
KINERET 100 mg/0.67 ml injectable solution in pre-filled syringe

How to use KINERET 100 mg/0.67 ml injectable solution in pre-filled syringe
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Kineret100mg/0.67ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
anakinra
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Kineret and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Kineret
- How to use Kineret
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Kineret
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Kineret and what is it used for
Kineret contains the active substance anakinra. It is a type of cytokine (an immunosuppressive agent) used to treat:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- COVID-19 in patients who have pneumonia, require supplemental oxygen, and are at risk of pulmonary failure
- Periodic fever syndromes:
- Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS)
- Neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID)/chronic infantile neurological cutaneous and articular syndrome (CINCA)
- Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS)
- Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome (FCAS)
- Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)
- Still's disease, including systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD)
Cytokines are proteins produced by our body that coordinate communication between cells and help control cellular activity. In RA, CAPS, FMF, Still's disease, and COVID-19 pneumonia, the body produces an excessive amount of a cytokine called interleukin-1. This leads to harmful effects that cause inflammation and the symptoms of the disease. Normally, the body produces a protein that blocks the harmful effects of interleukin-1. The active substance in Kineret, anakinra, acts similarly to the natural protein that blocks interleukin-1. Anakinra is obtained through recombinant DNA technology using the microorganism E.coli.
In RA, Kineret is used to treat the signs and symptoms of the disease in adults (from 18 years of age) in combination with another medicine called methotrexate. Kineret is intended for patients whose response to methotrexate alone is not sufficient to control rheumatoid arthritis.
In COVID-19, Kineret is used to treat hyperinflammation (more severe than usual inflammation) associated with the disease in adults (from 18 years of age) who have pneumonia, require supplemental oxygen to help them breathe (low or high flow oxygen), and are at risk of pulmonary failure.
In CAPS, Kineret is used to treat the signs and symptoms of inflammation associated with this disease, such as rash, joint pain, fever, headache, and fatigue, in both adults and children (from 8 months of age).
In FMF, Kineret is used to treat the signs and symptoms of inflammation associated with this disease, such as recurrent fever, fatigue, abdominal pain, muscle or joint pain, and rash. Kineret may be used along with colchicine when appropriate.
In Still's disease, Kineret is used to treat the signs and symptoms of inflammation associated with this disease, such as rash, joint pain, and fever.
2. What you need to know before you use Kineret
Do not use Kineret
- if you are allergic to anakinra or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you are allergic to other products produced by recombinant DNA technology that use the microorganism E.coli
- if you have neutropenia (low white blood cell count) as determined by a blood test.
Contact your doctor immediately
- if you experience a rash all over your body, shortness of breath, wheezing, rapid heartbeat, or sweating after injecting Kineret. These may be symptoms of an allergic reaction to Kineret.
- if you have ever experienced a generalized rash or skin peeling after taking Kineret.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor before starting to use Kineret:
- if you have a history of recurrent infections or if you have asthma, as Kineret may worsen these conditions
- if you have cancer. Your doctor will need to decide if you can receive Kineret
- if you have a history of elevated liver enzyme levels
- if you need to be vaccinated. You should not receive live vaccines while being treated with Kineret.
Still's disease
- Rarely, patients with Still's disease, especially children, may develop pulmonary disease, also during treatment with Kineret. The risk may be increased in patients with Down syndrome (trisomy 21). Symptoms of pulmonary disease may include shortness of breath during light exercise, morning cough, and difficulty breathing. If you develop signs of pulmonary disease, contact your doctor as soon as possible.
- A rare but serious skin reaction, DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms), has been reported in association with Kineret treatment, especially in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). Seek medical attention immediately if you observe an atypical generalized rash, which may occur along with high fever and swollen lymph nodes.
CAPS
- A few cases of systemic amyloidosis (a condition in which abnormal proteins accumulate in tissues and organs) have been reported in patients with NOMID/CINCA, who initially presented with lumps under the skin at the injection sites (amyloid deposits). These patients had been using anakinra at high doses for several years. Symptoms of systemic amyloidosis may include swelling (especially in the legs and ankles), foamy urine, increased or decreased frequency of urination, muscle cramps, unexplained weight loss, diarrhea or constipation, and fatigue. Inform your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms.
