

Fraxodi

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fraxodi

How to use Fraxodi
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Fraxodi, 11,400 IU AXa/0.6 ml, solution for injection
Fraxodi, 15,200 IU AXa/0.8 ml, solution for injection
Fraxodi, 19,000 IU AXa/1 ml, solution for injection
(Nadroparin calcium)
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Fraxodi and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Fraxodi
- 3. How to use Fraxodi
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fraxodi
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Fraxodi and what is it used for
Fraxodi is an anticoagulant medicine used to treat deep vein thrombosis.
The medicine is administered by subcutaneous injection.
Indications for use:
- treatment of venous thromboembolic disease.
2. Important information before using Fraxodi
When not to use Fraxodi:
- if the patient is allergic to the active substance nadroparin calcium, heparin or a similar product (such as enoxaparin, bemiparin, dalteparin) or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has previously experienced a decrease in platelet count (thrombocytopenia) after using Fraxodi;
- if the patient has bleeding or any disease that affects blood clotting;
- if the patient has a medical condition that increases the risk of bleeding [e.g. active peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and/or duodenum];
- if the patient has recently had a hemorrhagic stroke;
- if the patient has acute infectious endocarditis;
- if the patient has severe kidney dysfunction and is taking medications for thrombosis, e.g. in the lungs (pulmonary embolism) or leg (deep vein thrombosis);
- if the patient has severe kidney dysfunction and is taking medications for heart disease (e.g. unstable angina or myocardial infarction without Q-wave).
Warnings and precautions
During treatment with Fraxodi, a decrease in platelet count may rarely occur, which can sometimes be severe. During treatment, the doctor will recommend blood tests to check for this side effect.
Before using Fraxodi, the patient should tell their doctor if:
- they have conditions that increase the risk of bleeding, in particular, if:
- they have peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and/or duodenum,
- they have coagulation disorders,
- they have recently undergone surgery in the brain, spinal cord, or eye,
- they have high blood pressure;
- they have severe liver dysfunction;
- they have kidney dysfunction;
- they have eye diseases affecting blood vessels (vascular disorders of the retina and choroid);
- they are taking other medications that affect blood clotting (see section: "Fraxodi and other medications").
In case of bleeding, the patient should immediately contact their doctor.
In case of skin necrosis, which may be preceded by small subcutaneous hemorrhages or hard or painful skin redness, the patient should stop taking the medicine and contact their doctor immediately.
Using Fraxodi may cause an increase in blood potassium levels.
If the patient has diseases that may cause an increase in potassium levels, such as diabetes, severe kidney disease, previous metabolic acidosis, or is taking other medications that increase potassium levels, the doctor may recommend regular blood tests. If the patient is unsure whether they are taking such medications, they should ask their doctor.
Fraxodi and other medications
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medications they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medications they plan to take.
It is not recommended to use Fraxodi with the following medications due to the risk of bleeding. If this cannot be avoided, the doctor will closely monitor the patient's condition. This applies to the following medications:
- acetylsalicylic acid (e.g. aspirin),
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (medications used to relieve pain, e.g. ibuprofen),
- antiplatelet medications (used to prevent blood clots, e.g. clopidogrel).
Fraxodi should be used with caution with:
- oral anticoagulants (medications that prevent blood clotting, e.g. warfarin),
- glucocorticosteroids (steroid medications used to treat e.g. asthma),
- dextran (a medication administered intravenously to increase blood volume).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Fraxodi may be used during pregnancy only if the doctor considers that the expected benefits of using the medicine outweigh the potential risks.
It is not known whether the ingredients of Fraxodi pass into breast milk, so breastfeeding should not be done during treatment with Fraxodi.
Driving and using machines
There is no data on the effect of Fraxodi on the ability to drive and use machines.
The packaging of the medicine may contain latex (natural rubber)
The packaging of the medicine (needle shield) may contain latex. This can cause severe allergic reactions.
3. How to use Fraxodi
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Method of administration
Fraxodi should be administered by subcutaneous injection.
Fraxodi should not be administered by intramuscular injection.
The graduated syringe makes it easier to administer the correct dose if dose adjustment is necessary based on the patient's body weight.
When administering the medicine by subcutaneous injection, the anterior abdominal wall is usually chosen as the injection site, alternating between the right and left sides. Another injection site may be the thigh.
Detailed instructions for self-administering subcutaneous injections of Fraxodi can be found in the section: "Instructions for self-administering subcutaneous injections of Fraxodi".
Recommended dosage
The dosage is determined by the doctor, individually for each patient, based on the indication, clinical condition, and patient's body weight.
Use in children and adolescents
Fraxodi should not be used in children and adolescents.
Patient over 65 years of age
In these patients, kidney function may be impaired. Therefore, the doctor may recommend kidney function tests and adjust the dose of Fraxodi accordingly.
Kidney dysfunction
The doctor will adjust the dose of Fraxodi according to the severity of kidney dysfunction.
