
Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda

How to use Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda
Leaflet included in the packaging: information for the user
Antithrombin III NF Shire, 50 IU/ml, powder and solvent for solution for infusion
Human antithrombin III derived from plasma
Please read carefully the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if necessary.
- In case of any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed to you by a doctor for a specific condition. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Antithrombin III NF Shire and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Antithrombin III NF Shire
- 3. How to use Antithrombin III NF Shire
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Antithrombin III NF Shire
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Antithrombin III NF Shire and what is it used for
Antithrombin III NF Shire comes in the form of a pale yellow to pale green powder with a solvent for solution for infusion.
Antithrombin III NF Shire is available in packages containing:
500 IU of antithrombin III and 10 ml of solvent or
1000 IU of antithrombin III and 20 ml of solvent
- 500 IU of antithrombin III and 10 ml of solvent or
- 1000 IU of antithrombin III and 20 ml of solvent
Antithrombin III NF Shire belongs to the pharmacotherapeutic group of anticoagulants.
Antithrombin III NF Shire is used to treat congenital or acquired antithrombin III deficiency, where acquired deficiency may occur in the course of many clinical disorders.
2. Important information before using Antithrombin III NF Shire
When not to use Antithrombin III NF Shire:
- if the patient is allergic to antithrombin III or any other component of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (i.e., decreased platelet count) in their medical history
Warnings and precautions
- The patient should inform their doctor if they experience the first symptoms of an allergic reaction (e.g., hives, including generalized, chest tightness, wheezing, low blood pressure, and anaphylactic shock). Severe symptoms may require emergency treatment.
- The patient should inform their doctor if they are taking or have recently taken heparin-containing medications (e.g., for thrombosis treatment), as the effect of antithrombin is significantly enhanced by heparin.
- Antithrombin III NF Shire is produced from human plasma. When administering drugs obtained from human blood or plasma, it is not possible to completely exclude the transmission of infectious agents. This also applies to unknown pathogens. However, the risk of transmitting infectious agents is reduced through careful selection of donors and plasma, plasma bank testing, and virus inactivation/removal procedures.
Children
Do not use this medicine in children under 6 years of age, as the safety and efficacy of this medicine have not been established in this age group.
Antithrombin III NF Shire and other medicines
- The patient should inform their doctor about any medications they are currently taking or have recently taken, including heparin-containing medications (e.g., for thrombosis treatment), as the effect of antithrombin is significantly enhanced by heparin.
- The patient should inform their doctor or pharmacist about all medications they are currently taking or have recently taken, even those that are available without a prescription.
Antithrombin III NF Shire with food and drink
This is not applicable.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, or thinks they may be pregnant or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine. The doctor will decide whether it is possible to use Antithrombin III NF Shire during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Before taking any medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Driving and using machines
Although no effect on the ability to drive and use machines has been observed, such an effect cannot be ruled out. Therefore, it is recommended that the patient does not drive or operate machines without prior consultation with their doctor.
Antithrombin III NF Shire contains sodium
This medicine contains approximately 3.77 mg of sodium per ml. This should be taken into account in patients controlling their sodium intake.
3. How to use Antithrombin III NF Shire
Antithrombin III NF Shire will be administered exclusively under medical supervision. The dose will depend on the patient's body weight and individual needs. The doctor will determine the dose to be administered. Antithrombin III NF Shire will be administered by intravenous infusion.
Using a higher dose of Antithrombin III NF Shire than recommended
No symptoms of antithrombin overdose have been reported.
Missing a dose of Antithrombin III NF Shire
This is not applicable.
Stopping the use of Antithrombin III NF Shire
This is not applicable.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
- Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions such as angioedema, burning and stinging at the infusion site, chills, flushing, generalized hives, headache, pruritic rash, low blood pressure, drowsiness, nausea, anxiety, rapid heart rate, feeling of chest tightness, tingling, vomiting, wheezing have been observed rarely, but may in some cases lead to severe anaphylactic reactions (including anaphylactic shock).
- Fever has been observed in rare cases.
- In rare cases, thrombocytopenia (i.e., decreased platelet count) may occur, which is mediated by heparin-induced antibodies. A decrease in platelet count below 100,000/μl or a decrease in platelet count by 50% has been observed.