Children and adolescents
- RA: The use of Kineret in children and adolescents with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has not been extensively investigated and, therefore, cannot be recommended.
- COVID-19: The use of Kineret in children and adolescents with COVID-19 has not been investigated and, therefore, cannot be recommended.
- CAPS, FMF, Still's disease: The use of Kineret is not recommended in children under 8 months of age, as there are no data available for this age group.
Other medicines and Kineret
Tell your doctor if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Medicines called tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) inhibitors, such as etanercept, must not be used with Kineret, as this may increase the risk of infections.
When you start using Kineret, the chronic inflammation in your body will decrease. This may require adjustments to the doses of other medicines, such as warfarin or phenytoin.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before using this medicine.
Kineret has not been tested in pregnant women. The use of Kineret during pregnancy is not recommended, nor in women of childbearing potential who are not using a contraceptive method. It is important that you inform your doctor if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby. Your doctor will discuss the possible risks of taking Kineret during pregnancy.
It is not known whether anakinra is excreted in breast milk. Breastfeeding should be discontinued if you are using Kineret.
Kineret contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per 100 mg dose; it is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Kineret
Follow exactly the instructions for administration of this medicine given by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again. Kineret is injected under the skin (subcutaneous injection) daily. Try to inject yourself at the same time every day.
The recommended dose is 20 to 90 mg or 100 mg. Your doctor will tell you which dose you need or if you need a dose greater than 100 mg.
COVID-19: The recommended dose is 100 mg injected under the skin (subcutaneously) daily for 10 days.
Self-administration of Kineret
Your doctor may decide that it is more convenient for you to inject Kineret yourself. Your doctor or nurse will teach you how to do this. Do not attempt to inject yourself if you have not been instructed on how to do so.
For information on how to prepare and administer a Kineret injection yourself or to your child, please read the section "Instructions for preparing and administering a Kineret injection" included at the end of this leaflet.
If you use more Kineret than you should
You should not have any serious problems if you accidentally use more Kineret than you need. However, you should contact your doctor or pharmacist if this happens. If you do not feel well, you should contact your doctor immediately.
If you forget to use Kineret
If you forget to inject a dose of Kineret, you should contact your doctor to discuss when you should inject the next dose.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The possible side effects are similar whether Kineret is used for RA or for CAPS, FMF, Still's disease, or COVID-19.
If you experience any of the following side effects, tell your doctor immediately:
- Severe infectionssuch as pneumonia (chest infection) or skin infections may occur during treatment with Kineret. Symptoms may include persistent high fever, chills, cough, headache, and redness and pain in the skin. Other possible signs of infection are low-grade fever, weight loss, and persistent cough.
- Severe allergic reactionsare rare. However, any of the following symptoms may indicate an allergic reaction to Kineret for which you should seek immediate medical attention. Do not inject more Kineret:
- Swelling of the face, tongue, or throat
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Sudden rapid heartbeat or sweating
- Itching of the skin or rash
Very common side effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Redness, swelling, bruising, or itching at the injection site. These symptoms are usually mild to moderate and more frequent at the start of treatment.
- Headache.
- Increased total cholesterol levels in the blood.
Common side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Neutropenia (low white blood cell count) as determined by a blood test. Neutropenia may increase the risk of you getting an infection. Symptoms of an infection may include fever or sore throat.
- Severe infections such as pneumonia (chest infection) or skin infections.
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count in the blood).
Uncommon side effects(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Severe allergic reactions including swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, difficulty swallowing or breathing, sudden rapid heartbeat or sweating, itching of the skin or rash.
- Elevated liver enzyme levels detected by a blood test.
Side effects of unknown frequency(cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Signs of liver disorders, such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, nausea, loss of appetite, dark-colored urine, and pale-colored stools.
- If you inject Kineret repeatedly in the same spot, there is a risk of a lump (amyloid deposit) forming under the skin. Rotate the injection site to avoid this.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Kineret
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after "EXP". The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C). Do not freeze.
Keep the pre-filled syringe in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Do not use Kineret if you think it has been frozen. Once a pre-filled syringe has been removed from the refrigerator and reaches room temperature (up to 25°C), it must be used within 72 hours or discarded. Do not store it in the refrigerator again if it has been stored at room temperature.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Kineret Composition
- The active ingredient is anakinra. Each pre-filled syringe contains 100 mg of anakinra.
