JETREA 0.375mg/0.3ml Injectable Solution

How to use JETREA 0.375mg/0.3ml Injectable Solution
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
JETREA 0.375 mg/0.3 ml Solution for Injection
Ocriplasmin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, even if you think they might be unrelated to this medicine. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Jetrea and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you are given Jetrea
- How Jetrea is given
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Jetrea
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Jetrea and what is it used for
Jetrea contains the active substance ocriplasmin.
Jetrea is used to treat adults with a condition in the eye called vitreomacular traction (VMT), including cases where a small hole in the macula (the center of the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye) is present.
VMT is caused by traction resulting from the persistent adhesion of the vitreous gel (the gel-like substance at the back of the eye) to the macula. The macula is responsible for central vision, which is necessary for everyday tasks such as driving, reading, and recognizing faces. VMT can cause symptoms including distorted or decreased vision. As the disease progresses, there is a risk that the traction may eventually cause the formation of a hole in the macula (called a macular hole).
Jetrea works by separating the vitreous gel from the macula and promoting the closure of the macular hole, if present, which may reduce the symptoms caused by VMT.
2. What you need to know before you are given Jetrea
Jetrea must not be given in the following cases
- if you are allergic to ocriplasmin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if you have (or suspect you may have) an infection in the eye or the surrounding area.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or eye specialist before you are given Jetrea.
This medicine is given by injection into the eye. Your doctor or eye specialist will monitor you in case you get an infection or any other complication after the injection. If you experience any of the eye symptoms described in section 4 after the injection, contact your doctor or eye specialist immediately.
Jetrea will not be given in both eyes at the same time.
Jetrea will not be given more than once in the same eye.
Tell your doctor or eye specialist if you have or have had any other eye disorder or if you are or have been under treatment for your eyes. Your doctor or eye specialist will decide if treatment with Jetrea is suitable for you.
Children and adolescents
There is no recommendation for the use of Jetrea in children and adolescents under 18 years. Therefore, the use of Jetrea is not recommended in this patient group.
Using Jetrea with other medicines
Tell your doctor or eye specialist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. Inform your doctor or eye specialist if you have been injected with any other medicine in the same eye recently, as this information will be taken into account when assessing whether you can be injected with Jetrea in that eye and when.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
There are no data on the use of Jetrea in pregnant or breastfeeding women, therefore this medicine should not be used during these conditions unless your doctor or eye specialist considers it absolutely necessary. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or eye specialist before you are given this medicine.
Driving and using machines
After treatment with Jetrea, you may experience a decrease in vision for a short period of time. If this happens, do not drive or use tools or machines until your vision improves.
3. How Jetrea is given
Jetrea must be given by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) who is qualified and experienced in giving injections into the eye.
Jetrea is given as a single injection into the affected eye. The recommended dose is 0.125 mg.
Your doctor or eye specialist may advise you to use antibiotic eye drops before and after the injection to prevent any possible infection in the eye.
On the day of the injection, your doctor or eye specialist will put antibiotic drops in your eye and clean your eye and eyelid thoroughly to prevent infection, and will also give you local anesthesia so that the injection does not hurt.
After the injection, your doctor or eye specialist will monitor your vision.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or eye specialist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you experience any of the following symptomsafter receiving the Jetrea injection, contact your doctor or eye specialist immediatelyso that they can monitor you and take corrective action if necessary.
- Up to 1 in 10 patients have reported a severedecrease in vision within one week after treatment with Jetrea. This decrease in vision is usually reversible and resolves without treatment.
- Symptoms such as eye pain, increasing redness of the eyes, considerablyblurred or decreased vision, increasedsensitivity to light, or increasednumber of dark floating spots in the field of vision (floaters) have also been observed in up to 1 in 10 patients and may be signs of infection, bleeding, retinal detachment, or increased pressure inside the treated eye.
- Symptoms such as fluctuating vision, double vision, headache, seeing halos around lights, nausea, and vomiting, which may be signs of a shift or oscillation in the normal position of the lens in the eye, have been reported in up to 1 in 100 patients.
Tell your doctor or eye specialistif you experience any of the following additional side effects:
Very common side effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- dark floating spots in the field of vision (floaters)
- eye pain
- bleeding on the surface of the eye
- changes in color perception
Common side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- decreased vision that can be severe
- visual disturbances
- decreased vision or blind spots in parts of the field of vision
- blurred vision
- bleeding inside the eye
- blind spot or missing area in the center of the field of vision
- distorted vision
- swelling of the surface of the eye
- swelling of the eyelid
- eye inflammation
- flashes of light in the eye
- redness of the eye
- irritation of the surface of the eye
- dry eye
- feeling of having something in the eye
- itching of the eye
- eye discomfort
- sensitivity to light
- increased production of tears
Uncommon side effects(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- temporary severe decrease in vision
- difficulty seeing well at night or in low light
- abnormal reaction of the eye to light, which may increase sensitivity to light (altered pupillary reflex)
- double vision
- accumulation of blood in the front part of the eye
- abnormal constriction of the pupil (the black area in the center of the eye)
- pupils of different sizes
- a scratch or abrasion of the cornea (the transparent layer covering the front of the eye)
It has been seen that after administration of Jetrea, some tests and images of the back of the eye (retina) are abnormal. Your doctor is aware of this and will take it into account when monitoring your eye.
Some effects (such as flashes, floaters) may also be perceived in the untreated eye in some cases.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or eye specialist, even if you think they might be unrelated to this medicine. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Annex V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Jetrea
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Information on the storage and use of Jetrea after thawing is described in the section intended only for healthcare professionals.
