
DARAPRIM 25 mg TABLETS


How to use DARAPRIM 25 mg TABLETS
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Daraprim 25 mg Tablets
Pyrimethamine
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again. If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Daraprim and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you take Daraprim
- How to take Daraprim
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Daraprim
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Daraprim and what is it used for
Daraprim contains pyrimethamine, which belongs to a group of medicines called antimalarials. It is indicated in adults and children for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria caused by sensitive strains of Plasmodium falciparum.
Daraprim in combination with a sulfonamide is indicated for the treatment of congenital and acquired toxoplasmosis.
Pyrimethamine should not be used as monotherapy in the treatment of malaria and toxoplasmosis.
2. What you need to know before you take Daraprim
Do not take Daraprim
- if you are allergic to the active substance or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine listed in section 6.
Warnings and precautions
- if you have a type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia or symptoms of malnutrition, as pyrimethamine may exacerbate the folate deficiency associated with this type of anemia. Accordingly, these individuals should receive a folinic acid supplement.
- if you have a history of seizures; in these patients, high initial doses of pyrimethamine should be avoided.
When pyrimethamine is administered with a sulfonamide, the general precautions applicable to sulfonamides should be taken into account. In any case, adequate fluid intake should be ensured to minimize the risk of crystalluria.
Use of Daraprim with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
In particular, pyrimethamine may alter the effect of the following medicines: antibiotics such as cotrimoxazole or trimethoprim, antimalarials such as proguanil, antivirals such as zidovudine, or cytostatic agents (such as methotrexate). Concomitant administration with a trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole combination may develop megaloblastic anemia.
Concomitant administration of lorazepam (benzodiazepine) and pyrimethamine may induce mild liver damage.
Cases of total or partial disappearance of the cells normally found in the bone marrow (fatal bone marrow aplasia) have been associated with the administration of the antibiotic daunorubicin and pyrimethamine to individuals suffering from a type of white blood cell cancer known as acute myeloid leukemia.
Anti-acid salts and the anti-diarrheal agent kaolin reduce the absorption of pyrimethamine.
Pyrimethamine may affect the efficacy or toxicity of drugs such as the antimalarial quinine or anticoagulants such as warfarin if administered concomitantly.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Daraprim is only recommended in combination therapy with sulfonamide during the second and third trimester of pregnancy. In the first trimester, alternative therapy is recommended.
Concomitant administration of calcium folinate is recommended if Daraprim is administered during pregnancy.
Pyrimethamine passes into breast milk, so its use is not recommended during breastfeeding, unless your doctor considers it necessary.
Driving and using machines
No effects on the ability to drive or use machines have been observed with Daraprim.
Daraprim 25 mg Tablets contain lactose and sodium
This medicine contains lactose. If your doctor has told you that you have an intolerance to some sugars, contact them before taking this medicine.
This medicine contains less than 23 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per tablet; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to take Daraprim
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medicine given by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Remember to take your medicine.
Your doctor will tell you if you should increase or reduce the dose of the medicine during the treatment period, as well as the duration of the treatment.
Daraprim is a tablet for oral administration. It should be taken in the morning or at night, with or without food. The tablets should be swallowed without chewing with the help of a little liquid (a glass of water).
All patients receiving pyrimethamine should receive a folinic acid supplement to reduce the risk of bone marrow affection.
Malaria treatment:
Daraprim should be administered in a single dose concomitantly with sulfadiazine and another antimalarial.
Adults:
A single dose of two to three Daraprim tablets (50 to 75 mg of pyrimethamine), together with 1,000 mg to 1,500 mg of sulfadiazine.
In general, a higher dose should be administered to adults weighing more than 60 kg.
Use in children:
Pyrimethamine can be used orally with sulfadoxine/sulfadiazine in children from 2 months of age.
The following dosage is recommended based on body weight:
- Children from 5 to 10 kg: 12.5 mg of pyrimethamine in a single dose.
- Children from 11 to 20 kg: 25 mg of pyrimethamine in a single dose.
- Children from 21 to 30 kg: 37.5 mg of pyrimethamine in a single dose.
- Children from 31 to 45 kg: 50 mg of pyrimethamine in a single dose.
- Children over 45 kg: use the same dose as for adults.
Use in elderly patients:
There is no information on the effect of Daraprim in elderly patients. At the recommended doses for malaria, it is unlikely that pyrimethamine will have adverse effects in elderly people.
Toxoplasmosis treatment
Daraprim should be administered concomitantly with sulfadiazine or clindamycin. The use of an alternative sulfonamide may require a dose adjustment.
Immunocompetent adults:
Pyrimethamine: An initial dose of four tablets (100 mg of pyrimethamine) followed by a dose of one to two tablets daily (25 to 50 mg per day of pyrimethamine).
Immunodeficient adults:
Daraprim should be administered concomitantly with sulfadiazine or clindamycin.
- < 60 kg: pyrimethamine 200 mg orally as a loading dose, continue with 50 mg per day.
- ≥ 60 kg: pyrimethamine 200 mg orally as a loading dose, followed by 75 mg per day.
Subsequently, the secondary prophylaxis regimen will be administered.
Use in children:
In the treatment of toxoplasmosis, the following dosage regimens are recommended:
- Children under 3 months (congenital toxoplasmosis): for the treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis, it is recommended that newborns receive pyrimethamine 2 mg/kg/day for 2 days; 1 mg/kg/day for 2-6 months, and then 1 mg/kg/day three times a week until completing 12 months of treatment.