Fraxodi is contraindicated in patients with severe kidney dysfunction.
Using a higher dose of Fraxodi than recommended
In case of using a higher dose of Fraxodi than recommended, the patient should immediately contact their doctor. The main symptom of overdose is bleeding.
Missing a dose of Fraxodi
The patient should continue using the medicine without increasing the next dose. The interval between doses should not be shortened.
The patient should not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping treatment with Fraxodi
Fraxodi should be used for as long as the doctor recommends. The patient should not stop using Fraxodi without consulting their doctor.
If the patient wants to stop using Fraxodi, they should discuss this with their doctor or pharmacist first.
In case of any further doubts about using this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Fraxodi can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The patient should stop using the medicine and contact their doctor immediately if they experience:
- an allergic reactioncharacterized by: hives (light red, itchy blisters on the skin), angioedema (swelling of the face or lips that can make breathing difficult),
- skin necrosis at the injection site- this is preceded by subcutaneous hemorrhages or hard or painful skin redness with or without general symptoms.
Very common side effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 patients):
- bleeding at various locations, more frequent in patients with other risk factors,
- small hematomas at the injection site. In some cases, hard lumps may appear, which do not indicate heparin crystallization and should disappear after a few days.
Common side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 patients):
- skin reaction at the injection site,
- increased liver enzyme activity (transaminases), usually transient (visible in blood test results).
Rare side effects(may affect up to 1 in 1000 patients):
- decrease in platelet count (thrombocytopenia),
- increase in platelet count (thrombocytosis),
- rash, hives, redness, skin itching,
- calcification under the skin at the injection site.
Very rare side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients):
- allergic reactions, including angioedema and skin reactions,
- pseudo-anaphylactic reaction (symptoms are similar to anaphylaxis - an allergic reaction
- see the beginning of this section),
- skin necrosis,
- increase in eosinophil count (a type of white blood cell) - transient after treatment completion (visible in blood test results),
- increase in blood potassium levels,
- prolonged, painful erection of the penis (priapism) - if this occurs, the patient should immediately contact their doctor, as they may require treatment to avoid serious complications.
Unknown(frequency cannot be determined from available data)
- headache,
- migraine.
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in the leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects can help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Fraxodi
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 25°C.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the given month.
Medicines and syringes should not be disposed of in the sewage system or household waste containers.
The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Fraxodi contains
- The active substance of the medicine is: 11,400 IU AXa nadroparin calcium in 0.6 ml solution for injection, 15,200 IU AXa nadroparin calcium in 0.8 ml solution for injection, 19,000 IU AXa nadroparin calcium in 1 ml solution for injection
- The other ingredients are: calcium hydroxide solution or diluted hydrochloric acid to adjust pH, water for injections.
What Fraxodi looks like and what the package contains
Fraxodi is a solution for injection. The pre-filled syringe contains a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless or slightly colored solution. The medicine is packaged in pre-filled syringes with a protective needle shield.
Marketing authorization holder
Viatris Healthcare Sp. z o.o.
ul. Postępu 21B
02-676 Warsaw
tel.: 22 546 64 00
Manufacturer
Aspen Notre Dame de Bondeville
1, rue de l’Abbaye
76960 Notre-Dame de Bondeville
France
or
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals S.A.
ul. Grunwaldzka 189
60-322 Poznań
Date of last update of the leaflet: 02/2024
Information for healthcare professionals
Detailed dosing and administration instructions can be found in section 4.2 of the approved Summary of Product Characteristics.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR SELF-ADMINISTERING SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTIONS OF FRAXODI
FRAXODI
- 1. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water and dry them with a towel.
- 2. Sit or lie down in a comfortable position. Choose an injection site on the side of your abdomen (Figure 1). Injections should be administered alternately on the right and left sides.
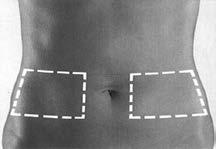
Figure 1
- 3. Clean the injection site with a swab moistened with spirit.
- 4. Remove the needle shield. Dispose of the needle shield.
Important notes
- Do not touch the needle and do not allow the needle to come into contact with other surfaces before injection.
- The presence of a small air bubble in the pre-filled syringe is normal. Do not remove the air bubble before administering the injection - this may lead to loss of part of the medicine.
- 5. Hold the previously cleaned skin with your fingers, creating a skin fold. Hold the skin fold between your thumb and index finger during the entire injection process (Figure 2).
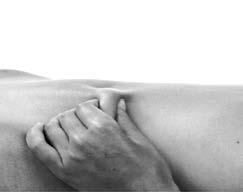
Figure 2
- 6. Hold the pre-filled syringe with your fingers on the handle in a firm manner. Insert the entire length of the needle at a right angle into the skin fold (Figure 3).
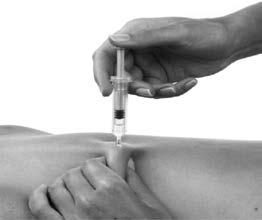
Figure 3
- 7. Inject the entire contents of the pre-filled syringe by pressing the plunger down until resistance is felt.
- 8. Remove the needle with the pre-filled syringe from the skin (Figure 4). Do not rub the injection site.
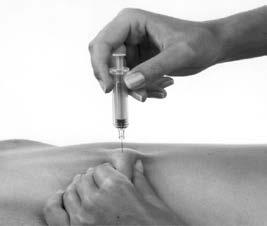
Figure 4
- 9. Appearance of the pre-filled syringe after injection (Figure 5).