- The other ingredients (excipients) are: anhydrous citric acid, sodium chloride, disodium edetate dihydrate, polysorbate 80, sodium hydroxide, and water for injectable preparations.
Product Appearance and Container Contents
Kineret is a clear, colorless to white solution presented in a pre-filled syringe ready for use. The solution may contain protein particles with a translucent to white appearance, whose presence does not affect the quality of the product.
Container sizes of 1, 7, or 28 (multiple container with 4 packs of 7 pre-filled syringes) pre-filled syringes.
Not all container sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB (publ)
SE-112 76 Stockholm
Sweden
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: 11/2024
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND ADMINISTERING A KINERET INJECTION
This section contains information on how to inject Kineret yourself or inject it into your child. It is important that you do not attempt to administer the injection yourself or administer it to your child if you have not been instructed on how to do so by a doctor, nurse, or pharmacist. If you have any doubts about how to administer the injection, consult your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.
How should you or the person administering the injection use the Kineret pre-filled syringe?
You will need to administer an injection to yourself or your child every day at the same time. Kineret is injected under the skin. This is known as a subcutaneous injection.
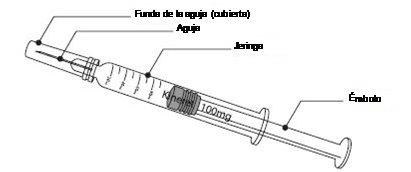
Materials:
To administer a subcutaneous injection to yourself or your child, you will need:
- a Kineret pre-filled syringe;
- an alcohol swab or similar, and
- a sterile gauze or pad
What should you do before administering the subcutaneous injection of Kineret?
- Remove the Kineret pre-filled syringe from the refrigerator.
- Do not shake the pre-filled syringe.
- Check the expiration date on the pre-filled syringe label (EXP). Do not use it if the current date has exceeded the last day of the indicated month.
- Check the appearance of Kineret. It should be a clear, colorless to white solution. The solution may contain protein particles with a translucent to white appearance, whose presence does not affect the quality of the product. Do not use this medication if it has a different color, is cloudy, or the particles present are not translucent to white.
- For more comfortable administration, leave the pre-filled syringe at room temperature for approximately 30 minutes or carefully hold it in your closed hand for a few minutes. Do not heat Kineret in any other way (e.g., do not put it in the microwave or hot water).
- Do not remove the syringe cap until you are ready for injection.
- Wash your hands carefully.
- Find a comfortable, clean, and well-lit surface and place all the materials you need within reach.
- Make sure you know the dose of Kineret prescribed by your doctor; 20 to 90 mg, 100 mg, or more than 100 mg.
- If your doctor has prescribed a dose of 100 mg, go to the section "How to prepare a 100mg dose?"
- If your doctor has prescribed a dose less than 100 mg, go to the section "How to prepare a dose of20to 90mg?"
How to prepare a 100mg dose?
Before injecting Kineret, do the following:
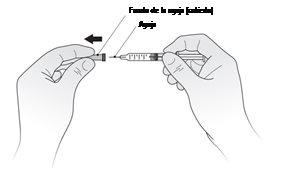
- Hold the syringe and gently remove the needle cap without twisting, as shown in Figure A. Do not touch the needle or push the plunger. Immediately discard the needle cap.
- There may be a small air bubble in the pre-filled syringe. It is not necessary to remove it before injection. Injecting the solution with an air bubble is not harmful.
- You can now use the pre-filled syringe as described in the section "Where should you administer the injection?" and in the section "How to administer the injection?"
 How to prepare a dose of 20 to 90mg?
How to prepare a dose of 20 to 90mg?
Before injecting Kineret, do the following:
- Hold the syringe and gently remove the needle cap without twisting, as shown in FigureA. Do not touch the needle or push the plunger. Immediately discard the needle cap.
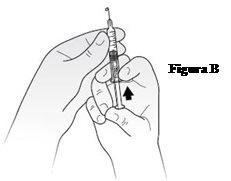
 Place the syringe in one hand, with the needle pointing upwards, as shown in FigureB. Place your thumb on the plunger and gently push until you see a small drop of liquid appear at the tip of the needle.