- Children from 3 to 9 months: 6.25 mg daily of pyrimethamine together with sulfadiazine: 100 mg/kg body weight (maximum 1 g) per day in four divided doses.
- Children from 10 months to 2 years: 1 mg/kg body weight/day of pyrimethamine together with 150 mg/kg body weight of sulfadiazine (maximum 1.5 g) per day in four divided doses.
- Children from 3 to 6 years: a loading dose of pyrimethamine 2 mg/kg body weight (up to a maximum of 50 mg) followed by a dose of 1 mg/kg/day (maximum dose of 25 mg); together with 150 mg/kg body weight of sulfadiazine (maximum 2 g) per day in four divided doses.
- Children over 6 years: the same as for adults.
Use in immunodepressed children:
Dosage regimens are not defined. As a general guideline, refer to the dosage regimens indicated in children with toxoplasmosis infections.
Use in elderly patients:
There is no information on the effect of Daraprim in elderly patients. In theory, it is possible that such patients under treatment for toxoplasmosis may be more susceptible to bone marrow affection caused by folate deficiency associated with daily administration of Daraprim.
Use during pregnancy:
25 mg per day until delivery.
If you take more Daraprim than you should
If you have taken more Daraprim than you should, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately. The most frequent symptoms in case of acute overdose are: vomiting and convulsions. Ataxia, tremor, and respiratory depression may also occur.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicological Information Service, telephone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount ingested.
If you forget to take Daraprim
Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses. Take the next dose when it is due.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Symptoms to which you must pay attention
Bone marrow damage(bone marrow failure to produce blood cells)
This increases the risk of bleeding and reduces your ability to fight infections. The symptoms include:
- unexplained bleeding or bruising
- fever
- sore throat
- mouth ulcers
- extreme pallor or weakness
Tell your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of these symptoms – either for the first time or if they worsen.
Adverse effects observed are classified according to their frequency of occurrence in: very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people), common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people), uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people), rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people), very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
Very common adverse effects
May affect more than 1 in 10patients:
- headache
- vomiting, nausea, diarrhea
- skin rash
Very common adverse effects that may appear in blood tests:
- anemia (reduction in the number of red blood cells)
Common adverse effects
May affect up to 1 in 10patients:
- dizziness
Common adverse effects that may appear in blood tests are:
- leukopenia (reduction in the number of white blood cells)
- thrombocytopenia (reduction in the number of platelets)
Daily therapeutic doses of pyrimethamine have been shown to depress hematopoiesis (formation of blood cells) in 25-50% of patients. The probability of inducing leukopenia, anemia, or thrombocytopenia is reduced by concomitant administration of calcium folinate.
Uncommon adverse effects
May affect up to 1 in 100patients:
- fever
- abnormal skin pigmentation
Very rare adverse effects
May affect up to 1 in 10,000patients:
- colic
- seizures
Seizures have been observed predominantly in patients treated for toxoplasmosis.
- mouth ulcers
- pneumonia with cellular and eosinophilic infiltration
Observed when pyrimethamine is administered once a week in combination with sulfadoxine.
- dermatitis.
The very rare adverse effects that may appear in blood tests are:
- pancytopenia (reduction in the number of all types of blood cells)
Pancytopenia, in response to folates, has been observed in patients with a probable pre-existing folate deficiency. Deaths have occurred in the absence of folate treatment.
If you experience any side effect, contact your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly to the Spanish Medicines and Health Products Agency (AEMPS) at http://www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Daraprim
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 25°C. Store protected from light.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date (EXP) stated on the packaging. The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Return the packaging and any unused medicine to a pharmacy. If you are unsure, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Daraprim
- The active substance is pyrimethamine. Each tablet contains 25 mg of pyrimethamine.
- The other ingredients (excipients) are: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, hydrolyzed corn starch, sodium docusate, and magnesium stearate.
Appearance of the product and contents of the pack
Daraprim is a white, biconvex, scored, and engraved tablet with an identification code. It is available in packs of 30 tablets.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
SmithKline Beecham Farma, S.A.
P.T.M. C/ Severo Ochoa, 2
28760 Tres Cantos (Madrid)
Tel: +34 900 202 700
Manufacturer
GlaxoSmithKline Trading Services Limited
12 Riverwalk
Citywest Business Campus
Dublin 24
Ireland
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:October 2020.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
Daraprim is packaged in a child-resistant blister pack.
How to remove a tablet
- Separate a tablet: pull along the pre-cut line to separate a blister from the pack.
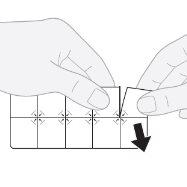
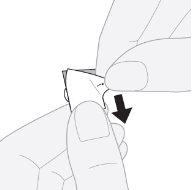
- Remove the outer layer: starting from the corner, lift and remove the outer layer of the blister.
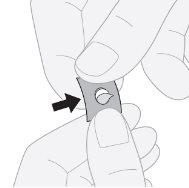
- Press to remove the tablet: press on one side of the tablet to remove it from the aluminum foil.
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price4.9 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DARAPRIM 25 mg TABLETSDosage form: INJECTABLE, 110 mgActive substance: artesunateManufacturer: Amivas Ireland LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 250 mg/100 mgActive substance: proguanil and atovaquoneManufacturer: Viatris LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 200 mgActive substance: hydroxychloroquineManufacturer: Products And Technology S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for DARAPRIM 25 mg TABLETS
Discuss questions about DARAPRIM 25 mg TABLETS, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