Protective shield
Syringe handle
Figure 5
- 10. After injection, slide the protective shield over the pre-filled syringe to protect against needlestick injury (Figure 6). Holding the syringe handle firmly with one hand, use the other hand to grasp the outer shield of the pre-filled syringe and slide it towards the needle. The shield will click into place. When releasing and locking the shield, resistance is felt.
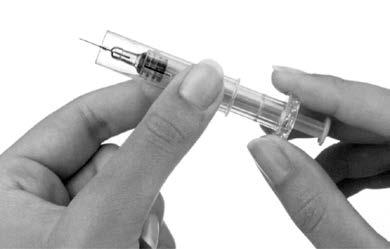
Figure 6
- 11. Appearance of the pre-filled syringe after sliding the protective shield (Figure 7).

Protective shield
Syringe handle
Figure 7
- 12. Used pre-filled syringes should not be disposed of in household waste containers. They should be disposed of in accordance with the doctor's or pharmacist's instructions.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAspen Notre Dame de Bondeville GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FraxodiDosage form: Solution, 5700 IU/0.6 mlActive substance: nadroparinPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 9500 IU aXa/mlActive substance: nadroparinPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 2850 IU aXa/0.3 mlActive substance: nadroparinPrescription required
Alternatives to Fraxodi in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fraxodi in Ukraine
Alternative to Fraxodi in Spain
Online doctors for Fraxodi
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fraxodi – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