Your doctor/eye specialist or pharmacist is responsible for the storage of this medicine and for the disposal of any unused solution.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Jetrea
- The active substance is ocriplasmin. One vial of Jetrea contains 0.375 mg of ocriplasmin in 0.3 ml of solution.
- The other ingredients are sodium chloride (NaCl), mannitol, citric acid, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (for pH adjustment), hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), and water for injections.
Appearance and pack contents
Jetrea is a solution for injection that comes in a vial. The solution is clear and colorless.
Each pack contains one vial.
Marketing authorisation holder
Inceptua AB
Gustavslundsv. 143
16751 Bromma
Sweden
Manufacturer
Oxurion NV
Gaston Geenslaan 1
B-3001 Leuven
Belgium
Date of last revision of this leaflet
Other sources of information
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Jetrea must be given by an eye specialist who is qualified and experienced in giving injections into the eye. The diagnosis of vitreomacular traction (VMT) should be made considering a complete clinical picture including patient history, clinical examination, and investigation using currently recognized diagnostic tests, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT).
JETREA 0.375 mg/0.3 ml Solution for Injection is a "ready-to-inject" formulation that does not require further dilution. The recommended dose is 0.125 mg in 0.1 ml of the solution given as a single injection into the affected eye. Each vial should only be used once and for the treatment of one eye. It is not recommended to treat the other eye at the same time or within 7 days after the initial injection in order to monitor the evolution after the injection, including the potential for decreased vision in the injected eye. Repeated administration in the same eye is not recommended.
See section 4.4 of the Summary of Product Characteristics for instructions on follow-up after the injection.
Single-use vial only for intravitreal use.
Antibiotic eye drops may be given before the procedure at the discretion of the eye specialist.
The intravitreal injection procedure should be carried out under controlled aseptic conditions, which include surgical hand disinfection, use of sterile gloves, a sterile draping system, a sterile eyelid speculum (or equivalent), and the availability of a sterile paracentesis device (if needed). Before the injection, the periocular skin, eyelid, and ocular surface should be disinfected, and an adequate amount of topical anesthetic and broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent should be given according to standard medical practice.
Only 0.1 ml of the total 0.3 ml of the solution in the vial should be administered. Before the injection, any excess volume should be expelled to administer a single dose of 0.1 ml containing 0.125 mg of ocriplasmin.
The injection needle should be inserted 3.5 to 4.0 mm posterior to the limbus and directed towards the center of the vitreous cavity, avoiding the horizontal meridian. The 0.1 ml injection volume is then released into the mid-vitreous.
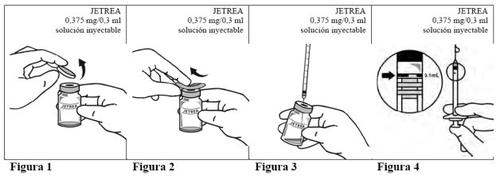
Instructions for use
- Remove the vial from the freezer and let it thaw at room temperature (this takes about 2 minutes).
- Once the product has thawed completely, remove the blue flip-off polypropylene protective cap from the vial (Figure 1).
- Disinfect the top of the vial with an alcohol swab (Figure 2).
- Visually inspect the vial for any particles. The solution should only be used if it is clear and colorless and free of visible particles.
- Using an aseptic technique, withdraw the entire contents of the vial with a suitable sterile needle (tilt the vial slightly to facilitate withdrawal) (Figure 3)and discard the needle after withdrawing the contents. This needle should not be used for the intravitreal injection.
- Replace the needle with a new sterile needle that is suitable for intravitreal injection, and carefully expel any excess volume from the syringe by gently pressing the plunger until the tip of the plunger is aligned with the 0.1 ml mark on the syringe (corresponding to 0.125 mg of ocriplasmin) (Figure 4).
- Inject immediately into the mid-vitreous 0.1 ml of the solution.
- Discard the vial and any unused solution after a single use.
The disposal of unused medicine and all materials that have come into contact with it should be done according to local regulations.
|
Storage information
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after EXP/CAD respectively. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
Store in a freezer (-20 °C ± 5 °C).
After thawing
The unopened vial, in its original carton and protected from light, may be stored in a refrigerator (between 2 °C and 8 °C) for up to 1 week. The new expiry date should be calculated and written on the carton before storing in the refrigerator.
Once removed from the freezer or refrigerator, the medicine can be stored below 25 °C for a maximum of 8 hours. At the end of this period, the medicine should be used or discarded.
Do not re-freeze the vial once it has been thawed.
After opening
From a microbiological point of view, the medicine should be used immediately after opening. The vial and any unused solution should be discarded after a single use.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to JETREA 0.375mg/0.3ml Injectable SolutionDosage form: EYEDROP, 5.5 mg sodium chloride; 3 mg hypromellose/mlActive substance: artificial tears and other indifferent preparationsManufacturer: Alcon Healthcare S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: EYEDROP, 3.2 mg/mlActive substance: artificial tears and other indifferent preparationsManufacturer: Bausch & Lomb S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: EYE DROP, 3.2 mg/mlActive substance: artificial tears and other indifferent preparationsManufacturer: Bausch & Lomb S.A.Prescription not required
Online doctors for JETREA 0.375mg/0.3ml Injectable Solution
Discuss questions about JETREA 0.375mg/0.3ml Injectable Solution, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions