate analgesic should be used during surgical procedures, 1-2 minutes before administration of Hypnomidate.
Hypnomidate and other medicines
The patient should inform their doctor or nurse about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines that are available without a prescription.
The effect of Hypnomidate may be enhanced by:
- neuroleptics (used to treat mental illnesses);
- opioids (strong painkillers, e.g. morphine, fentanyl);
- sedatives;
- alcohol. Hypnomidate may enhance the effect of:
- medicines that lower blood pressure. Caution is advised when administering etomidate with alfentanil or fentanyl intravenously.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, or thinks they may be pregnant or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
Hypnomidate should not be used in pregnant women unless the potential benefits of treatment for the mother outweigh the risks to the fetus. The doctor will decide whether to use Hypnomidate.
If the patient thinks they may be pregnant, they should inform their doctor. Some animal studies have shown a harmful effect on fetal development.
Breastfeeding
Hypnomidate passes into human milk. Breastfeeding should be avoided during treatment and for 24 hours after administration of Hypnomidate.
Driving and using machines
Hypnomidate has a significant impact on the ability to drive and use machines.
Patients should not operate machines or drive vehicles for 24 hours after administration of this medicine. The time to return to normal fitness may vary depending on the duration of the procedure, the total dose administered, and other medications used. Therefore, the anesthesiologist will decide when the patient can drive and use machines.
Hypnomidate contains propylene glycol
This medicine contains 3626 mg of propylene glycol in 10 ml.
Before administering the medicine to a child under 5 years of age, the doctor or pharmacist should be consulted, especially if the child is taking other medicines containing propylene glycol or alcohol.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take this medicine without consulting their doctor. The doctor may decide to perform additional tests on such patients.
Patients with liver or kidney dysfunction should not take this medicine without consulting their doctor. The doctor may decide to perform additional tests on such patients.
3. How to use Hypnomidate
Hypnomidate is intended for administration only by a doctor trained in endotracheal intubation.
In case of any doubts, the patient should consult their doctor.
How to administer Hypnomidate
- only intravenously - in slow injection;
- Hypnomidate does not have analgesic properties, so the patient will receive an appropriate analgesic before administration of Hypnomidate.
How much Hypnomidate to administer
The doctor will decide on the dose, depending on:
- the type of surgical procedure
- body weight
- age
- overall health.
The effective dose for inducing sleep is 0.3 mg/kg body weight. In adult patients, one ampoule usually suffices to induce sleep lasting 4-5 minutes.
Sleep may be prolonged by administering additional doses of Hypnomidate, but no more than 3 ampoules (30 ml).
Elderly patients
Elderly patients should be given a single dose of 0.15-0.2 mg/kg body weight, which will then be individually adjusted according to the patient's reaction (see section 2).
Children and adolescents
In children under 15 years of age, it may be necessary to increase the dose to achieve the same depth of sleep and sleep time as in adults. Sometimes it is necessary to increase the dose by about 30% of the usual dose for adults.
Using more than the recommended dose of Hypnomidate
In case of overdose of etomidate administered as a bolus, sleep becomes deeper and may be accompanied by hypotension, adrenal insufficiency, respiratory depression, or even apnea. In case of apnea, appropriate respiratory support measures should be taken. Disorientation and prolonged recovery may also occur.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Hypnomidate can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
In clinical trials, the most commonly reported side effects were dyskinesia and vein pain.
The following side effects (including those listed above) have been reported during clinical trials or after the marketing of Hypnomidate.
Very common side effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 patients):
- dyskinesia (movement disorder);
- decreased cortisol levels. Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 patients):
- myoclonic seizures;
- vein pain, decreased blood pressure;
- apnea, hyperventilation (rapid or deep breathing), stridor;
- vomiting, nausea;
- rash.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients):
- hypertonia (increased muscle tone), involuntary muscle contractions, oculogyric crisis;
- bradycardia (slow heart rate), extra heartbeats, ventricular extra beats;
- phlebitis, hypertension (high blood pressure);
- hypoventilation (slow and shallow breathing), hiccups, cough;
- excessive salivation;
- flushing;
- muscle stiffness;
- pain at the injection site;
- anesthesia complications, delayed recovery of consciousness after anesthesia, insufficient analgesic effect, nausea during procedures.
Side effects with unknown frequency (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- hypersensitivity reactions [including anaphylactic shock (sudden circulatory failure)], anaphylactic reactions (severe allergic reactions causing breathing difficulties or dizziness) and pseudo-anaphylactic reactions;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- seizures (including grand mal seizures);
- cardiac arrest, complete atrioventricular block;
- shock, thrombophlebitis (deep and superficial);
- respiratory depression, bronchospasm (including death);
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (characterized by non-permanent blisters on mucous membranes, mainly in the mouth and genital areas, which burst to form painful ulcers that make eating difficult. It may also be accompanied by fever, joint pain, and urticaria.
- trismus.
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309,
website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Hypnomidate
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoule label. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Store in a temperature below 25°C.
For single use only. After opening the ampoule, any unused medicine should be discarded.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Hypnomidate contains
- The active substance of Hypnomidate is etomidate. One ml of the solution contains 2 mg of etomidate. One ampoule contains 20 mg of etomidate.
- The other excipients are: propylene glycol, water for injections.
What Hypnomidate looks like and contents of the pack
Hypnomidate is a sterile, clear, colorless aqueous solution for intravenous injection.
