LEVOTHYROXINE ARISTO 137 MICROGRAMS TABLETS

How to use LEVOTHYROXINE ARISTO 137 MICROGRAMS TABLETS
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Levotiroxina Aristo 137 micrograms tablets
levotiroxina sodium
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Levotiroxina Aristo and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you take Levotiroxina Aristo
- How to take Levotiroxina Aristo
- Possible side effects
- Storing Levotiroxina Aristo
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Levotiroxina Aristo and what is it used for
Thyroxine is a hormone that is naturally produced in the body by the thyroid gland. Levotiroxina sodium is a synthetic thyroid hormone that is chemically identical to this hormone.
This medicine is used to replace the missing thyroid hormone or to relieve the stress on the thyroid gland.
Levotiroxina is used to:
- replace the missing thyroid hormone in all forms of underactive thyroid function (hypothyroidism) or after the removal of the thyroid gland,
- prevent the recurrence of new goiters after goiter surgery in patients with normal thyroid function,
- treat non-malignant goiter (benign struma) in patients with normal thyroid function, as additional therapy in the antithyroid treatment of an overactive thyroid, after the normal metabolic state has been achieved,
- for malignant thyroid tumors, particularly after surgery to suppress the growth of new tumors and as a supplement for the missing thyroid hormone.
2. What you need to know before you take Levotiroxina Aristo
Do not takeLevotiroxinaif:
- you are allergic to levotiroxina or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- you have an untreated overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxicosis);
- you have untreated adrenal gland dysfunction (adrenal insufficiency) and do not have adequate replacement therapy;
- you have an untreated pituitary gland deficiency;
- you have the following diseases or conditions:
- acute myocardial infarction,
- acute myocarditis,
- acute pancreatitis,
- if you are pregnant, do not take levotiroxina with other medicines used to treat overactive thyroid gland (antithyroid medicines).
Before starting treatment with levotiroxina, the following disorders or conditions should be ruled out or treated:
- coronary artery disease,
- chest pain with chest pressure (angina pectoris),
- fat deposits in the arteries (arteriosclerosis),
- high blood pressure (hypertension),
- conditions in which the pituitary gland/suprarenal glands do not produce enough hormones (pituitary and/or adrenal insufficiency)
- areas of the thyroid gland that produce uncontrolled amounts of thyroid hormone (thyroid autonomy)
Warnings and precautions
Thyroid hormones should not be used for weight loss. Taking thyroid hormones will not help you lose weight if your thyroid hormone levels are normal. If you increase the dose without being specifically indicated by your doctor, you may experience serious side effects or even put your life in danger, especially in combination with certain weight loss products (see section 2 "Other medicines and levotiroxina").
If you need to change your medicine to another one that contains levotiroxina, a thyroid imbalance may occur. Talk to your doctor if you have any doubts about changing your medicine. During the transition period, close monitoring (clinical and biological) is required. You should tell your doctor if you experience any side effects, as this may indicate that your dose needs to be adjusted by increasing or decreasing it.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking levotiroxina,
- if you have had an underactive thyroid gland since birth or acquired in childhood;
- if you have heart problems such as angina pectoris, coronary artery disease, weak heart muscle, heart rhythm disorders, or high blood pressure or arteriosclerosis;
- if you have recently had a heart attack;
- if you are being treated with certain anticoagulants (blood-thinning medicines) (e.g. phenprocoumon). You may need to change the dose of this medicine (see section 2. "Other medicines and levotiroxina");
- if you have diabetes, as you may need to adjust the dose of your antidiabetic treatment, as levotiroxina may increase blood sugar levels (see section 2. "Other medicines and levotiroxina");
- in postmenopausal women. Thyroid function should be monitored more frequently to avoid an increase in levotiroxina levels in the blood, which can cause osteoporosis (brittle bones);
- if you have epilepsy (seizures). Rarely, seizures have been reported when starting treatment with levotiroxina or rapidly increasing the dose;
- if you have myxedema (swelling of the skin and subcutaneous tissue), as the dose of levotiroxina may need to be reduced;
- if you have intestinal disease, as it may also inhibit the absorption of the medicine (malabsorption syndromes, e.g. celiac disease, lactose intolerance), and you may need treatment to ensure that your treatment with levotiroxina works well;
- if you have an underactive adrenal gland (adrenal insufficiency), a pituitary gland dysfunction, or a thyroid gland dysfunction with uncontrolled overproduction of thyroid hormones, as this should be medically controlled before starting to take levotiroxina.
- If you are going to have laboratory tests to check your thyroid hormone levels, you should inform your doctor or the laboratory staff that you are taking or have recently taken biotin (also known as vitamin H, vitamin B7, or vitamin B8). Biotin can affect the results of laboratory tests. Depending on the test, the results may be falsely elevated or falsely reduced due to biotin. Your doctor may advise you to stop taking biotin before having the tests. You should also be aware that other products you may be taking, such as multivitamin preparations or supplements for hair, skin, and nails, may also contain biotin. This could affect the results of laboratory tests. Inform your doctor or the laboratory staff if you are taking these products (see the information in the section "Other medicines and levotiroxina").