Other side effects observed after the introduction of Antithrombin III NF Shire to the market include hypersensitivity, anaphylactic reaction, chills, and flushing.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the patient should inform their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, e-mail: [email protected]. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Antithrombin III NF Shire
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children. Store in a refrigerator (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze. Store in the original packaging to protect from light. Do not use Antithrombin III NF Shire after the expiry date stated on the label and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated. Do not use Antithrombin III NF Shire if the solution is cloudy or contains sediment. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Antithrombin III NF Shire contains
- The active substance of the medicine is human antithrombin derived from plasma
- The other ingredients are glucose, sodium chloride, disodium citrate dihydrate, and Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
What Antithrombin III NF Shire looks like and what the packaging contains
Antithrombin III NF Shire comes in the form of a powder for solution for infusion containing nominally 500 IU (or 1000 IU) of antithrombin derived from human plasma in a vial and solvent. After reconstitution in 10 ml (or 20 ml) of water for injection, the medicine contains approximately 50 IU/ml (500 IU/10 ml or 1000 IU/20 ml) of human antithrombin from plasma. Antithrombin III NF Shire is a pale yellow or pale green powder. Each package also contains:
- 1 transfer needle
- 1 filter needle
- 1 venting needle
- 1 single-use needle
- 1 infusion set
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Shire Polska Sp. z o.o. Plac Europejski 1, 00-844 Warsaw
Manufacturer
Baxter AG, Industriestrasse 67, A-1220 Vienna, Austria
Date of last revision of the leaflet: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
Dosing and method of administration
Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor with experience in treating patients with antithrombin deficiency. Dosing: The dose should be individually tailored for each patient and take into account the patient's family history of thromboembolic events, current risk factors, and laboratory results. The dose and duration of substitution therapy in acquired deficiency depend on the antithrombin level in plasma, the presence of symptoms of increased consumption, the cause of the disorder, and the severity of the patient's clinical condition. In each case, the dose and frequency of administration should be determined based on laboratory results and the patient's clinical condition and response to treatment. The number of antithrombin units administered is expressed in international units (IU), which refer to the current WHO standard for antithrombin. Antithrombin activity in plasma is expressed as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in international units (relative to the International Standard for antithrombin in plasma). The activity of one international unit (IU) of antithrombin corresponds to the amount of antithrombin in one ml of normal human plasma. The calculation of the required dose of antithrombin is based on empirical data that the administration of 1 international unit (IU) of antithrombin per kilogram of body weight increases the antithrombin activity in plasma by approximately 2%. The initial dose is calculated according to the following formula:
Required amount of units = body weight (kg) x (Target level - current antithrombin activity [%]) x 0.5
The target antithrombin activity in plasma depends on the assessment of the patient's clinical condition. After establishing the indication for antithrombin substitution, a single dose should ensure the achievement of the target antithrombin activity in plasma and subsequently maintain its normal level. The dose should be determined and controlled based on antithrombin activity measurements, which should be performed at least twice a day until the patient's condition stabilizes, and then once a day, preferably shortly before the next infusion. Dose adjustment should take into account both the increased consumption of antithrombin and laboratory results and clinical symptoms. During treatment, antithrombin activity should be maintained at a level above 80%, unless clinical reasons require a different, effective level. The initial dose in congenital deficiency is 30-50 IU/kg body weight. Subsequently, the dose and frequency of administration, as well as the duration of treatment, should be adjusted based on laboratory results and the patient's clinical condition. Children and adolescents: The safety and efficacy of Antithrombin III NF Shire have not been established in children under 6 years of age. Therefore, the use of this medicine is not recommended in this patient group. Method of administration: Administer intravenously. The maximum infusion rate is 5 ml/min.
Special precautions for disposal and preparation of the medicine for use
Antithrombin III NF Shire should be reconstituted immediately before administration. Only the provided infusion set should be used. During the preparation of the solution, aseptic techniques should be used. The prepared solution should be used immediately after preparation (as it does not contain preservatives). Before administration, the reconstituted medicine should be inspected for any visible particles or discoloration. The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent. Do not use solutions that are cloudy or contain sediment. Any unused medicine or waste should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Preparing the solution:
- 1. Bring the closed vial containing the solvent (water for injection) to room temperature (max. 37°C).
- 2. Remove the protective caps from the vials with the powder and solvent (Fig. A) and disinfect the rubber stoppers of both vials.
- 3. Remove the protective cap from one end of the transfer needle by twisting and pulling (Fig. B). Insert the exposed end of the needle into the rubber stopper of the vial with the solvent (Fig. C).
- 4. Remove the protective cap from the other end of the transfer needle, taking care not to touch the exposed part.
- 5. Invert the vial with the solvent and insert the free end of the transfer needle into the vial with the powder (Fig. D). The solvent will be drawn into the vial with the powder by vacuum.
- 6. Separate the two vials by withdrawing the needle from the vial with the powder (Fig. E). Gently swirl the vial to facilitate dissolution.
- 7. After complete dissolution of the powder, insert the provided venting needle (Fig. F), and the formed foam will settle. Remove the venting needle.
Administration:
- 8. Remove the protective cap from the provided filter needle by twisting and pulling, and attach it to a sterile single-use syringe. Draw the solution into the syringe (Fig. G).
- 9. Detach the filter needle from the syringe and, after attaching the provided single-use needle (or the provided infusion set), slowly administer the solution intravenously (maximum infusion rate: 5 ml/min).
If the medicine was not filtered during reconstitution, a single-use infusion set with a suitable filter should be used (maximum infusion rate: 5 ml/min).
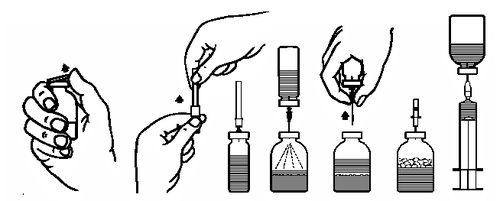
Fig. A Fig. B
Fig. C Fig. D
Fig. E Fig. F Fig. G
Incompatibilities
The medicine should not be mixed with other medicines.
Special warnings and precautions for use
As with other protein-containing medicines administered intravenously, the administration of Antithrombin III NF Shire may cause allergic reactions. During the infusion, patients should be closely monitored and carefully observed for any signs of side effects. The patient should be informed about early signs of allergic reactions, such as pruritic rash, generalized hives, feeling of chest tightness, wheezing, low blood pressure, and anaphylactic shock. If these symptoms occur after administration of the medicine, the patient should contact their doctor. In case of anaphylactic shock, standard treatment should be applied. Shire is a registered trademark of Shire Pharmaceutical Holdings Ireland Limited or its affiliates.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterTakeda Manufacturing Austria AG
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Antithrombin Iii Nf TakedaDosage form: Powder, 500 IUActive substance: antithrombin IIIManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 1000 IUActive substance: antithrombin IIIManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 50 IU/ml; 500 IUActive substance: antithrombin IIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription not required
Alternatives to Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda in Ukraina
Alternative to Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda in Hiszpania
Online doctors for Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Antithrombin Iii Nf Takeda – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