Place the syringe in one hand, with the needle pointing upwards, as shown in FigureB. Place your thumb on the plunger and gently push until you see a small drop of liquid appear at the tip of the needle.
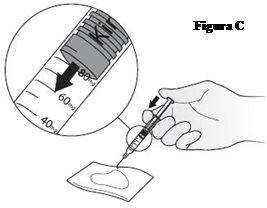
- Turn the syringe so that the needle points downwards. Place a sterile gauze or pad on a flat surface and hold the syringe above it, with the needle pointing towards the gauze or pad, as shown in FigureC. Do not let the needle touch the gauze or pad.
- Place your thumb on the plunger and slowly press until the front of the plunger reaches the mark on the scale corresponding to your Kineret dose (your doctor will have told you what dose you need). The liquid that comes out will be absorbed by the gauze or pad, as shown in FigureC.
- If you are unable to obtain the correct dose, discard the syringe and use a new one.
- You can now use the pre-filled syringe as described in the section "Where should you administer the injection?" and in the section "How to administer the injection?"
Where should you administer the injection?
The most suitable places to administer the injection to yourself or your child are (see FigureD):
- the abdomen (except the area around the navel)
- the upper part of the thighs
- the upper outer part of the buttocks
- the upper outer part of the arms
AdultChild
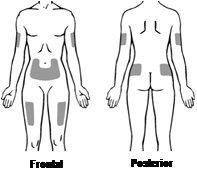
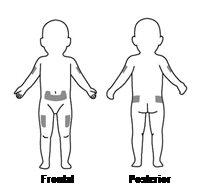
Change the injection site from time to time so that you do not have discomfort in any area. If someone else is administering the injection, it can also be given in the back of the arms.
How to administer the injection?
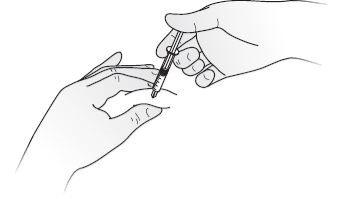
- Disinfect the skin using an alcohol swab and pinch the skin between your thumb and index finger, without squeezing.
- Insert the needle completely into the skin as your nurse or doctor has shown you.
- Inject the liquid slowly and regularly, keeping the skin pinched, as shown in Figure E.
- After injecting the solution, remove the needle and release the skin.
- Any unused medication should be discarded. Each syringe should only be used for one injection. Do not reuse syringes, as this can cause infection.
Remember
If you have difficulty, ask for help and advice from your doctor or nurse.
How to dispose of used syringes and additional materials
- Do not put the cap back on used needles.
- Keep used syringes out of the reach and sight of children.
- Never throw away used pre-filled syringes in your household trash.
- If your dose is less than 100 mg, you will need to pour the excess liquid from the syringe onto a gauze or pad. After injection, discard the wet gauze or pad along with the syringe and clean the surface with a clean cloth.
- Pre-filled syringes, as well as gauze or pads impregnated with Kineret solution, should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of unused medications. This will help protect the environment.
ANNEX IV
SCIENTIFIC CONCLUSIONS AND GROUNDS FOR AMENDMENT OF THE TERMS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORIZATION
Scientific Conclusions
Taking into account the provisions of the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) Assessment Report on the periodic safety update reports (PSURs) for anakinra, the scientific conclusions of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) are as follows:
In light of the available data on the risk of SAM in patients with Still's disease from clinical trials, literature, and observational studies, the PRAC considers that the available data do not support a causal association between the risk of SAM and anakinra. The PRAC concluded that the product information for anakinra-containing products should be amended accordingly.
The CHMP agrees with the PRAC's scientific conclusions.
Grounds for Amendment of the Marketing Authorization
In accordance with the scientific conclusions for anakinra, the CHMP considers that the benefit-risk balance of the medicinal product(s) containing anakinra is not affected by the proposed changes to the product information.
The CHMP recommends that the marketing authorization be amended.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to KINERET 100 mg/0.67 ml injectable solution in pre-filled syringeDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 130 mgActive substance: ustekinumabManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 45 mgActive substance: ustekinumabManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 90 mgActive substance: ustekinumabManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for KINERET 100 mg/0.67 ml injectable solution in pre-filled syringe
Discuss questions about KINERET 100 mg/0.67 ml injectable solution in pre-filled syringe, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