Ampoule of 10 ml in a carton.
Pack size: 5 ampoules of 10 ml.
Marketing authorization holder
Piramal Critical Care B.V.
Rouboslaan 32, 2252 TR, Voorschoten
Netherlands
[email protected].
Manufacturer
Piramal Critical Care B.V.
Rouboslaan 32, 2252 TR, Voorschoten
Netherlands
Date of last revision of the leaflet: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
This medicinal product must be administered only by doctors trained in endotracheal intubation. During the administration of Hypnomidate, resuscitation equipment should be available in case of respiratory depression and apnea.
1. Preparation of the medicinal product for administration
Before opening the ampoule, protective gloves should be put on.
Ampoules
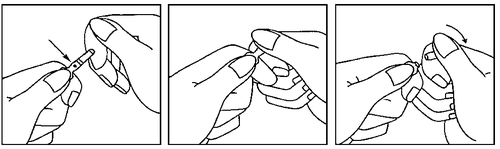
- 1. Hold the ampoule between the thumb and index finger, leaving the other end free
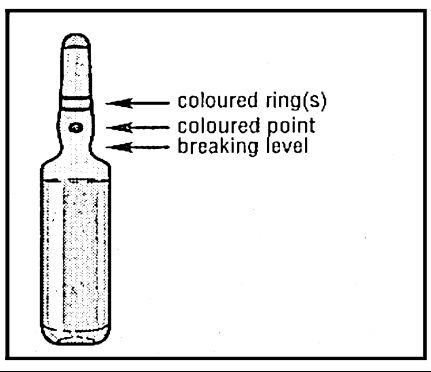
- 2. With the other hand, hold the end of the ampoule, placing the index finger at the end of the ampoule and the thumb on the colored point, parallel to the colored ring on the end of the ampoule.
- 3. Holding the thumb on this point, break the end of the ampoule energetically, while holding the rest of the ampoule firmly with the other hand.
In case of accidental exposure of the skin to the medicinal product, the area should be washed with water.
Soap, alcohol, and other cleaning agents that may cause chemical or mechanical skin damage should not be used.
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations. The unused part of the medicinal product should not be stored for future administration.
2. Special warnings and precautions for use
Hypnomidate should be administered only intravenously.
Induction of anesthesia with Hypnomidate may be accompanied by a slight, transient decrease in blood pressure, related to the decrease in peripheral vascular resistance.
In weak patients, in whom hypotension may be dangerous, the following measures should be taken:
- 1. The patient should be placed in a supine position.
- 2. Access to a vein should be obtained to ensure adequate blood volume. Hypnomidate should be injected slowly (e.g. 10 ml over 1 minute).
- 3. If possible, the use of other medicines for induction of anesthesia should be avoided.
During the administration of Hypnomidate, resuscitation equipment should be available in case of respiratory depression and apnea.
The use of Hypnomidate may cause spontaneous muscle movements or muscle group movements, especially if no premedication has been used. These movements are attributed to subcortical disinhibition. They can usually be prevented by administering a small dose of fentanyl with diazepam 1-2 minutes before the start of anesthesia with Hypnomidate.
During the administration of Hypnomidate, myoclonic seizures and pain at the injection site have been reported, especially during injection into small veins. This can usually be prevented by administering a small dose of an opioid, such as fentanyl, 1-2 minutes before the start of anesthesia.
Caution should be exercised when administering Hypnomidate to elderly patients, as it may decrease cardiac minute volume, which has been reported with doses higher than recommended.
Hypnomidate does not have analgesic properties, so an appropriate analgesic should be used during surgical procedures.
Neuroleptics, opioids, sedatives, and alcohol may enhance the sedative effect of etomidate.
Induction with etomidate may be accompanied by a slight and transient decrease in peripheral resistance, which may enhance the effect of other medicines that lower blood pressure.
Effect of other medicines on etomidate
Concomitant administration of etomidate with alfentanil reduces the terminal half-life of etomidate to 29 minutes. Caution should be exercised when using etomidate and alfentanil concomitantly, as the etomidate concentration may decrease below the threshold for sedation.
The total clearance and volume of distribution of etomidate are reduced 2-3 times without affecting the half-life when administered with fentanyl intravenously. It may be necessary to reduce the dose when etomidate is administered concomitantly with fentanyl intravenously.
Effect of etomidate on other medicines
Concomitant administration of etomidate and ketamine does not have a significant effect on the serum concentration or pharmacokinetic parameters of ketamine or its main metabolite, norketamine.
3. Overdose
In case of overdose of etomidate administered as a bolus, sleep becomes deeper and may be accompanied by hypotension, adrenal insufficiency, respiratory depression, or even apnea. In case of apnea, appropriate respiratory support measures should be taken. Disorientation and prolonged recovery may also occur.
Besides supportive measures (e.g. respiration), it may be necessary to administer 50 mg - 100 mg of hydrocortisone (and not adrenocorticotropic hormone - ACTH). General supportive measures and close monitoring are recommended.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterPiramal Critical Care B.V.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to HipnomidateDosage form: Emulsion, 2 mg/mlActive substance: etomidateManufacturer: B. Braun Melsungen AGPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 2 mg/mlActive substance: etomidatePrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 2 mg/mlActive substance: etomidatePrescription not required
Alternatives to Hipnomidate in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Hipnomidate in Hiszpania
Online doctors for Hipnomidate
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Hipnomidate – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