Contact your doctor if you experience signs of psychotic disorders.
Blood pressure will be monitored periodically when starting treatment with levotiroxina in premature newborns with very low birth weight, as a rapid drop in blood pressure (known as circulatory collapse) may occur.
In the elderly, the dose should be carefully and individually adjusted, for example, for those with heart problems, and they should be supervised by their doctor.
Blood testsBefore starting to take levotiroxina, your doctor will perform a blood test to determine how much thyroxine your thyroid gland is producing and what dose of medicine you will need. Once you start taking the medicine, your doctor will want you to have regular blood tests to see if the medicine is working correctly.
Other medicines andlevotiroxina
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. This includes medicines that you buy without a prescription, herbal remedies, and vitamin supplements. Many medicines affect the way levotiroxina works. The effects of other medicines may also be affected by levotiroxina.
If you are about to have a test with iodine-based contrast agents, you should inform your doctor that you are taking levotiroxina.
If you are taking or have recently taken biotin, you should inform your doctor or the laboratory staff when they are going to perform laboratory tests to check your thyroid hormone levels. Biotin can affect the results of laboratory tests (see "Warnings and precautions").
The following medicines may affect how levotiroxina works:
- medicines to treat epilepsy or seizures, such as carbamazepine, phenytoin, primidone, and barbiturics,
- products containing St. John's Wort (a herbal medicine),
- sertraline, lithium: to treat depression, mood, and anxiety disorders,
- statins such as simvastatin and lovastatin (used to treat high cholesterol),
- rifampicin, to treat infections,
- 5-fluorouracil, imatinib, and sunitinib (used for anticancer treatment),
- beta-blocker medicines such as propranolol, atenolol, and sotalol, used to treat high blood pressure and heart problems,
- medicines containing estrogens for hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and contraception ("the pill"),
- medicines containing androgens for male hormone replacement therapy,
- glucocorticoids, such as cortisone, hydrocortisone, prednisolone, and dexamethasone, used to treat inflammation,
- amiodarone: to treat irregular heartbeats,
- anti-inflammatory medicines, such as phenylbutazone or acetylsalicylic acid,
- methadone, used for opioid substitution treatment,
- furosemide: to treat high blood pressure or edema,
- propylthiouracil, used to treat overactive thyroid gland,
- iodide (used to protect the thyroid gland from radiation),
- oral contrast agents - taken before certain examinations to make parts of the body visible in the scan,
- chloroquine, proguanil, used for malaria prophylaxis and rheumatic diseases
- ritonavir, used to control HIV and chronic hepatitis C virus,
- weight loss medicines (e.g. orlistat),
- proton pump inhibitors (such as omeprazol, esomeprazol, pantoprazol, rabeprazol, and lansoprazol) are used to reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach, which may reduce the intestinal absorption of levotiroxina and make it less effective. If you are taking levotiroxina at the same time as receiving a proton pump inhibitor, your doctor should monitor your thyroid function and may need to adjust the dose of levotiroxina.
Levotiroxina should be taken at least 4-5 hours before taking the following medicines:
- calcium, magnesium, aluminum, iron, or lanthanum supplements;
- cholestyramine, colestipol, or clofibrate (used to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood);
- sodium polystyrene sulfonate (used to treat kidney disease);
- orlistat (weight loss medicines);
- cimetidine (used to reduce excess stomach acid);
- proton pump inhibitors, such as omeprazol, esomeprazol, used to treat excess stomach acid;
- sucralfate, antacids (to treat stomach ulcers);
The following medicines may be affected by levotiroxina:
- anticoagulant medicines to prevent blood clot formation, such as warfarin, dicumarol, and phenprocoumon;
- medicines to treat diabetes, such as insulin and metformin;
- tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, imipramine, and dosulepin;
- medicines that stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, such as adrenaline (used to treat severe allergic reactions) or phenylephrine (a decongestant found in many cold and flu treatments);
- digoxin, to treat heart problems;
- phenytoin, an antiepileptic medicine.
Takinglevotiroxinawith food and drink
Products containing soy and foods with high fiber content may affect the absorption of levotiroxina. As a result, your doctor may need to adjust the dose of levotiroxina.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
Uniform treatment with thyroid hormones is especially important during pregnancy and breastfeeding and should continue under the supervision of the treating physician.
The need for levotiroxina may increase during pregnancy due to the increase in blood levels of estrogen (female sex hormone). Therefore, thyroid function should be monitored during and after pregnancy, and the dose of levotiroxina should be adjusted as necessary.
Even during treatment with high doses of levotiroxina, the amount of thyroid hormone that passes into breast milk during breastfeeding is very low and, therefore, harmless.
Suppression tests should not be performed during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Levotiroxina Aristo is not expected to have any influence on the ability to drive and use machines, as levotiroxina is identical to the natural thyroid hormone.
Levotiroxina Aristo contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 23 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per tablet; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to Take Levotiroxina Aristo
Follow the administration instructions for this medication exactly as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Special attention should be paid when starting treatment with thyroid hormones in older patients, patients with coronary heart disease, and patients with chronic or severe hypothyroidism. This means that a lower initial dose should be selected, which is then increased slowly and at longer intervals, with frequent monitoring of thyroid hormones.
Experience has shown that a lower dose is also sufficient in patients with low body weight and in patients with extensive nodular goiter.
Dose
For individual treatment, tablets are available with graduated levels ranging from 25 to 200 micrograms of levotiroxine, which means that in most cases only one tablet per day is necessary.
Your doctor will determine your individual dose based on exams and laboratory tests. In general, a low dose is started, which is increased every 2 to 4 weeks, until the complete individual dose is reached. During the first weeks of treatment, you will have an appointment for laboratory tests to adjust the dose.
Use of Levotiroxina Aristo | Recommended daily dose of Levotiroxina Aristo | |
to replace natural thyroid hormones when your thyroid gland or your child's does not produce enough
| adults 25–50 micrograms 100–200 micrograms | children 12.5–50 micrograms 100–150 micrograms per m2 of body surface |
to replace natural thyroid hormones when your baby's thyroid gland does not produce enough initial dose during the first 3 months maintenance dose | Newborns and babies 10–15 micrograms per kg individual dose as recommended by the doctor | |
to prevent the recurrence of goiter after surgery | 75–200 micrograms | |
to treat benign goiter in patients with normal thyroid function | 75–200 micrograms | |
to suppress tumor growth in patients with thyroid cancer | 150–300 micrograms | |
to balance thyroid hormone levels when overproduction of hormones is treated with antithyroid medications | 50–100 micrograms |
Method of administrationThe total daily dose is taken in the morning on an empty stomach, at least half an hour before breakfast, since the active ingredient is better absorbed with an empty stomach than before or after a meal. The tablets are swallowed whole without chewing, with a glass of water.
The daily dose should be given to infants at least half an hour before the first meal of the day. For this, it is allowed to dissolve the tablet in a little water. If necessary, the tablet can be divided. It is not recommended to crush or dissolve it in water or other liquids, as the dose may not be exact.
Levotiroxina can be divided into equal doses.
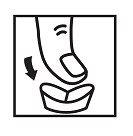
Divisibility notice. Place the tablet with the notch facing up on a flat and hard surface. To divide it, push with your thumb straight in the center of the tablet. |
|
Duration of administration
You should take this medication for the time indicated by your doctor.
If you have an underactive thyroid gland or have undergone thyroid surgery for a malignant thyroid tumor, you will normally take levotiroxine for life.
For benign goiter and to prevent the recurrence of goiter, you should take levotiroxine for a variable period of time, from several months or years to a lifetime.
In additional therapy for the treatment of hyperactive thyroid, you should take levotiroxine while taking a thyrostatic medication.
For the treatment of benign goiter with normal thyroid function, a treatment period of 6 months to 2 years is necessary. If treatment with levotiroxine has not produced the desired result within this period, other treatment options should be considered.
If you take morelevotiroxinathan you should
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount ingested.
The signs of an overdose may include: agitation, confusion, irritability, fever, chest pain (angina), rapid or irregular heartbeat, rapid breathing, muscle cramps, headache, restlessness, hyperactivity, hot flashes, sweating, dilated pupils, diarrhea, tremors, difficulty sleeping, anxiety or nervousness, fatigue or emotions, convulsions. These symptoms may take up to 6 days to appear. Bring all remaining tablets and this prospectus so that medical personnel know exactly what you have taken.
If you forget to takelevotiroxina
If you forget a dose, take the usual dose when your next dose is due. Do not take a double dose to make up for missed individual doses. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
If you interrupt treatment withlevotiroxina
For your treatment to be successful, you must take levotiroxina regularly at the dose prescribed by your doctor. Under no circumstances should you change, suspend, or interrupt the prescribed treatment without consulting your doctor, as symptoms may recur.
If you have any other doubts about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medications, this medication can produce adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Stop taking the tablets and go to the hospital immediately if you have:
- an allergic reaction such as swelling of the eyelids, tongue, lips, and/or throat and/or difficulty swallowing or hives with difficulty breathing (angioedema), exanthema or itching (especially if it affects the whole body), joint pain, sensitivity to the sun, general feeling of discomfort (frequency unknown). You may need urgent medical attention.
Some patients may experience a severe adverse reaction to high levels of thyroid hormone. This is called "thyroid crisis". Stop taking the tablets and go to the hospital if you have any of the following symptoms (frequency unknown):
- Very high temperature, rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), irregular heartbeats, low blood pressure, heart failure, jaundice, confusion, seizures, and coma.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if any of the following adverse effects continue, worsen, or if you notice other adverse effects that do not appear in the list.
Most adverse effects are similar to those of an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroxine), especially if the dose is increased too quickly at the start of treatment. They usually disappear when the dose is reduced or treatment is interrupted. Inform your doctor if side effects occur. He/she will decide if the daily dose should be reduced or if the tablets should be stopped for a few days. However, do not change the dose or stop taking the tablets without consulting your doctor first.
Unknown frequency: the frequency cannot be estimated from the available data.
- Increased appetite;
- restlessness, excitability, difficulty sleeping (insomnia);
- agitation (tremor), headache, seizures;
- chest pain (angina pectoris), palpitations, irregular heartbeats, palpitations (very strong heartbeats), heart failure, heart attack;
- hypertension, flushing;
- difficulty breathing (dyspnea);
- diarrhea, vomiting, discomfort, stomach pain;
- increased sweating, itching, skin rash, urticaria;
- muscle cramps, muscle weakness, joint pain;
- decrease in bone density (osteoporosis), particularly in postmenopausal women taking high doses for prolonged periods;
- in women: irregular periods;
- fever (high temperature), swelling (edema), general feeling of discomfort;
- weight loss;
- overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism);
Additional side effects in children
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- increased intracranial pressure in children not caused by a tumor or other diseases (benign intracranial hypertension).
Unknown frequency: the frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- premature interruption of child growth due to changes in bone growth;
- mild hair loss in children;
- skull deformity in babies caused by early closure of the joints in the skull bone (craniosynostosis);
- heat intolerance.
In case of hypersensitivity to levotiroxine or to any of the other components of Levotiroxina Aristo, allergic reactions may occur in the skin and respiratory tract.
Reporting of adverse effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Conservation of Levotiroxina Aristo
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date that appears on the box and on the blister after "CAD". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not store above 30 °C.
Medications should not be thrown down the drain or into the trash. Deposit the containers and medications you no longer need in the SIGRE Pointof the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the containers and medications you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
- The active ingredient is anhydrous levotiroxine sodium. Each tablet contains 137 micrograms of anhydrous levotiroxine sodium.
- The other components are microcrystalline cellulose, cornstarch, heavy magnesium oxide, sodium carboxymethylcornstarch (Type A), vegetable magnesium stearate.
Product Appearance and Package Contents
White, round, uncoated tablets, domed (pressure score) with a notch on one face and engraved with 137 on the other face. The tablets have an approximate diameter of 7 mm and an approximate height of 3 mm.
The tablets are presented in blisters in packages with 25, 30, 50, 60, 90, and 100 tablets.
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Aristo Pharma GmbH
Wallenroder Straße 8-10
13435 Berlin
Germany
Manufacturer
Aristo Pharma GmbH
Wallenroder Straße 8-10
13435 Berlin
Germany
You can request more information about this medication by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Aristo Pharma Iberia, S.L.
C/ Solana, 26
28850, Torrejón de Ardoz
Madrid, Spain
This medication is authorized in the member states of the European Economic Area with the following names:
Austria Levothyroxin Aristo 137 Mikrogramm Tabletten
Czech Republic Levothyroxine Aristo 137 mikrogramu tablety
Germany L-Thyroxin Aristo 137 Mikrogramm Tabletten
Ireland Levothyroxine sodium Aristo 137 micrgram tablets
Italy Levotiroxina Aristo 137 mikrogrammi compresse
Netherlands Levothyroxinenatrium Aristo 137 microgram tabletten
Poland Eferox 137 mikrogramów tabletki
Portugal Levotiroxina Aristo 137 microgramas comprimidos
Spain Levotiroxina Aristo 137 microgramos comprimidos
Sweden Levothyroxine Aristo 137 mikrogram tabletter
Date of the last revision of this prospectus: December 2023
Other sources of information
Detailed information about this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to LEVOTHYROXINE ARISTO 137 MICROGRAMS TABLETSDosage form: TABLET, 100 mcg sodium levothyroxineActive substance: levothyroxine sodiumManufacturer: Merck S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 112 mcg sodium levothyroxineActive substance: levothyroxine sodiumManufacturer: Merck S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 125 mcg levothyroxine sodiumActive substance: levothyroxine sodiumManufacturer: Merck S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for LEVOTHYROXINE ARISTO 137 MICROGRAMS TABLETS
Discuss questions about LEVOTHYROXINE ARISTO 137 MICROGRAMS TABLETS, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions